Biological Activity of Several Fungicides against Ustilaginoidea virens
2015-12-14XianyanSUYuCHENXuexiangRENAifangZHANGZhengheYE
Xianyan SU, Yu CHEN, Xuexiang REN, Aifang ZHANG, Zhenghe YE
Insititute of Plant Protection and Agro-products safety, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
Rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) occurs in many countries,especially in the rice producing countries of Asia, but also in the US and Africa. In China, it occurs mainly in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui,Guangdong,Guangxi,Hunan,Sichuan,Beijing,and Tianjin[1-2].Since the 1970s,the disease is deteriorating and even results in eruption in middle and lower reaches plain of Yangtze River.What’s worse, the disease usually infects middle-season and late-season rice, as well as hybrid rice[2]. It is notable that the disease at light degrees would not lead severe loss of rice yield,but would increase rate of shrivelled kernel and decrease thousandgrain weight. Because false smut or black, it affects rice appearance and lower rice quality. On the other hand,with toxin, false smut poses threats to human and domestic animals. Therefore,it is crucial for rice and crop safety to control false smut[3].
False smut pathogen can be classified into Ustilaginoidea virens (Cook)Takahashi (anamorph)and Claviceps oryzae-sativae Has. (sexual stage).The yellow chlamydospores are capable of germination, but black chlamydospores would not germinate[3].
At present, the infection cycle of false smut is not clear, but it is known that the pathogens overwinter relying on diseased plants or soils in the forms of sclerotium and chlamydospore.However, the issue of primary infection is unsettled either. Because both chlamydospore and ascospore produce thin-wall conidia from germination, it is speculated that the thin-wall conidia are primary sources of infection[1]and it is believed that rice floral organ is the location the earliest infected from booting stage to rice rupturing stage[3]. What’s more, Dai et al. researched that conidia of false smut forms mycelium on glumes, extending to inner part of glumes,which providesreferences for direct infection of rice grains by conidia[4]. Based on practical experience, control effects are insignificant before booting stage or after rice rupturing stage by spraying insecticides. The inhibitory activities of the fungicide against mycelial growth of Ustilaginoidea virens were measured to in vitro evaluate the EC50values, and 17 fungicides were sprayed to evaluate the efficacy and effect of the fungicides tested in the field trials on the rice characters.
Materials and Methods
Test agentia
In the test, 98% carbendazim technical,produced by Shanghai Wusong Chemical Plant, was collected and dissolved into mother liquor(5 000 μg/ml) prepared with 0.1 mol/ml hydrochloric acid solution; 97% difenoconazole from Jiangsu Gengyun Chemicals Company, 97% epoxiconazole from Gongdong Deli Co., Ltd.,97%propiconazole from Zhangjiagang Qizhou Co. Ltd., and 97% prochlorazfrom Nantong Jinling Agriculural Chemicals were dissolved into acetone to prepare 5 000 μg/ml mother liquor.

Table 1 Dosage of the tested fungicides infield trials
Cultural medium and bacterial strain
The bacterial strain included fresh false smut balls collected from Mountain Huang and wild sensitive strain by single spore isolation based on WA culture medium.
Specifically, WA culture medium contained 20 g agar and fixed to a constant volume of 1 L added with water and rice-water culture medium contained 200 g brown rice,20 g agar,which was fixed to a constant volume of 1 L.
Effects of bactericides on growth of mycelia false smut pathogen
According to measurement of growth rates of mycelium[5], difenoconazole, carbendazim, propiconazole, prochloraz, and epoxiconazolewere measured on PSA plates of 0,0.025,0.05,0.10,0.20,0.40,0.80 and 1.60 μg/ml in terms of the inhibition effects on mycelia growth. Every treatment was designed with three replications, and every test was with two replications. The culture media were placed in an incubator at 25 ℃for 30 d. Finally, the concentration (EC50) of different bactericides the most effective in controlling growth of mycelia can be computed on rice-water culture medium in accordance with inhibition rates of bactericides at different concentrations.

Table 2 Inhibitory effect of different fungicides against mycelial growth of Ustilaginoidea viren isolates
Field control on false smut by different bactericides
As shown in Table 1,the test was conducted in Nishui Village, Chashui Town, Qianshan County, Anhui Province,and it is located in the Dabie Mountains,with frequent rainy or foggy days at low temperatures. Therefore,the environment is suitable for false smut development, as well as a frequent occurring area. Specifically, rice was sown on April 25, 2014 and transplanted in the end of May, with planting spacing of 20×27 cm. With field management the same as local method, 25% compound fertilizer at 375 kg/hm2and urea at 300 kg/hm2were applied as base fertilizers and another urea was applied at 150 kg/hm2after seedling grew to accelerate tillering. Besides, fungicides were applied on August 7 and August 17,respectively,and the results were surveyed on September 17.
Test medicines were designed as per randomized block design. For example,every test bactericide was used by recommended doses and sprayed uniformly with a sprayer (Gongnong-16 type). It is notable that concentration gradient was not designed temporarily. Furthermore, the test designed two control groups with Aimiao(a kind of fungicide) and carbendazim,which were applied as per local method or recommended doses. In addition,a control group was arranged with water. It can be concluded that the test totaled 18 treatments. Specifically, test fields were constructed with rows for protection, and every treatment was with four replications. Besides,every test plot had an area of 30 m2. The fungicides were applied at 16:00 and rice was isolated with plastics in case of cross-border pollution.And the applications were conducted 6-9 d before rice rupturing stage and peak-heading stage respectively. Every treatment should be added with water of 750 kg/hm2.
100 ears or 10 clumps of rice were collected from 5 sampled sites to record the number of diseased plant,disease index and averaged protection effects. Rice yields should be measured at harvesting.
The disease degree can be classified into grade 0 meaning rice was free from disease, grade 1 meaning with a false smut ball, grade 3 meaning with two false smut balls, grade 5 meaning with 3 -5 false smut balls, grade 7 meaning with 6-10 balls and grade 9 meaning with over 10 balls.
Fungicide effect was computed as follows:
Disease index =[∑(The number of diseased rice at different grades×the value of relative grade/The total number of surveyed plant×9]×100
Relative control effect ∥% =(1 -Disease index in treatments/Disease index in control)×100.
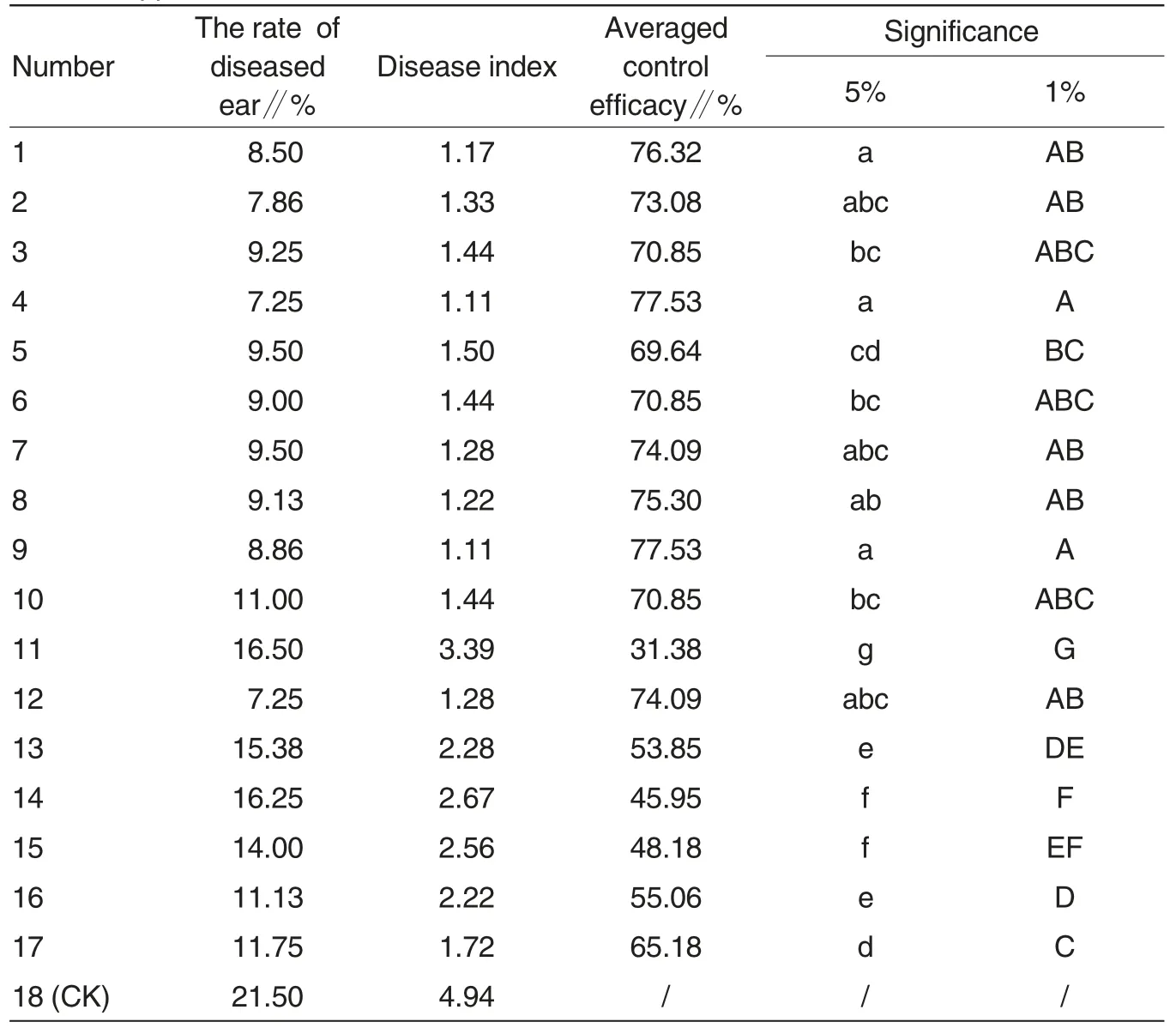
Table 3 Efficacy of 11 fungicides in controlling rice false smut after the second fungicide application
Results and Analysis
Inhibitory effect of different fungicides against mycelial growth of Ustilaginoidea viren isolates
As shown in Table 2, epoxiconazole performed the best in inhibitory effect on mycelial growth, with EC50of 0.04 μg/ml,followed by difenoconazole with EC50of 0.07 μg/ml, procloraz with EC50of 0.11 μg/ml and propiconazole with EC50of 0.12 μg/ml. Carbendazim performed the weakest with EC50of 0.68 μg/ml.
Efficacy of fungicides in controlling rice false smut and effects on rice yield
Nishui Village is situated in Qian-shan County, Anhui Province, and it belongs to a part of Dabie Mountains,so that foggy days or rainy days are much more, with low temperatures.Therefore, false smut becomes much common here. In 2014, for example,the disease rate kept around 20%. As shown in Table 3, the treatments with 25% epoxiconazole (suspending agent) and 28% propiconazole and prochloraz (emulsion) reached the highest in control effect of 77.53% ,with the lowest disease rate of 1.11%.What’s more, except of the control treatments with carbendazim and Aimiao, the rest treatments all achieved 70% or even higher in terms of control effect. Additionally, the treatment with Wenquning (a kind of fungicide) also performed well in controlling false smut, which reached 70.85%, and the treatments showed control effects in the range of 30%-50%with berberine,DQC-1,sf-62 and PBS-1.
According to analysis of variance,efficacy of fungicides in controlling rice false smut, showed insignificant differences, including difenoconazole,prochloraz, epoxiconazole, difenoconazole·prochloraz, difenoconazole·epoxiconazole,propiconazole·prochloraz,tebuconazole·fenaminstrobin,but kept higher than those of other treatments,followed by the treatments with propiconazole,carbendazim·epoxiconazole,and Wenquning.Other treatments also showed control efficacy, but significantly lower.
The measurements showed that per unit area yields both achieved about 8 250 kg/hm2in test plots with fungicides and control group with water, suggesting that the fungicides have insignificant effects on increasing rice yield(Table 4).
In the test, the 17 fungicides showed none phytotoxicity on rice leaf and seed.
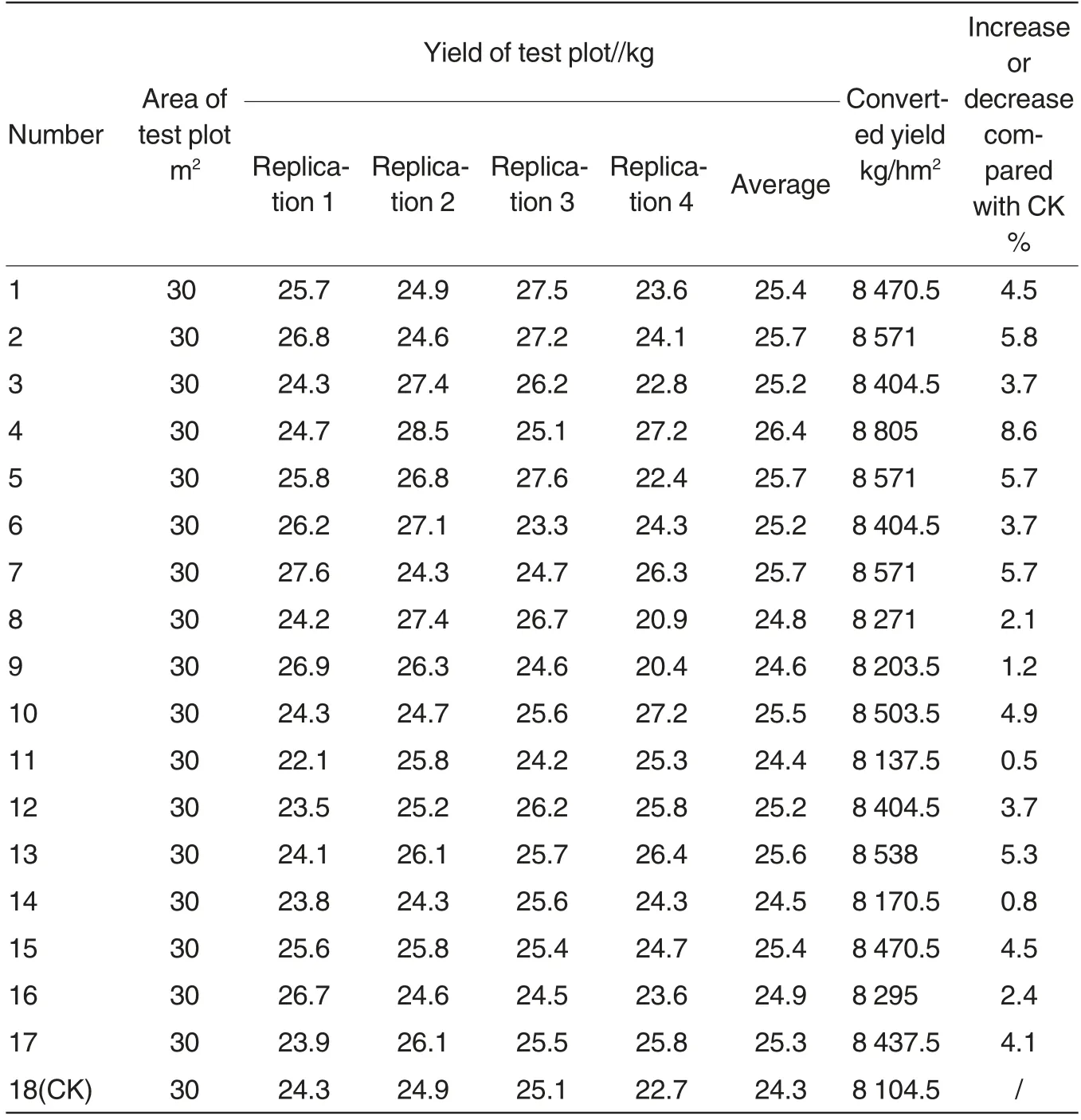
Table 4 Yield evaluation after the second fungicide application in controlling rice false smut
Discussions
Since discovered in 1878, false smut has been researched a lot at home and abroad.However,some unknown fields required further exploration, such as primary infection, infection process,structure of false smut pathogen, and mechanism of false smut pathogen. Besides, host ranges and the diseasing process are not precisely determined. With disease grading and distribution model available,the tolerance standard is not uniform and can not be references for breeding false smut-tolerant cultivars.Additional, the inoculation technology should be further improved and specific pesticides are ready to be developed[1].
It is key for effective control of false smut to determine pathogenic mechanism, but there are two technique difficulties should be resolved.The first is to seek a precise and rapid inoculation method.It is known that the diseasing time lasts longer in field, but infection time concentrates,which multiplies the difficulties for exploring pathogenic mechanism of false smut.It can be concluded that low diseasing rate of rice by artificial inoculation constitutes a major cause of slow advancing of researching disease tolerance and pathogenicity. Zhang et al. made progress on inoculation technology of false smut and the results showed that the diseasing rate of ear by artificial inoculation can be as high as 100%, disease index of 85.5 in farmlands, and the number of diseased kernel of 106[6-7].Chen et al.investigated the rice tolerance against false smut and pathogenicity differentiation[8]. The 2nd is to establish a rapid detection method in different stages of infection, which will facilitate treatment mechanism,for infection process lasts longer. Therefore, it is of significance for further recognition on pathogenesis of false smut to investigate false smut with advanced technology.It is notable that effective control on false smut should be based on specific prevention measures and medicines upon specific infection stage.
From practical experience, it can be concluded that fungicide spraying is useless before booting stage or after rice rupturing stage, and the period from booting to rupturing stages is key for the infection. Therefore, flag-leaf spreading stage is a morphological index for preventing false smut.Liu et al.believed that the term 5-7 d before rice rupturing stage is an optimal time for controlling false smut,when it is the most effective to apply validamycinand cuaminosulfate[9]. However, the term 7 d before rice rupturing stage is inferred from the stage of rice rupturing,which is difficult to be grasped and hard to be implemented. Xu et al. determined the term when flag-leaf grew and overlapped the penultimate pulvinus as a start point to observe jointing,rice rupturing, and sprouting, and the results showed that the period 5 d after the start point is an appropriate terms for medicine application[10]. We conducted research during 2007 -2008 and concluded that the control effect proved better during flag-leaf spreading term which is early for identification[11]. The research the 17 fungicides all can well control false smut and the treatments even kept around or over 70% in control efficacy with Wenquning,difenoconazole,prochloraz,propiconazole, and epoxiconazole. Therefore, it requires further exploration on select agentia capable of significantly reducing diseasing rate and index of false smut.
[1]WANG HK (王洪凯),LIN FC (林福呈).Research progress of false smut (稻曲病研究进展)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis(浙江农业学报),2008,20(5):385-390.
[2]JI HP (季宏平). Advances in study on false smut of rice(国内外稻曲病研究进展)[J].Heilongjiang Agricultural Science(黑龙江农业科学),2002,(4):34-37.
[3]HUANG SW(黄世文),YU LQ(余柳青).Present situation of studies on rice false smut in China(国内稻曲病的研究现状)[J].Acta Agriculturae J iangxi (江西农业学报),2002,14(2):45-51.
[4]DAI GH (代光辉),ZHAO J (赵杰),HE RM (何润梅), et al. Histochemical observation on the resistant and susceptible varieties to Ustilaginoidea virens(Cooke)Tak and way of conidia(稻曲病不同抗性水稻品种的组织化学及分生孢子侵染途径的初步观察)[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica (植物病理学报),2005,35(1):37-42.
[5]ZHOU MG (周明国),YE ZY (叶钟音),LIU JF(刘经芬).Research progress on disease tolerance of fungicides(杀菌剂抗药性研究进展)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University(南京农业大学学报),1994,17(3):33-41.
[6]ZHANG JC (张君成),CHEM ZY (陈志谊), ZHANG BX (张炳欣), et al. Research on inoculation technology of false smut (稻曲病的接种技术研究)[J].Acta Phytopathologica Sinica (植物病理学报),2004,34(5):463-467.
[7]ZHANG JC(张君成), ZHANG BX(张炳欣),CHEN ZY (陈志谊), et al. Preliminary study on inoculation method of rice false smut and its effect (稻曲病的接种方法及其效果初探)[J].Chinese Journal of Rice Science (中国水稻科学),2003,17(4):390-392.
[8]CHEN ZY(陈志谊),NIE YF(聂亚锋),LIU YF (刘永锋).Identification of rice resistant to rice false smut and the virulence differentiation of Ustilaginoidea virens in Jangsu province (江苏省水稻品种对稻曲病的抗病性鉴定及病菌致病力分化)[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences (江苏农业学报), 2009, 25 (4):737-741.
[9]LIU YF(刘永锋),CHEN ZY(陈志谊),LU F(陆凡),et al.Study on controlling rice falsesmut (水稻稻曲病控制技术研究)[J]. Journal of Jinling Institute of Technology (金陵科技学院学报),2004,20(3):42-45.
[10]XU ML (许美良), CHEN YB (陈永兵),ZHOU YM(周有铭),JIN ZX(金再欣).Optimum period of controlling rice false smut and its strategy(水稻稻曲病防治适期及策略初探)[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis (浙江农业学报),2005,17(3):161-162.
[11]HUANG M (黄茂), DING KJ (丁克坚),CHEN L(陈莉),et al.Optimization and selection of controlling time of rice false smut (水稻稻曲病防治时期的优化筛选)[A]. Crop Safety and Plant Protection Science and Technology Innovation (粮食安全与植保科技创新)[C].2009:86-87.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Research Advances in Gene Regulation and Genetic Improvement of Fish Feeding
- Instrucions for Authors
- Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)
- Overview of Pharmaceutical Research on the Poria with Hostwood of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
- Study on Relative Soil and Water Conservation Benefits of Ridge Tillage in Different Terrain Conditions in the Black Soil Area of Northeast China
