石墨烯
2015-10-29基于石墨烯的多维度材料构筑及性能研究进展
基于石墨烯的多维度材料构筑及性能研究进展
万武波,赵宗彬,胡超,郗玲冲,邱介山
(大连理工大学炭素材料研究室;辽宁能源材料化工重点实验室;精细化工国家重点实验室,大连 116024)
石墨烯的功能化及其相关应用
黄毅,陈永胜
热点追踪
石墨烯
·编者按·
石墨烯(Graphene)是一种由碳原子构成的单层片状结构的新材料.相关研究最早始于20世纪70年代,一直被认为是假设性的结构,无法单独稳定存在.直到2004年,英国曼彻斯特大学安德烈·海姆教授等用胶带反复剥离高定向热解石墨的方法,成功地从石墨中分离出石墨烯,从而证实石墨烯可以单独存在.该发现立即引起了物理学家、化学家和材料学家的广泛关注,掀起了继富勒烯和碳纳米管之后碳材料的又一次研究热潮.它的发现者英国曼彻斯特大学物理学家安德烈·海姆(Andre·Geim)和康斯坦丁·诺沃肖洛夫(Konstantin·Novoselov)因“二维石墨烯材料的开创性实验”,共同获得2010年诺贝尔物理学奖.
作为最具代表性的二维原子晶体材料,石墨烯拥有非常优异的性能:1)很高的导热率(5300 W·m-1·K-1)和很大的杨氏模量(1.0 TPa);2)超大的比表面积,理论值为2630 m2/g;3)很高的光透射率(97.7%),几乎完全透明;4)其电子运动速度达到光速的1/300,室温下电子迁移率达15000 cm2/(V·s),是目前已知材料中电子传导速度较快的.因此,石墨烯在材料、微电子、光学、能源、生物医学等领域有广阔的应用前景.欧盟于2013年启动了为期十年的石墨烯旗舰计划.韩国以三星公司为核心,形成了由企业和大学组成的庞大的石墨烯协同创新网络,并制定了详细的产业化路线图.剑桥大学、曼切斯特大学、新加坡国立大学等许多科研机构纷纷成立了石墨烯研究中心.我国的石墨烯研究论文总数已超过美国,跃居世界第一位.近三年来地方政府和企业在产业化研发方面已投入逾四亿元,年产能达到数百吨,在锂离子电池、手机触摸屏等领域已进入量产阶段.石墨烯研究已经逐渐走出象牙塔,进入产业化阶段,在未来二十年间,石墨烯制品必将走进人们的生活.
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年3月2日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以石墨烯(graphene)为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为2482和35540条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下.

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以石墨烯(graphene)为词条检索的高被引论文排行结果如下.
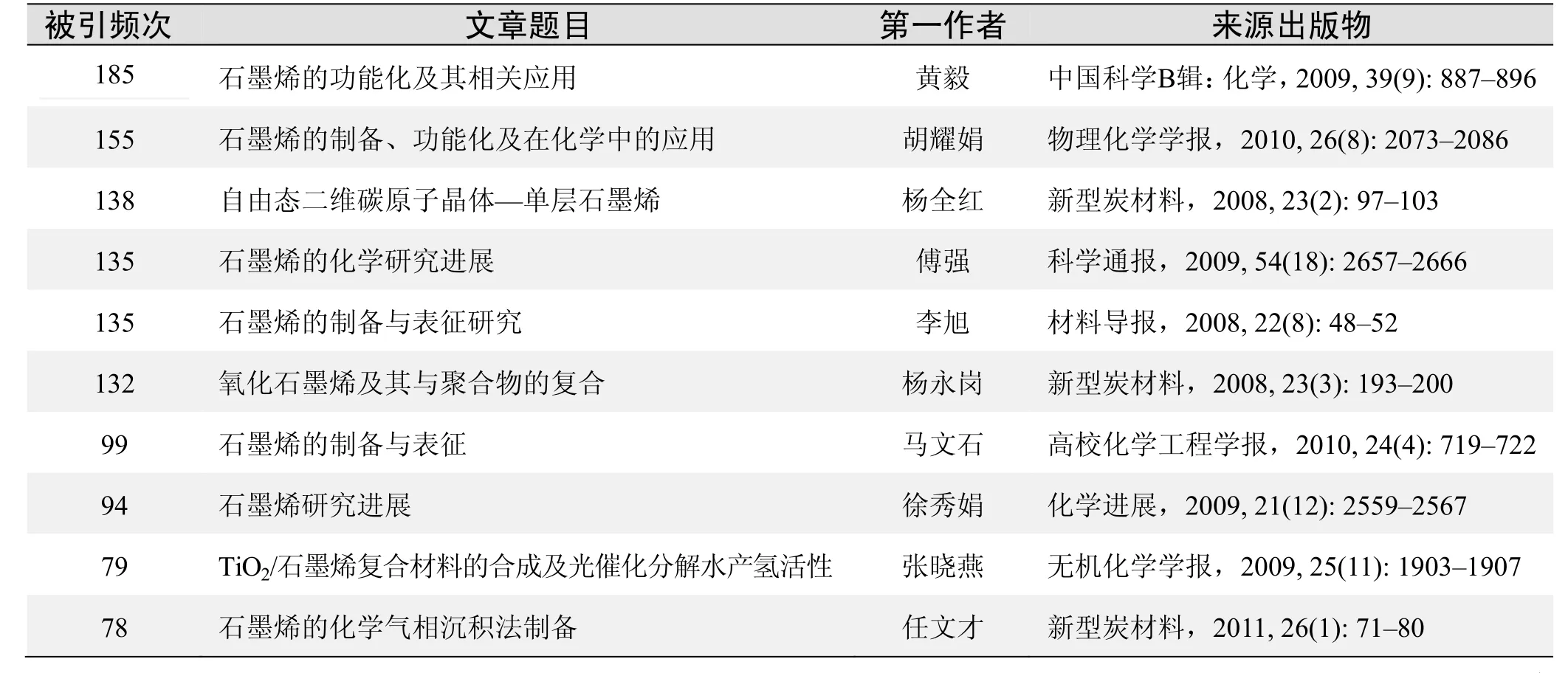
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以石墨烯(graphene)为词条检索的高被引论文排行结果如下.

国外数据库高被引论文排行
基于石墨烯的多维度材料构筑及性能研究进展*
万武波,赵宗彬,胡超,郗玲冲,邱介山
(大连理工大学炭素材料研究室;辽宁能源材料化工重点实验室;精细化工国家重点实验室,大连 116024)
20世纪80年代,随着纳米技术的飞速发展,多种碳纳米材料应运而生.1985年,来自英国和美国的3位科学家率先报道由60个碳原子构成的类似足球形状的碳纳米结构—C60(称为足球烯或者富勒烯).随后,研究者们又陆续发现了C70、C80等一系列类富勒烯结构的大分子.零维富勒烯的发现丰富了碳材料家族.3位发现者Robert F. Curl, Jr、Harold W. Kroto和Richard E. Smalley也因此于1996年荣获诺贝尔化学奖.1991年,日本NEC公司基础研究实验室的Sumio Iijima在高分辨透射电子显微镜下观察电弧放电样品时,意外发现多层管状的碳分子结构的存在,即后来为大家广泛熟知的碳纳米管.一维碳纳米管的发现引发了人们前所未有的兴趣,同时给纳米材料研究和技术领域研究注入了新活力.2004年,Novoselov等首次报道了单层石墨烯的存在,从此掀开了石墨烯研究的序幕.2位发现者Andre Geim和Konstantin Novoselov因在二维晶体材料石墨烯方面的杰出贡献荣获2010年诺贝尔物理学奖.至此,碳材料家族中的零维(0D)富勒烯、一维(1D)碳纳米管、二维(2D)石墨烯,加上此前已被熟知的宏观碳晶体材料——三维(3D)金刚石和石墨,所有已知维度上具有晶体结构的碳材料均被人们认识和发现.
石墨烯是sp2杂化连接的单原子碳层构成的二维原子晶体,其基本结构单元可以看做是有机化合物中稳定的苯六元环结构.石墨烯晶体结构中,六边形密堆积的相邻碳原子之间的距离约为0.142 nm.构成石墨烯的碳原子之间以sp2杂化的方式连接在一起使整个石墨烯片层形成离域的大π键.这种特殊的结构使得π电子可以在石墨烯内部自由移动,因而赋予其优异的导电性.从结构形态上看,石墨烯可以看做是富勒烯、碳纳米管以及石墨等碳材料的基本组成单元.石墨烯片层通过包裹成球可以得到零维的富勒烯,片层绕着固定轴卷曲可以形成类似碳纳米管的空腔管状结构,无数层石墨烯片堆叠就形成石墨片结构.
在石墨烯被发现之初Geim等就提出各种不同结构的碳纳米材料之间相互转化的可能性.直到2009年,材料研究者才从实验结果中观察到单原子片层向富勒烯和碳纳米管等结构的转化.Wang等首先发现超声作用下,在氧化石墨烯的硝酸(70%)溶液中可得到富勒烯、碳纳米管和氧化石墨烯纳米带等低维度碳纳米结构.与其相对应,研究者们也陆续发现富勒烯和碳纳米管在一定条件下也可以转化为各种类石墨烯的结构,如石墨烯量子点和石墨烯纳米带等.
随着石墨烯研究的深入,其应用探索受到越来越多的重视,以二维石墨烯片为基础构建不同尺度的微纳米结构对于其实际应用至关重要.自组装法为制备各种高性能的石墨烯基材料提供了借鉴思路.自组装法是一种高效的材料制备方法,属于自下而上的材料合成策略.以石墨烯,特别是氧化石墨烯这一水溶性的石墨烯前驱体为构筑单元,已经合成了多种不同尺度和形态的石墨烯基自组装结构,微纳米尺度上包括纳米级石墨烯颗粒,一维(1D)的石墨烯线和碳纳米卷(CNSs),宏观上包括二维(2D)的石墨烯薄膜(或石墨烯纸)和三维(3D)的石墨烯组装体(或气凝胶,石墨烯泡沫).本文从石墨烯的片层结构出发,系统论述了石墨烯从0D到3D不同结构、性能的组装体系,并对各种不同维度石墨烯组装体的性能和应用做了对比和评述.
1零维(0D)石墨烯基纳米颗粒
石墨烯具有柔性的六边形碳骨架网络结构,借助外力作用,易发生褶皱、卷曲等形态变化,形成各种不同的纳米结构.2011年,Luo等采用超声雾化法制备了球形石墨烯纳米颗粒,先用医用超声雾化器形成微米级的氧化石墨烯液滴,液滴随着载气(N2)一起进入 800℃的加热炉中迅速脱水;液滴脱水过程中,由于水的巨大表面张力,分散于水滴之中的氧化石墨烯片发生卷曲、褶皱形成稳定的球形颗粒结构;在热处理作用下,氧化石墨烯发生脱氧,最终被还原为石墨烯.改变前驱体氧化石墨烯溶液的浓度,可调控球形石墨烯颗粒尺寸在200~800 nm之间变化.进一步研究发现2D石墨烯片层卷曲成为0D球形结构后,在水中的稳定性大大增加.传统热处理方法得到的石墨烯片层由于强烈的片层间π-π作用力在水中会迅速团聚形成沉淀,而球形的石墨烯颗粒之间的接触面积与原始石墨烯片层相比大为减少,因而表面π-π作用无法使其团聚.石墨烯颗粒即使被高达2 GPa的压力挤压后仍能保持其单分散的颗粒结构,不影响样品的水溶性.此外超声雾化溶液中事先加入制备好的纳米颗粒(如金纳米颗粒),则可得到包裹特定纳米粒子(如纳米金)的零维(0D)石墨烯结构.随后,Mao等在氧化石墨烯溶液中加入各种金属盐的溶液,利用超声雾化技术成功制备了一系列复合型的石墨烯球形颗粒(如Mn3O4、SnO2、Au、Pt纳米颗粒等复合的石墨烯球形颗粒).Zhou等采用喷雾雾化技术一步法制备得到了包覆三氧化二铁的石墨烯纳米颗粒(Fe2O3@GS),该工作开创性地将喷雾雾化技术应用于 0D石墨烯纳米颗粒的制备当中,将得到的复合型石墨烯纳米颗粒用作锂离子电池正极材料,其倍率特性和循环寿命都大大优于单纯的Fe2O3纳米颗粒.
模板法也是制备球形石墨烯基纳米结构的有效方法.Xie等最早提出利用氧化镁纳米颗粒作为模板,苯为碳源,通过化学气相沉积(CVD)过程得到超高比表面积(2053 m2/g)的空心石墨烯囊泡结构.这种结构的零维碳纳米材料作为超级电容器电极材料在1 A/g的电流密度下表现出216 F/g的比电容,即使电流密度达到100 A/g循环1000次后其比电容值仍然保持在112 F/g.Yoon等利用纳米级的金属镍颗粒作为模板,在高温下通过碳化多元醇制备得到多层石墨烯包裹的纳米颗粒,酸洗除去金属颗粒后得到空心的石墨烯球形结构.目前一系列的硬模板(包括SiO2纳米球,聚苯乙烯球,TiO2,Al2O3纳米颗粒和铜纳米颗粒等)相继被开发出来制备零维的石墨烯球形结构.此外,利用氧化石墨烯本身具有的类表面活性剂性质也可以形成球形的微米级乳液.
将二维的石墨烯纳米片进行氧化切割和物理剪裁则可得到另外一种零维度的石墨烯基材料——石墨烯量子点(graphene quantum dots,GQDs).Pan等最早通过水热切割方法制备石墨烯量子点,在混酸环境下首次得到具有蓝色荧光发射的GQDs,该研究提出GQDs的荧光发射效应和紫外吸收带来源于其边界效应.除石墨烯外,研究者们还开发出利用其他前驱体碳源来控制制备GQDs的方法.Hu等通过控制煤炭中石墨微晶的结构和大小,将煤炭氧化刻蚀成具有不同粒径的单层或少层GQDs,将得到的煤基碳量子点作为监测水体中铜离子的高灵敏度荧光探针,检测限可以达到2 nmol/L,这一性能比肩昂贵的电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法和电感耦合质谱法的检测效果.Peng等通过化学氧化炭纤维的方式,得到了荧光颜色可变的碳量子点,该研究发现GQDs的粒径还受到硝酸氧化温度的影响.除上述“由上到下”的剪切策略外,还可以通过“自下而上”的方式制备 GQDs.例如,Lu等利用Ru的催化“开笼”作用,成功地将C60富勒烯转变成纳米碳微簇,再经过扩散和聚合,形成GQDs;Li等以小分子芳烃化合物为碳源,通过溶液化学途径的氧化聚合作用,分别得到了由168、132和170个碳原子构筑的GQDs.
2一维(1D)石墨烯纤维的制备及其应用
当前对超长一维石墨烯纤维的研究成为石墨烯研究领域的一个新兴方向.2011年Xu等继发现氧化石墨烯的液晶现象后,又提出利用高浓度的氧化石墨烯液晶溶液进行纺丝并首次得到宏观的石墨烯纤维.这种方法基于工业化的湿法纺丝技术,先得到氧化石墨烯的纤维,然后再利用氢碘酸对其还原最终制备出具有一定机械强度(抗拉强度为140 MPa)的石墨烯纤维.纺丝法作为一种连续制备石墨烯组装结构的策略,有望成为石墨烯实现实际应用的关键技术.为了进一步提高石墨烯纤维的力学强度,研究者们发现含有二价阳离子(如Ca2+和Cu2+)的凝固浴可以提高石墨烯纤维的力学强度.Jalili等发现氧化石墨烯纤维的凝固过程在Ca2+的促进下可以达到412 MPa的断裂强度,Xu等也证明二价Ca2+在纺丝凝固过程中提供的离子键可以有效增强石墨烯纤维的抗拉强度(达到501 MPa).改变纺丝的固化条件或者针头形状还可以制备出各种结构不同的石墨烯纤维.比如,利用液氮对纺丝进行固化,冻干后碳化处理可以得到具有定向孔道结构的石墨烯纤维气凝胶,纺丝得到的气凝胶具有高达884 m2/g的比表面积和3.3 MPa的抗压强度.此外,石墨烯纤维气凝胶内部的孔道结构为后续制备功能化的多孔石墨烯纤维提供了可能性.
模板法为可控制备石墨烯纤维提供了另外一种可行的路径.Dong等首先提出利用中空毛细玻璃管作为硬模板制备各种形态的石墨烯纤维.他们先将高质量浓度氧化石墨烯溶液(8 mg/mL)灌注到内径0.4 mm的玻璃管中,然后将玻璃管密封后230℃加热2 h即得到了宏观的石墨烯纤维.原始的石墨纤维强度仅有180 MPa,热处理后其抗拉强度可达420 MPa.这种柔性的石墨烯纤维可以方便地编织成各种形态,此外这种简单而有效的模板法还可制备得到各种功能化的石墨烯纤维,如Fe3O4和TiO2功能化的复合型石墨烯纤维.采用不同孔道结构的硬模板还可以加工出中空甚至是多通道的石墨烯纤维结构.2013年Cheng等以模板法得到的氧化石墨烯纤维为基础,采用微加工激光还原技术首次制备出具有良好湿度响应的智能石墨烯纤维.对石墨烯纤维进行预旋转加工后,该课题组开创性地制备出第一台石墨烯基湿气发电机,其最高转速可达5190 r/min,该发电机可以利用周围环境湿度的变化发电.除了前文论述的纺丝法和模板法,Li等还开发出CVD法制备高质量的石墨烯纤维的技术,此外,各种复合型石墨烯纤维也相继被制备出来,它们在传感器,太阳能电池和超级电容器等领域展现出了广阔的应用前景.
计算化学结果表明,柔韧的2D石墨烯片层本身也能够发生形态转变(如卷曲、褶皱和折叠等),在纳米尺度形成各种不同形态的自组装构型,如0D纳米球(nanospheres)或者纳米笼(nanocages)、1D纳米卷(nanoscrolls)、1D纳米结(nanoknots)等.Viculis等在2003年最早提出和证明单层的石墨层(现在被称为石墨烯)可以通过化学方法进行卷曲形成类似碳纳米管的1D空心管状结构——碳纳米卷(carbon nanoscrolls).当时由于石墨烯的研究成果还未被报道,因此该发现一开始并没有被引起足够的关注.直到2004年,Novoselov等首次报道单层石墨烯的制备,1D碳纳米卷的研究才被关注.在碳纳米卷的制备和性能研究领域,Xie和Zheng等分别采用溶剂挥发法和微波法制备得到高质量的碳纳米卷,并研究了其作为场发射效应晶体管(FET)的性能.最近Wan等发现二维石墨烯片层还可经过折叠形成稳定的1D带状结构——折叠形态的石墨烯纳米带(FGBs).原位电镜力学测试表明,纳米带具有超弹性,可以承受反复压缩和弯曲而瞬间(<35 ms)恢复到原始状态,该材料在柔性电子器件和传感器等领域具有广阔的应用前景.
3二维(2D)石墨烯薄膜的组装及其应用
石墨烯是第一种被人类制备出来的二维原子晶体材料,其完美的片层结构为二维宏观石墨烯基薄膜的有效制备和组装提供了良好的基本构成单元.氧化石墨烯以其良好的分散性成为溶液法制备二维石墨烯薄膜首选的前驱体.2007年Dikin等首次采用真空诱导的自组装策略制备了厚度由 1 μm到 30 μm的氧化石墨薄膜,他们提出氧化石墨烯可以面面堆叠形成柔性的宏观薄膜结构.材料力学性能测试表明氧化石墨烯薄膜的模量可达32 GPa,这一强度要远高于传统的石墨薄膜和其他薄膜材料.2012年Nair等研究发现氧化石墨烯薄膜可以作为良好的膜分离材料,对于气体和挥发性有机物具有很好的隔绝作用,而水分子能够畅通无阻地通过.该研究提出这一现象是由于氧化石墨烯层间堆积留下的二维毛细管结构有利于水分子扩散,而且氧化石墨烯表面丰富的含氧官能团对水分子具有良好的亲和力,进一步使得到的薄膜有利于水分子快速通过却阻隔有机物气体的通过.
氧化石墨烯为绝缘体,这限制了其更加广泛的应用.2008年Li等首次制备得到宏观的石墨烯薄膜.实验过程中首先利用氨水辅助的水合肼还原策略得到稳定的石墨烯分散液,最后同样采用真空诱导的自组装方法得到了柔性的石墨烯薄膜,其电导率高达7200 S/m,这一数值与之前报道的碳纳米管薄膜的电导率相当.由于石墨烯之间强烈的π-π作用力,石墨烯薄膜的力学强度达到42.3 GPa.Wan等通过研究石墨烯薄膜的形成过程发现,柔性石墨烯薄膜的形成受控于干燥过程中水分的挥发速率:自然干燥条件下,水分缓慢挥发,石墨烯片之间慢慢形成密堆积的层状结构,得到的2D石墨烯薄膜表面平整;而烘箱干燥条件下,材料水分迅速蒸发,石墨烯片层之间没有足够时间和驱动力来形成完美的面面堆积结构,继而得到表面粗糙且易碎的石墨烯薄膜.Yang等对石墨烯薄膜进行了系统研究,他们提出化学还原得到的石墨烯薄膜最开始是以水凝胶的形式存在,石墨烯层间的水分子为离子扩散提供了良好的通道,同时石墨烯的高导电性为电子的传输提供了导电网络,因此湿基的石墨烯薄膜可以直接作为高性能的超级电容器电极材料.电化学测试表明,石墨烯水凝胶薄膜在1080 A/g的超大充放电电流密度下,仍然具有156 F/g的比容量,同时该材料在100 A/g的电流密度下循环10000次后仍然表现出97%的电容保持率.2014年,该课题组将石墨烯薄膜应用于有机系的超级电容器中,在接近实际应用的操作条件下连续测试300 h仍然表现出95%的电容保持率,而且通过调变石墨烯片在电解液中的堆积密度,该材料表现出高达59.9 Wh/L的能量密度,与商业化的铅酸电池相当.以上研究结果说明了石墨烯基薄膜在超级电容器领域的巨大应用潜力.
真空诱导自组装方法需要外界提供高的真空环境,并且这种方法制备得到的石墨烯薄膜很难从滤膜上直接剥离下来.石墨烯薄膜的界面组装策略提供了另外一种更容易的二维薄膜制备方法.2009年,Chen等提出气液界面自组装制备无支撑氧化石墨烯薄膜的技术策略.该方法操作简单,只需将氧化石墨烯水溶液在80℃下加热20 min即可在溶液表面得到厚度约为5 μm的氧化石墨烯薄膜.这种界面成膜的方法还可制备石墨烯和氧化石墨烯复合的宏观二维薄膜结构.该课题组还以气液界面自组装的氧化石墨烯薄膜为基础,通过调节薄膜中水分的脱除过程,在微纳米尺度上对其微观结构进行调控,得到了具有层次孔道结构的氧化石墨烯薄膜.热处理后得到的石墨烯薄膜对重油的吸附量可以达到自身重量的40倍.柔性薄膜由于对多硫化物良好的吸附性能,作为自支撑电极材料应用于锂硫电池测试过程中,在500个循环后仍然保持600 mAh/g的容量.这种多功能二维薄膜在环境和新能源领域为新材料以及新型储能器件的开发和设计提供了新的思路和途径.
除了纯碳结构的石墨烯基薄膜外,各种功能化的复合型二维石墨烯薄膜材料相继被开发出来.Wang等采用原位聚合的方法,将石墨烯分散液和苯胺单体在阳极进行电聚合得到了复合型的石墨烯薄膜.通过电场作用,聚苯胺和石墨烯紧密地复合在一起,该复合材料兼有石墨烯的高导电率(电阻仅为0.36 Ω)和聚苯胺的高电容率(比容量达233 F/g),同时表现出良好的柔韧性,在电极材料领域展现出广泛的应用前景.Chen等用氨水作为氮源,将化学修饰的石墨烯与CNT通过一步抽滤法构造出层层自组装的氮、氧共掺杂石墨烯复合水凝胶膜.碳纳米管和石墨烯的复合膜作为电催化剂用于电化学析氧(oxygen evolution eeaction,OER)过程,在0.1 mol/L KOH中其过电位仅为315 mV,在过电位为564 mV处的电流密度达到了14.8 mA/cm2,高于常用的贵金属催化剂IrO2.此外酸性环境中(0.5 mol/L H2SO4)石墨烯复合膜也表现出很好的催化活性,其性能明显优于IrO2.由于石墨烯与碳纳米管之间的强相互作用使其在酸性和碱性条件下均表现出很好的催化稳定性,而且双原子掺杂的协同作用使这种复合材料表现出很好的OER活性.
4三维石墨烯组装体的制备及其应用
石墨烯组装体(graphene monolith)是指由石墨烯片层堆积在一起形成的具有三维多孔网络结构的宏观块体.氧化石墨烯由于具备良好的水溶性,被视为制备各种石墨烯组装结构理想的前驱体材料.2010年Tang等首先报道了利用贵金属诱导的水热组装过程制备三维的石墨烯组装体.得到的柱形石墨烯块体材料原位担载Pd纳米颗粒后,可以作为固定床直接用于Heck反应中,实现了100%的转化率和92%的选择性.同年Worsley等利用溶胶凝胶策略合成了高导电率的石墨烯气凝胶,并申请了第一个石墨烯气凝胶的美国专利.接着Xu等研究发现纯的氧化石墨溶液经过水热过程就可以很方便地形成石墨烯组装体结构,利用该组装体作为超级电容器的整体电极材料,在2和5 mV/s的扫速下分别表现出了175、152 F/g的比电容.之后该课题组开发了一系列制备石墨烯组装体的方法,包括 DNA分子诱导的氧化石墨自组装方法和各种有机小分子与氧化石墨烯之间通过静电作用力形成三维组装体结构的方法.2012年Ling等提出基于冰模板的石墨烯组装策略,制备得到了具有规则孔道结构的石墨烯组装体.同年Sun等和Hu等几乎同时报道了超轻的石墨烯基气凝胶结构,2个课题组利用不同的组装策略实现了超弹性石墨烯组装体的构筑.不同之处在于,前者先冻干碳纳米管和氧化石墨烯混合液,然后利用水合肼还原得到了世界上最轻的气凝胶结构(密度为0.16 mg/cm3,仅是空气密度的1/6,低于氦气的密度);而后者采用乙二胺还原和交联的步骤,然后微波处理的策略得到了纯石墨烯基的气凝胶结构,其密度最低可达3.0 mg/cm3.最近Wan等基于点击化学的思想和分子动力学模拟研究结果,开发出利用环氧开环反应快速制备3D氧化石墨烯组装体的新方法.该研究提出以商业化环氧树脂——聚醚胺(D400)为交联剂,快速得到共价键交联的氧化石墨烯组装体结构.整个材料制备过程可控性好,最快在10 s内即可快速完成氧化石墨烯片的共价交联.这种低密度、高孔隙率的氧化石墨烯组装体具有优异的形状记忆性和生物相容性,在能源、环保、生物工程等领域有广阔的应用前景.
前面报道的石墨烯基三维结构都是基于氧化石墨为前驱体的液相自组装策略.2011年Chen等提出一种CVD生长三维石墨烯泡沫结构的方法.该方法以泡沫镍或者泡沫铜作为模板,利用传统的 CVD过程在泡沫金属表面生长出一层或者多层的石墨烯结构,最后利用溶液将金属模版溶解掉就得到泡沫结构的石墨烯三维组装体材料.这种方法由于在高温下直接生成石墨烯组装体,得到的产物一般具有比液相法更高的结晶度和导电性.此外经过高分子(如PDMS)灌注后,该材料变为具有良好拉伸性能和柔性的石墨烯基导电泡沫.接着,该课题组将这种石墨烯泡沫结构作为整体电极材料组装成柔性的锂离子电池,表现出超快的充放电速率,在18 s内即可完成充放电.此外利用石墨烯作为电极基底材料组装锂离子电池可以避免使用导电剂和黏结剂,因此该方法简单易行,利于放大.这一研究结果使得大规模制备高速充放电的柔性锂离子电池成为可能.2014年Ito开发出一种制备新型3D石墨烯结构——纳米孔道石墨烯(nanoporous graphene)的方法,他们利用具有规则纳米孔的金属镍作为硬模板,采用苯作为碳源通过CVD过程得到氮掺杂或者非氮掺杂的纳米孔道石墨烯结构,这种石墨烯三维结构是由具有纳米孔道的石墨烯材料组成,该研究小组还证实氮掺杂的纳米孔道的石墨烯材料有望替代贵金属(如Pt)用于氧还原反应中.
5展望
综上所述,石墨烯自发现至今大约只有10个年头,经过各领域研究者的共同努力,这一原子片层材料的制备技术日趋完善.目前的研究重点已经从简单的材料制备逐渐转向石墨烯片层的可控组装及其实际应用研究.基于胶体和界面化学的技术手段,从零维(0D)到三维(3D)的一系列石墨烯基自组装材料相继被开发出来.然而,目前距离石墨烯基多维度材料的完全可控组装及实际应用还有一定距离,今后的研究亟需在以下几个方面取得突破:目前的石墨烯自组装技术大多基于水溶性氧化石墨烯这一前驱体材料,合成过程中必然需要引入还原这一步骤来得到石墨烯的各种自组装结构,因此从天然石墨或者石墨烯纳米片出发,直接对石墨烯进行可控组装的技术尤为关键;石墨烯二维片层结构向不同维度组装形态变化过程中的构效关系尚不明确,这方研究面需注重理论计算与材料制备的结合与互补;有待开发出一种通用技术,用以控制石墨烯纳米片在所有维度上的自组装行为;计算化学结果预测出柔性的石墨烯片层能够发生形态转变(如卷曲、褶皱和折叠等),在纳米尺度形成各种不同形态的自组装构型,然而目前许多预测的结构还有待试验的检验,材料制备研究任重而道远,具有分级结构的多维度组装材料鲜被报道.
总之,石墨烯这一二维晶体材料的研究已经不单单局限于其原子片层结构,如同中国传统折纸艺术一样,柔韧的石墨烯片层就像一张自由纸片,能够产生绚丽的形态和结构变化,演绎从0D到3D的不同组装结构.随着研究的深入,我们有理由相信石墨烯的多维度材料构筑领域将不断出现新的研究结果,得到一系列结构独特性能优异的组装结构,从而为石墨烯的实际应用奠定坚实的基础.
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:185
石墨烯的功能化及其相关应用
黄毅,陈永胜
石墨烯是2004年才被发现的一种新型二维平面纳米材料,其特殊的单原子层结构决定了它具有丰富而新奇的物理性质.过去几年中,石墨烯已经成为了备受瞩目的国际前沿和热点.在石墨烯的研究和应用中,为了充分发挥其优良性质,并改善其成型加工性(如分散性和溶解性等),必须对石墨烯进行功能化,研究人员也在这方面开展了积极而有效的工作.但是,关于石墨烯的功能化方面的研究还处在探索阶段,对各种功能化的方法和效果还缺乏系统的认识.如何根据实际需求对石墨烯进行预期和可控的功能化是我们所面临的机遇和挑战.本文重点阐述了石墨烯的共价键和非共价键功能化领域的最新进展,并对功能化石墨烯的应用作了介绍,最后对相关领域的发展趋势作了展望.
石墨烯;共价键;非共价键;功能化;应用
来源出版物:中国科学B辑:化学,2009, 39(9): 887-896联系邮箱:陈永胜,yschen99@nankai.edu.cn.
被引频次:155
石墨烯的制备、功能化及在化学中的应用
胡耀娟,金娟,张卉,等
摘要:石墨烯是最近发现的一种具有二维平面结构的碳纳米材料,它的特殊单原子层结构使其具有许多独特的物理化学性质.有关石墨烯的基础和应用研究已成为当前的前沿和热点课题之一.本文仅就目前石墨烯的制备方法,功能化方法以及在化学领域中的应用作一综述,重点阐述石墨烯应用于化学修饰电极、化学电源、催化剂和药物载体以及气体传感器等方面的研究进展,并对石墨烯在相关领域的应用前景作了展望.
关键词:石墨烯;碳材料;石墨烯氧化物;石墨烯功能化;石墨烯应用
来源出版物:物理化学学报,2010, 26(8): 2073-2086联系邮箱:蔡称心,cxcai@njnu.edu.cn
被引频次:138
自由态二维碳原子晶体——单层石墨烯
杨全红,吕伟,杨永岗,等
摘要:石墨烯是近年发现的二维碳原子晶体,是目前碳质材料和凝聚态物理领域的研究热点之一.石墨烯是构筑零维富勒烯、一维碳纳米管、三维体相石墨等sp2杂化碳的基本结构单元,具有更多奇特的性质.通过简要介绍石墨烯的发现历史及分子结构,重点评述了石墨烯奇特的性质(特别是电学性质)和潜在的应用领域.
关键词:石墨烯;二维晶体;层状材料;电子性质
来源出版物:新型炭材料,2008, 23(2): 97-103联系邮箱:杨全红,qhyangcn@tju.edu.cn
被引频次:135
石墨烯的化学研究进展
傅强,包信和
摘要:评述了近3年来在石墨烯(graphene)制备化学、石墨烯化学改性、石墨烯表面化学和催化等方面取得的重要进展.阐述了通过化学方法实现非支撑(freestanding)或准非支撑(quasifree-standing)石墨烯结构的可控和规模制备;通过表面反应对石墨烯进行掺杂和官能化,制备了石墨烷、石墨烯氧化物等具有特殊结构和性质的石墨烯相关化合物;这些石墨烯及石墨烯相关材料(graphene and related materials)在催化、储氢等领域展现出非常重要的应用前景.
关键词:石墨烯;石墨烯氧化物;石墨烷;石墨烯掺杂;碳纳米管;碳催化
来源出版物:科学通报,2009, 54(18): 2657-2666联系邮箱:傅强,qfu@dicp.ac.cn
被引频次:135
石墨烯的制备与表征研究
李旭,赵卫峰,陈国华
摘要:石墨烯材料是近两年的一个研究热点.简要回顾了石墨分离的历史,着重介绍了石墨烯的制备方法:GICs插层法、还原氧化石墨法、微机械剥离法和化学沉积法,分析了各种制备方法的特点以及所面临的问题,概述了石墨烯的不同表征方法以及应用,并展望了其未来发展前景.
关键词:石墨烯;性质;制备方法;表征;应用
来源出版物:材料导报,2008, 22(8): 48-52联系邮箱:陈国华,hdcgh@qu.edu.cn
被引频次:132
氧化石墨烯及其与聚合物的复合
杨永岗,陈成猛,温月芳,等
摘要:石墨烯是单原子厚度的二维碳原子晶体,也是性能优异的新型纳米复合填料.近三年来,石墨烯从概念上的二维材料变成现实材料,在化学和物理学界均引起轰动.通过述评氧化石墨及氧化石墨烯的制备、结构、改性及其与聚合物的复合,展望了石墨烯及其复合材料的研究前景,认为通过机械剥离氧化石墨可规模化制备氧化石墨烯,进一步将其化学改性并制备复合材料已取得较大进展,这一途径被认为是石墨烯规模化应用的战略起点.
关键词:石墨烯;氧化石墨;复合材料
来源出版物:新型炭材料,2008, 23(3): 193-200联系邮箱:杨永岗,yangyg@VIP.163.com
被引频次:99
石墨烯的制备与表征
马文石,周俊文,程顺喜
摘要:采用液相氧化法制备了氧化石墨,并通过水合肼还原氧化石墨制备了石墨烯.采用傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)、拉曼光谱(RS)、X-射线衍射(XRD)、热失重法(TG)等测试方法对石墨、氧化石墨和石墨烯的结构与耐热性进行了对比分析.研究结果表明,氧化石墨被水合肼还原成石墨烯后,氧化石墨的一部分sp3杂化碳原子被还原成石墨的sp2杂化碳原子,石墨烯sp2杂化碳层平面的平均尺寸比氧化石墨大,但结晶强度和规整度比石墨有所降低.在本实验条件下,氧化石墨的还原状态结构不可能被完全恢复到原有的石墨状态,也就是说石墨烯的结构和石墨结构还是有差别的.热分析结果表明,石墨烯具有比氧化石墨更为优异的热稳定性.
关键词:石墨烯;氧化石墨;结构;性能
来源出版物:高校化学工程学报,2010, 24(4): 719-722联系邮箱:马文石,mcwshma@scut.edu.cn
被引频次:94
石墨烯研究进展
徐秀娟,秦金贵,李振
摘要:石墨烯是目前发现的唯一存在的二维自由态原子晶体,它是构筑零维富勒烯、一维碳纳米管、三维体相石墨等 sp2杂化碳的基本结构单元,具有很多奇异的电子及机械性能.因而吸引了化学、材料等其他领域科学家的高度关注.本文介绍了近几年石墨烯的研究进展,包括石墨烯的合成、去氧化、化学修饰及应用前景等方面的内容.
关键词:石墨烯;氧化石墨烯(GO);功能化石墨烯;传感器
来源出版物:化学进展,2009, 21(12): 2559-2567联系邮箱:李振,lizhen@whu.edu.cn
被引频次:79
TiO2/石墨烯复合材料的合成及光催化分解水产氢活性
张晓艳,李浩鹏,崔晓莉
摘要:利用石墨粉根据Hummers氧化法制得氧化石墨,并进一步还原得到石墨烯.采用溶胶一凝胶法以钛酸四丁酷和石墨烯为起始材料制备了二氧化钛(TiO2)和石墨烯的复合光催化材料.研究了该复合材料在紫外-可见光以及可见光条件下的光催化分解水制氢活性.结果表明,紫外-可见光照射下,TiO2/石墨烯复合光催化材料的光催化分解水产氢速率为8.6 μmol·h-1,远大于同条件下商业P25的产氢速率(4.5 μmol·h-1),光解水产氢活性提高了近2倍;可见光下光照3 h,TiO2/石墨烯复合材料的光催化分解水产氢量约为0.2 μmol·h-1.
关键词:石墨烯;二氧化钛;光解水;产氢
来源出版物:无机化学学报,2009, 25(11): 1903-1907联系邮箱:崔晓莉,xiaolicui@fudan.edu.cn
被引频次:78
石墨烯的化学气相沉积法制备
任文才,高力波,马来鹏,等
摘要:化学气相沉积(CVD)法是近年来发展起来的制备石墨烯的新方法,具有产物质量高、生长面积大等优点,逐渐成为制备高质量石墨烯的主要方法.通过简要分析石墨烯的几种主要制备方法(胶带剥离法、化学剥离法、SiC外延生长法和CVD方法)的原理和特点,重点从结构控制、质量提高以及大面积生长等方面评述了 CVD法制备石墨烯及其转移技术的研究进展,并展望了未来CVD法制备石墨烯的可能发展方向,如大面积单晶石墨烯、石墨烯带和石墨烯宏观体的制备与无损转移等.
关键词:石墨烯;制备;化学气相沉积法;转移
来源出版物:新型炭材料,2011, 26(1): 71-80联系邮箱:任文才,wcren@inr.ac.cn
被引频次:16662
来源出版物:Science, 2004, 306(5696): 666-669联系邮箱:Geim, AK; geim@man.ac.uk
被引频次:11833
The rise of graphene
Geim, AK; Novoselov, K S
Abstract: Graphene is a rapidly rising star on the horizon of materials science and condensed-matter physics. This strictly two-dimensional material exhibits exceptionally high crystal and electronic quality, and, despite its short history, has already revealed a cornucopia of new physics and potential applications, which are briefly discussed here. Whereas one can be certain of the realness of applications only when commercial products appear, graphene no longer requires any further proof of its importance in terms of fundamental physics. Owing to its unusual electronic spectrum, graphene has led to the emergence of a new paradigm of 'relativistic' condensed-matter physics, where quantum relativistic phenomena, some of which are unobservable in high-energy physics, can now be mimicked and tested in table-top experiments. More generally, graphene represents a conceptually new class of materials that are only one atom thick, and, on this basis,offers new inroads into low-dimensional physics that has never ceased to surprise and continues to provide a fertile ground for applications.
Keywords: dirac fermions; berrys phase; electronic-structure; bilayer graphene; graphite; films; gas; semiconductors; nucleation; surface
来源出版物:Nature Materials, 2007, 6(7):183-191联系邮箱:Geim, AK; geim@man.ac.uk
被引频次:7657
Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene
Novoselov, KS; Geim, AK; Morozov, SV; et al.
Abstract: Quantum electrodynamics(resulting from the merger of quantum mechanics and relativity theory)has provided a clear understanding of phenomena ranging from particle physics to cosmology and from astrophysics to quantum chemistry(1-3). The ideas underlying quantum electrodynamics also influence the theory of condensed matter(4, 5), but quantum relativistic effects are usually minute in the known experimental systems that can be described accurately by the non-relativistic Schrodinger equation. Here we report an experimental study of a condensed-matter system(graphene, a single atomic layer of carbon(6,7))in which electron transport is essentially governed by Dirac's(relativistic)equation. The charge carriers in graphene mimic relativistic particles with zero rest mass and have an effective ‘speed of light’ c* approximate to 106m s-1. Our study reveals a variety of unusual phenomena that are characteristic of two-dimensional Dirac fermions. In particular we have observed the following: first, graphene's conductivity never falls below a minimum value corresponding to the quantum unit of conductance, even when concentrations of charge carriers tend to zero; second, the integer quantum Hall effect in graphene is anomalous in that it occurs at half-integer filling factors; and third, the cyclotron mass m(c)of massless carriers in graphene is described by E= m(2)c(*)(2). This two-dimensional system is not only interesting in itself but also allows access to the subtle and rich physics of quantum electrodynamics in a bench-top experiment.
Keywords: graphite; states
来源出版物:Nature, 2005, 438(7065): 197-200联系邮箱:Geim, AK; geim@man.ac.uk
被引频次:6745
The electronic properties of graphene
Castro Neto, AH; Guinea, F; Peres, NMR; et al.
Abstract: This article reviews the basic theoretical aspects of graphene, a one-atom-thick allotrope of carbon, with unusual two-dimensional Dirac-like electronic excitations. The Dirac electrons can be controlled by application of external electric and magnetic fields, or by altering sample geometry and/or topology. The Dirac electrons behave in unusual ways in tunneling, confinement, and the integer quantum Hall effect. The electronic properties of graphene stacks are discussed and vary with stacking order and number of layers. Edge(surface)states in graphene depend on the edge termination(zigzag or armchair)and affect the physical properties of nanoribbons. Different types of disorder modify the Dirac equation leading to unusual spectroscopic and transport properties. The effects of electron-electron and electron-phonon interactions in single layer and multilayer graphene are also presented.
Keywords: carbon; electron-phonon interactions; nanostructured materials; quantum Hall effect; surface states; tight-binding calculations;tunnelling
来源出版物:Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(1): 109-162
被引频次:5954
Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry's phase in graphene
Zhang, YB; Tan, YW; Stormer, HL; et al.
Abstract: When electrons are confined in two-dimensional materials, quantum-mechanically enhanced transport phenomena such as the quantum Hall effect can be observed. Graphene, consisting of an isolated single atomic layer of graphite, is an ideal realization of such a two-dimensional system. However, its behaviour is expected to differ markedly from the well-studied case of quantum wells in conventional semiconductor interfaces. This difference arises from the unique electronic properties of graphene, which exhibits electron -hole degeneracy and vanishing carrier mass near the point of charge neutrality(1, 2). Indeed, a distinctive half-integer quantum Hall effect has been predicted(3-5)theoretically, as has the existence of a non-zero Berry's phase( a geometric quantum phase)of the electron wavefunction-a consequence of the exceptional topology of the graphene band structure(6, 7). Recent advances in micromechanical extraction and fabrication techniques for graphite structures(8-12)now permit such exotic two-dimensional electron systems to be probed experimentally. Here we report an experimental investigation of magneto-transport in a high-mobility single layer of graphene. Adjusting the chemical potential with the use of the electric field effect, we observe an unusual half-integer quantum Hall effect for both electron and hole carriers in graphene. The relevance of Berry's phase to these experiments is confirmed by magneto-oscillations. In addition to their purely scientific interest, these unusual quantum transport phenomena may lead to new applications in carbon-based electronic and magneto-electronic devices.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; graphite
来源出版物:Nature, 2005, 438(7065): 201-204联系邮箱:Kim, P; pkim@phys.columbia.edu
被引频次:4570
Graphene-based composite materials
Stankovich, Sasha; Dikin, Dmitriy A; Dommett, Geoffrey HB; et al.
Abstract: Graphene sheets-one-atom-thick two-dimensional layers of sp2-bonded carbon-are predicted to have a range of unusual properties. Their thermal conductivity and mechanical stiffness may rival the remarkable in-plane values for graphite(similar to 3000 W m-1K-1and 1060 GPa, respectively); their fracture strength should be comparable to that of carbon nanotubes for similar types of defects(1-3); and recent studies have shown that individual graphene sheets have extraordinary electronic transport properties(4-8). One possible route to harnessing these properties for applications would be to incorporate graphene sheets in a composite material. The manufacturing of such composites requires not only that graphene sheets be produced on a sufficient scale but that they also be incorporated, and homogeneously distributed, into various matrices. Graphite, inexpensive and available in large quantity, unfortunately does not readily exfoliate to yield individual graphene sheets. Here we present a general approach for the preparation of graphene-polymer composites via complete exfoliation of graphite(9)and molecular-level dispersion of individual, chemically modified graphene sheets within polymer hosts. A polystyrene-graphene composite formed by this route exhibits a percolation threshold(10)of similar to 0.1 volume per cent for room-temperature electrical conductivity, the lowest reported value for any carbon-based composite except for those involving carbon nanotubes(11); at only 1 volume per cent, this composite has a conductivity of similar to 0.1 S m-1, sufficient for many electrical applications(12). Our bottom-up chemical approach of tuning the graphene sheet properties provides a path to a broad new class of graphene-based materials and their use in a variety of applications.
Keywords: thin-film particles; graphite oxide; electrical applications; carbon nanotubes; nanoplatelets; polymers; gas
来源出版物:Nature, 2006, 442(7100): 282-286联系邮箱:Nguyen, ST; stn@northwestern.edu
被引频次:4036
Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer grapheme
Lee, Changgu; Wei, Xiaoding; Kysar, Jeffrey W; et al.
Abstract: We measured the elastic properties and intrinsic breaking strength of free-standing monolayer graphene membranes by nanoindentation in an atomic force microscope. The force-displacement behavior is interpreted within a framework of nonlinear elastic stress-strain response, and yields second- and third-order elastic stiffnesses of 340 newtons per meter(N m-1)and -690 N m-1, respectively. The breaking strength is 42 N m-1and represents the intrinsic strength of a defect-free sheet. These quantities correspond to a Young's modulus of E=1.0 terapascals, third-order elastic stiffness of D=-2.0 terapascals, and intrinsic strength of sigma(int)=130 gigapascals for bulk graphite. These experiments establish graphene as the strongest material ever measured, and show that atomically perfect nanoscale materials can be mechanically tested to deformations well beyond the linear regime.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; mechanical-properties; constants; graphite; modulus; sheets; ropes
来源出版物:Science, 2008, 321(5887): 385-388联系邮箱:Hone, James; jh2228@columbia.edu
被引频次:3932
Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers
Ferrari, AC; Meyer, JC; Scardaci, V; et al.
Abstract: Graphene is the two-dimensional building block for carbon allotropes of every other dimensionality. We show that its electronic structure is captured in its Raman spectrum that clearly evolves with the number of layers. The D peak second order changes in shape,width, and position for an increasing number of layers, reflecting the change in the electron bands via a double resonant Raman process. The G peak slightly down-shifts. This allows unambiguous, high-throughput, nondestructive identification of graphene layers, which is critically lacking in this emerging research area.
Keywords: berrys phase; graphite; scattering; nanotubes; crystals; carbons; route; gas
来源出版物:Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(18)文献号:187401联系邮箱:Ferrari, AC; acf26@eng.cam.ac.uk
被引频次:3698
Graphene: Status and Prospects
Geim, AK
Abstract: Graphene is a wonder material with many superlatives to its name. It is the thinnest known material in the universe and the strongest ever measured. Its charge carriers exhibit giant intrinsic mobility, have zero effective mass, and can travel for micrometers without scattering at room temperature. Graphene can sustain current densities six orders of magnitude higher than that of copper, shows record thermal conductivity and stiffness, is impermeable to gases, and reconciles such conflicting qualities as brittleness and ductility. Electron transport in graphene is described by a Dirac-like equation, which allows the investigation of relativistic quantum phenomena in a benchtop experiment. This review analyzes recent trends in graphene research and applications, and attempts to identify future directions in which the field is likely to develop.
Keywords: layer graphene; sheets; films; membranes; graphite
来源出版物:Science, 2009, 324(5934): 1530-1534
被引频次:3541
Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes
Kim, Keun Soo; Zhao, Yue; Jang, Houk; et al
Abstract: Problems associated with large-scale pattern growth of graphene constitute one of the main obstacles to using this material in device applications(1). Recently, macroscopic-scale graphene films were prepared by two-dimensional assembly of graphene sheets chemically derived from graphite crystals and graphene oxides(2, 3). However, the sheet resistance of these films was found to be much larger than theoretically expected values. Here we report the direct synthesis of large-scale graphene films using chemical vapour deposition on thin nickel layers, and present two different methods of patterning the films and transferring them to arbitrary substrates. The transferred graphene films show very low sheet resistance of similar to 280 Omega per square, with 80 per cent optical transparency. At low temperatures, the monolayers transferred to silicon dioxide substrates show electron mobility greater than 3700 cm2V-1s-1and exhibit the half-integer quantum Hall effect(4, 5), implying that the quality of graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition is as high as mechanically cleaved graphene(6). Employing the outstanding mechanical properties of graphene(7), we also demonstrate the macroscopic use of these highly conducting and transparent electrodes in flexible, stretchable, foldable electronics(8, 9).
Keywords: epitaxial graphene; silicon; oxide
来源出版物:Nature, 2009, 457(7230): 706-710联系邮箱:Hong, BH; jaeyoung88.choi@samsung.com
·推荐论文摘要·
NaOH处理对石墨烯电学性能的影响
汤春苗,陈志蓥,朱博,等
摘要:在CVD石墨烯的转移过程中无法避免会出现胶残留,导致了材料不必要的p型掺杂.研究表明,通常来自这种残余胶的p型掺杂影响了石墨烯的电学特性.本文发现NaOH溶液能够有效地去除这种PMMA(聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(C5H8O2)x)中的含氧官能团,减少胶残留,并首次将其运用在CVD生长的石墨烯单层薄膜上.通过不同浓度NaOH溶液的选择,我们有效地解决了NaOH与SiO2/Si衬底反应的问题.处理结果显示,通过NaOH溶液浸泡石墨烯的载流子浓度变为原来的三分之一甚至更少,而且处理效果最明显的石墨烯样品的迁移率从880 cm2/Vs升高到2260 cm2/Vs.同时我们比较了水和NaOH处理效果的稳定性,结果显示用水处理的样品迁移率很快回到了处理前的数据,而用NaOH溶液处理的石墨烯薄膜迁移率最终稳定在原有迁移率的1.5倍.
关键词:石墨烯;迁移率;PMMA;NaOH
来源出版物:材料科学与工程学报,2015, 33(3): 133-138联系邮箱:余广辉,ghyu@mail.sim.ac.cn
石墨烯在场发射器件中的应用与研究现状
李剑,王小平,王丽军,等
摘要:场电子发射是一种独特的量子隧穿效应,也是真空微电子学的基础之一.基于场发射技术的冷阴极发射体一直被视为未来理想的电子发射阴极.石墨烯是一种具备单层碳原子结构的新型碳材料,其电子迁移率高、机械强度高、热导率高,具有稳定的物理化学特性,因此受到科研工作者的广泛关注.与此同时石墨烯具有较高的长径比(横向尺寸与厚度的比值),这一结构特性能够获得较大的场增强因子.石墨烯的上述特性使得其成为具有广阔应用前景的场发射阴极.本文主要综述石墨烯场发射理论的研究进展、石墨烯/石墨烯基场发射阴极的研究现状、场发射阴极结构以及场发射阴极的制备方法,并对场发射领域的石墨烯研究进行了展望.
关键词:石墨烯;场发射;复合阴极
来源出版物:材料科学与工程学报, 2015, 33(1): 145-150联系邮箱:王小平,wxpchina64@aliyun.com
石墨烯层数测量方法的研究进展
姚雅萱,任玲玲,高思田,等
摘要:石墨烯具有高导电性、高韧度、高强度、超大比表面积等特点,在电子、航天工业、新能源、新材料等领域有广泛应用.对石墨烯层数测量方法的研究有助于深入理解石墨烯性能与微观结构之间的关系.本文着重阐述了包括光学显微镜、拉曼光谱、原子力显微镜和透射电镜等测量石墨烯层数的方法,同时比较了各种测量方法的优点及局限性,并指出石墨烯层数的测量方法还有待进一步完善.
关键词:石墨烯;层数;测量方法;
来源出版物:化学通报,2015, 78(2): 100-106联系邮箱:任玲玲,renll@nim.ac.cn
1维石墨烯光子晶体的电磁吸收特性
宁仁霞,刘少斌,章海锋,等
摘要:为了研究1维石墨烯光子晶体在可见光波段的吸收特性,采用传输矩阵的方法进行了理论分析和数值仿真,得到了1维石墨烯吸收特性与石墨烯层数、缺陷层介质厚度、电磁波模式有关的结果.结果表明,增加石墨烯层数时,对波长为556 nm左右的绿光的吸收作用明显增强;缺陷层介质厚度增加时会引起吸收峰的增加;在TE模式下,入射角对石墨烯光子晶体吸收特性影响较小.该研究结果为1维石墨烯光子晶体吸收器的设计提供了理论依据.
关键词:光电子学;吸收特性;传输矩阵法;石墨烯光子晶体;
来源出版物:激光技术,2015, 39(1): 28-32联系邮箱:宁仁霞,nrxxiner@hsu.edu.cn
SnS2-SnO2/石墨烯复合材料的合成及其电化学储锂性能的研究
马琳,叶剑波,黄国创,等
摘要:目的:制备高容量和循环性能稳定的锂离子电池复合电极材料.方法:通过L-半胱氨酸(Lcys)辅助水热法合成SnS2-SnO2/石墨烯复合纳米材料,采用XRD,SEM,TEM和HRTEM技术对其进行结构表征,并采用循环伏安、恒流充放电和电化学阻抗技术研究了其电化学贮锂性能.结果:随着水热溶液中L-cys的量增加,复合材料中少层数结构SnS2的含量也增加.当Sn4+/L-cys的物质的量之比为1:4时,制得了SnS2/石墨烯复合纳米材料,而且石墨烯的存在在一定程度上抑制了SnS2沿c轴方向的生长,减少了层状SnS2的层数.结论:由于二维层状结构的SnS2具有与石墨烯类似的微观结构和形貌,与石墨烯的复合具有更好的匹配性和相互协同效应,增强了SnS2/石墨烯复合材料的电化学贮锂性能,使其具有较高的可逆储锂容量、良好的循环性能和增强的倍率特性.
关键词:二硫化锡;二氧化锡;石墨烯;复合纳米材料;锂离子电池;
来源出版物:表面技术,2015, 44(1): 8-14
氮掺杂石墨烯柔性薄膜的制备及其超电容性能
钟奇能,粟泽龙,李新禄
摘要:目的:改善超级电容器用石墨烯薄膜的超电容性能.方法:采用水热和高温热解法制备多孔氮掺杂的石墨烯柔性薄膜,采用SEM形貌、XRD图谱和等温曲线分析其结构,采用三电极体系测试循环伏安曲线和恒流充放电曲线,分析其超电容性能.结果:氮掺杂石墨烯柔性薄膜保持了氧化石墨烯的褶皱透明,同时具有网络式的多孔洞结构.氮气吸脱附测试表明,氮掺杂多孔石墨烯的比表面积为280.78 m2/g.氮掺杂石墨烯薄膜在1.0 mol/L硫酸钠溶液中,当电流密度为0.1 A/g时,其比容量达到169 F/g.结论:氮原子的掺杂以及氮掺杂石墨烯柔性薄膜的多孔结构可以有效提高石墨烯材料的超电容性能.
关键词:氮掺杂石墨烯;多孔结构;超级电容器;
来源出版物:表面技术,2015, 44(1): 51-55
石墨烯负载纳米Fe3O4复合材料的摩擦学性能
乔玉林,赵海朝,臧艳,等
摘要:采用液相超声直接剥离法制备了石墨烯负载纳米Fe3O4复合材料,用SEM、TEM对其形貌进行了表征,利用多功能往复摩擦磨损试验仪考察了石墨烯负载纳米Fe3O4复合材料在纯水中的摩擦磨损性能.通过SEM、XPS分别分析了磨痕表面的形貌、典型元素的化学状态,初步探讨了石墨烯负载纳米Fe3O4复合材料在纯水中的润滑机理.结果表明:纳米Fe3O4均匀分布于多层石墨烯片层表面和层间,粒径为20~90 nm;其作为纯水添加剂具有良好的减摩抗磨性能,如试验载荷为10 N,浓度为0.01wt%的石墨烯负载纳米Fe3O4复合材料水分散体系润滑时比纯水润滑的摩擦系数和磨损体积分别下降26.7%和35.4%,这主要是由于复合材料在磨损表面形成了吸附膜、含石墨烯和纳米Fe3O4的边界润滑膜,抑制了Fe的氧化,减轻了摩擦表面的磨损.
关键词:石墨烯;Fe3O4;复合材料;摩擦学性能;磨损机理
来源出版物:无机材料学报,2015, 30(1): 41-46联系邮箱:乔玉林,qiaoyulin1010@sina.com
石墨烯中热脉冲传播的分子动力学研究
姚文俊,曹炳阳
摘要:基于非平衡分子动力学方法,模拟研究了梯形、三角形和矩形热脉冲在石墨烯中的传播过程和规律.三种类型的温度脉冲采用直接速度修正法,通过调整对控温区原子施加的温度增量来实现.结果表明,热扰动在石墨烯中以有限的速度传播,并表现出明显的波动传递特征.热扰动在传播过程中激发出两道以不同速度传递的行波,一道波具有宏观动量,波速等于石墨烯声子群速度,为声波;另一道波是无宏观动量的热量的传播,波速是声速的为热波.研究还发现,热脉冲形状对热波现象的产生以及声波、热波的传播速度没有影响,但对其峰值温度影响显著.
关键词:石墨烯;热脉冲传播;热波;分子动力学模拟
来源出版物:工程热物理学报,2015, 36(1): 116-119联系邮箱:曹炳阳,caoby@tsinghua.edu.cn
基于石墨烯的隔离器理论设计与分析
肖丙刚,谢治毅,孙润亮
摘要:基于石墨烯,理论设计与分析了应用于3G通信领域的新型隔离器.隔离器由2个线栅偏振器和1个旋转器组成,旋转器由硅/二氧化硅薄膜、多层石墨烯和二氧化硅基板叠加而成.由于石墨烯在磁场偏置下具有法拉第效应和非互异性,当平面波从正、反两个方向入射隔离器时.电场沿入射方向发生±30°的偏转,使得正向传输的平面波几乎无损通过,而反向传输的平面波被全反射,实现了隔离.利用传输矩阵法计算了隔离度,结果表明,设计的隔离器在工作频段1.8~2.2 GHz内具有良好的隔离特性,隔离度均在12 dB以上,且插入损耗均小于-1.63 dB.
关键词:隔离器;石墨烯;法拉第旋转器;3G移动通信
来源出版物:浙江大学学报(工学版),2015, 49(1): 42-46联系邮箱:肖丙刚,bgxiao@cjlu.edu.cn
铜基底化学气相沉积石墨烯的研究现状与展望
喻佳丽,辛斌杰
摘要:以铜作为基底的化学气相沉积法(CVD)是目前制备石墨烯的重要方法和手段.简单介绍了石墨烯的几种主要制备方法,突出化学气相沉积法能够有效制备出大规模可控高质量的石墨烯,并阐述了铜基底上化学气相沉积石墨烯的生长机理,主要从基底材料、不同的工艺条件以及石墨烯转移技术出发评述了化学气相沉积法制备石墨烯的研究进展,指出由铜网基底材料替代铜箔基底的良好应用前景,最后展望了铜基底化学气相沉积石墨烯的发展方向.
关键词:石墨烯;铜基底;化学气相沉积;生长机理
来源出版物:材料导报A:综述篇,2015, 29(1): 66-71联系邮箱:辛斌杰,xiaobo2000@gmail.com
单层石墨烯在空气中的热稳定性研究
李允,王权
摘要:采用化学气相沉积方法制备了高质量的大面积单层石墨烯,利用拉曼光谱、X射线光电子能谱和原子力显微镜对在空气中热处理前后的石墨烯进行了表征,研究了单层石墨烯在空气中的热稳定性.结果表明,在空气中热处理后,石墨烯的缺陷明显增加,晶粒发生细化,其主要是由于热处理后石墨烯会发生轻微的氧化,表面形成C=O及C—OH键.另外,由于石墨烯与衬底的结合形态有所变化,使得热处理后石墨烯表面更趋平整.
关键词:石墨烯;化学气相沉积;热处理;拉曼光谱;XPS;原子力显微镜
来源出版物:电子元件与材料,2015, 34(1): 18-21联系邮箱:王权,wangq@mail.ujs.edu.cn
Generic miniband structure of graphene on a hexagonal substrate
Wallbank, JR; Patel, AA; Mucha-Kruczynski, M; et al
Abstract: Using a general symmetry-based approach, we provide a classification of generic miniband structures for electrons in graphene placed on substrates with the hexagonal Bravais symmetry. In particular, we identify conditions at which the first moire miniband is separated from the rest of the spectrum by either one or a group of three isolated mini Dirac points and is not obscured by dispersion surfaces coming from other minibands. In such cases, the Hall coefficient exhibits two distinct alternations of its sign as a function of charge carrier density.
Keywords: scanning-tunneling-microscopy; boron-nitride; band-structure; scale
来源出版物:Physical Review B, 2013, 87(24)文献号:245408
Hyperbolic metamaterials based on multilayer graphene structures
Iorsh, Ivan V; Mukhin, Ivan S; Shadrivov, Ilya V; et al
Abstract: We propose metamaterials for THz frequencies based on multilayer graphene structures. We calculate the dielectric permittivity tensor of the effective nonlocal medium with a periodic stack of graphene layers and demonstrate that tuning from elliptic to hyperbolic dispersion can be achieved with an external gate voltage. We reveal that such graphene structures can demonstrate a giant Purcell effect that can be used for boosting the THz emission in semiconductor devices. Tunability of these structures can be enhanced further with an external magnetic field which leads to the unconventional hybridization of the TE and TM polarized waves.
Keywords: boron-nitride; plasmons; transparency; hyperlens; photonics
来源出版物:Physical Review B, 2013, 87(7)文献号:075416
Effect of grain boundaries on thermal transport in graphene
Serov, Andrey Y; Ong, Zhun-Yong; Pop, Eric
Abstract: We investigate the influence of grain boundaries(GBs), line defects(LDs), and chirality on thermal transport in graphene using non-equilibrium Green's functions. At room temperature, the ballistic thermal conductance is similar to 4.2 GW m-2K-1, and single GBs or LDs yield transmission from 50% to 80% of this value. LDs with carbon atom octagon defects have lower thermal transmission than that of GBs with pentagon and heptagon defects. We apply our findings to study the thermal conductivity of polycrystalline graphene for practical applications, and find that the type and size of GBs play an important role when grain sizes are smaller than a few hundred nanometers.
Keywords: molecular-dynamics; nanoribbon interconnects; resistivity; defect
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(3)文献号:033104联系邮箱:Pop, E; epop@illinois.edu
Production of a 100-m-long high-quality graphene transparent conductive film by roll-to-roll chemical vapor deposition and transfer process
Kobayashi, Toshiyuki; Bando, Masashi; Kimura, Nozomi; et al
Abstract: A high-quality graphene transparent conductive film was fabricated by roll-to-roll chemical vapor deposition(CVD)synthesis on a suspended copper foil and subsequent transfer. While the high temperature required for the CVD synthesis of high-quality graphene has prevented efficient roll-to-roll production thus far, we used selective Joule heating of the copper foil to achieve this. Low pressure thermal CVD synthesis and a direct roll-to-roll transfer process using photocurable epoxy resin allowed us to fabricate a 100-m-long graphene transparent conductive film with a sheet resistance as low as 150 Omega/sq, which is comparable to that of state-of-the-art CVD-grown graphene films.
Keywords: monolayer graphene; copper; growth; Cu
来源出版物:Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(2)文献号:023112联系邮箱:Kobayashi, T; Toshiyuki.Kobayashi@jp.sony.com
Graphene-based transparent strain sensor
Bae, Sang-Hoon; Lee, Youngbin; Sharma, Bhupendra K; et al
Abstract: Transparent strain sensors based on graphene were fabricated in a form of rosette on a flexible plastic or stretchable rubber substrate by using reactive ion etching and stamping techniques. Their piezoresistive properties were investigated under a tensile strain up to 7.1%. We demonstrated this sensor on a transparent glove and measured magnitudes and directions of the principal strains on the glove induced by the motion of fingers.
Keywords: light-emitting-diodes; thin-films; carbon; mechanics
来源出版物:Carbon, 2013, 51: 236-242联系邮箱:Kim, JH; jaehkim@kimm.re.kr
The effect of graphene dispersion on the mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites
Tang, Long-Cheng; Wan, Yan-Jun; Yan, Dong; et al
Abstract: The effect of dispersion state of graphene on mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites was investigated. The graphene sheets were exfoliated from graphite oxide(GO)via thermal reduction(thermally reduced GO, RGO). Different dispersions of RGO sheets were prepared with and without ball mill mixing. It was found that the composites with highly dispersed RGO showed higher glass transition temperature(T-g)and strength than those with poorly dispersed RGO, although no significant differences in both the tensile and flexural moduli are caused by the different dispersion levels. In particular, the T-g was increased by nearly 11 degrees C with the addition of 0.2 wt% well dispersed RGO to epoxy. As expected, the highly dispersed RGO also produced one or two orders of magnitude higher electrical conductivity than the corresponding poorly dispersed RGO. Furthermore, an improved quasi-static fracture toughness(K-IC)was measured in the case of good dispersion. The poorly and highly dispersed RGO at 0.2wt% loading resulted in about 24% and 52% improvement in K-IC of cured epoxy thermosets, respectively. RGO sheets were observed to bridge the micro-crack and debond/delaminate during fracture process due to the poor filler/matrix and filler/filler interface, which should be the key elements of the toughening effect.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; polymer nanocomposites; graphite oxide; electrical-conductivity; functionalized graphene; epoxy nanocomposites; fracture mechanisms; poly(vinyl alcohol); thermal-properties; sheets
来源出版物:Carbon, 2013, 60: 16-27联系邮箱:Tang, Long-Cheng; lctang@hznu.edu.cn
An overview of the engineered graphene nanostructures and nanocomposites
Zhu, Jiahua; Chen, Minjiao; He, Qingliang; et al
Abstract: This critical reviewfocuses on the property analysis of graphene and graphene nanocomposites(GNCs)and their demonstrated superior performances in energy storage and conversion, electrochemical-and biosensing, environmental remediation and flame retardant application and atomic thickness membrane separation. The performances of graphene and GNCs are strongly dependent on their chemical component, synthetic method, nanoscale morphology, and assembling structure of the hybrids. The current progress in supercapacitor energy storage density, solar cell power conversion efficiency, thermoelectric energy conversion efficiency, electrochemical sensing capability, biosensor sensitivity, heavy metal adsorption capacity and efficiency, photocatalytic degradation rate of organic dye, flame retardant polymer nanocomposites, graphene and porous graphene membranes is discussed with detailed examples through extensive analysis of the literature.
Keywords: intumescent flame-retardant; high-performance supercapacitors; sensitized solar-cells; step electrochemical synthesis;chemical-vapor-deposition; hydrogen-peroxide sensor; in-situ polymerization; one-pot synthesis; functionalized graphene; graphite oxide
来源出版物:RSC Advances, 2013, 3(45): 22790-22824联系邮箱:Guo, ZH; zhanhu.guo@lamar.edu
Designing band gap of graphene by B and N dopant atoms
Rani, Pooja; Jindal, V. K
Abstract: Ab initio calculations have been performed to study the geometry and electronic structure of boron(B)and nitrogen(N)doped graphene sheets. The effect of doping has been investigated by varying the concentrations of dopants from 2%(one atom of the dopant in 50 host atoms)to 12%(six dopant atoms in 50 atoms host atoms)and also by considering different doping sites for the same concentration of substitutional doping. All of the calculations have been performed using VASP(Vienna Ab initio Simulation Package)based on density functional theory. By B and N doping, p-type and n-type doping are induced, respectively, in the graphene sheet. While the planar structure of the graphene sheet remains unaffected on doping, the electronic properties change from semi-metal to semiconductor with increasing number of dopants. It has been observed that isomers formed by choosing different doping sites differ significantly in the stability, bond length and band gap introduced. The band gap is found to be at a maximum when dopants are placed at same sublattice points of graphene due to the combined effect of symmetry breaking of sublattices and the band gap is closed when dopants are placed at adjacent positions(alternate sublattice positions). These interesting results provide the possibility of tuning the band gap of graphene as required and its application in electronic devices, such as replacements to Pt-based catalysts in Polymer Electrolytic Fuel Cells(PEFCs).
来源出版物:RSC Advances, 2015, 3(3): 802-812联系邮箱:Rani, P; jindal@pu.ac.in
Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Two-Dimensional Materials Beyond Graphene
Butler, Sheneve Z; Hollen, Shawna M; Cao, Linyou; et al
Abstract: Graphene’s success has shown that it is possible to create stable, single and few-atom-thick layers of van der Waals materials,and also that these materials can exhibit fascinating and technologically useful properties. Here we review the state-of-the-art of 2D materials beyond graphene. Initially, we will outline the different chemical classes of 2D materials and discuss the various strategies to prepare single-layer, few-layer, and multilayer assembly materials in solution, on substrates, and on the wafer scale. Additionally, we present an experimental guide for identifying and characterizing single-layer-thick materials, as well as outlining emerging techniques that yield both local and global information. We describe the differences that occur in the electronic structure between the bulk and the single layer and discuss various methods of tuning their electronic properties by manipulating the surface. Finally, we highlight the properties and advantages of single-, few-, and many-layer 2D materials in field-effect transistors, spin- and valley-tronics, thermoelectrics, and topological insulators, among many other applications.
Keywords: two-dimensional materials; graphene; nanosheets; graphane; van der Waals epitaxy; van der Waals solid
来源出版物:ACS NANO, 2013, 7(4): 2898-2926联系邮箱:Goldberger, JE; goldberger@chemistry.ohio-state.edu
Graphene Nanoribbon and Nanostructured SnO2Composite Anodes for Lithium Ion Batteries
Lin, Jian; Peng, Zhiwei; Xiang, Changsheng; et al
Abstract: A composite made from graphene nanoribbons(GNRs)and tin oxide(SnO2)nanoparticles(NPs)is synthesized and used as the anode material for lithium ion batteries(LIBs). The conductive GNRs, prepared using sodium/potassium unzipping of multiwall carbon nanotubes, can boost the lithium storage performance of SnO2NPs. The composite, as an anode material for LIBs, exhibits reversible capacities of over 1520 and 1130 mAh/g for the first discharge and charge, respectively, which is more than the theoretical capacity of SnO2. The reversible capacity retains similar to 825 mAh/g at a current density of 100 mA/g with a Coulombic efficiency of 98% after 50 cycles. Further, the composite shows good power performance with a reversible capacity of similar to 580 mAh/g at the current density of 2 A/g. The high capacity, good power performance and retention can be attributed to uniformly distributed SnO2NPs along the high-aspect-ratio GNRs. The GNRs act as conductive additives that buffer the volume changes of SnO2during cycling. This work provides a starting point for exploring the composites made from GNRs and other transition metal oxides for lithium storage applications.
Keywords: graphene nanoribbons; GNRs; SnO2; lithium ion batteries; capacity
来源出版物:ACS NANO, 2013, 7(7): 6001-6006
(责任编辑卫夏雯,王帅帅)
Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films
Novoselov, KS; Geim, AK; Morozov, SV; et al
We describe monocrystalline graphitic films, which are a few atoms thick but are nonetheless stable under ambient conditions,metallic, and of remarkably high quality. The films are found to be a two-dimensional semimetal with a tiny overlap between valence and conductance bands, and they exhibit a strong ambipolar electric field effect such that electrons and holes in concentrations up to 1013per square centimeter and with room-temperature mobilities of similar to10000 square centimeters per volt-second can be induced by applying gate voltage.
graphite; nanotubes; graphene; devices
*摘编自《科技导报》2015年33卷5期26~33页
