地质学
2015-10-31
地质学

来源出版物:SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences,2015,58(6): 859-875联系邮箱:LI Lin-lin,lill@pku.edu.cn
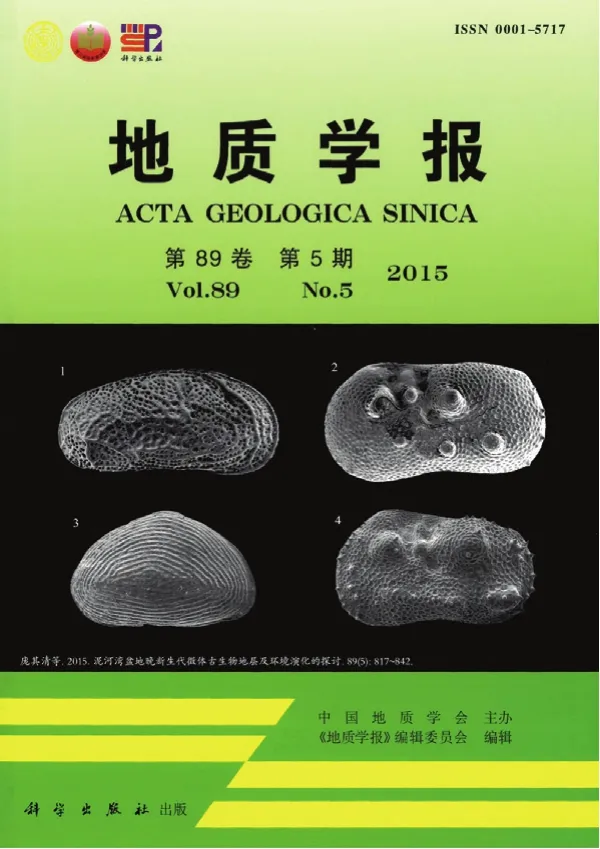
泥河湾盆地晚新生代微体古生物地层及环境演化的探讨
庞其清,翟大有,赵筑簾,等
通过对泥河湾盆地43条剖面和6个钻孔晚新生代地层和微体古生物(介形类和有孔虫)的调查研究,发现非常丰富的介形类,计26属70余种,有孔虫4属4种,其中介形类自下而上可明显地划分为5个组合带:(1)Potamocypris plana-Candoniella-Ilyocypris组合带;(2)Leucocythere-Ilyocypris-Candoniella组合带;(3)Leucocythere-Cytherissa-Limnocythere组合带;(4)Ilyocypris-Limnocythere flexa-Limnocythere dubiosa组合带;(5)Limnocythere dubiosa-Limnocythere sancti-Patricii-Ilyocypris组合带.按以上5个介形类组合带的分布,第1组合带及所含地层红崖村组和石匣组的时代为上新世;第2~4组合带及所含地层泥河湾组的时代为早更新世;第5组合带为中-晚更新世,分布于虎头梁组和许家窑组,虎头梁组置中更新世为宜,许家窑组为晚更新世.根据5个介形类组合带和有孔虫的分布及介形类的始现、繁盛、兴衰的演替特征,对泥河湾古湖和盆地的形成经历了上新世的起始,早更新世早期的扩展,中、晚期稳定、发展、湖面最大,中更新世向西部退缩和晚更新世消亡、桑干河水系形成五个发展阶段的演化进行了探讨.
介形类;有孔虫;生物地层;晚新生代;环境演化;泥河湾盆地
来源出版物:地质学报,2015,89(5): 817-842联系邮箱:庞其清,pangqq802@163.com
封面介绍:Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of southwestern Qaidam Basin shows fluvial,delta and lacustrine facies depositional environments. The evolution of paleogeographic and provenance would be controlled by the tectonism of Altyn Tagh fault zone and Qimen Tagh-East Kunlun fault zone. It is a good way to rebuild the filling history and tectonic condition of the basin by heavy minerals. For more details see the research paper by LI Lin-lin et al. on pages 859-875.
Heavy mineral assemblage characteristics and the Cenozoic paleogeographic evolution in southwestern Qaidam Basin
LI Lin-lin,GUO Zhao-jie,GUAN Shu-wei,et al.
Based on the analysis of heavy mineral assemblages in Cenozoic southwestern Qaidam Basin,we found that different areas have variable heavy mineral assemblage characteristics,which suggested that there were two source areas—the Altyn Mountains and the Qimen Tagh-East Kunlun Mountains. In Ganchaigou-Shizigou-Huatugou(Area A),which was mainly source from the Altyn Mountains,its heavy minerals were mainly composed of zircon,Ti-oxides,and wollastonite in the Paleocene-early Eocene and mainly of unstable minerals,especially amphibole,in the middle Eocene-Oligene. Since the late Oligocene-Miocene,the heavy minerals were still mainly unstable minerals,but the content of epidote increased and the content of amphibole decreased. In Qigequan-Hongliuquan(Area B),which was the mixed source from the Altyn Mountains and the Qimen Tagh-East Kunlun Mountains,its heavy minerals were mainly garnet,epidote,and amphibole. The source of Lücaotan-Dongchaishan-Kunbei(Area C)was mainly from the Qimen Tagh-East Kunlun Mountains,heavy minerals in the sediments in Area C were mainly zircon and Ti-oxides in Paleogene and garnet,epidote,and amphibole in Neogene. In Yuejin-Youshashan(Area D),where the stable minerals and unstable minerals were present simultaneously,the heavy mineral assemblages was controlled by multi-direction source. The variation of heavy mineral assemblages in southwestern Qaidam Basin shows that Altyn Mountains was of low-lying topographic relief in Paleocene-early Eocene,and the rapid uplift of Altyn Mountains started from the middle Eocene. InPaleogene,the Altyn Tagh Fault had a slow strike-slip velocity,but the strike-slip velocity increased greatly since the late Oligocene,leading to a strike-slip displacement above 300 km since Neogene. Meanwhile,the Qimen Tagh-East Kunlun fault zone was under a stable tectonic stage in Paleogene with the Qimen Tagh Mountain being low-lying hills; since the late Oligocene,the fault zone started to activate and the Qimen Tagh Mountain began to uplift rapidly.
southwestern Qaidam Basin; Cenozoic; heavy mineral assemblages; provenance analysis; paleogeography evolution
