Rheological behaviorsof Graphitic oxide/Sodium alginatedispersions
2015-12-30ZHANGQingxu
ZHANG Qing-xu
(Qingdao University,Qingdao Shandong 266071,China)
0 Introduction
Alginate,consisted of 1,4-linkedβ-d-mannuronic (M)andα-lguluronic (G)segments in varying proportions,is a kind of polyanionic copolymers.In recent years,SA has been extensively used as drug release materials,[1]scaffolds for tissue engineering[2]and medical dressing,owing to its fascinating advantages.Graphitic is twodimensional material exhibits exceptionally high crystal and electronic quality.[3]As well known,carbonaceous materials such as CB,MWNTS,and GO have attracted great interest of researchers over the past decades due to their unique structural and the resultant electrical,optical and mechanical properties[4].The study with respect to graphene oxide(GO)suspended in SA solution was rarely reported.This article aims to study the influence of different content of GOon the rheological behavior of the SA solution,which will provide certain theoretical basis for fiber modification and pharmaceutical processing of SA.
1 Experimental
Materials.Sodium alginate (SA)isolated from Laminaria japonica Aresch(450 cP).GO prepared from natural graphitewas.The SA and SA/GO suspensions was prepared by dissolved amount of SA powder in distilled water to produce a 3 wt%viscous solution,after mechanical agitation until a homogeneous solution was formed.Then amount of GO were added into SA solution,following ultrasonic 15min to achieve homogeneous dispersion.
Rheological measurements. Rheological measurements were performed on a AntonPaar MCR301 controlled stress rheometer.All measurements were performed at 25℃except otherwise stated.
Results and discussion
Effect of GOon the Steady and dynamic rheological behaviors of SA
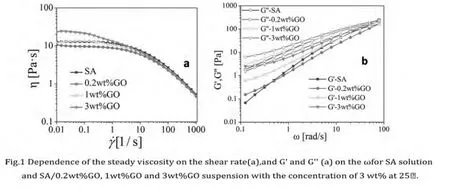
From Fig.1(a),it was apparent that show that GO/SA dispersions showed a typical shear thinning behavior,belong to pseudoplastic fluids.With the increase of GO content,the viscosity of the complex solution increased gradually,newton platform area become shorter,shear thinned phenomenon is obvious pseudoplastic flow occurred for SA solutions at lower shear rate.Fig.1 b.shows the G'and G''as a function ofωfor the SA solutions of different content of GO with the concentration of 3 wt%.Both moduli increase with frequency;however,the rate of increase becomes less the higher the GO content.The data shows that the G''is larger than the G'for the SA and SA/GO suspension in the whole frequency range,which are typical viscoelastic behavior of polymer solutions[5].
The cole-cole craves of SA solution and GO/SA suspensions
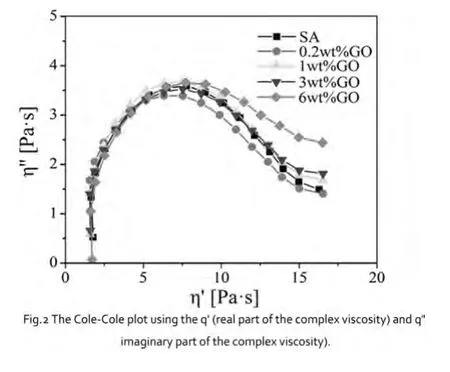
The Cole-Cole plot is often used to analyze the miscibility of polymer blends;thus a smooth,semicircular shape suggests good compatibility.[6]The Cole-Cole plot representing the relationship between the real(q')and imaginary viscosities(q")of the suspension.As seen in this Figure.2,the curves for each sample are close to semicircular or bimodal shapes for all four suspension.reflecting good dispersibility of GO nanosheets in SA solution.When content of GO up to 6 wt%,the tail warping is larger,reflect his system dispersion decrease when compared to the dispersion of GO content is less.
2 Conclusions
The results show that GO/SA dispersions showed a typical shear thinning behavior,belong to pseudoplastic fluids.The addition of GO does not change the fluid types of the SA solution.With the increase of GO content,the viscosity of the complex solution increased gradually.Dynamic rheological test results show that adding small GO can significantly increase the G'and G''of SA spinning solution,reflecting good dispersibility of GO nanosheets in SA solution,Cole-Cole curves also proved.
[1]Meera George,T.Emilia Abraham.Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs Alginate and chitosan—a review[J].ELSEVIER Journal of Controlled Release,114(2006):1-14.
[2]C.J.Knill,J.F.Kennedy,J.Mistry,M.Miraftab,G.Smart.lginate fibres modified with unhydrolysed and hydrolysed chitosans for wound dressings[J].ELSEVIER Carbohydrate Polymers,55(2004):65-76.
[3]A.K.Geim,K.S.Novoselov.The rise of graphene[J].Nature Materials 6,183-191(2007).
[4]Iijima S.Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J].Nature,354(1991):56-58.
[5]Kuang Q L,Zhao J C,Niu Y H,et al..Celluloses in an Ionic Liquid:the Rheological Properties of the Solutions Spanning the Dilute and Semidilute RegimesJ[J].Phys.Chem.B.,112(2008):10234-10240.
[6]Cho K.,Lee B.H.,Hwang K.M.,Lee H.,Choe S.Rheological and mechanical properties in polyethylene blends[J].Polymer Engineeringffamp;Science,1998,38(12):1969-1975.
