和肽素与肌钙蛋白联合检测在急性心肌梗死期诊断中的应用价值
2015-11-24李伟宁魏殿军宁莉
李伟宁,魏殿军,宁莉
应用研究
和肽素与肌钙蛋白联合检测在急性心肌梗死期诊断中的应用价值
李伟宁,魏殿军,宁莉
目的探讨和肽素(copeptin)和心肌肌钙蛋白I(cTnI)、高敏心肌肌钙蛋白T(hs-TnT)联合检测时对急性心肌梗死(AMI)的诊断价值。方法AMI患者152例(AMI组),同期健康体检者143例(对照组)。(1)考察2组0、4、6及12 h copeptin、cTnI及hs-TnT水平差异。(2)对2组行copeptin与cTnI联合检测(cop/cTnI)、copeptin与hs-TnT联合检测(cop/hs-TnT)。考察AMI组发病后不同时间点上述不同检测指标阳性检出率情况。(3)判断发病即刻各种心肌标志物对AMI诊断的敏感度、特异度及准确度。结果(1)2组copeptin在发病0、4、6和12 h时差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2组cTnI与hs-TnT在0 h时差异无统计学意义。(2)cop/cTnI和cop/hs-TnT联合检测组在不同发病时刻较各自单独检测均具有更高的阳性检出率。(3)cop/cTnI和cop/hs-TnT联合检测的敏感度、特异度以及准确度均高于其单独检测。cop/hs-TnT联合检测最佳。结论cop/cTnI和cop/hs-TnT联合检测在AMI发病早期即具有较高的敏感度、特异度和准确度,在临床疾病诊断中具有很好的应用价值。
心肌梗死;急性病;早期诊断;敏感性与特异性;和肽素;心肌肌钙蛋白I;高敏肌钙蛋白T
急性心肌梗死(AMI)病情发展迅速、病死率高,早期、快速、准确地诊断AMI是降低其死亡率的关键[1]。目前临床多以病史、心电图(ECG)、心肌标志物来初步判断是否为AMI[2]。ECG诊断AMI有较高的特异性,但对非ST段抬高心肌梗死(NSTEMI)、不稳定型心绞痛及心肌缺血的敏感性不足。肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)、乳酸脱氢酶、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶等血清酶为心肌损伤标志物,但特异性不高,多于AMI晚期出现异常,不能用作早期诊断指标[3]。和肽素(copeptin)是精氨酸加压素原(pro-AVP)的羧基
端部分,对心血管疾病如AMI、心力衰竭的诊断及预后评价有重要的价值。本研究旨在探讨copeptin、心肌肌钙蛋白I(cTnI)和超敏心肌肌钙蛋白T(hs-TnT)的水平变化在AMI早期诊断中的价值。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象选取2005年8月—2014年8月于本院因胸痛就诊并行冠状动脉造影术检查明确为非ST段抬高型的AMI患者(AMI组)152例,男85例,女67例,年龄(63.35± 3.41)岁。AMI患者诊断标准参考文献[1],即入院后12 h内有典型心梗心电图者确诊为AMI患者,且符合2001年中华医学会心血管病学分会标准[4]。同期健康体检者143例为对照组,男69例,女74例,年龄(60.12±8.12)岁。2组年龄(t= 0.327)和性别(χ2=0.042)差异无统计学意义(P>0.01)。
1.2 方法采集2组即刻及发病后4、6及12 h后肘正中静脉血3~5 mL,以3 000 r/min离心15 min,血清于-70℃冻存。采用酶联免疫吸附(ELISA)法检测(试剂盒购自上海江莱生物科技有限公司)copeptin。免疫荧光法测定(试剂盒购自德国罗氏公司)cTnI和hs-TnT。
1.3 检测指标检测2组0、4、6及12 h copeptin、cTnI及hs-TnT水平。对2组行copeptin与cTnI联合检测(cop/cTnI)、copeptin与hs-TnT联合检测(cop/hs-TnT),其中一项或者联合检测的2项同时为阳性,均判定为联合检测阳性。co⁃peptin的临界值以对照组第90百分位数为判断值。cTnI和hs-TnT单项检测均以罗氏公司提供的表面健康人群第99百分位数为判断值,即cTnI>0.02 g/L或hs-TnT>0.014 g/L判断为阳性[5]。考察AMI组发病后不同时间点不同检测指标阳性检出率情况。判断发病即刻各种心肌标志物对AMI诊断的敏感度、特异度及准确度。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0软件进行数据分析。正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差表示,非正态分布的计量资料以M(P25,P75)表示。计数资料以例(%)表示,对不符合正态分布的2组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 copeptin临界值的确定对照组copeptin分布,见图1。取第90百分位数≥18.1 pmol/L为AMI诊断临界值。
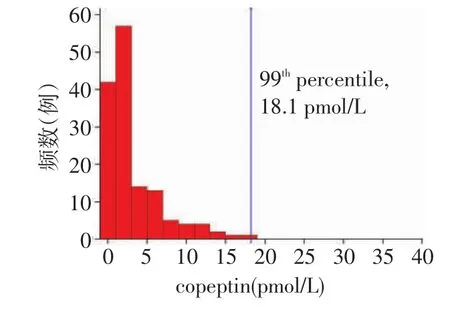
Fig.1Histogram of copeptin in the general population图1 对照组copeptin分布
2.2 AMI组发病后不同时间copeptin、cTnI、hs-TnT比较2组copeptin在发病0、4、6和12 h时差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。2组cTnI与hs-TnT在0 h时差异无统计学意义,但在4、6及12 h照差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
2.3 AMI组发病后不同时间点各项指标阳性检出率cTnI和hs-TnT在发病0 h的阳性检出率略低于copeptin,copeptin检出阳性率随着发病时间的延长呈现先增加后降低的趋势,在发病4~6 h阳性率达到最高值。cTnI和hs-TnT随发病时间的延长阳性检出率增高。cop/cTnI和cop/hs-TnT联合检测组在不同发病时刻均具有更高的阳性检出率,见表2。
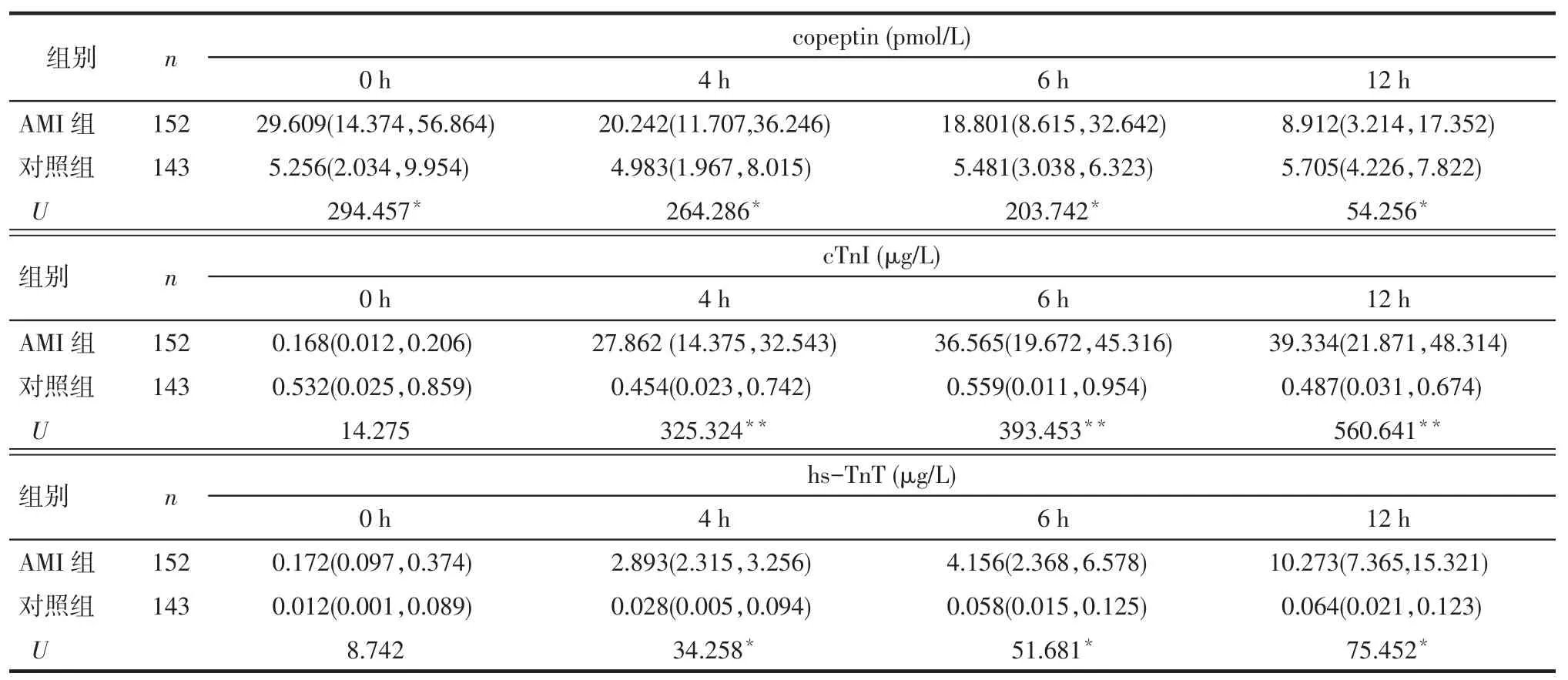
Tab.1Concentrations of copeptin,cTnI and hs-TnT at different time points between two groups表1 2组不同时间copeptin、cTnI、hs-TnT M(P25,P75)

Tab.2The positive rates of various measurements at different time points in AMI group表2 AMI组发病后不同时间点各项指标检出阳性率[n=152,例(%)]
2.4 发病即刻各种心肌标志物对AMI的诊断效能cop/cTnI联合检测的敏感度、特异度以及准确度均高于其单独检测。cop/hs-TnT联合检测相对于cop/cTnI具有更高的敏感度、特异度和准确度,见表3。

Tab.3Diagnostic characteristics of various measurements at the onset of AMI表3 各项心肌损伤标志物在发病即刻对AMI的诊断特性
3 讨论
对AMI的早期诊断可以确保患者在早期即接受积极的治疗。AMI诊断的经典指标为典型的临床胸痛症状、ECG动态改变和CK-MB测量值异常。但研究显示25%的AMI患者在发病早期没有典型的临床症状,因此,早期标志物的检测对AMI诊断至关重要[6]。近年研究表明,cTnI在AMI后血中浓度很快升高,这和CK-MB出现时间相当或稍早3~8 h,检测的敏感度和特异度均高于CK-MB[7]。随着心脏生物标志物技术的不断发展,hs-TnT的检测限度降低,能检测到血液中更低浓度的肌钙蛋白。Co⁃peptin为精氨酸加压素(AVP)的C末端部分,当出现心肺血管疾病时,患者的AVP水平升高。因此,AVP通常被认为是心肺血管疾病的标志性预警分子。多项研究表明,血清中copeptin水平在胸痛症状发生0~4 h以后明显升高,而此时血液中的肌钙蛋白检测仍为阴性[8-9]。Keller等[5,10]发现,联合测定copeptin与cTnT较单独测定cTnT的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)下面积明显增加。Khan等[11]报道,对入选莱斯特急性心肌梗死多肽(LAMP)试验的980例AMI患者进行前瞻性研究,血浆中copeptin于AMI后第一日最高,与未发生心血管事件的存活者相比,死亡或因心力衰竭再次入院的患者copeptin水平更高,认为copeptin可预测不良预后,可作为新的AMI预后评判的标志物。
本研究结果显示,2组copeptin在发病0、4、6和12 h时照差异有统计学意义,而2组cTnI与hs-TnT在0 h时差异无统计学意义,提示copeptin有望成为AMI发病早期的预警分子。发病即刻的诊断效能可以充分反映检测项目是否适合作为AMI早期检测指标。本研究结果显示,单独检测copeptin的敏感度要高于cTnI和hs-TnT,而cop/cTnI联合检测可以将敏感度提高到80%,cop/hs-TnT联合检测则更高。因此,笔者认为在发病早期,利用co⁃peptin单独检测的敏感度及特异度均有待提高,但联合cTnI或hs-TnT检测可弥补其早期诊断敏感度和特异度不高的缺陷。因此,笔者认为cop/cTnI和cop/hs-TnT联合检测具有更好的临床应用价值,有利于缩短诊断时间,提高AMI检出率,缩短监护时间,避免抽血反应,节约医疗资源。
综上所述,copeptin单独检测AMI时敏感度和特性度均有待提高,而cTnI和hs-cTnT虽然目前已用于AMI的诊断,但是由于其出现时间相对较晚,对AMI早期诊断意义不大,cop/cTnI与cop/hs-cTnT的联合检测有望成为AMI早期诊断新的预测方法。
[1]Reiter M,Twerenbold R,Reichlin T,et al.Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarctionin the elderly using more sensitive cardiactro⁃ponin assays[J].Eur Heart J,2011,32(11),1379-1389.doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr033.
[2]Michael L,Ricardo EA,Fabrizio D,et al.Copeptin levels in the triage of patients presenting to the emergency department with chest pain:a collaborative metaanalysis[J].ACS,2014,63(12):60264-60263.
[3]Sivaranjani N,Ravi KVS,Venkataraman DD,et al.Evaluation of cardiac specific Troponin T as a specific and sensitive biomarker over creatine Kinase-MB in acute myocardial infarction patients-A cor⁃relation analysis study[J].Int J Biomed Res,2014,5(2):0976-9633.
[4]Chinese medical association cardiovascular disease branch,editori⁃al committee of Chinese journal of cardiology,editorial committee of Chinese circulation journal.Guide for diagnosis and treatment of acute myocardial infarction[J].Chin J Cardiol,2001,29(12):710-725.[中华医学会心血管病学分、中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会、中国循环杂志编辑委员会.急性心肌梗死诊断和治疗指南[J].中华心血管病杂志,2001,29(12):710-725].
[5]Keller T,Tzikas S,Zeller T,et al.Copeptin improves early diagno⁃sis of acute myocardial infarction[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2010,55
(19):2096-2106.
[6]Zhang YM,Shao HH.Biochemical indexes for acute myocardial in⁃farction in early clinical diagnosis[J].Journal of health manage⁃ment cadre,institute of Sichuan province,2001,20(4):289-290.[张玉明,邵怀淮.急性心肌梗塞早期诊断生化指标[J].四川省卫生管理干部学院学报,2001,20(4):289-290].
[7]Joarder S,Hoque M,Towhiduzzaman M,et al.Cardiac Troponin-I and CK-MB for risk stratification in acute myocardial infarction(first attack):a comparative study[J].Bangladesh J Med Biochem,2011,4(1):10-15.
[8]Evangelos G,Tzveta K,Mehrshad V,et al.Combined testing of high-sensitivity troponin T and Copeptin on presentation at prespec⁃ified cutoffs improves rapid rule-out of non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J].Clinical Chemistry,2011,57(10):1452-1455.doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.161265.
[9]Mueller C.Biomarkers and acute coronary syndromes:an update[J]. Eur Heart J,2014,35(9):552-556.doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht530.
[10]Reichlin T,Hochholzer W,Stelzig C,et al.Incremental value of co⁃peptin for rapid rule out of acute myocardial infarction[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2009,54(1):60-68.doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.076.
[11]Khan SQ,Dhillon OS,O’Brien RJ,et al.C-terminal provasopressin(copeptin)as a novel and prognostic marker in acute myocardial in⁃farction:Leicester Acute Myocardial Infarction Peptide(LAMP)study[J].Circulation,2007,115(16):2103-2110.
(2014-12-23收稿 2015-03-05修回)
(本文编辑 陆荣展)
The diagnostic value of copeptin combined with cardiac troponin in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction
LI Weining,WEI Dianjun,NING Li
Department of Laboratory,The Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin 300211,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the diagnostic value of combined copeptin,cardiac troponin I(cTnI)and high sen⁃sitive cardiac troponin T(hs-TnT)in determination of acute myocardial infarction(AMI).MethodsA total of 152 patients with AMI were selected as AMI group and 143 healthy examinees during the same period were selected as control group.(1)The levels of copeptin,cTnI and hs-TnT were detected at 0,4,6 and 12 h in two groups.(2)The combined detection of cop/ cTnI and cop/hs-TnT were studied.The positive rates of these items were evaluated at different time points of AMI.(3)The diagnostic sensitivity,specificity and accuracy of different cardiac biomarkers for AMI were compared.Results(1)There were significant differences in copeptin at 0,4,6 and 12 h between two groups(P<0.05).There were no significant differ⁃ences in cTnI and hs-TnT between two groups.(2)cop/cTnI and cop/hs-TnT combined detection showed better positive rates than those of copeptin,cTnI or hs-TnT detection alone.(3)In addition,the combined detection of cop/cTnI and cop/cTnI improved significantly the diagnostic sensitivity of AMI.Compared to cop/cTnI combination,cop/hs-TnT combination detec⁃tion showed better diagnostic sensitivity,specificity and accuracy for AMI.ConclusionThe combined detection of cop/cTnI and cop/hs-TnT are very helpful for early diagnosis of AMI,which shows a very good diagnostic value in clinical application.
myocardial infarction;acute disease;early diagnosis;sensitivity and specificity;copeptin;cardiac troponin I;high sensitive cardiac troponin T
R542.22;R540.49
A
10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.11.026
天津医科大学第二医院检验科(邮编300211)
李伟宁(1983),女,初级检验技师,主要从事临床生物化学检验工作
