Current Situation and Management Recommendations about Betel Nut Planting in Hainan
2016-01-11,,
, ,
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, Danzhou 571737, China
1 Current situation of betel nut planting in Hainan
Betel nut originated from Malaysia, and is mainly distributed in Asia and tropical regions of the Americas. China is the world’s second largest producer of betel nut, and the main producing area is in Hainan Province, accounting for 99% of total betel nut yield in mainland China[1]. The betel nut in Hainan is mainly spontaneously planted by farmers, and few of enterprises plant it. In recent years, the low price of natural rubber has seriously affected the enthusiasm of farmers for planting rubber. Meanwhile, during 2013-2014, the prices of betel nut continued to rise, which increased farmers’ willingness to plant betel nut; betel nut was planted in some incomplete rubber plantations in the main producing areas of betel nut, showing a good trend of development.
1.1PlantingareaThe planting area of Hainan betel nut was 1047 ha in 1952, 1120 ha in 1980, 27000 ha in 2000, 69000 ha in 2010, 94000 ha in 2014. The planting of betel nut in Hainan during 2000-2014 can be shown in Table 1. From Table 1, it can be found that the planting area of betel nut in Hainan during 2000-2014 continuously increased, and the harvested area also increased. The betel nut is widely grown in Hainan, because betel nut is easily managed and requires a small investment, and the economic benefits of betel nut are high under normal management.
1.2YieldChina’s betel nut yield was 1100 t in 1952, 35500 t in 2000, and 231000 t in 2014. The betel nut yield in Hainan Province during 2000-2014 is shown in Table 2. From Table 2, it is found that from 2000 to 2014, the total output of betel nut continued to increase, but from 2007 to 2014, betel nut yield never increased. According to statistics, the province’s betel nut yield was 3562.95 kg/ha in 2014, 4 kg of fresh fruit could be processed into 1 kg of dried fruit, and the fresh betel nut yield was 14251.8 kg/ha. Obviously, Hainan’s betel nut yield is significantly low, mainly due to betel nut yellow leaf disease and extensive management of betel nut plantations.
Table1TheplantingofbetelnutinHainanduring2000-2014
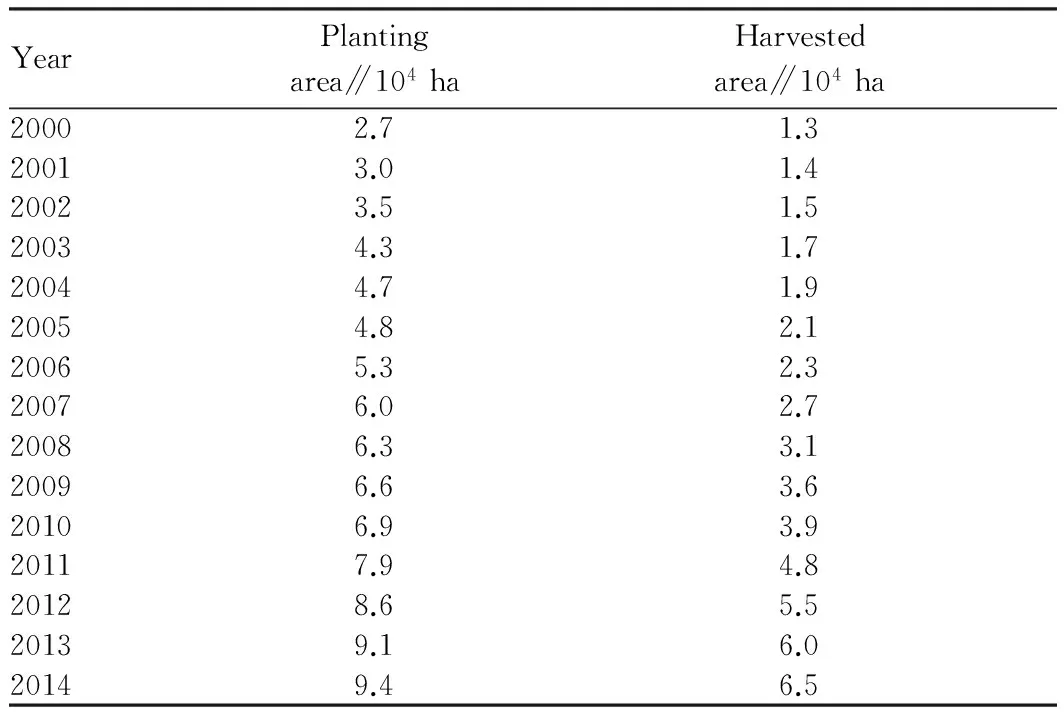
YearPlantingarea∥104haHarvestedarea∥104ha20002.71.320013.01.420023.51.520034.31.720044.71.920054.82.120065.32.320076.02.720086.33.120096.63.620106.93.920117.94.820128.65.520139.16.020149.46.5
Note: Data are from Hainan Provincial Department of Agriculture.
Table2BetelnutyieldinHainanProvinceduring2000-2014

YearPlantingarea∥104haHarvestedarea∥104ha20002818.953.5520013002.854.1820023256.954.9720033313.205.5020043383.106.2720053101.256.4320062958.157.4820073546.459.5420083721.2011.6520093976.5014.3520103860.4015.2120113511.5016.9220123621.6019.8120133711.3022.3320143562.9523.10
Note: Data are from Hainan Provincial Department of Agriculture.
2 Problems in Hainan’s betel nut planting
2.1Seriousbetelnutyellowleafdisease"yellow leaf disease" is one of plant diseases usually caused by fungi of the genus Fusarium or viruses of the genus Chlorogenus and characterized by yellow or yellowish discoloration. It is an infectious devastating disease for the betel nut, and currently it is still a technological fix having not yet been overcome in the world[2]. yellow leaf disease poses a serious threat to the development of betel nut industry in Hainan Province, and it is the main problem for the betel nut planting. The disease occurs universally in the contiguous betel nut plantations of Hainan’s Tunchang, Qionghai, Wanning, Lingshui, Sanya and Baoting. The incidence of disease reaches as high as 90% in the plantations with serious yellow leaf disease, a decrease of 78% to 80% in production; the incidence of disease is 30% to 40% in some betel nut plantations. Currently, the incidence areas and the disease-affected area continue to expand, and after the betel nut suffers from yellow leaf disease, it can not be cured.
2.2ToodenseplantingAt present, Hainan’s betel nut is still mostly planted by farmers spontaneously, and the plantation lacks scientific planning. The planting technical measures are neglected and the betel nut is densely planted. The planting amount per unit area is seriously over the standard. In the hilly land with a steep slope, the insufficient light and accumulated temperature make the betel nut grow poorly, leading to low yield and short economic life. Normal betel nut can be harvested for 50 to 60 years, but in some Hainan’s betel nut plantations, it begins to degenerate in 20 years.
2.3IrrationalplantinglayoutThe betel nut can be planted in the mountains with an altitude of below 300 meters and swampy ground. Most of the farmers plant betel nut in unreasonable sites, and in some betel nut plantations, the water table is too high, but there is no high ridge and drain ditch, so the water logging in betel nut plantations causes the betel nut root to be long immersed, resulting in poor growth and low yield of betel nut. In the hilly land with steep slope, the planting of betel nut has caused serious soil erosion and severe water shortage in betel nut plantation due to lack of rows of land reclaimed around mountains in advance. In some betel nut plantations, the spacing between betel nut and other intercrops is not increased, so that they can not grow in harmony, thereby failing to achieve the best economic benefit of intercropping ecological model.
3 Conclusions and recommendations
3.1ConclusionsThere have long been some problems in Hainan’s betel nut planting, such as excessively emphasizing sowing, harvesting but ignoring management, planting on a small scale, and paying no attention to soil improvement and fertilizer management, resulting in inadequate nutrients for betel plant, and low yield and short harvest period in many betel nut plantations. Therefore, for the sustained development of Hainan’s betel nut, it is necessary to focus on building the ecological disease-resistant betel nut plantations to prevent and cure diseases such as yellow leaf disease, implement agronomic measures, and strengthen water and fertilizer management to increase betel nut yield.
3.2Recommendations
3.2.1Building ecological disease-resistant betel nut plantations. yellow leaf disease has posed a serious threat to the sustainable development of betel nut industry, becoming a major constraint on the development of betel nut industry. In order to build ecological disease-resistant betel nut plantations, it is necessary to focus on the following three aspects. (i) Retaining the weeds and dwarf plants around the trunk as covering in the betel nut plantations. There is a need to preserve the weeds and dwarf plants around betel nut trunk, because they can increase the surface shading, and reduce direct sunlight on the ground, so as to form a growth environment with adequate sunlight on upper canopy and shade covering on the lower part. (ii) Avoiding the use of herbicides when controlling the weeds in betel nut plantations. The betel nut root is shallow, and avoiding the use of herbicides can help to prevent the damage of herbicides to betel nut root and the impact on betel nut root’s absorption of nutrients. (iii) Strengthening the soil and water conservation in betel nut plantations. The betel nut plantations should try to create the environmental conditions suitable for the growth of betel nut based on local conditions, strengthen soil and water conservation, and reduce soil erosion, in order to maintain moisture and nutrients, and improve the soil microbial environment for betel nut. (iv) Applying the organic fertilizer. The 30-40 cm deep half-moon-shaped hole is dug around tree crown, 10-15 kg of compost, manure or manure fertilizer is applied on each plant, and then it is earthed up. Biogas is one of the best fertilizer for betel nut, and 10-50 kg of biogas can be applied on each plant.
3.2.2Improving the low-yielding betel nut plantations.The planting density of betel nut is generally 1600-1650 plants/ha, it begins to fruit 5-6 years after planting, and the production period can be up to 30 years; the betel nut yield per plant is generally about 15 kg, and can be up to 25 kg. However, the majority of Hainan’s betel nut growers have long emphasized planting and harvesting but ignored management, resulting in generally low yield in many betel nut plantations, mainly due to extensive management, poor water conditions and plant diseases[3]. Hainan’s low-yielding betel nut plantations account for about 20% to 30% at present, and these plantations need to be transformed into high-yielding plantations in order to increase yield per unit area. The betel nut plantations should carry out timely weeding, and cut down the bushes, leaving the annual leaf weeds to cover the ground. There is a need to use betel nut leaf, green manure and vines to cover the soil so as to increase soil organic matter and nutrients, improve the growth environment of betel nut and promote root growth. The low-yielding betel nut plantations should seek to build irrigation systems, strengthen irrigation during the dry season, and dig drains during the rainy season. The low-yielding betel nut plantations with serious pests and diseases need to remove the diseased plants, make the soil of plantations under the blazing sun for quite a long time before planting, and strengthen planting, water and fertilizer management in strict accordance with the technical requirements of betel nut planting.
3.2.3Strengthening betel nut production management. Strengthening the betel nut production management can help to tap betel nut’s potential for high yield. According to the survey of Wanning Liqing Planting and Breeding Cooperative in September 2015, this cooperative established 4 ha of standard betel nut plantations, with betel nut yield of 18750 kg/ha. It is necessary to strengthen the management of fertilization, vegetation management and pest management. In recent years, due to the increase in labor costs, decline in the source of organic fertilizer and reduction of organic fertilizer input, the soil fertility is reduced and soil’s aggregate structure is damaged in betel nut plantations. The fertilization management of betel nut should focus on the application of organic fertilizer, and combine the use of organic manure and chemical fertilizer, in order to keep betel plant’s nutritional balance and improve fertilization effect. It is necessary to maintain good ground cover, and retain dwarf plants and weeds between the rows of plants. There is a need to take the manual weeding, and avoid the use of chemical weeding to reduce the impact of chemicals on betel nut. There are about 5-7 t of leaves, buds, ear, fruits and other wastes dropping in mature betel nut plantations per hectare per year, if these wastes can be converted into the organic fertilizer to be effectively used, it can not only improve the soil fertility, but also reduce pests and diseases in betel nut plantations. As for the pest management, there is a need to build the ecological diseases-resistant betel nut plantations.
[1] FU ZX, LIU LY, LI Y,etal. On agricultural production technology of betelnut[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2014,42(14):4229-4230,4292.(in Chinese).
[2] FAN HK, LIU LY, YU FY,etal. The occurrence and comprehensive control of yellow leaf disease of arecanut[J]. South China Fruits,2008,37(2):42-43.(in Chinese).
[3] CHEN XM. The technical measurements for improvement of low-yield betelnutpalm (Areca cathecu) orchard in Hannan Province[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology,2007.8:68-69.(in Chinese).
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research Progress in Tomato Responses to Abiotic Stress
- Current Situations and Recommendations for Non-grain Tendency of Farmland in Anhui Province
- A Study on the Reform and Further Development of "Chongzhou Mode" Based on the Perspective of Modern Enterprise Management
- Spatiotemporal Coupling of Water and Fertilizer for Double-cropping Grape in Guangxi
- On the Government Function Orientation in China’s Agricultural Management Reform
- Connection of Farmland Consolidation Construction Works in Northern Anhui Plain: A Case Study of Si County of Anhui Province
