Changes and Correlations of Duroc Muscle pH,Glycogen,Lactic Acid and TBA under Different Storage Condition
2015-11-08JianfengGUOJiyingWANGHaichaoLlNYinZHANGHongmeiHUChengWANGYingWU
Jianfeng GUO,Jiying WANG,Haichao LlN,Yin ZHANG,Hongmei HU,Cheng WANG,Ying WU
Institute of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Animal Disease Control&Breeding,Jinan 250100,China
Changes and Correlations of Duroc Muscle pH,Glycogen,Lactic Acid and TBA under Different Storage Condition
Jianfeng GUO*,Jiying WANG,Haichao LlN,Yin ZHANG,Hongmei HU,Cheng WANG,Ying WU
Institute of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Animal Disease Control&Breeding,Jinan 250100,China
The changes and correlations of muscle pH,glycogen,lactic acid and intramuscular fat oxidation in Duroc pigs 10 d after their slaughter,and the effects of different storage temperature and time on Duroc muscle pH value,water loss rate,glycogen,lactic acid and 2-thiobarbituric acid (TBA)were studied.The results showed that during the 10 h after the slaughter,the pH value was decreased rapidly,the lactic acid content was increased significantly,while the glycogen and TBA contents were remained stable.At the storage temperature of 4℃,storage time showed no significant effects on Duroc muscle pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents.At the storage temperature of-20°C,storage temperature had significant effects on pH value,while no significant effects on other indicators.The correlation analysis demonstrated that during the 10 h after the slaughter,the TBA content was negatively related to glycogen content(P<0.05),but positively related to lactic content (P<0.05);the pH value was negatively related to lactic acid content(P<0.05).At the storage temperature of 4℃,the TBA content was negatively related to water loss rate(P<0.01)and lactic acid content(P<0.05);the water loss rate was positively related to pH value(P<0.01)and lactic acid content(P<0.05).At the storage temperature of-20℃,the TBA content was negatively related to pH value(P<0.01)and positively related to water loss rate (P<0.05);the water loss rate was negatively related to pH value(P<0.01)and lactic acid content(P<0.05).
Duroc;Temperature;Time;pH value;Glycogen;Lipid oxidation;Correlation
W ith the improvement of people’s living standards and health awareness, pork quality attracts more and more attention from pig academics and consumers.Pork quality is a comprehensive refection of the physical and chemical properties.Quality indicators of pork include intramuscular fat,pH value,color,marbling,water loss rate,drip loss,tenderness,and so on. Among them,pH value is a very important indicator.Muscle pH value is an important indicator reflecting glycolysis rate in slaughtered pigs,and is also a physiological basis for judging normal or abnormal pork(PSE or PFD meat). However,muscle pH value is only an apparent influencing factor,but glycogen content is an essential influencing factor on pork quality[1].Reduced pH value in slaughtered pigs is mainly due to anaerobic glycolysis ofmuscle glycogen into lactic acid and phosphoric acid produced by ATP decomposition.The former is a major factor.It is generally believed that lipid oxidation,besides microbial corruption,is the main reason for deterioration of meat. During storage process of meat,aldehydes,alcohols,ketones and other organic compounds will be generated from lipid oxidation,thus the smell and taste of meat will be difficult to be ac-cepted by consumers.Lipid oxidation begins from phospholipids on cell membrane.This will not only lead to the generation of odor(i.e.,stale smell of cooked meat during storage),but also lead to the destruction of the integrity of biofilm,resulting in severer juice drip loss and further reduced eating quality of processing yield.In addition,lipid oxidation also reduces contents of polyunsaturated fatty acids,fat-soluble vitamins and pigment.Even worse,the peroxidation products may be harmful to human health,leading to cancers and deformities.This study aimed to investigate the changes in pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle after the slaughter and during the storage under refrigeration and freezing conditions.In addition,the correlations in pH value,glycogen content,lactic acid content and TBA content in Duroc muscle were studied,thereby providing some useful reference for production,processing and storage of pork.
Materials and Methods
Experimental animal
A total of 50 healthy Duroc pigs with good growth,basically the same age and weight of 30 kg,were selected as the experimental material.
Feeding experiment
The Duroc pigs were reared in the same enclosed piggery with cement floor.According to the principle of male and female separated and similar weight,the pigs were randomly divided into 10 groups with 5 pigs in each group.The pigs in the same group were fed in the same column.The feed was corn-soybean meal powder,and the water was provided ad libitum.The nutritional levels of the diet were as follows (early/late period):digestible energy (MJ/kg)13.18/12.80,crude protein(%)16.6/14.6,lysine(%)0.9/0.75. The fattening trail ended when the body weight of pigs reached 100 kg in average.
Slaughter experiment
After the fattening trail ended,total 11 pigs with moderate body weight and good growth were selected.They were fasted for 24 h,and then weighed and slaughtered according to Amendments to National Meat Quality Cooperative Group(1987).The meat quality was analyzed.
lndicator measurement and methods
The longissimus dorsi muscles during last 1 and 2 thoracic segments were sampled for measurement of pH values.The measurement of pH values was conducted 45 min after the slaughter and then once every one hour(till 10 h after the slaughter).Simultaneously,the muscle samples were stored at 4℃,and their pH values were measured once every 24 hours(6 times).The longissimus dorsi muscles during last 3 and 4 thoracic segments were sampled for determination of drip loss.The determination was carried out once every 24 hours(6 times).At the same time,the longissimus dorsi muscles during first 6 and last 4 thoracic segments were sampled and stored at-20℃.Their pH values and water loss rates were determinedonceevery24hours(5 times)[2].The water loss rate was determined according to NY5029-2001.
The muscle samples were collected and stored in liquid nitrogen. The pH value of Duroc muscles were measured once every one hour 10 h after the slaughter.During the pH measurement,the muscles were sampled and stored in liquid nitrogen for determination of glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents.Similarly,during the pH measurement,the glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle samples stored at-4 and-20℃ were determined.The glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents were determined using glycogen assay,lactic acid assay and malondialdehyde assay,respectively.The assays were all produced by the Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute.
Data statistics and analysis
1.2.1 样品采集 于2014年5月(初花期)在各样地随机采集5份植株、根际土壤和田间土壤,8月(成熟期)田间收集种子,并清选。分别装于自封袋,标记,冰桶冷藏条件下带回实验室。
The variance analysis was conductedusingOne-Way-ANOVA of SPSS 15.0.Whenthedifferences were significant,Duncan’s multiple comparisons were conducted.The final data were expressed as mean± standard error.The correlation analysis was conducted using Bivariate Correlations.

Table1 Changes in Duroc muscle pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents within 10 hours after slaughter
Results and Analysis
Changes of pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle within 10 h after the slaughter
As shown in Table1,with the extension of post-slaughter time,the pHvalue in Duroc longissimus dorsi was reduced significantly(P<0.05).It was highest (6.455)0.75 h afterthe slaughter,and was lowest at hour 10. Within the 10 hours,the decrement of Duroc muscle pH value was larger in the first 7 hours,but was smaller in the last 3 hours.The pH value at hour 0.75 was significantly higher than those in hour 5-10 (P<0.01),and the pH values in the first 6 hours were significantly higher than those in the last 4 hours(P<0.01).There were significant differences in Duroc muscle pH value between hour 0.75 and 1 (P<0.05),hour 1-2 and 6 (P<0.05).In short,within the 10 hours after slaughter,the decrement of Duroc muscle pH value was fast in the first 7 hours,but slow in the last 3 hours.
Within the 10 hours after slaughter,the Duroc muscle glycogen and TBA contents did not change significantly(P>0.05).The glycogen content ranged from 1.431 to 2.708 mg/g.The Duroc muscle glycogen content was decreased during hour 1-3,increased during hour 3-4,decreased during hour 4-5,increased during hour 5-6,and decreased during hour 6-10.The TBA content ranged from 0.124 to 0.364 mg/kg.The Duroc muscle TBA content was increased during hour 1-3,decreased during hour 3-4,increased during hour 4-6,decreased during hour 6-7,increased during hour 7-9,and decreased during hour 9-10.
TheDurocmusclelacticacid contentwas increased significantly with the extension of post-slaughter time.It ranged from 0.565 to 1.276 mmol/g prot.In overall,the lactic acid content was increased in the first hour,decreased during hour 1-3,increased during hour 3-6,decreased during hour 6-8,and increased during hour 8-10.The Duroc muscle lactic acid content did not change significantly during hour 0.75-4(P>0.05).There were significant differences in lactic acid content between hour 0.75-4 and 10 (P<0.01),hour 0.75-3 and 9 (P<0.01),hour 0.75 and 6(P<0.01),hour 0.75 and 5 (P<0.05),hour 7-8 and 0.75 (P<0.05),hour 1-3 and 6 (P<0.05),and hour 4 and 9(P<0.05).

Table 2 Correlations among pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle 10 h after the slaughter
Correlations among pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle within 10 h after the slaughter
As shown in Table 2,the Duroc muscle TBA content was positively related to pH value (P>0.05),negatively related to glycogen content(-0.295,P<0.05),and positively related to lactic acid content (0.268,P<0.05).The Duroc muscle pH value was positively related to glycogen content(P>0.05),and negatively related to lactic acid content(-0.338,P<0.01).There was a negative correlation between glycogen content and lactic acid content in Duroc muscle(P>0.05).
At the storage temperature of 4℃,storage time showed no significant effects on Duroc muscle pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents(P>0.05),but showed significant effect on drip loss(P<0.05)(Table 3).During the intervals of 24-48 h and 48-120 h,Duroc muscle pH value was remained stable;but during the interval of 120-144 h,Duroc muscle pH value was trended to be increased.In overall,Duroc muscle pH value did not change significantly.The glycogen content ranged from 0.770 3 to 0.903 8 mg/g. During hour 24-48,it was trended to be increased;during hour 48-96,it was trended to be decreased;during hour 96-144,it was trended to be increased.However,there was no significantchange in Duroc muscle glycogen content with the extension of post-slaughtertime.The drip loss ranged from 0.739 6%to 1.623 8%. During hour 24-48,it was reduced significantly (P<0.01);during hour 48-144,it was remained stable.There were significantly differences in drip loss between hour 48-144 and 24. The lactic acid content ranged from 1.316 6 to 1.628 7 mmol/g prot.During hour 24-48,it was remained unchanged;during hour 48-96,it was increased;during hour 96-144,it was trended to be reduced.There were no significant differences overall in Duroc muscle lactic acid content with the extension of post-slaughter time.The TBA content ranged from 0.253 5 to 0.601 0 mg/kg,and was trended to be increased in overall.During the interval of 24-96 h,it was trended to be increased;during the interval of 96-120 h,it was trended to be decreased;during the interval of 120-144 h,it was trended to be increased.In general,when TBA content in raw meat is higher than 0.5 mg/kg,oxidative smell canbe felt by people[3].At the storage temperature of 4℃,Duroc muscle TBA content was lowest(0.253 5 mg/kg)24 h after the slaughter,but was highest(0.601 0 mg/kg)144 h after the slaughter.At hour 96 and 144,the TBA content in Duroc muscle was all higher than 0.5 mg/kg,thus the meat was no longer suitable for human to consume.In addition,the TBA content at hour 120 was lower than that at hour 96,which was inconsistent with the truth that with the extension of storage time,the oxidation degree of meat becomes greater.This still needs further study.

Table 3 Effects of different storage time on Duroc muscle pH value,drip loss and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents at 4°C

Table 4 Correlations among Duroc muscle pH value,drip loss and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents at storage temperature of 4°C
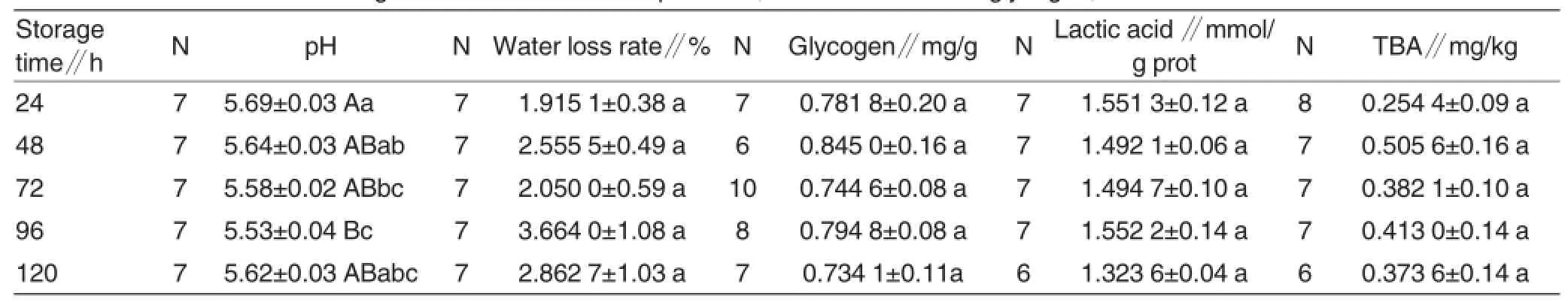
Table 5 Effects of different storage time on Duroc muscle pH value,water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents at-20°C
Correlations among pH value,water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle at storage temperature of 4℃
Table 4 showed that the Duroc muscle TBA content was positively related to glycogen content(P>0.05),and negatively related to drip loss(-0.467,P<0.01)and lactic acid content (-0.335,P<0.05).The Duroc muscle pH value was positively related to drip loss(0.316,P<0.01),and negatively related to glycogen lactic acid contents(P>0.05).The drip loss was positively related to glycogen(P>0.05)and lactic acid (0.335,P<0.05)contents.There was a positively correlation between glycogen and lactic acid contents(P>0.05).
Changes in pH value,water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle during the storage at-20℃
At the storage temperature of-20℃,Duroc muscle pH value differed significantly with the extension of postslaughter time,but water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents did not change significantly.The Duroc muscle pH value was decreased significantly during the interval of 24-96 h,and was trended to be increasedduring the interval of 96-120 h.There were significant differences in pH value between hour 24 and 96 (P<0.01),hour 24 and 72(P<0.05),and hour 48 and 96 (P<0.05).The water loss rate ranged from 1.915 1%to 3.664 0%,and was trended to be increased with the extension of storage time (P>0.05).The glycogen content ranged from 0.734 1 to 0.845 0 mg/g,and was trended to be decreased with the extension of storage time (P>0.05).The lactic acid content ranged from 1.323 6 to 1.552 2 mmol/g prot (P>0.05). There was no regular or significant change in TBA content(P>0.05).At the storage temperature of-20℃,the TBA content in Duroc muscle was lowest(0.254 4mg/kg)24 h after the slaughter,and was highest(0.505 6 mg/kg)48 h after the slaughter.However,at hour 48,the TBA content in Duroc muscle stored at-20℃ was higher than 0.5 mg/kg,and was higher than that in Duroc muscle stored at 4℃,which was repugnant to common sense that meat can be preserved for a longer time if stored at lower temperature.This also needs further study(Table 5).

Table 6 Correlations among Duroc muscle pH value,water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA conten at storage temperature of-20℃
Correlations among pH value,water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents in Duroc muscle at storage temperature of-20℃
As shown in Table 6,the Duroc muscle TBA content was negatively related to pH value (-0.559,P<0.01),glycogen content(P>0.05)and lactic acid content(P>0.05),and was positively related to water loss rate(0.681,P<0.05).The pH value was negatively related to water loss rate (-0.520,P<0.01),and was positively related to glycogen(P>0.05)and lactic acid(P>0.05)contents.The water loss rate was negatively related to glycogen(P>0.05)and lactic acid (-0.347,P<0.05)contents.There was a positive correlation between glycogen and lactic acid contents(P>0.05).
Conclusions and Discussion
Muscle pH change is a complex physiological and biochemical process after slaughter. After pigs were slaughtered,with the proceeding of glycolysis,a large amount of lactic acid was accumulated,leading to muscle pH decreasing from pre-slaughter 7.0-7.4 to post-slaughter 5.2-5.7[4].Within 92 h after slaughter,Wang et al.[5]measured muscle pH values of wild hybrid pig and Duroc pig every four hours at storage temperature of 0-4℃.They found that the muscle pH value of wild hybrid pig was decreased rapidly in the first 8 hours,but of Duroc pig was decreased rapidly in the first 4 hours.Duan et al.[6]measured muscle pH values of over 700 F2hybrids of White Duroc×Erhualian 45 min,3 h,9 h,15 h and 24 h after the slaughter, respectively.With the extension of post-slaughter time,the average muscle pH values of the F2population were 6.4,6.26,5.92,5.75 and 5.67,respectively.The post-slaughter muscle pH of experimental pigs was decreased gradually in the first 24 hours.In this study,with the extension of storage time,the pH value of Duroc longissimus dorsi was reduced gradually from 6.4 to 5.67.In the first 7 hours,the pH value was decreased rapidly,but in the late 3 hours,the pH value was decreased relatively slow.These were consistent with the study results of Duan et al[6].There have been no reports on changes of glycogen and lactic acid contents in Duroc longissimus dorsi with the extension of postslaughter time.In this study,within the first10 hours afterslaughter,the glycogen content in Duroc longissimus dorsi ranged from 1.431 to 2.708 mg/g,and was trended to be decreased (P>0.05);the lactic acid contentranged from 0.565 to 1.276 mmol/g prot,and was increased in overall(P<0.05).The lactic acid content was increased in the first one hour,decreased during hour 1-3,increased during hour 3-6,decreased during hour 6-8,and increased during hour 8-10.In overall,the changes in Duroc muscle pH value and glycogen and lactic acid contents accorded with objective law that glycolysis leads to generation of lactic acid,resulting indecreased muscle pH value.
Lipid oxidation in meat products is commonly evaluated by 2-thiobarbituric acid assay (TBA value method). This method is relatively simple,and generally has good correlation with sensory analysis data.It is widely applied in degree evaluation of lipid oxidation.With the deepening of the degree of oxidation,more secondary products are produced,so the TBA value is increased.Usually,when TBA content is higher than 0.5 mg/kg,people can feel oxidative smell[3].Within the post-slaughter 10 hours,the TBA content ranged from 0.124 to 0.364 mg/kg(lower than 0.5 mg/kg),and was trended to be increased in overall.The correlation analysis showed that the TBA content was negatively related to glycogen content(-0.295,P<0.05),and was positively related to lactic acid content(0.268,P<0.05);the pH value was negatively related to lactic acid content(-0.338,P<0.01);the other correlations were insignificant (P>0.05).
There have been no reports on effects of different storage temperature and time on Duroc muscle pH value,water loss rate,glycogen content,lactic acid content and lipid oxidation.The results ofthis study showed that at the storage temperature of 4℃,storage time showed no significant effects on Duroc muscle pH value and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents,but showed significant effect on drip loss.The correlation analysis showed that the TBA content was negatively related to drip loss (-0.467,P<0.05)and lactic acid content(-0.335,P<0.01);the pH value was positively related to drip loss(0.316,P<0.01);the drip loss was positively related to lactic acid content(0.335,P<0.05).At the storage temperature of-20 ℃ ,storage time showed significant effect on Duroc muscle pH value,but insignificant effects on water loss rate and glycogen,lactic acid and TBA contents.The correlation analysis showed that the TBA content was negatively related to pH value(-0.559,P<0.01),and positively related to water loss rate (0.681,P<0.05);the pH value was negatively related to water loss rate (-0.520,P<0.01);the water loss rate was negatively related to lactic acid content(-0.347,P<0.05);the other correlations were insignificant(P>0.05).
At the storage temperature of 4℃,the TBA content in Duroc muscle reached 0.489 1 mg/kg at 48 h after the slaughter,and reached 0.552 6 mg/kg(higher than 0.5 mg/kg)at 96 h after the slaughter.Therefore,raw meat should not be stored for too long time at 4℃.In addition to lipid oxidation,microorganisms are prone to be generated.Raw meat is better eaten as soon as possible,preferable within 72 hours.At the storage temperature of-20℃,raw meat can be stored for a longer time,about 3 months.At-20℃,the TBA content in Duroc muscle reached 0.505 6 mg/kg at 48 h after the slaughter,but then was decreased to 0.37-0.42 mg/kg,which was repugnant to common sense.This might be related to ambient temperature during sampling,measurement temperature in testchamber,stability of test reagents,proficiency of relevant tester and other factors.
Overall,raw meat should be consumed as soon as possible after lactic acid is generated.No matter at what temperature,raw meat should not be stored for too long time.Otherwise,both meat quality and flavor will be changed.Once pork goes bad,is should not be eaten or used for processing.
[1]ZHAO GM(赵光民).Glycogen,an important factor for ensuring quality of freezing pork(冻猪肉肌糖原是确保肉质的重要因素)[J].Meat Industry(肉类工业),1993(6):35-37.
[2]CHEN QM(陈清明),WANG LC(王连纯). Modern Swine Production(现代养猪生产)[M].Beijing:China Agricultural University Press(北京:中国农业大学出版社),1997:352-357.
[3]HUO XN(霍晓娜),LI XM(李兴民),LI HQ(李海芹),et al.Relationship between fatty acids composition and oxidative stability of chilled pork(不同部位冷却猪肉中脂肪酸组成与脂肪氧化的变化)[J]. Food Science and Technology(食品科技),2005(12):26-30.
[4]ZHOU LH(周利华),DUAN YY(断艳宇),MA JW (麻骏武).Effect of slaughter season on pork colour and pH in the White Duroc×Erhualian intercross(白色杜洛克二花脸资源群体中屠宰季节对猪肉pH值和肉色的影响)[J].Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University(江西农业大学学报),2009,31(4):585-588.
[5]WANG YH(王永辉),MA LZ(马俪珍),ZHANG YJ(张亚杰),et al.Study on meat quality of crossbred wild pig(杂种野猪宰后肌肉品质特性的研究)[J].A-griculture Products Processing(农产品加工),2005,50(12):15-19.
[6]DUAN YY(段艳宇),ZHOU LH(周利华),YUAN F (袁飞),et al.Correlation of muscle glycolytic potential and its components with meat quality,fat deposition and blood indexes in pigs(猪肌肉糖原酵解潜能及其组分与肉质,脂肪沉积和血液性状的相关性)[J].Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University(江西农业大学学报),2010,32(6):1224-1229.
Responsible editor:Tingting XU
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
不同储藏条件下杜洛克猪肌肉pH、糖原、乳酸及TBA的变化及相关关系
郭建凤*,王继英,蔺海朝,张印,呼红梅,王诚,武英 (山东省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所,山东省畜禽疫病防治与繁育重点实验室,山东济南250100)
该研究测定了杜洛克猪屠宰后10 h肌肉pH、糖原、乳酸和脂质氧化的变化,分析了不同储藏温度和时间对肌肉pH值、失水率、糖原、乳酸及脂质氧化的影响及相关关系。结果表明:宰后10 h杜洛克猪背最长肌pH值显著降低,乳酸含量显著升高,肌肉糖原和TBA值含量变化不显著。4℃冷藏条件下,储存时间对杜洛克猪肌肉pH、糖原、乳酸和TBA含量影响不显著,对滴水损失影响显著。-20℃冷冻条件下,储存时间对杜洛克猪肌肉pH影响极显著,对解冻失水率、糖原、乳酸和TBA值含量影响不显著。相关性分析表明,宰后10 h TBA值与糖原呈显著负相关,与乳酸呈显著正相关,pH与乳酸极显著负相关;4℃冷藏条件下,TBA与滴水损失和乳酸呈极显著和显著负相关,pH与滴水损失极显著正相关;滴水损失与乳酸显著正相关,其他相关性不显著。-20℃冷冻条件下,TBA与pH极显著负相关,与解冻失水率显著正相关,pH与解冻失水率极显著负相关,解冻失水率与乳酸呈显著负相关,其他相关不显著。
杜洛克猪;温度;时间;pH值;糖原;脂质氧化;相关性
山东省现代农业产业技术体系生猪创新团队建设项目 (SDAIT-06-011-03);山东省农业良种工程项目(2011LZ013-01);国家生猪产业技术体系(CARS-36)。
郭建凤(1973-),女,山东莒县人,硕士,研究员,主要从事猪的遗传育种研究。*通讯作者,E-mail:g250100@126.com。
2015-09-02
Supported by Funds for Swine Innovation Team Construction of Shandong Provincial Modern Agriculture Industry Technology System (SDAIT-06-011-03);Fine Breeds Engineering Project of Shandong Province (2011LZ013-01);China Swine Industry Technology System(CARS-36).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:g250100@126.com
Received:September 2,2015 Accepted:November 4,2015
修回日期 2015-11-04
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Study on Engineering Characteristics and Application of Sticky Rice
- Periodical Development Trend of Vertical Greening
- Advances in Microbial Remediation on the Application of Heavy Metal Pollution in Agricultural Water Resources
- Analysis on Status quo and Future Development of Fruit and Vegetable Protreatment
- Effect of Three Treatment Measures on Harmless Seedling Raising of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv.
- Discussions and Recommendations for Supervision of Vegetable Quality and Safety in Miyun County
