Study on Multiplication,Rooting and Transplanting of Tissue Culture Plantlets of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall
2015-12-13LeiWANGChunyingBAHounanCAOChengwenZONGHangYAO
Lei WANG, Chunying BA, Hounan CAO, Chengwen ZONG, Hang YAO
Department of Horticulture and Gardening, College of Agronomy, Yanbian University, Yanbian 133002, China
Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall is evergreen shrub, and it has large and shining leaves,funnel-shaped corolla and light yellow or white flowers.Rh.chrysanthum Pall is very beautiful, and can be used as flower-, leaf- and fruit-watching plant.Rh. chrysanthum Pall is rare broadleaved evergreen plant. It is rarely distributed in China,and is only distributed between the birch forest and alpine tundra with an altitude of 1 700-2 400 m in the Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve.The wild resources of Rh. chrysanthum Pall are extremely limited. Due to human’s excessive digging, the Rh. chrysanthum Pall has been greatly damaged.So it has been classified as national third-level protected species[1].
At present, there are reports on Rh. chrysanthum Pall, except for its morphological characteristics and composition[2-4]. Ding et al[5], Xu et al[6]and Gu et al.[7]ever studied the tissue culture of Rh. chrysanthum Pall from the aspects of rapid multiplication and primary transplanting. The rooting period of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets is relatively long. This study aimed to establish a more comprehensive multiplication, rooting and transplanting technology system for Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets, providing a theoretical basis for further large-scale production and population multiplication of Rh.chrysanthum Pall.
Materials
The Rh. chrysanthum Pall young stems were collected nearby the weather station in Changbai Mountain, and their differentiation culturewas performed in the medium composed of modified MS,TDZ(0.3 mg/L)and IBA (0.5 mg/L).Thus the Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets were prepared.
Methods
Subculture
The subculture was carried out in MS media,in which the ZT concentrations were 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mg/L respectively, the IBA concentrations were 2.0 and 3.0 mg/L respectively,the sucrose concentration was 30 g/L and the pH value was 5.4. The culture temperature was about 25 ℃. There were three replicates for each treatment. The growth status of Rh.chrysanthum Pall young seedlings was investigated 30 d after the inoculation. In the screened optimum hormone combination, 0, 100 and 150 ml/L of coconut milk was added respectively, and the growth status of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets was also investigated 30 d after the inoculation.
Rooting culture
For the screening of basic medium,healthy and robust Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets were respectively inoculated in modified MS,1/2 modified MS and 1/4 modified MS as basic medium; the IBA concentration was 5 mg/L; the sucrose concentration was 30 g/L; the pH was 5.2. There were three replicates for each treatment. The rooting status was investigated 10 d after the inoculation, and the rooting rate and root development situation were investigated 30 d after the inoculation.
For the screening of IBA concentration, the 1/4 modified MS was selected as basic medium;the IBA concentrations were arranged as 1.0, 3.0,5.0 and 7.0 mg/L respectively; the pH value was adjusted to 5.2. There were three replicates for each treatment.The rooting status was investigated 10 d after the inoculation, and the rooting rate and root development situation were investigated 30 d after the inoculation.
Transplanting of rooted plantlets
The rooted tissue culture plantlets were taken out. The agar on the root surface was cleaned off, and then the tissue culture plantlets were transplanted in sandboxes for root induction.The sandboxes were covered with plastic film, and the inside humidity was reduced from the saturated status to the optimum level for (60%-70%) root induction of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets. Meanwhile, the light intensity (removing film time) was increased gradually. After a two-week root induction, the newly-rooted Rh.chrysanthum Pall plantlets were transplanted into nutrition bowls. A total of three kinds of matrixes were designed,including turfy soil ∶humus soil = 2 ∶1(A),turfy soil∶humus soil∶perlite=2∶1∶1(B)and turfy soil∶humus soil∶fine sand=2 ∶1 ∶1 (C). The nutrition bowls were covered with plastic film, placed in a sunny and airy place and watered once a day. The film-covered duration was reduced gradually until the throwing off the film. The transplanting survival rate and growth status of Rh.chrysanthum Pall plantlets were investigated 30 d after the transplanting.
Data analysis
The Duncan’s test and variance analysis were carried out using SPSS 11.5.

Table 1 Effects of different hormone combinations on multiplication of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Results and Analysis
Effects of different hormone combinations on multiplication of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
The effects of different combinations of IBA and ZT on the multiplication of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets were investigated. As shown in Table 1,the coordination between different concentrations of IBA and ZT showed great effect on multiplication of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets. When the concentrations of IBA and ZT were 3 and 1.5 mg/L respectively, the multiplication-promoting effect was greatest with multiplication multiple of 5.21, robust growth of plantlets, dark green leaves and robust plantlets and more effective plantlets. When the concentrations of IBA and ZT were 2.5 and 1.5 mg/L respectively, although the growth of plantlets was good, the multiplication multiple was less than the former. Considering the multiplication multiple and growth status of plantlets, the medium composed of modified MS,IBA(3 mg/L)and ZT(1.5 mg/L)was more suitable for subculture multiplication of Rh. chrysanthum Pallwith multiplication multiple of 5.21.The growth status of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets in the optimum medium was shown in Fig.1.
Effect of coconut milk on subculture multiplication of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Table 2 showed that the coconut milk showed significant promoting effects on the multiplication and average plant height of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture seedlings. When the coconut milk concentration was 100 ml/L,the multiplication multiple differed significantly from that of the control,but there was no significant difference in average plant height. When the coconut milk concentration was 150 mg/L, there were significant differences in both multiplication multiple and average plant height between the treatment and control groups. As shown in Fig.2, the multiplication-promoting effect of 150 ml/L of coconut milk was better than that of 100 ml/L of coconut milk. So the optimum coconut milk concentration was 150 ml/L.
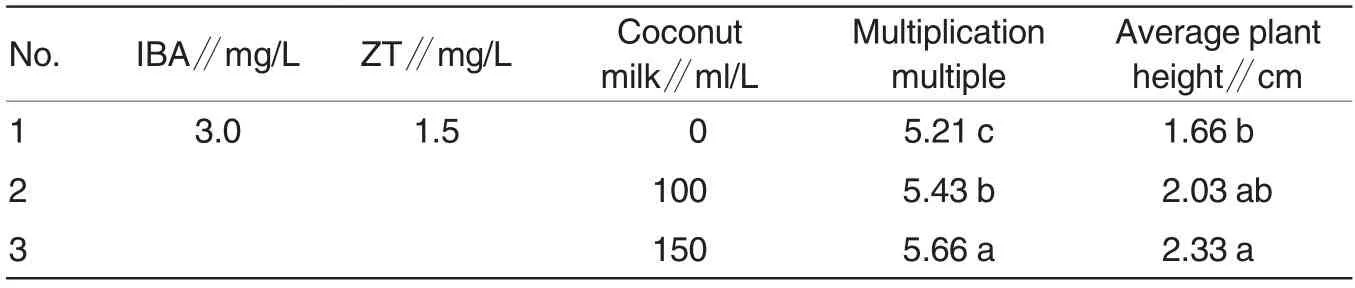
Table 2 Effects of different coconut milk concentrations on growth of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Effect of basic medium concentration of rooting of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Table 3 showed that with the decrease of basic medium concentration,the rooting rate was increased gradually, and the root number was also increased slightly. In the 1/4 modified MS medium, the rooting rate reached 86.67% with earlier rooting, highest root number and best rooting effect but basically without callus. The growth status of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlet in the 1/4 modified MS medium was shown in Fig.3.

Table 3 Effect of basic medium concentration on rooting of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Effect of IBA concentration on rooting of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
As shown in Table 4, with the increase of IBA concentration, the rooting rate of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets was increased correspondingly,and the duration from inoculation to rooting was also shortened gradually.When the IBA concentration was 7 mg/L,the rooting rate was highest; but there were large pieces of callus in roots, and the roots were also thinner,which were adverse to hardening transplanting. When the IBA concentration was 5 mg/L, although the early rooting was one day after that under IBA concentration of 7 mg/L, the roots showed better growth, and there was no significant difference in rooting rate between the two concentrations.Therefore,the suitable rooting medium for Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets was 1/4 modified MS + IBA 5.0 mg/L.
Effect of transplanting matrix on transplanting survival rate of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Table 5 showed that when the transplanting matrix was composed of turfy soil,humus soil and perlite(2∶1∶1),the survival rate of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets was highest(95.66%), followed by that of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets cultured in the matrix com-posed of turfy soil,humus soil and fine sand (2∶1∶1). This might be because that turfy soil can improve soil porosity,and humus soil contains rich nutrients and has good water- and fertilizer-retaining capacity; when the turfy soil and humus soil were mixed with perlite, the soil permeability can be enhanced, improving the growth of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets.

Table 4 Effect of IBA concentration on rooting of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets

Table 5 Effect of transplanting matrix on survival rate of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets
Discussion
Rh.chrysanthum Pall grows slowly.In the subculture, the combinations of different concentrations of IBA and ZT showed significant effects on growth of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets. In this study, the IBA and ZT concentrations in the multiplication medium for Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets were all relatively high, which greatly differed from the report of Yu et al[8]. Yu et al.fount that the optimum IBA and ZT concentrations were 0.5 and 1.0 mg/L, respectively, which were all much lower than those in this study.This might be caused by different materials. In this study, the Rh. chrysanthum Pall young stems were collected nearby the weather station in Changbai Mountain with an altitude of about 1 700 m; while in Yu et al.’s study, the Rh. chrysanthum Pall was collected nearby the Xiaotianchi in Changbai Mountain, and the Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets were prepared by seed embryo culture. Different sampling altitudes and plant parts might be the main reasons for great differences in hormone concentrations.
This study also explored the effect of adding coconut milk into basic medium on multiplication of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets. The results showed that the coconut milk could significantly improve the multiplication multiple of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets, which was consistent with the report by Liu et al.[9]on multiplication-promoting effect of coconut milk on cell proliferation.
In the screening of rooting culture medium for Rh. chrysanthum Pall,high-concentration IBA significantly shortened the growth period of roots.The duration from inoculation to transplanting in this study was 11 d shorter than that in Gu et al.’s report, greatly shortening the rooting period of Rh.chrysanthum Pall. This study also found that the rooting of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets required relatively a large amount of air.When the agar concentration in rooting culture was same with that in subculture,more aerial roots were produced.Therefore, in further researches on rooting culture of Rh.chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets,the culture device with good ventilation or special culture media, such as agar-reduced medium and sponge-or absorbent cotton-added liquid medium, should be selected. However, some aerial roots have little effect on hardening transplanting survival rate.
The ratios among transplanting matrix components were different for different palnts[9]. In this study, total 3 kinds of matrixes were adopted, and there were significant differences in survival rate of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets among the 3 matrixes. Yu et al. adopted the matrix composed of turfy soil,humus soil and rive sand(1∶2∶1),and the transplanting survival rate reached 90% . In this study, the optimum transplanting matrix was composed of turfy soil,humus soil and perlite(2∶1∶1),and the survival rate of Rh. chrysanthum Pall tissue culture plantlets was up to 95%.Under natural conditions, Rh. chrysanthum Pall grows in acidic soil rich in humus.In addition, azalea plants require loose, porous and well-aerated soil.Turfy soil is acidic,humus soil is loose,and perlite has large pores and good aeration performance.So their mixture can effectively avoid soil compaction,thereby improving transplanting survival rate.
[1]ZHOU Y (周繇). On protection of rare and endangered plants in Changbai mountains(长白山区珍稀濒危植物的现状与保护) [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College (浙江林学院学报),2004,21(3):263-268.
[2]LIU CD (刘初钿). Rare and Precious Wild Flowers of China(中国珍稀野生花卉)[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House (北京: 中国林业出版社),2001.
[3]YAN ZK (严仲铠), LI WL (李万林).Medicinal Plants Color Pictorial in Changbai Mountain of China (中国长白山药用植物彩色图志)[M].Beijing:People's Health Publishing House(北京: 人民卫生出版社),1997.
[4]ZHU TC (祝廷成). Alpine Plants on the Changbaishan Massif of China (中国长白山高山植物)[M]. Beijing: Science Press(北京: 科学出版社),1999.
[5]DING HL(丁洪玲),G Y(宫宇).Study on the tissue culture and anatome plantarum of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall.(牛皮杜鹃组织培养及植株解剖学研究)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science Yanbian University(延边大学农学学报),2008,30(2):13-18.
[6]XU Y(徐颖),JIN C(金灿),ZONG CW(宗成文), et al. Tissue culture, rapid multiplication and primary domestication cultivation of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall. in Changbai Mountain (长白山牛皮杜鹃组培快繁及初步驯化栽培研究)[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业科学),2010,2:47-49.
[7]GU DZ (顾地周), CONG XL (丛小力).Tissue culture and rapid propagation of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall.(牛皮杜鹃的组织培养与快速繁殖)[J]. Plant Physiology Communications (植物生理学通讯),2005,4(2):1.
[8]YU YQ (于秋艳). Technique of tissue culture and rapid propagation of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall and analysis of effective constitute(牛皮杜鹃组培快繁技术及有效成分研究)[D].Yanbian:Yanbian University(延边: 延边大学),2010.
[9]LIU XY (刘晓燕),XIANG QY (向青云),LIU LL (刘玲玲),et al.The effect of basic culture media and additional compounds on the propagation of Phalaenosis PLB(基本培养基及附加物对蝴蝶兰原球茎增殖效果的影响)[J]. Seed(种子),2005,24(6):18-20.
[10]GU DZ (顾地周),CONG XL (丛小力),JIANG HZ (姜海智),et al.Tissue culture and rapid propagation of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall.(牛皮杜鹃的组织培养与快速繁殖)[J]. Plant Physiology Communications(植物生理学通讯),2008,44(2):300.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Variation in Enzymes Activities of Rhizospheric Substrate and Influencing Factors during Nursing of Watermelon Seedlings
- Determination of Iprobenfos Residue in Rice by GC-FTD using Two-dim Ensional Purification
- In vitro Rapid Propagation of Ficus carica L.‘Masui Dauphine’
- Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides in Yam Bulbils and Their Hypoglycemic Effect in Diabetic Mice
- Adsorption Kinetics of NH4+by Purple Soils with Different pH Values
- Inhibition of Chlamydospore Germination and Mycelial Growth of Trichoderma spp.by Chemical Fungicides
