黄腐酚—环糊精包合物的研制
2015-10-21吴婕刘玉梅
吴婕 刘玉梅


摘要 [目的]为改善黄腐酚水溶性。[方法]采用研磨法,比较黄腐酚与7种环糊精的包合效果。在此基础上,通过单元素试验考察主客体分子比、研磨时间、温度和纯度对黄腐酚HPβCD包合物包合效果的影响,以随机质心优化设计试验优化黄腐酚HPβCD包合物的制备工艺。[结果]黄腐酚与羟丙基β环糊精(HPβCD)的包合效果最好,即在主客分子比50∶1,包合温度42 ℃,研磨时间37 min的条件下,黄腐酚HPβCD包合物的包合率達99%以上。[结论] 黄腐酚HPβCD包合物改善黄腐酚的水溶性,拓宽黄腐酚的应用范围。
关键词 黄腐酚;环糊精;包合工艺
中图分类号 S-03 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2015)20-023-04
Abstract [Objective] The purpose was to improve the watersolubility of xanthohumol. [Method]The adduction effects of xanthohumol were compared using seven kinds of cyclodextrins. On the basis of above results, the influences of the hostguest molecular ratio, triturate time, adduction temperature and purity on the adduction effect of xanthohumolHPβCD were evaluated by single factor experiment in grinding methods. And the inclusion process was further optimized by the methods of random centroid optimization. [Result]There was a best adduction effect when maxed xanthohumol with HPβCD, and the inclusion rate of xanthohumolHPβCD clathrate was up to 99% when the hostguest molecular ratio was 50∶1, the adduction temprature was 42 ℃, and the triturate time was 37min. [Conclusion] XanthohumolHPβCD improved the watersolubility of xanthohumol and widened its application.
Key words Xanthohumol; Cyclodextrin; Inclusion process
黄腐酚是来源于啤酒花的一种含异戊二烯基的查耳酮[1-2],因其具有抑制肿瘤[3-4]、预防动脉硬化[5]、抗氧化[6]、抗炎抗病毒[7]等多种生理活性,近年来受到研究人员的广泛关注。由于啤酒花苦味极强,除应用于啤酒酿造外,在其他食品中很少使用,而它又是黄腐酚的唯一天然来源。因此,饮用啤酒基本上就成为人们摄取黄腐酚的唯一来源。黄腐酚在啤酒花中的含量最高可达1%左右,而且我国西北地区也是全球啤酒花的主要种植区之一,来源极为丰富。作为一种活性很强的天然黄酮类成分,若能将其开发应用于更多的食品领域,则无疑会对增进和改善人体的健康状况起到积极的作用。但是,黄腐酚水溶性较差,在一定程度上会限制其使用。因此,若能提高其水溶性,则更有望将其推广应用于更多的食品及饮料中,也就增加了人们摄取黄腐酚的途径。环糊精(Cyclodextrin,简称CD)是在没有水分子参与的情况下,淀粉经葡萄糖糖基转移酶发酵后得到的由α1,4葡萄糖苷键连接而成的环状低聚糖,其外部边缘是亲水的羟基,内部为一定结构的疏水腔,因此可以结合有机分子、生物小分子等[8-9]。环糊精自发现至今已有上百年的历史,由于其特殊的结构和性质,近年来被广泛应用于各个领域如食品、制药、化妆品、化学分析、纳米涂料等,以改善一些功能性化合物的性质。
为了增加黄腐酚的水溶性,笔者选择几种常见的环糊精,以黄腐酚与环糊精的包合率为指标,制备黄腐酚-环糊精的包合物,筛选出最适合的的环糊精类型。在此基础上,利用随机质心映射试验优化黄腐酚-环糊精包合物的制备工艺。黄腐酚与环糊精包合物可以有效地提高黄腐酚的水溶性,扩大黄腐酚的应用领域,为黄腐酚的研制开发提供一定的理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 黄腐酚包合物的制备
1.1.1 制备方法。
采用研磨法完成。称取环糊精适量于研钵中,加入极少量的40 ℃热水溶解,再按照设定的环糊精与黄腐酚的比例加入相应质量的黄腐酚,室温研磨一定时间后,在烘箱内低温干燥至恒重。取出,研成粉末,即得黄腐酚包合物。
1.1.2 不同环糊精包合效果的比较。
以主(环糊精)/客(黄腐酚)质量比为100∶1的比例,将黄腐酚分别与αCD、βCD、γ CD、2甲基βCD、2,6二甲基βCD、2,3,6三甲基βCD、羟丙基βCD(以下简称为HPβCD)混合,室温下按“1.1.1”项所述方法处理。以包合物的收率和包合率为考核指标,选择环糊精品种。
1.1.3 主客分子对包合效果的影响。
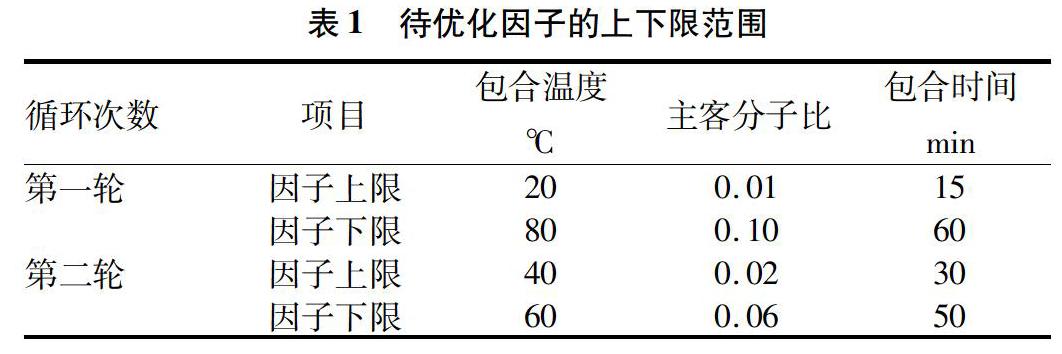
选择HPβCD与黄腐酚质量比20∶1、30∶1、40∶1、50∶1、100∶1、200∶1,混合,室温下按“1.1.1”项所述方法处理。以包合物的收率和包合率为考核指标,考察主客比的影响。
1.1.4 包合时间对包合效果的影响。
3 结论
通过比较7种环糊精及其衍生物对黄腐酚的包合效果,确定HPβCD为最适合的环糊精类型。在单因素试验的基础上,采用随机质心优化试验确定制备黄腐酚HPβCD的最佳包合工艺。在此条件下,黄腐酚的包合率可达99%以上。经HPβCD包合后,环糊精在水溶液中的溶解度明显提高。这将拓宽黄腐酚这一具有多种生物活性的天然黄酮类化合物的应用范围,也为啤酒花的综合利用提供一条新的途径。
参考文献
[1]STEVENS J F,PAGE J E.Xanthohumol and related prenylflavonoids from hops and beer:to your good health![J].Phytochemistry,2004,65(10):1317-1330.
[2] KARABIN M,HUDCOVA T,JELINEK L,et al.The importance of hop prenylflavonoids for human health[J].Chemicke Listy,2012,106(12):1095-1103.
[3] TAN K W,COONEY J,JENSEN D,et al.Hopderived prenylflavonoids are substrates and inhibitors of the efflux transporter breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2)[J].Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2014,58(11):2099-2110.
[4] VEN R,BENELLI R,MINGHELLI S,et al.Xanthohumol impairs human prostate cancer cell growth and invasion and diminishes the incidence and progression of advanced tumors in TRAMP mice[J].Molecular Medicine,2012,18(1):1292-1302.
[5] HIRATA H,TAKAZUMI K,SEGAWA S,et al.Xanthohumol,a prenylated chalcone from Humulus lupulus L.,inhibits cholesteryl ester transfer protein[J].Food Chemistry,2012,134(3):1432-1437.
[6] WANG X,YANG L,YANG X,et al.In vitro and in vivo antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of polyphenols extracted from hops (Humulus lupulus L.)[J].Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture,2014,94(8):1693-1700.
[7] HUDCOV T,BRYNDOV J,FIALOV K,et al.Antiproliferative effects of prenylflavonoids from hops on human colon cancer cell lines[J].JournalInstitute of Brewing,2014,120(3):225-230.
[8] 仲貴.环糊精包合物技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008.
[9] 周春燕.β环糊精与几种客体的分子识别及药物包结研究[D].天津:天津大学,2010.
[10] NAKAI S.Comparison of optimization techniques for application to food product and process development[J].Journal of Food Science,1982,47(1):144-176.
