青蒿素
2015-12-24Selectivecancercellcytotoxicityfromexposuretodihydroartemisininandholotransferrin
Selective cancer cell cytotoxicity from exposure to dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin
Lai, H; Singh, NP
Effects of artesunate-mefloquine combination on incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria and mefloquine resistance in western Thailand: A prospective study
Nosten, F; van Vugt, M; Price, R; et al.
Amodiaquine-artesunate versus amodiaquine for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in African children: A randomised, multicentre trial
Adjuik, M; Agnamey, P; Babiker, A; et al.
Identification of intermediates and enzymes involved in the early steps of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua
Bertea, CM; Freije, JR; van der Woude, H; et al.
The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine
Tu, YY
Total synthesis of Qinghaosu
Schmid, G; Hofheinz, W
High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin
Paddon, CJ; Westfall, PJ; Pitera, DJ
Ri质粒转化的青蒿发根培养及青蒿素的生物合成
蔡国琴,李国珍,叶和春,等
热点追踪
青蒿素
·编者按·
青蒿素(artemisinin,qinghaosu)及其衍生物是临床上治疗疟疾的一线药物,也是现今所有药物中起效最快的抗恶性疟原虫疟疾药。青蒿素提取自常用中药一年生菊科植物黄花蒿,1972年,中国科学家屠呦呦领导的课题组首次从这种植物中分离得到抗疟疾的有效单体,她本人也因此获得2011年拉斯克-德贝基临床医学奖和2015年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖。
青蒿素及其衍生物(主要包括双氢青蒿素、蒿甲醚、蒿乙醚和青蒿琥酯)结构中具有一个包括过氧基团在内的1,2,4-三噁烷结构单元,一般认为这种结构与青蒿素的抗疟活性有关。临床证明,使用基于青蒿素类抗疟药的联合治疗方案(artemisinin-based combination therapies,ACTs)治疗疟疾能够取得很好的效果。因而,ACTs被世界卫生组织推荐为治疗疟疾的一线药物。近年来,研究发现青蒿素类药物除抗疟作用外,还有多种其他的药理作用,包括抗多种寄生虫(血吸虫和弓形虫等)、抗细菌脓毒症、放疗增敏、抗菌增敏、抗肿瘤、抗心律失常等作用,在这些方面具有潜在的开发价值。
药用青蒿素主要是从中药青蒿的原植物黄花蒿的叶和花蕾中分离获得,但是含量较少,需要采集大量自然资源,加工环节也比较多,导致青蒿素的供需矛盾。因而,青蒿素的来源问题成为该领域研究重点之一。对该问题的研究主要包括青蒿素的化学合成方法和生物合成方法。其中,青蒿素化学合成有全合成和半合成2种,全合成的原料主要是香茅醛(citronellal)、柠檬烯(isolimonene)、薄荷酮(pulegone)、β-蒎烯(β-pinene)、异胡薄荷醇(isopulegol)等,半合成原料主要是青蒿酸。青蒿素的生物合成途径尚未完全清楚,其合成相关基因包括紫穗槐-4,11-二烯氧化酶基因、细胞色素P450氧化还原酶基因、青蒿醛双键还原酶和醛脱氢酶基因。2013年Keasling J D以及Lévesque F等研究者报道了采用合成生物学方法,利用基因工程酵母成功生产青蒿酸,并进一步高效半合成得到青蒿素的研究结果。这一成果有望进一步实现产业化应用。目前青蒿素的现实来源主要还是从中药青蒿的原植物中提取。
本专题得到了曾庆平教授(广州中医药大学)、王满元副教授(首都医科大学)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年10月30日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“青蒿素(artemisinin)”为主题检索到的期刊文献分别为3026为与5659条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。
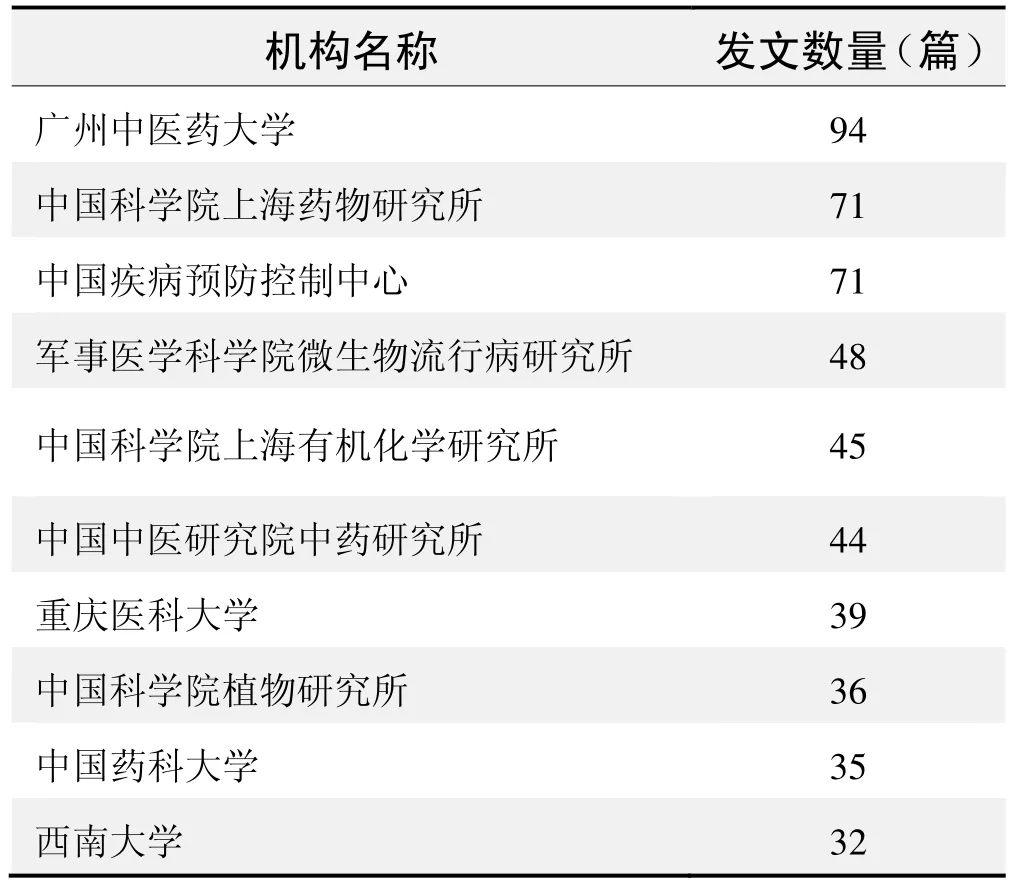
研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
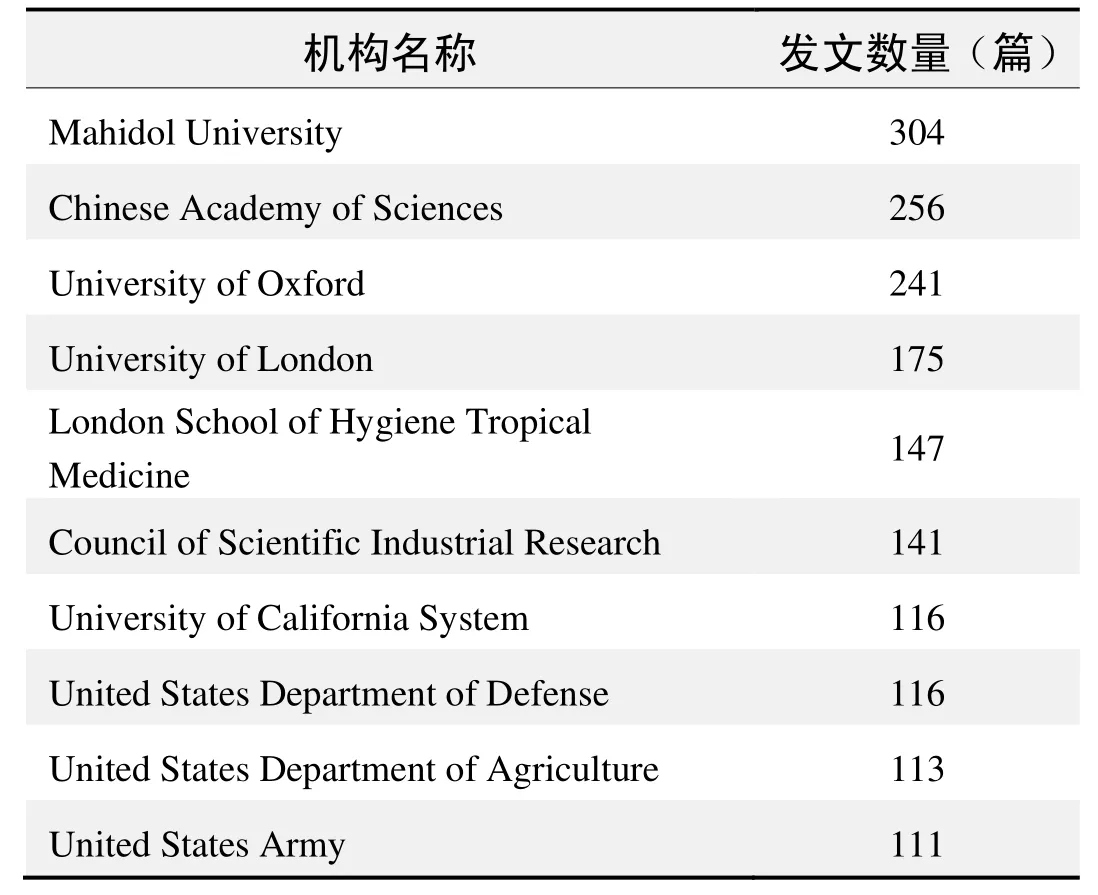
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)
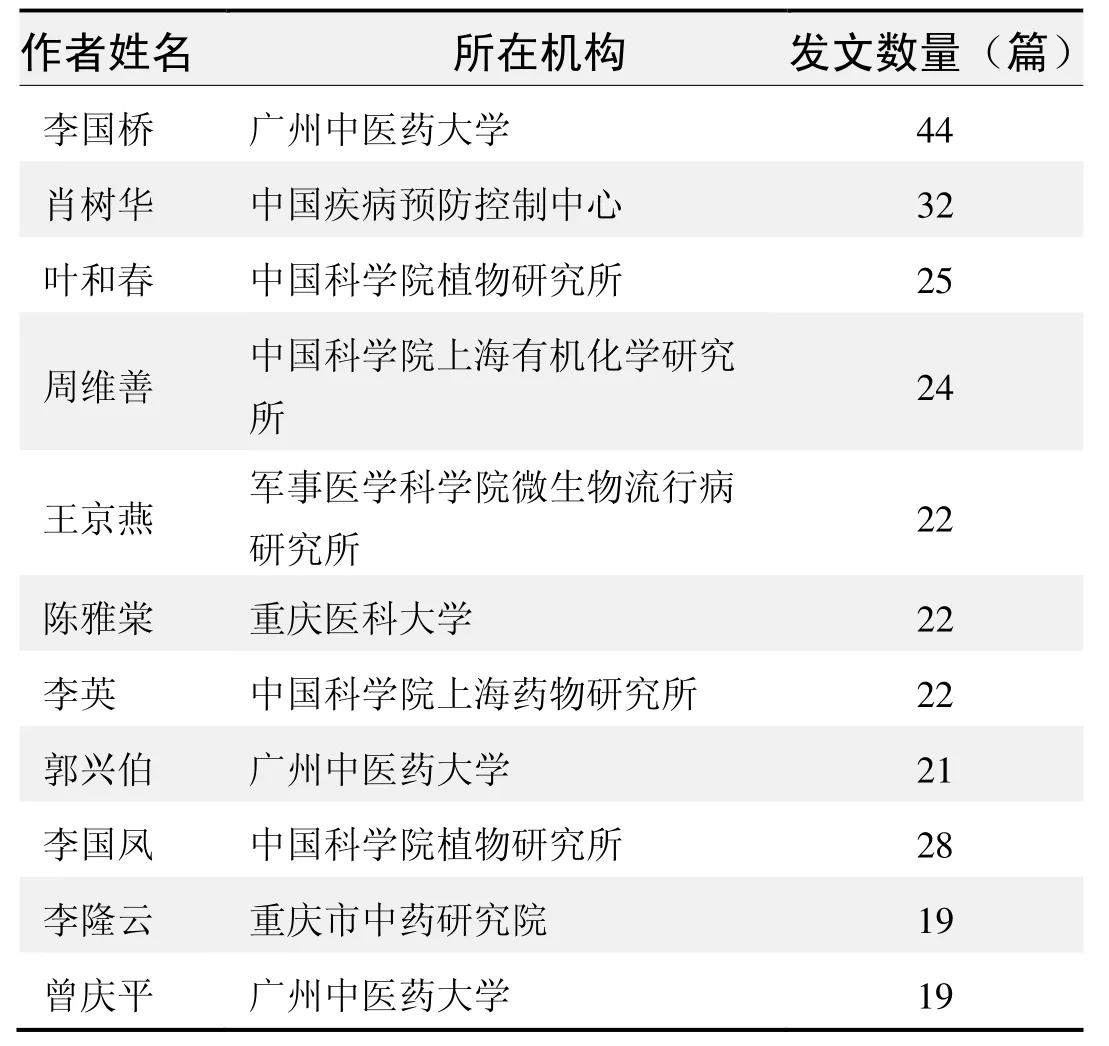
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“青蒿素(artemisinin)”为主题检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
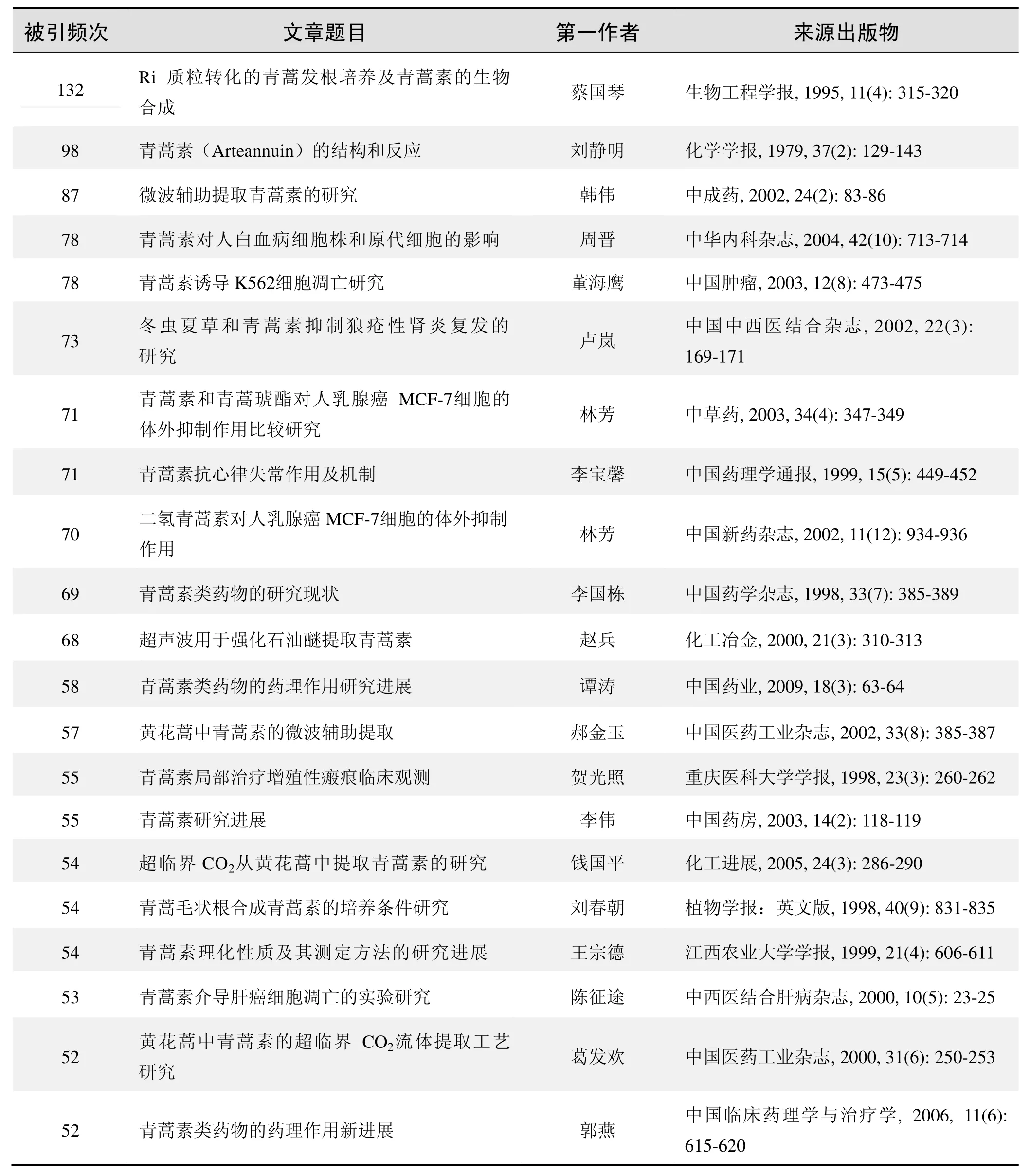
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“青蒿素(artemisinin)”为词条检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 50文献作为节点进行分析,结合专家意见,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。

经典文献
来源出版物:Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1993, 37(5): 1108-1114
Selective cancer cell cytotoxicity from exposure to dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin
Lai, H; Singh, NP
Abstract: Rapid cell death, as evidenced by a decrease in cell counts, was observed when molt-4-lymphoblastoid cells, a human leukemia cell line, were exposed to holotransferrin (12 micro M) and dihydroartemisinin (1-200 micro M).Incubation with either compound alone was significantly less effective.Significantly less cell death was observed when normal human lymphocytes were exposed to a combination of these 2 drugs.Probit analysis of dose-response functions shows that the drug combination is approximately 100 times more effective on molt-4 cells than lymphocytes (LD(50)s for molt-4 and lymphocytes were 2.59 micro M and 230 micro M, respectively).This drug combination may provide a novel approach for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Molt-4-lymphoblastoid cells; lymphocytes; holotransferrin; dihydroartemisinin
来源出版物:Cancer letters, 1995, 91(1): 41-46
Effects of artesunate-mefloquine combination on incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria and mefloquine resistance in western Thailand: A prospective study
Nosten, F; van Vugt, M; Price, R; et al.
Abstract: Background: Worsening drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a major threat to health in tropical countries.We did a prospective study of malaria incidence and treatment in an area of highly multidrug-resistant P falciparum malaria.Methods: We assessed incidence of P falciparum malaria and the in-vivo responses to mefloquine treatment over 13 years in two large camps for displaced Karen people on the northwest border of Thailand.During this time, the standard mefloquine dose was first increased, and then combined artesunate and mefloquine was introduced as first-line treatment for uncomplicated P falciparum malaria.Findings: Early detection and treatment controlled P falciparum malaria initially while mefloquine was effective (cure rate with mefloquine [15 mg/kg] and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine in 1985, 98% [95% CI 97-100]), but as mefloquine resistance developed, the cure rate fell (71% [67-77] in 1990).A similar pattern was seen for high-dose (25 mg/kg) mefloquine monotherapy from 1990-94.Since the general deployment of the artesunate-mefloquine combination in 1994, the cure rate increased again to almost 100% from 1998 onwards, and there has been a sustained decline in the incidence of P falciparum malaria in the study area.In-vitro susceptibility of P falciparum to mefloquine has improved significantly (P=0.003).Interpretation: In this area of low malaria transmission, early diagnosis and treatment with combined artesunate and mefloquine has reduced the incidence of P falciparum malaria and halted the progression of mefloquine resistance.Werecommend that antimalarial drugs should be combined with artemisinin or a derivative to protect them against resistance.
Keywords: Burmese border; monoclonal-antibodies; elisa development; bed nets; sporozoites; epidemiology; prevention; pregnancy; area
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2000, 356(9226): 297-302
Amodiaquine-artesunate versus amodiaquine for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in African children: A randomised, multicentre trial
Adjuik, M; Agnamey, P; Babiker, A; et al.
Abstract: Background: Increasing drug resistance limits the choice of efficacious chemotherapy against Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Africa.Amodiaquine still retains efficacy against P falciparum in many African countries.We assessed the safety, treatment efficacy, and effect on gametocyte carriage of adding artesunate to amodiaquine in three randomised trials in Kenya, Senegal, and Gabon.Methods: We enrolled 941 children (400 in Kenya, 321 in Senegal, and 220 in Gabon) who were 10 years or older and who had uncomplicated P falciparum malaria.Patients were randomly assigned amodiaquine (10 mg/kg per day for 3 days) plus artesunate (4 mg/kg per day for 3 days) or amodiaquine (as above) and placebo (for 3 days).The primary endpoints were parasitological cure rates at days 14 and 28.Analysis was by intention to treat and by an evaluability method.Findings: Both regimens were well tolerated.Six patients in the amodiaquine-artesunate group and five in the amodiaquine group developed early, drug-induced vomiting, necessitating alternative treatment.By intention-to-treat analysis, the day-14 cure rates for amodiaquine-artesunate versus amodiaquine were: 175/192 (91%) versus 140/188 (74%) in Kenya (Delta=16.7% [95% CI 9.3-24.1], P<0.0001), 148/160 (93%) versus 147/157 (94%) in Senegal (-1.1% [-6.7 to 4.5], P=0.7), and 92/94 (98%) versus 86/96 (90%) in Gabon (8.3% [1.5-15.1], P=0.02).The corresponding rates for day 28 were: 123/180 (68%) versus 75/183 (41%) in Kenya (27.3% [17.5-37.2], P<0.0001), 130/159 (82%) versus 123/156 (79%) in Senegal (2.9% [-5.9 to 11.7], P=0.5), and 80/94 (85%) versus 70/98 (71%) in Gabon (13.7% [2.2-25.2], P=0.02).Similar rates were obtained by evaluability analysis.Interpretation: The combination of artesunate and amodiaquine improved treatment efficacy in Gabon and Kenya, and was equivalent in Senegal.Amodiaquine-artesunate is a potential combination for use in Africa.Further investigations to assess the potential effect on the evolution of drug resistance, disease transmission, and safety of amodiaquine-artesunate are warranted.
Keywords: pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine; antimalarial drug; double-blind; efficacy; chloroquine; resistance; artemether; benflumetol; combination; CGP-56697
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2002, 359(9315): 1365-1372
Identification of intermediates and enzymes involved in the early steps of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua
Bertea, CM; Freije, JR; van der Woude, H; et al.
Abstract: An important group of antimalarial drugs consists of the endoperoxide sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin and its derivatives.Only little is known about the biosynthesis of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L., particularly about the early enzymatic steps between amorpha-4,11-diene and dihydroartemisinic acid.Analyses of the terpenoids from A.annua leaves and gland secretory cells revealed the presence of the oxygenated amorpha-4,11-diene derivatives artemisinic alcohol, dihydroartemisinic alcohol, artemisinic aldehyde, dihydroartemisinic aldehyde and dihydroartemisinic acid.We also demonstrated the presence of a diene synthase and the -so far unknown -amorpha-4,11-diene hydroxylase as well as artemisinic alcohol and dihydroartemisinic aldehyde dehydrogenase activities in both leaves and glandular trichomes.From these results, we hypothesise that the early steps in artemisinin biosynthesis involve amorpha-4,11-diene hydroxylation to artemisinic alcohol, followed by oxidation to artemisinic aldehyde, reduction of the C11-C13 double bond to dihydroartemisinic aldehyde and oxidation to dihydroartemisinic acid.
Keywords: artemisia annua; asteraceae; artemisinin; glandular trichomes; biosynthetic pathway; sesquiterpenoids
来源出版物:Planta medica, 2005, 71(1): 40-47
The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine
Tu, YY
Abstract: Joseph Goldstein has written in this journal that creation (through invention) and revelation (through discovery) are two different routes to advancement in the biomedical sciences.In my work as a phytochemist, particularly during the period from the late 1960s to the 1980s, I have been fortunate enough to travel both routes.
来源出版物:Nature Medicine, 2011, 17(10):1217-1220
Total synthesis of Qinghaosu
Schmid, G; Hofheinz, W
Abstract: Since ancient time Artemisia annua also called qinghao has been used to treat fever in china.The effective constituent waslsolate by chinese scientist in 1972 named qinghaosu also known as Artemisinin.It can be used to treat drug-resistant malaria which causes millions death every year in developing countries of Asia Africa and America.
来源出版物:Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1983, 105(3): 624-625
High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin
Paddon, CJ; Westfall, PJ; Pitera, DJ
Abstract: In 2010 there were more than 200 million cases of malaria, and at least 655000 deaths.The World Health Organization has recommended artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Artemisinin is a sesquiterpene endoperoxide with potent antimalarial properties, produced by the plant Artemisia annua.However, the supply of plant-derived artemisinin is unstable, resulting in shortages and price fluctuations, complicating production planning by ACT manufacturers.A stable source of affordable artemisinin is required.Here we use synthetic biology to develop strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast) for high-yielding biological production of artemisinic acid, a precursor of artemisinin.Previous attempts to produce commercially relevant concentrations of artemisinic acid were unsuccessful, allowing production of only 1.6 grams per litre of artemisinic acid.Here we demonstrate the complete biosynthetic pathway, including the discovery of a plant dehydrogenase and a second cytochrome that provide an efficient biosynthetic route to artemisinic acid, with fermentation titres of 25 grams per litre of artemisinic acid.Furthermore, we have developed a practical, efficient and scalable chemical process for the conversion of artemisinic acid to artemisinin using a chemical source of singlet oxygen, thus avoiding the need for specialized photochemical equipment.The strains and processes described here form the basis of a viable industrial process for the production of semi-synthetic artemisinin to stabilize the supply of artemisinin for derivatization into active pharmaceutical ingredients (for example, artesunate) for incorporation into ACTs.Because all intellectual property rights have been provided free of charge, this technology has the potential to increase provision of first-line antimalarial treatments to the developing world at a reduced average annual price.
来源出版物:Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 528-532
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:132
Ri质粒转化的青蒿发根培养及青蒿素的生物合成
蔡国琴,李国珍,叶和春,等
用发根农杆菌(Agrobacterium rhizogenes)转化药用植物青蒿(Artemisia annua L.)并建立了发根体外培养系统。Southern杂交、NPTⅡ酶的检测证明Ri质粒的T-DNA转移并整合到植物的核基因组上。在发根培养系统中,检测了青蒿的重要次生代谢物—青蒿素的含量,检测了不同理化因子对发根生长及青蒿素含量的影响。结果表明:光照(日光灯,12 h光周期,2000 Lx)有利于次生产物青蒿素的积累。培养基的pH值为5.4。蔗糖浓度为3%不仅促进发根的生长,而且促进青蒿素的积累。低浓度亲乙酸(NAA)对发根生长具有促进作用,但抑制青蒿素的合成。赤霉素GA3对发根的生长及次生产物的合成都具有促进作用,其最适浓度为4.8 mg/L。
青蒿;Ri质粒;发根;青蒿素
来源出版物:生物工程学报, 1995, 11(4): 315-320
被引频次:98
青蒿素(Arteannuin)的结构和反应
刘静明,倪慕云,樊菊芬,等
摘要:青蒿素是一个含过氧基团的新型倍半萜化合物,系从黄花蒿中分得。它的结构是由红外光谱、核磁共振谱、质谱和化学反应以及X-射线衍射等方法确定的。它的绝对构型是根据与化合物(6)构型联系以及利用氧原子的反常散射测定的。
关键词:青蒿素;Arteannuin;倍半萜化合物;乙醚提取;红外光谱;过氧基;青篙素;核磁共振谱;绝对构型;反常散射
来源出版物:化学学报, 1979, 37(2): 129-143
被引频次:87
微波辅助提取青蒿素的研究
韩伟,郝金玉,薛伯勇,等
摘要:目的:运用新型分离方法微波辅助提取法(MAE)来提取黄花蒿中的青蒿素。方法:分别选用乙醇、三氯甲烷、环己烷、正己烷、30℃~60℃石油醚、60℃~90℃石油醚、120号溶剂油、6号抽提溶剂油作为萃取介质,在间歇微波辅助提取装置中,进行微波辅助提取实验。结果:从微波辐射时间、溶剂比、物料粉碎度等工艺条件对青蒿素得率的影响。评价最佳溶剂是6号抽提溶剂油。结论:微波辅助提取法适合于提取黄花蒿中的青蒿素。
关键词:微波辅助提取;微波萃取;青蒿素;黄花蒿
来源出版物:中成药, 2002, 24(2): 83-86
被引频次:78
青蒿素对人白血病细胞株和原代细胞的影响
周晋,孟然,李丽敏,等
摘要:青蒿素是一种低毒、有效的抗疟药,最近发现其有抑制实体瘤细胞增殖的作用。我们研究了青蒿素对人白血病细胞株和原代细胞的影响及可能机制,以期为其抗白血病新用途提供实验证据。
关键词:人白血病细胞株;青蒿素;原代细胞;细胞内钙;细胞超微结构;细胞凋亡;瘤细胞增殖;胞膜破坏;血液病研究所;实验分组
来源出版物:中华内科杂志, 2004, 42(10): 713-714
被引频次:78
青蒿素诱导K562细胞凋亡研究
董海鹰,王知非,宋维华,等
摘要:目的:研究青蒿素对体外培养的K562细胞的凋亡诱导作用及机制。方法:MTT法测定药物对K562细胞生长的抑制作用;透射电镜观察药物对K562细胞形态学的影响;流式细胞仪检测经药物作用后的细胞凋亡率;用Rhodamine(Rh123)色法检测细胞线粒体跨膜电位(Δψm)的变化。结果:青蒿素对 K562细胞生长有明显的抑制作用,细胞经药物作用48小时后的 IC50为26.5 μmol/L;电镜观察细胞有典型的凋亡形态特征;细胞凋亡率在一定范围内与药物浓度正相关。给药后跨膜电位明显下降。结论:青蒿素可抑制K562细胞的生长,诱导K562细胞跨膜电位下降而导致细胞凋亡。
关键词:青蒿素;细胞;MTT法;凋亡
来源出版物:中国肿瘤, 2003, 12(8): 473-475
被引频次:73
冬虫夏草和青蒿素抑制狼疮性肾炎复发的研究
卢岚
摘要:目的:观察冬虫夏草(简称虫草)和青蒿素抑制狼疮性肾炎复发的作用。方法:61例经用激素及环磷酰胺冲击治疗已无狼疮活动的狼疮性肾炎患者,随机分为两组,治疗组(31例)予虫草粉每日3~4 g,分3次空腹口服;青蒿素粉每日0.6 g,分3次餐后口服,连续服用3年。对照组(30例)口服雷公藤多甙片和(或)保肾康片等药物治疗。两组均连续观察5年,监测血肌酐、肌酐清除率、抗核抗体等实验室有关指标及有否狼疮活动的临床表现。结果:治疗组显效26例(83.9%),有效4例(12.9%),无效1例(3.2%);对照组显效15例(50.0%),有效8例(26.7%),无效7例(23.3%),两组显效率比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。治疗组补体C3持续稳定在(1.21 ± 0.20)g/L正常水平,肌酐清除率治疗前后比较差异无显著性,与对照组比较差异有显著性;治疗组同时减少了药物本身的不良反应。结论:冬虫夏草和青蒿素可以抑制狼疮肾炎的复发,保护肾功能。
关键词:冬虫夏草;青蒿素;狼疮性肾炎;复发
来源出版物:中国中西医结合杂志, 2002, 22(3): 169-171
被引频次:71
青蒿素和青蒿琥酯对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的体外抑制作用比较研究
林芳,钱之玉,薛红卫,等
摘要:目的:对比研究青蒿素及其衍生物青蒿琥酯对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响并探讨其作用机制。方法采用体外培养的人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞株,利用SRB法测定青蒿素和青蒿琥酯对MCF-7细胞增殖的影响,FCM法测定细胞周期的变化,亚G1期含量测定和DAPI荧光染色法观察细胞凋亡。结果:10 μmol/L青蒿素和1 μmol/L青蒿琥酯能明显改变MCF-7细胞的细胞周期,使S期细胞显著减少,G0+G1期细胞明显增加。青蒿素对 MCF-7细胞增殖仅有微弱抑制作用,但其衍生物青蒿琥酯却有显著的抑制作用,IC50为0.31 μmol/L。同样,1 μmol/L青蒿琥酯引起MCF-7细胞的凋亡和直接的细胞毒作用明显强于10 μmol/L青蒿素的作用。结论:体外研究表明,对肿瘤细胞增殖的抑制青蒿琥酯比青蒿素作用强。
关键词:青蒿素;青蒿琥酯;MCF-7细胞
来源出版物:中草药, 2003, 34(4): 347-349
被引频次:71
青蒿素抗心律失常作用及机制
李宝馨,杨宝峰,李玉荣
摘要:目的:观察青蒿素抗心律失常作用,并探讨其作用机制。方法:采用冠脉结扎,氯化钙,氯仿所致心律失常模型进行青蒿素的抗心律失常作用研究。应用膜片钳技术研究药物对内向整流钾电流的作用。结果:青蒿素能明显对抗结扎冠脉引起的心律失常,对氯化钙、氯仿引起的心律失常,可使其发生时间明显延长,室颤明显减少。膜片钳实验表明,该药可剂量依赖性的明显抑制内向整流钾电流。结论:该药是一有效的抗心律失常药,其作用机制与其抑制内向整流钾电流有关。
关键词:青蒿素;心律失常;内向整流钾电流
来源出版物:中国药理学通报, 1999, 15(5): 449-452
被引频次:70
二氢青蒿素对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的体外抑制作用
林芳,钱之玉,丁健,等
摘要:目的:研究二氢青蒿素(青蒿素生物合成中的可能前体)对肿瘤细胞增殖的影响和机制。方法:采用体外培养的人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞株,利用SRB法测定青蒿素和青蒿琥酯对MCF-7细胞增殖的影响,用流式细胞检定法(FCM)测定细胞周期的变化,用亚G1期含量测定法和DAPI荧光染色法观察细胞凋亡。结果:二氢青蒿素能显著抑制MCF-7细胞的增殖,IC50为0.26 μmol·L-1;二氢青蒿素作用后细胞周期发生明显变化,细胞被阻滞在G0+G1期,S期细胞显著减少。二氢青蒿素作用细胞24 h后可轻微诱导MCF-7细胞凋亡。结论:二氢青蒿素能强烈抑制MCF-7细胞增殖,将细胞阻滞于G0+G1期。
关键词:二氢青蒿素;人乳腺癌细胞MCF-7;细胞周期
来源出版物:中国新药杂志, 2002, 11(12): 934-936
被引频次:69
青蒿素类药物的研究现状
李国栋,周全,赵长文,等
摘要:目的:从几个方面介绍青蒿素类药物的研究现状,为青蒿素类药物的研究提供参考。方法:依据国内外文献进行综述,包括人工栽培青蒿提取有效成分和人工合成方法两种制备青蒿素的途径以及青蒿素类药物活性成分测定方法、抗疟作用机制、药动学、药效学和毒理学的研究进展及临床应用情况。结果:青蒿素类药物是有发展前途的药物,它们的各方面研究已取得一定的进展。结论:青蒿素类药物为人类对疟疾的斗争注入了新的活力。
关键词:青蒿素;衍生物;疟疾
来源出版物:中国药学杂志, 1998, 33(7): 385-389
被引频次:68
超声波用于强化石油醚提取青蒿素
赵兵,王玉春,吴江,等
摘要:研究了用超声波强化石油醚提取青蒿素的工艺过程。与常规石油醚提取比较,用超声波不仅可以大大缩短提取时间,减少提取产物中杂质含量,而且还可以降低溶剂消耗。
关键词:青蒿素;提取;超声波
来源出版物:化工冶金, 2000, 21(3): 310-313
被引频次:58
青蒿素类药物的药理作用研究进展
谭涛,秦宗会,谭蓉
摘要:青蒿素是从植物黄花蒿中提取的抗疟疾活性成分,在临床上广泛用于治疗疟疾。由于青蒿素类药物还具有抗疟疾、抗孕、抗纤维化、抗血吸虫、抗弓形虫、抗心律失常和肿瘤细胞毒性等药理作用,且具有安全、高效、无耐药性等优点,备受国内外学者关注。笔者对近年来青蒿素类药物的其他主要药理学作用研究的现状进行了综述。
关键词:青蒿素;药理作用;进展
来源出版物:中国药业, 2009, 18(3): 63-64
被引频次:57
黄花蒿中青蒿素的微波辅助提取
郝金玉,韩伟,施超欧,等
摘要:采用微波辅助提取法提取黄花蒿中的青蒿素。对提取溶剂乙醇、三氯甲烷、环己烷、正己烷、石油醚(30~60°C和 60~90℃两种)、120号溶剂油和6号抽提溶剂油进行了比较,考察了溶剂的介电常数对青蒿素得率的影响。并将微波辅助提取法同索氏提取、超临界CO2提取以及加热搅拌提取法进行了比较。
关键词:微波辅助提取;青蒿素;黄花蒿;超临界CO2提取
来源出版物:中国医药工业杂志, 2002, 33(8): 385-387
被引频次:55
青蒿素局部治疗增殖性瘢痕临床观测
贺光照,黄崇本,张代录,等
摘要:青蒿素局部治疗60例增殖性瘢痕。定量测定用药前和用药后1月、2月、3月瘢痕的硬度、温度和厚度。以便客观评价青蒿素的药物疗效。结果表明:瘢痕厚度在治疗后显著低于治疗前(P<0.01);瘢痕硬度在治疗后逐渐降低,依次为3月<2月<1月(P<0.01);瘢痕硬度在治疗后3月显著低于治疗前(P<0.05)。瘢痕温度改变在治疗前后无统计学显著意义(P>0.05)。根据疗效评价标准,青蒿素治疗50例病人总有效率为88%,其中显效率为46%,无效率为12%。
关键词:青蒿素;增殖性瘢痕
来源出版物:重庆医科大学学报, 1998, 23(3): 260-262
被引频次:55
青蒿素研究进展
李伟,石崇荣
摘要:青蒿素(Artemisinin)是我国药学工作者1971年从菊科植物黄花蒿Artemisia annua L.叶中提取分离到的一种具有过氧桥的倍半萜内酯类化合物。在青蒿素的基础上又开发出了多种衍生物双氢青蒿素(Dihydro artemisinin)、青蒿琥酯(Artesunate)、蒿甲醚(Artemether)、蒿乙醚(Arteether),均有抗疟、抗孕、抗纤维化、抗血吸虫、抗弓形虫、抗心律失常和肿瘤细胞毒性等作用。青蒿素类药作用广泛,其作用机制、特点、应用研究仍处于初级阶段, 有待进一步开发。现就青蒿素近年在上述各方面的研究进展作一综述。
关键词:青蒿素;青蒿琥酯;弓形虫感染小鼠;胚胎吸收;大鼠;蒿甲醚;作用机制;剂量相关性;抗疟药;金黄地鼠
来源出版物:中国药房, 2003, 14(2): 118-119
被引频次:54
超临界CO2从黄花蒿中提取青蒿素的研究
钱国平,杨亦文,吴彩娟,等
摘要:研究了用超临界二氧化碳从黄花蒿中萃取青蒿素的影响因素。在152~297 MPa和40~60℃范围内,萃取压力和萃取温度升高,萃取率增大,萃取选择性下降。以萃取率和萃取选择性为目标,优化了超临界萃取工艺条件,得到较佳的操作条件萃取压力20 MPa,萃取温度50℃,CO2流量1 kg/(h·kg原料),原料粒径60~80目。在优化条件下萃取4 h,萃取率达到95%以上,萃取物纯度10%以上。
关键词:青蒿素;超临界二氧化碳;萃取;黄花蒿
来源出版物:化工进展, 2005, 24(3): 286-290
被引频次:54
青蒿毛状根合成青蒿素的培养条件研究
刘春朝,王玉春,欧阳藩,等
摘要:对影响青蒿(Artemisia annua L.)毛状根生长及青蒿素合成的培养条件进行了研究,确定最适的培养条件为:初始PH5.8~6.0,摇瓶转速130~150 r/min,摇瓶装液量体积分数为25%,光照周期为16 h/d,温度为30℃。在此条件下,经过25 d培养获得青蒿素产量为223.3 mg/L。
来源出版物:植物学报:英文版, 1998, 40(9): 831-835
被引频次:54
青蒿素理化性质及其测定方法的研究进展
王宗德,孙芳华
摘要:菊科植物黄花蒿(Artemisia annua L,即中药青蒿)在我国用作抗疟中药已有二千多年的历史。我国科学工作者70年代首次从中分离出一个含过氧基团的新型倍半萜内酯,并命名为青蒿素(Artemisinin;Arteannuin;Qinghaosu;QHS)。国内外大量理化实验,药理研究及临床应用表明,青蒿素是抗疟的有效成分。其结构独特,抗疟机制特别,对抗氯喹的恶性疟和脑性疟有特效,正因为它具有结构上的新颖性和药理作用中高效低毒等特点,国际上有关方面认为青蒿素的发现是抗疟研究史上的重大突破,并已成为世界卫生组织推荐的抗疟药品。
关键词:青蒿素;理化性质;测定方法
来源出版物:江西农业大学学报, 1999, 21(4): 606-611
被引频次:53
青蒿素介导肝癌细胞凋亡的实验研究
陈征途,黄真炎,吴玲霓
摘要:目的:探讨抗疟药青蒿琥酯对肝癌细胞株HepG2的凋亡诱导作用。方法:用MTT测定、流式细胞术、梯状DNA电泳和透射电镜术检测细胞凋亡。结果:经青蒿琥酯处理的HepG2细胞可见梯状DNA和凋亡小体等典型细胞凋亡特征。当青蒿琥酯浓度(80 μmol/L)接近TC50(74.21 μmol/L)时,HepG2细胞破坏率可达51.76%,细胞凋亡率为19.91%。结论:青蒿琥酯可诱导HepG2细胞凋亡。
关键词:青蒿琥酯;细胞凋亡;肝癌
来源出版物:中西医结合肝病杂志, 2000, 10(5): 23-25
被引频次:52
黄花蒿中青蒿素的超临界CO2流体提取工艺研究
葛发欢,张镜澄,陈列,等
摘要:研究了用超临界CO2流体萃取法从黄花蒿中提取青蒿素的工艺,主要探讨了压力、时间、CO2流量等因素对产品收率的影响,确定了最佳工艺条件,并进行了中试放大和工业化试验,所得产品质量达药品标准,与传统生产工艺(如汽油法)相比,收率提高了1.9倍,生产周期缩短近100 h,生产成本降低了447 元/kg。
关键词:超临界CO2萃取;青蒿素;工艺研究;工业化试验
来源出版物:中国医药工业杂志, 2000, 31(6): 250-253
被引频次:52
青蒿素类药物的药理作用新进展
郭燕,王俊,陈正堂
摘要:青蒿素是从植物黄花蒿中提取的抗疟疾的活性成份,目前在临床上广泛用于治疗疟疾。近些年研究发现青蒿素不仅可以抗寄生虫,包括疟原虫、血吸虫,而且具有显著的抗炎、调节免疫和抗肿瘤等多方面的药理作用。本文在介绍青蒿素抗疟疾作用、应用和作用机制的基础上,对近年来青蒿素类药物的其它主要生物学作用研究的现状进行综述。
关键词:青蒿素;抗疟疾;抗肿瘤;脓毒症;抗寄生虫
来源出版物:中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2006, 11(6): 615-620
被引频次:1400
Qinghaosu (Artemisinin): An antimalarial drug from China
Klayman, DL
Abstract: The herb Artemisia annua has been used for many centuries in Chinese traditional medicine as a treatment for fever and malaria.In 1971, Chinese chemists isolated from the leafy portions of the plant the substance responsible for its reputed medicinal action.This compound, called qinghaosu (QHS, artemisinin), is a sesquiterpene lactone that bears a peroxide grouping and, unlike most other antimalarials, lacks a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring system.The compound has been used successfully in several thousand malaria patients in China, including those with both chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum.Derivatives of QHS, such as dihydroqinghaosu, artemether, and the water-soluble sodium artesunate, appear to be more potent than QHS itself.Sodium artesunate acts rapidly in restoring to consciousness comatose patients with cerebral malaria.Thus QHS and its derivatives offer promise as a totally new class of antimalarials.
来源出版物:Science, 1985, 228(4703): 1049-1055
被引频次:1091
Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Dondorp, AM; Nosten, F; Yi, P; et al.
Abstract: Background: Artemisinin-based combination therapies are the recommended first-line treatments of falciparum malaria in allcountries with endemic disease.There are recent concerns that the efficacy of such therapies has declined on the Thai-Cambodian border, historically a site of emerging antimalarial-drug resistance.Methods: In two open-label, randomized trials, we compared the efficacies of two treatments for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Pailin, western Cambodia, and Wang Pha, northwestern Thailand: oral artesunate given at a dose of 2 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, for 7 days, and artesunate given at a dose of 4 mg per kilogram per day, for 3 days, followed by mefloquine at two doses totaling 25 mg per kilogram.We assessed in vitro and in vivo Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility, artesunate pharmacokinetics, and molecular markers of resistance.Results: We studied 40 patients in each of the two locations.The overall median parasite clearance times were 84 hours (interquartile range, 60 to 96) in Pailin and 48 hours (interquartile range, 36 to 66) in Wang Pha (P<0.001).Recrudescence confirmed by means of polymerase-chain-reaction assay occurred in 6 of 20 patients (30%) receiving artesunate monotherapy and 1 of 20 (5%) receiving artesunate-mefloquine therapy in Pailin, as compared with 2 of 20 (10%) and 1 of 20 (5%), respectively, in Wang Pha (P=0.31).These markedly different parasitologic responses were not explained by differences in age, artesunate or dihydroartemisinin pharmacokinetics, results of isotopic in vitro sensitivity tests, or putative molecular correlates of P.falciparum drug resistance (mutations or amplifications of the gene encoding a multidrug resistance protein [PfMDR1] or mutations in the gene encoding sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase6 [PfSERCA]).Adverse events were mild and did not differ significantly between the two treatment groups.Conclusions: P.falciparum has reduced in vivo susceptibility to artesunate in western Cambodia as compared with northwestern Thailand.Resistance is characterized by slow parasite clearance in vivo without corresponding reductions on conventional in vitro susceptibility testing.Containment measures are urgently needed.
Keywords: Artesunate-mefloquine; Artemether-lumefantrine; combination therapy; in-vitro; Thailand; Cambodia; border; efficacy; epidemiology; deployment
来源出版物:New England Journal of Medicine, 2009, 361(5): 455-467
被引频次:941
Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast
Ro, DK; Paradise, EM; Ouellet, M
Abstract: Malaria is a global health problem that threatens 300-500 million people and kills more than one million people annually(1).Disease control is hampered by the occurrence of multi-drug-resistant strains of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum(2,3).Synthetic antimalarial drugs and malarial vaccines are currently being developed, but their efficacy against malaria awaits rigorous clinical testing(4,5).Artemisinin, a sesquiterpene lactone endoperoxide extracted from Artemisia annua L (family Asteraceae; commonly known as sweet wormwood), is highly effective against multi-drug-resistant Plasmodium spp., but is in short supply and unaffordable to most malaria sufferers(6).Although total synthesis of artemisinin is difficult and costly(7), the semi-synthesis of artemisinin or any derivative from microbially sourced artemisinic acid, its immediate precursor, could be a cost-effective, environmentally friendly, high-quality and reliable source of artemisinin(8,9).Here we report the engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce high titres (up to 100 mg L-1) of artemisinic acid using an engineered mevalonate pathway, amorphadiene synthase, and a novel cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (CYP71AV1) from A.annua that performs a three-step oxidation of amorpha-4,11-diene to artemisinic acid.The synthesized artemisinic acid is transported out and retained on the outside of the engineered yeast, meaning that a simple and inexpensive purification process can be used to obtain the desired product.Although the engineered yeast is already capable of producing artemisinic acid at a significantly higher specific productivity than A.annua, yield optimization and industrial scale-up will be required to raise artemisinic acid production to a level high enough to reduce artemisinin combination therapies to significantly below their current prices.
Keywords: catalyzes 3 steps; gibberellin biosynthesis; Saccharomyces-cerevisiae; expression; malaria; pathway; cytochrome-p450; identification; reductase; oxidase
来源出版物:Nature, 2006, 440(7086): 940-943
被引频次:534
Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum
Eckstein-Ludwig, U; Webb, RJ; van Goethem, IDA; et al.
Abstract: Artemisinins are extracted from sweet wormwood (Artemisia annua) and are the most potent antimalarials available(1), rapidly killing all asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum(2).Artemisinins are sesquiterpene lactones widely used to treat multidrug-resistant malaria(1), a disease that annually claims 1 million lives.Despite extensive clinical and laboratory experience(3-5) their molecular target is not yet identified.Activated artemisinins form adducts with a variety of biological macromolecules, including haem, translationally controlled tumour protein (TCTP) and other higher-molecular-weight proteins(6).Here we show that artemisinins, but not quinine or chloroquine, inhibit the SERCA orthologue (PfATP6) of Plasmodium falciparum in Xenopus oocytes with similar potency to thapsigargin (another sesquiterpene lactone and highly specific SERCA inhibitor).As predicted, thapsigargin also antagonizes the parasiticidal activity of artemisinin.Desoxyartemisinin lacks an endoperoxide bridge and is ineffective both as an inhibitor of PfATP6 and as an antimalarial.Chelation of iron by desferrioxamine abrogates the antiparasitic activity of artemisinins and correspondingly attenuates inhibition of PfATP6.Imaging of parasites with BODIPY-thapsigargin labels the cytosolic compartment and is competed by artemisinin.Fluorescent artemisinin labels parasites similarly and irreversibly in an Fe2+-dependent manner.These data provide compelling evidence that artemisinins act by inhibiting PfATP6 outside the food vacuole after activation by iron.
Keywords: calcium-pump; antimalarial; derivatives; malaria; in vitro; resistance; reticulum; qinghaosu; parasite; drugs
来源出版物:Nature, 2003, 424(6951): 957-961
被引频次:421
Qinghaosu
Zhang, H; Wu, J; Zhang, J; et al.
Abstract: In December, 1979, an extraordinary paper in the Chinese Medical Journa[1 chronicled the discovery and evaluation of a group of antimalarial drugs derived from the Chinese medicinal herb qing hao (Artemisia annua L).This plant, also known as annual or sweet wormwood, is widely distributed in Europe, North America, India, and Eastern Asia.Medicinal use of qing hao (as a treatment for haemorrhoids!) was first described in the “52 Prescriptions” unearthed in 168 BC from the Mawangdui Han dynasty tomb in Changsha, Hunan province.The herb was specifically recommended for fevers in the Zhou Hou Bei Ji Fang, a handbook of prescriptions for emergencies written by Ge Heng and published in 341 AD.Thereafter qing hao appears in several standard Chinese materia medica texts as a treatment for febrile illnesses.
Keywords: acute falciparum-malaria; antimalarial activity; oral quinine; artemisinin; mefloquine; dihydroartemisinin; suppositories; drugs
来源出版物:The Lancet, 1993, 341(8845): 603-608
被引频次:396
Artesunate versus quinine for treatment of severe falciparum malaria: A randomised trial
Faiz, MA; Bin Yunus, E; Rahman, MR
Abstract: Background: In the treatment of severe malaria, intravenous artesunate is more rapidly acting than intravenous quinine in terms of parasite clearance, is safer, and is simpler to administer, but whether it can reduce mortality is uncertain.Methods: We did an open-label randomised controlled trial in patients admitted to hospital with severe falciparum malaria in Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, and Myanmar.We assigned individuals intravenous artesunate 2.4 mg/kg bodyweight given as a bolus (n=730) at 0, 12, and 24 h, and then daily, or intravenous quinine (20 mg salt per kg loading dose infused over 4 h then 10 mg/kg infused over 2-8 h three times a day; n=731).Oral medication was substituted when possible to complete treatment.Our primary endpoint was death from severe malaria, and analysis was by intention to treat.Findings: We assessed all patients randomised for the primary endpoint.Mortality in artesunate recipients was 15% (107 of 730) compared with 22% (164 of 731) in quinine recipients; an absolute reduction of 34.7% (95% CI 18.5%-47.6%; P=0.0002).Treatment with artesunate was well tolerated, whereas quinine was associated with hypoglycaemia (relative risk 3.2, 1.3-7.8; P=0.009).Interpretation Artesunate should become the treatment of choice for severe falciparum malaria in adults.
Keywords: cerebral malaria; plasmodium-falciparum; intramuscular artesunate; intravenous quinine; antimalarial-drugs; artemether; children; dihydroartemisinin; pharmacokinetics; tetracycline
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2005, 366(9487): 717-725
被引频次:361
Hydraulic lift - substantial nocturnal water transport between soil layers by artemisia-tridentata roots
Richards, JH; Caldwell, MM
Abstract: Diel soil water potential fluctuations reflected daytime depletion and nocturnal resupply of water in upper soil layers.Transpiration suppression experiments demonstrated that water absorption by roots caused the daytime depletion.The soil water potential data and experimental results suggest that at night water absorbed from moist soil by deeper roots is transported to and lost from roots into drier upper soil layers.The deeper roots appear to absorb and transport water both day and night.Implications for the efficiency of deep roots and water storage, nutrient uptake and water parasitism in upper soil layers are discussed.
Keywords: root water efflux; roots; soil water potential; plant water relations; desert shrubs
来源出版物:Oecologia, 1987, 73(4): 486-489
被引频次:324
Effects of artesunate-mefloquine combination on incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria and mefloquine resistance in western Thailand: A prospective study
Nosten, F; van Vugt, M; Price, R; et al.
Abstract: Background: Worsening drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a major threat to health in tropical countries.Wedid a prospective study of malaria incidence and treatment in an area of highly multidrug-resistant P falciparum malaria.Methods: We assessed incidence of P falciparum malaria and the in-vivo responses to mefloquine treatment over 13 years in two large camps for displaced Karen people on the northwest border of Thailand.During this time, the standard mefloquine dose was first increased, and then combined artesunate and mefloquine was introduced as first-line treatment for uncomplicated P falciparum malaria.Findings: Early detection and treatment controlled P falciparum malaria initially while mefloquine was effective (cure rate with mefloquine [15 mg/kg] and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine in 1985, 98% [95% CI 97-100]), but as mefloquine resistance developed, the cure rate fell (71% [67-77] in 1990).A similar pattern was seen for high-dose (25 mg/kg) mefloquine monotherapy from 1990-94.Since the general deployment of the artesunate-mefloquine combination in 1994, the cure rate increased again to almost 100% from 1998 onwards, and there has been a sustained decline in the incidence of P falciparum malaria in the study area.In-vitro susceptibility of P falciparum to mefloquine has improved significantly (P=0.003).Interpretation: In this area of low malaria transmission, early diagnosis and treatment with combined artesunate and mefloquine has reduced the incidence of P falciparum malaria and halted the progression of mefloquine resistance.We recommend that antimalarial drugs should be combined with artemisinin or a derivative to protect them against resistance.
Keywords: Burmese border; monoclonal-antibodies; elisa development; bed nets; sporozoites; epidemiology; prevention; pregnancy; area
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2000, 356(9226): 297-302
被引频次:323
Effects of artemisinin derivatives on malaria transmissibility
Price, RN; Nosten, F; Luxemburger, C; et al.
Abstract: Background: On the western border of Thailand the efficacy of mefloquine in the treatment of falciparum malaria has declined while gametocyte carriage rates have increased, which suggests increased transmissibility of these resistant infections.We compared the following antimalarial drugs in relation to subsequent Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte carriage: mefloquine, halofantrine, quinine, and the artemisinin derivatives.Methods: Between 1990 and 1995 we assessed gametocytaemia in a series of prospective studies of antimalarial drug treatment in 5193 adults and children with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria in an area of malarious hill forest on the western border of Thailand, Weekly parasite counts from thick and thin blood films were done during the 4-week (1990-93) or 9-week (1993-95) follow-up period, Gametocyte positivity rates and person gametocyte week (PGW) rates were calculated to measure gametocyte carriage and transmission potential.Findings: In primary P falciparum infections the gametocyte carriage rate was significantly higher after treatment with mefloquine than after treatment with the artemisinin (PGW 34.1 [95% CI 25.2-42.9] vs 3.9 [1.9-5.9] per 1000 person weeks; relative risk 8.0 [41-156]; P<00001).Recrudescent infections were associated with increased gametocyte carrier rates (relative risk 2.2 [1.6-3.0]; P<0.0001), but retreatment with artemisinin derivatives reduced subsequent gametocyte carriage 18.5 fold [3.5-98] compared with mefloquine retreatment and 6.8 fold (3.1-15.1) compared with quinine retreatment (P<0.001).The introduction of the artemisinin derivatives in routine treatment at this study site in mid 1994 was associated with a reduction in the subsequent incidence of falciparum malaria of 47 (25-69)%.Interpretation: Although environmental changes affect.vector numbers, and hence malaria incidence, artemisinin derivatives were found to reduce the transmission potential of falciparum malaria.Widespread introduction of artemisinin derivatives in the treatment of falciparum malaria may prevent the spread of multidrug resistance.
Keywords: resistant falciparum-malaria; Thai-burmese border; plasmodium-falciparum; mefloquine; pyrimethamine; sulfadoxine; gametocytes
来源出版物:The Lancet, 1996, 347(9016): 1654-1658
被引频次:307
Artemisinin: Mechanisms of action, resistance and toxicity
Meshnick, SR
Abstract: Artemisinin and its derivatives are widely used throughout the world.The mechanism of action of these compounds appears to involve the heme-mediated decomposition of the endoperoxide bridge to produce carbon-centred free radicals.The involvement of heme explains why the drugs are selectively toxic to malaria parasites.The resulting carbon-centred free radicals are alkylate heme and proteins, one of which is the translationally controlled tumour protein.Clinically relevant artemisinin resistance has not been demonstrated, but it is likely to occur since artemisinin resistance has been obtained in laboratory models.At high doses, artemisinin can be neurotoxic but toxicity has not been found in clinical studies.The mechanism of neurotoxicity may be similar to the mechanism of action.
Keywords: artemisinin; qinghaosu; endoperoxide; antimalarial; malaria; plasmodium
来源出版物:International Journal for Parasitology, 2002, 32(13): 1655-1660
被引频次:301
Resistance of Plasmodium falciparum field isolates to in-vitro artemether and point mutations of the SERCA-type PfATPase6
Jambou, R; Legrand, E; Niang, M
Abstract: Artemisinin derivatives are an essential component of treatment against multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria.We aimed to investigate in-vitro resistance to arternisinin derivatives in field isolates.In-vitro susceptibility of 530 P faliciparum isolates from three countries (Cambodia, French Guiana, and Senegal) with different arternisinin use was assessed with an isotopic microtest.Artemether IC50 up to 117 and 45 nmol/L was seen in French Guiana and Senegal, respectively.DNA sequencing in a subsample of 60 isolates lends support to SERCA-PfATPase6 as the target for artemisinins.The S769N PfATPase6 mutation, noted exclusively in French Guiana, was associated with raised (>30 nmol/L) artemether IC(50)s (P<0.0001, Mann-Whitney).All resistant isolates came from areas with uncontrolled use of arternisinin derivatives.This rise in resistance indicates the need for increased vigilance and a coordinated and rapid deployment of drug combinations.
Keywords: susceptibility; chloroquine; artesunate; mefloquine; gene
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2005, 366(9501): 1960-1963
被引频次:301
Artesunate combinations for treatment of malaria: Meta-analysis
Adjuik, M; Agnamey, P; Babiker, A; et al.
Abstract: Background: Addition of artemisinin derivatives to existing drug regimens for malaria could reduce treatment failure and transmission potential.We assessed the evidence for this hypothesis from randomised controlled trials.Methods: We undertook a meta-analysis of individual patients' data from 16 randomised trials (n=5948) that studied the effects of the addition of artesunate to standard treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria.We estimated odds ratios (OR) of parasitological failure at days 14 and 28 (artesunate combination compared with standard treatment) and calculated combined summary ORs across trials using standard methods.Findings: For all trials combined, parasitological failure was lower with 3 days of artesunate at day 14 (OR 0.20, 95% CI 0.17-0.25, n=4504) and at day 28 (excluding new infections, 0.23, 0.19-0.28, n=2908; including re-infections, 0.30, 0.26-0.35, n=4332).Parasite clearance was significantly faster (rate ratio 1.98, 95% CI 1.85-2.12, n=3517) with artesunate.In participants with no gametocytes at baseline, artesunate reduced gametocyte count on day 7 (OR 0.11, 95% CI 0.09-0.15, n=2734), with larger effects at days 14 and 28.Adding artesunate for 1 day (six trials) was associated with fewer failures by day 14 (0.61, 0.48-0.77, n=1980) and day 28 (adjusted to exclude new infections 0.68, 0.53-0.89, n=1205; unadjusted including reinfections 0.77, 0.63-0.95, n=1958).In these trials, gametocytes were reduced by day 7 (in participants with no gametocytes at baseline 0.11, 0.09-0.15, n=2734).The occurrence of serious adverse events did not differ significantly between artesunate and placebo.Interpretation: The addition of 3 days of artesunate to standard antimalarial treatments substantially reduce treatment failure, recrudescence, and gametocyte carriage.
Keywords: plasmodium-falciparum malaria; mefloquine combination; uncomplicated malaria; resistance; trial; amodiaquine; overviews; mortality; children
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2004, 363(9402): 9-17
被引频次:298
Impact of artemisinin-based combination therapy and insecticide-treated nets on malaria burden in Zanzibar
Bhattarai, Achuyt; Ali, AS; Kachur, SP; et al.
Abstract: Background: The Roll Back Malaria strategy recommends a combination of interventions for malaria control.Zanzibar implemented artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) for uncomplicated malaria in late 2003 and long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) from early 2006.ACT is provided free of charge to all malaria patients, while LLINs are distributed free to children under age 5 y (“under five”) and pregnant women.We investigated temporal trends in Plasmodium falciparum prevalence and malaria-related health parameters following the implementation of these two malaria control interventions in Zanzibar.Methods and Findings: Cross-sectional clinical and parasitological surveys in children under the age of 14 y were conducted in North A District in May 2003, 2005, and 2006.Survey data were analyzed in a logistic regression model and adjusted for complex sampling design and potential confounders.Records from all 13 public health facilities in North A District were analyzed for malaria-related outpatient visits and admissions.Mortality and demographic data were obtained from District Commissioner’s Office.P.falciparum prevalence decreased in children under five between 2003 and 2006; using 2003 as the reference year, odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were, for 2005, 0.55 (0.28-1.08), and for 2006, 0.03 (0.00-0.27); P for trend<0.001.Between 2002 and 2005 crude under-five, infant ( under age 1 y), and child ( aged 1-4 y) mortality decreased by 52%, 33%, and 71%, respectively.Similarly, malaria-related admissions, blood transfusions, and malaria-attributed mortality decreased significantly by 77%, 67% and 75%, respectively, between 2002 and 2005 in children under five.Climatic conditions favorable for malaria transmission persisted throughout the observational period.Conclusions: Following deployment of ACT in Zanzibar2003, malaria-associated morbidity and mortality decreased dramatically within two years.Additional distribution of LLINs in early 2006 resulted in a 10-fold reduction of malaria parasite prevalence.The results indicate that the Millennium Development Goals of reducing mortality in children under five and alleviating the burden of malaria are achievable in tropical Africa with high coverage of combined malaria control interventions.
Keywords: artemether-lumefantrine; children; mortality; Tanzania
来源出版物:Plos Medicine, 2007, 4(11): 1784-1790
被引频次:292
Emergence of artemisinin-resistant malaria on the western border of Thailand: A longitudinal study
Phyo, AP; Nkhoma, S; Stepniewska, K; et al.
Abstract: Background: Artemisinin-resistant falciparum malaria has arisen in western Cambodia.A concerted international effort is underway to contain artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum, but containment strategies are dependent on whether resistance has emerged elsewhere.We aimed to establish whether artemisinin resistance has spread or emerged on the Thailand-Myanmar (Burma) border.Methods: In malaria clinics located along the northwestern border of Thailand, we measured six hourly parasite counts in patients with uncomplicated hyperparasitaemic falciparum malaria (>=4% infected red blood cells) who had been given various oral artesunatecontaining regimens since 2001.Parasite clearance half-lives were estimated and parasites were genotyped for 93 single nucleotide polymorphisms.Findings: 3202 patients were studied between 2001 and 2010.Parasite clearance half-lives lengthened from a geometric mean of 2.6 h (95% CI 2.5-2.7) in 2001, to 3.7 h (3.6-3.8) in 2010, compared with a mean of 5.5 h (5.2-5.9) in 119 patients in western Cambodia measured between 2007 and 2010.The proportion of slow-clearing infections (half-life>= 6.2 h) increased from 0.6% in 2001, to 20% in 2010, compared with 42% in western Cambodia between 2007 and 2010.Of 1583 infections genotyped, 148 multilocus parasite genotypes were identified, each of which infected between two and 13 patients.The proportion of variation in parasite clearance attributable to parasite genetics increased from 30% between 2001 and 2004, to 66% between 2007 and 2010.Interpretation: Genetically determined artemisinin resistance in P falciparum emerged along the Thailand-Myanmar border at least 8 years ago and has since increased substantially.At this rate of increase, resistance will reach rates reported in western Cambodia in 2-6 years.
Keywords: antimalarial-drug resistance; falciparum-malaria; Plasmodium falciparum; multidrug-resistance; parasite clearance; southeast-asia; Cambodia; spread; heritability; artesunate
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2012, 379(9830): 1960-1966
被引频次:288
Isolation and identification of a senescence-promoting substance from wormwood (Artemisia-absinthium L)
Ueda, J; Kato, J
Abstract: The senescence-promoting substance of wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.) as detected by the oat (Avena sativa L.cv“Victory”) leaf assay has been identified as (-)-methyl jasmonate, methyl (1S, 2R)-3-oxo-2-(2’-cis-pentenyl)-cyclopentane-1-acetate, by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and optical rotatory dispersion.Its senescence-promoting effect was much stronger than that of abscisic acid, and even at such a low concentration as 1 to 2.5 micrograms per milliliter, it could completely eliminate the anti-senescence action of 2 micrograms per milliliter kinetin.Comparing the biological activity of the (-)- with the (±)- forms of methyl jasmonate, it seemed that only the (-)- form was biologically active.
来源出版物:Plant Physiology, 1980, 66(2): 246-249
被引频次:244
The anti-malarial artesunate is also active against cancer
Efferth, T; Dunstan, H; Sauerbrey, A; et al.
Abstract: Artesunate (ART) is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin, the active principle of the Chinese herb Artemisia annua.ART reveals remarkable activity against otherwise multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum and P.vivax malaria.ART has now been analyzed for its anticancer activity against 55 cell lines of the Developmental Therapeutics Program of the National Cancer Institute, USA.ART was most active against leukemia and colon cancer cell lines (mean GI(50) values: 1.11 +/-0.56 micro M and 2.13 +/-0.74 micro M, respectively).Non-small cell lung cancer cell lines showed the highest mean GI(50) value (25.62 +/- 14.95 micro M) indicating the lowest sensitivity towards NIT in this test panel.Intermediate GI(50) values were obtained for melanomas, breast, ovarian, prostate, CNS, and renal cancer cell lines.Importantly, a comparison of ART's cytotoxicity with those of other standard cytostatic drugs showed that ART was active in molar ranges comparable to those of established anti-tumor drugs.Furthermore, we tested CEM leukemia sub-lines resistant to either doxorubicin, vincristine, methotrexate, or hydroxyurea which do not belong to the N.C.I, screening panel.None of thesedrug-resistant cell lines showed cross resistance to ART.To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms of ART’s cytotoxicity, we used a panel of isogenic Saccaromyces cerevisiae strains with defined genetic mutations in DNA repair, DNA checkpoint and cell proliferation genes.A yeast strain with a defective mitosis regulating BUB3 gene showed increased ART sensitivity and another strain with a defective proliferation-regulating CLN2 gene showed increased ART resistance over the wild-type strain, wt644.None of the other DNA repair or DNA check-point deficient isogenic strains were different from the wildtype.These results and the known low toxicity of ART are clues that ART may be a promising novel candidate for cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: BUB3; chemotherapy; CLN2; drug resistance; neoplasms; Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant strains
来源出版物:International Journal of Oncology, 2001, 18(4): 767-773
被引频次:225
Artesunate versus quinine in the treatment of severe falciparum malaria in African children (AQUAMAT): An open-label, randomised trial
Dondorp, AM; Fanello, CI; Hendriksen, ICE; et al.
Abstract: Background: Severe malaria is a major cause of childhood death and often the main reason for paediatric hospital admission in sub Saharan Africa Quinine is still the established treatment of choice, although evidence from Asia suggests that artesunate is associated with a lower mortality We compared parenteral treatment with either artesunate or quinine in African children with severe malaria.Methods: This open label randomised trial was undertaken in 11 centres in nine African countries Children (<15 years) with severe falciparum malaria were randomly assigned to parenteral artesunate or parenteral quinine Randomisation was in blocks of 20, with study numbers corresponding to treatment allocations kept inside opaque sealed paper envelopes The trial was open label at each site, and none of the investigators or trialists apart from for the trial statistician had access to the summaries of treatment allocations The primary outcome measure was in hospital mortality analysed by intention to treat This trial is registered, number ISRCTN50258054.Findings: 5425 children were enrolled 2712 were assigned to artesunate and 2713 to quinine All patients were analysed for the primary outcome 230 (8.5%) patients assigned to artesunate treatment died compared with 297 (10.9%) assigned to quinine treatment (odds ratio [OR] stratified for study site 0.75, 95% CI 0.63-0.90, relative reduction 22.5%, 95% CI 8.1-36.9, P=0.0022) Incidence of neurological sequelae did not differ significantly between groups, but the development of coma (65/1832 [3.5%] with artesunate vs 91/1768 [5.1%] with quinine OR 0.69, 95% CI 0.49-0.95, P=0.0231) convulsions (224/2712 [8.3%] vs 273/2713 [10.1%] OR 0.80, 0.66-0.97 P=0.0199) and deterioration of the coma score (166/2712 [6.1%] vs 208/2713 [7.7%], OR 0.78, 0.64-0.97, P=0.0245) were all significantly less frequent in artesunate recipients than in quinine recipients Post treatment hypoglycaemia was also less frequent in patients assigned to artesunate than in those assigned to quinine (48/2712 [1.8%] vs 75/2713 [2.8%] OR 0.63 0.43-0.91 P=0.0134) Artesunate was well tolerated with no serious drug related adverse effects.Interpretation: Artesunate substantially reduces mortality in African children with severe malaria These data together with a meta analysis of all trials comparing artesunate and quinine, strongly suggest that parenteral artesunate should replace quinine as the treatment of choice for severe falciparum malaria worldwide.
Keywords: cerebral malaria; intramuscular artesunate; intravenous quinine; artemether; dihydroartemisinin; pharmacokinetics; mortality
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2010, 376(9753): 1647-1657
被引频次:218
Iron-dependent free-radical generation from the antimalarial agent artemisinin (qinghaosu)
Meshnick, SR; Yang, YZ; Lima, V; et al.
Abstract: Artemisinin is an important new antimalarial agent containing a bridged endoperoxide.The in vitro antimalarial activity of an artemisinin derivative, arteether, is antagonized by two iron chelators, pyridoxal benzoylhydrazone and 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one.Similarly, the acute toxicity of artemisinin in mice is antagonized by another chelator, deferoxamine-hydroxyethylstarch.A combination of artemisinin and hemin oxidizes erythrocyte membrane thiols in vitro, and this oxidation is also inhibited by an iron chelator.Thus, iron plays a role in the mechanisms of action and toxicity of artemisinin.The combination of artemisinin and hemin also decreases erythrocyte deformability.Iron probably catalyzes the generation of free radicals from artemisinin since alpha-tocopherol antagonizes the thiol-oxidizing activity of artemisinin and since a spin-trapped free radical signal can be seen by electron paramagnetic resonance only when artemisinin is incubated in the presence of iron.
Keywords: pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone; plasmodium-falciparum; cross-linking; hemoglobin; in vitro; malaria; desferrioxamine; erythrocytes; inhibition; chelators
来源出版物:Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1993, 37(5): 1108-1114
被引频次:215
Amodiaquine-artesunate versus amodiaquine for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in African children: A randomised, multicentre trial
Adjuik, M; Agnamey, P; Babiker, A; et al.
Abstract: Background: Increasing drug resistance limits the choice of efficacious chemotherapy against Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Africa.Amodiaquine still retains efficacy against P falciparum in many African countries.We assessed the safety, treatment efficacy, and effect on gametocyte carriage of adding artesunate to amodiaquine in three randomised trials in Kenya, Senegal, and Gabon.Methods: We enrolled 941 children (400 in Kenya, 321 in Senegal, and 220 in Gabon) who were 10 years or older and who had uncomplicated P falciparum malaria.Patients were randomly assigned amodiaquine (10 mg/kg per day for 3 days) plus artesunate (4 mg/kg per day for 3 days) or amodiaquine (as above) and placebo (for 3 days).The primary endpoints were parasitological cure rates at days 14 and 28.Analysis was by intention to treat and by an evaluability method.Findings: Both regimens were well tolerated.Six patients in the amodiaquine-artesunate group and five in the amodiaquine group developed early, drug-induced vomiting, necessitating alternative treatment.By intention-to-treat analysis, the day-14 cure rates for amodiaquine-artesunate versus amodiaquine were: 175/192 (91%) versus 140/188 (74%) in Kenya (Delta=16.7% [95% CI 9.3-24.1], P<0.0001), 148/160 (93%) versus 147/157 (94%) in Senegal (-1.1% [-6.7 to 4.5], P=0.7), and 92/94 (98%) versus 86/96 (90%) in Gabon (8.3% [1.5-15.1], P=0.02).The corresponding rates for day 28 were: 123/180 (68%) versus 75/183 (41%) in Kenya (27.3% [17.5-37.2], P<0.0001), 130/159 (82%) versus 123/156 (79%) in Senegal (2.9% [-5.9 to 11.7], P=0.5), and 80/94 (85%) versus 70/98 (71%) in Gabon (13.7% [2.2-25.2], P=0.02).Similar rates were obtained by evaluability analysis.Interpretation: The combination of artesunate and amodiaquine improved treatment efficacy in Gabon and Kenya, and was equivalent in Senegal.Amodiaquine-artesunate is a potential combination for use in Africa.Further investigations to assess the potential effect on the evolution of drug resistance, disease transmission, and safety of amodiaquine-artesunate are warranted.
Keywords: pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine; antimalarial drug; double-blind; efficacy; chloroquine; resistance; artemether; benflumetol; combination; CGP-56697
来源出版物:The Lancet, 2002, 359(9315): 1365-1372
被引频次:211
A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Frederic A; Witkowski, B; Amaratunga, C; et al.
Abstract: Plasmodium falciparum resistance to artemisinin derivatives in southeast Asia threatens malaria control and elimination activities worldwide.To monitor the spread of artemisinin resistance, a molecular marker is urgently needed.Here, using whole-genome sequencing of an artemisinin-resistant parasite line from Africa and clinical parasite isolates from Cambodia, we associate mutations in the PF3D7_1343700 kelch propeller domain (‘K13-propeller’) with artemisinin resistance in vitro and in vivo.Mutant K13-propeller alleles cluster in Cambodian provinces where resistance is prevalent, and the increasing frequency of a dominant mutant K13-propeller allele correlates with the recent spread of resistance in western Cambodia.Strong correlations between the presence of a mutant allele, in vitro parasite survival rates and in vivo parasite clearance rates indicate that K13-propeller mutations are important determinants of artemisinin resistance.K13-propeller polymorphism constitutes a useful molecular marker for large-scale surveillance efforts to contain artemisinin resistance in the Greater Mekong Subregion and prevent its global spread.
Keywords: kelch-repeat superfamily; in vitro; parasite clearance; western Cambodia; chloroquine resistance; antimalarial-drugs; point mutations; copy number; Keap1; Vivo
来源出版物: Nature, 2014, 505(7481): 50-55
Qinghaosu (artemisinin): An antimalarial drug from China
Klayman, DL
Background: Artemisinin-based combination therapies are the recommended first-line treatments of falciparum malaria in all countries with endemic disease.There are recent concerns that the efficacy of such therapies has declined on the Thai-Cambodian border, historically a site of emerging antimalarial-drug resistance.Methods: In two open-label, randomized trials, we compared the efficacies of two treatments for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Pailin, western Cambodia, and Wang Pha, northwestern Thailand: Oral artesunate given at a dose of 2 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, for 7 days, and artesunate given at a dose of 4 mg per kilogram per day, for 3 days, followed by mefloquine at two doses totaling 25 mg per kilogram.We assessed in vitro and in vivo Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility, artesunate pharmacokinetics, and molecular markers of resistance.Results: We studied 40 patients in each of the two locations.The overall median parasite clearance times were 84 hours (interquartile range, 60 to 96) in Pailin and 48 hours (interquartile range, 36 to 66) in Wang Pha (P<0.001).Recrudescence confirmed by means of polymerase-chain-reaction assay occurred in 6 of 20 patients (30%) receiving artesunate monotherapy and 1 of 20 (5%) receiving artesunate-mefloquine therapy in Pailin, as compared with 2 of 20 (10%) and 1 of 20 (5%), respectively, in Wang Pha (P=0.31).These markedly different parasitologic responses were not explained by differences in age, artesunate or dihydroartemisinin pharmacokinetics, results of isotopic in vitro sensitivity tests, or putative molecular correlates of P.falciparum drug resistance (mutations or amplifications of the gene encoding a multidrug resistance protein [PfMDR1] or mutations in the gene encoding sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase6 [PfSERCA]).Adverse events were mild and did not differ significantly between the two treatment groups.Conclusions: P.falciparum has reduced in vivo susceptibility to artesunate in western Cambodia as compared with northwestern Thailand.Resistance is characterized by slow parasite clearance in vivo without corresponding reductions on conventional in vitro susceptibility testing.Containment measures are urgently needed.Keywords: artesunate-mefloquine; artemether-lumefantrine; combination therapy; in-vitro; Thailand; Cambodia; border; efficacy; epidemiology; deployment来源出版物:New England Journal of Medicine, 2009, 361(5): 455-467Total synthesis of arteannuin and deoxyarteannuinXu, XX; Zhu, J; Huang, DZ ; et al.Abstract: Arteannuin 1 is a new sesquiterpene lactone containing a peroxide linkage and is an antimalarial principle isolated from Artemisia annua L..R(+)-Citronellal 5 as a starting material for the total synthesis was converted into 11R(-)-methyl dihydroarteannuinate 12 in 14 steps.The key intermediate 4 was obtained from compound 12 in 5 steps.The introduction of hydroperoxide in 4 by photooxidation followed by acid treatment gave 1.Hydroxylation of 4 with osmium tetraoxide afforded deoxyarteannuin 2.来源出版物:Tetrahedron, 1986, 42(3): 819-828Iron-dependent free-radical generation from the antimalarial agent artemisinin (qinghaosu)Meshnick, SR; Yang, YZ; Lima, V; et al.Abstract: Artemisinin is an important new antimalarial agent containing a bridged endoperoxide.The in vitro antimalarial activity of an artemisinin derivative, arteether, is antagonized by two iron chelators, pyridoxal benzoylhydrazone and 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one.Similarly, the acute toxicity of artemisinin in mice is antagonized by another chelator, deferoxamine-hydroxyethylstarch.A combination of artemisinin and hemin oxidizes erythrocyte membrane thiols in vitro, and this oxidation is also inhibited by an iron chelator.Thus, iron plays a role in the mechanisms of action and toxicity of artemisinin.The combination of artemisinin and hemin also decreases erythrocyte deformability.Iron probably catalyzes the generation of free radicals from artemisinin since alpha-tocopherol antagonizes the thiol-oxidizing activity of artemisinin and since a spin-trapped free radical signal can be seen by electron paramagnetic resonance only when artemisinin is incubated in the presence of iron.
pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone; plasmodium-falciparum; cross-linking; hemoglobin; Invitro; malaria; desferrioxamine; erythrocytes; inhibition; chelators
