传感网中不规则复杂3D平面定位策略研究
2015-09-06李泽军等
李泽军等

摘要:针对具有障碍物的复杂3D平面定位误差大以及能耗高的问题,如何进行未知节点的定位,提出了一种具有障碍物的不规则复杂3D平面定位策略,该策略将复杂三维平面划分为水平逻辑层并标记节点的所属层,然后在具有障碍物的水平层进行子区域的划分及合并,最后利用大气压传感器测距进行计算未知节点的坐标从而得到3D复杂平面的定位.通过与最新SV定位机制及COLA定位机制在定位误差及能耗进行综合仿真实验对比,本文的定位策略3DCCD平均定位误差比SV少了5%,比COLA的平均定位误差少8%以上,定位精度上比SV和COLA提高了6.5%以上,及在能耗上比SV和COLA减少了2.7%左右.因此该定位策略(3DCCD)在解决复杂不规则图形的不确定节点具有较大的优越性.
关键词:定位误差;逻辑层;子区域;定位机制
中图分类号:TP39 文献标识码:A
The Study of Positioning Strategy of Irregular 3D Plane
in Sensor Networks
LI Zejun1,2, CHEN Min1,2
(1.College of Information Science and Engineering, Hunan Univ,Changsha, Hunan 410082, China;
2.School of Computer and Information Science,Hunan Institute of Technology,Hengyang , Hunan412002,China)
Abstract:Considering the large positioning error and high energy consumption concerning irregular and complex 3D plane with obstacles, this paper put forward a new strategy to locate the unknown nodes. This policy divides the complex threedimensional plane into different logic layers and labels each layer node it belongs to. Then, subregions are divided and merged in horizontal layers. Finally, the positioning of 3D complex plane is possible by calculating the location coordinate of unknown nodes after atmospheric pressure sensor ranging. Compared with SV and COLA, the 3DCCD positioning strategy in the average positioning error is 5% less than SV and 8% less than COLA. Its positioning precision increases more than 6.5%, and the energy consumption reduces 2.7% than SV and COLA. The 3DCCD has great advantages in terms of positioning error, accuracy and energy.
Key words:positioning error;logic layer;subdomain ;positioning mechanism
复杂环境下的定位机制大多数都是基于2D网络拓扑环境,导致节点路径估算产生较大的误差以及误差难以控制、传感器节点能耗大等诸多因素.如:ACDL经典方法采用2D定位机制解决复杂网络定位问题,该方法设定一临界点,传感器节点利用邻居节点的通信来判定凹凸表面,并将复杂表面划分为几个子区域,节点通过MDS建立节点的相对位置.最后利用相对位置建立全局2D平面图.这样方法过度临界值的选择,当复杂不平表面无临界值时,该策略将导致失败,另外该定位方法对边界噪音比较敏感.目前,学者们尝试从2D平面扩展到3D平面,其主要采用的定位方法有两种,一是通过将3D复杂平面映射到2D平面来定位其坐标[1,2].二是采用特殊装置来测量凹凸平面的高度值和抛锚节点的距离[3].上述方法对于简单的3D表面定位具有较高的精确度,但对于复杂表面以及具有较大凸高时,其定位误差明显增大和定位不明确.而SV(SingleValue)根据不同节点映射到不同2D平面上且平面的点具有唯一性.然后根据二维平面来定位三维平面.一定程度上解决了较简单的3D平面节点重叠问题[4].但SV的代价较高,对于不规则三维平面也将导致节点重叠现象.COLA定位机制[5]采用移动锚节点来定位三维平面,该方法的精确度较高,但对于复杂3D的平面,由于锚节点的不断移动产生大量的误差值,难以适用大规模3D平面定位.
3.3合并子区域及构建层区域
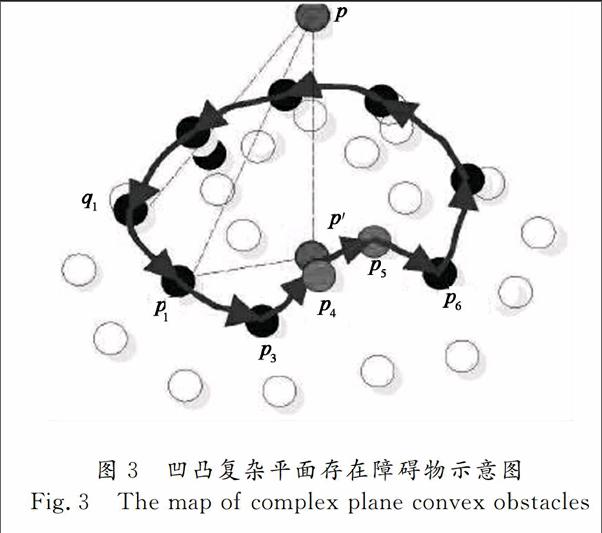
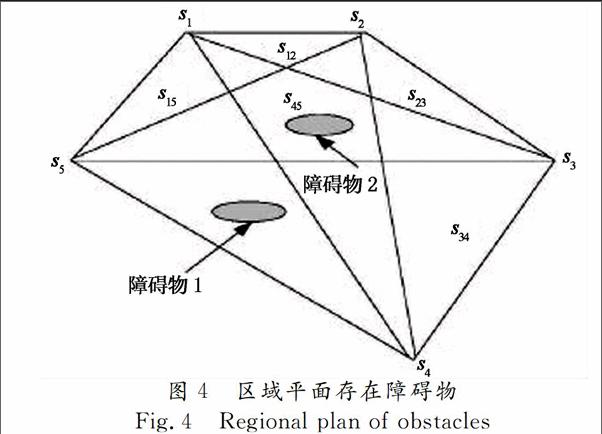
在进行子区域的建立时采用广播的方式进行信息传递,导致在层区域内形成若干个子区域并且子区域可能产生重叠现象.若节点p接收多个构建子区域信息时,以第一时间收到的信息作为标记加入到该子区域中,其余消息将被丢弃.否则若子区域标记不相同则合并两个子区域直到合并消息不存在.
复杂凹凸平面的分解与子区域的合并算法描述如下:
4复杂平面定位与计算
在复杂3D平面定位计算中主要考虑模型构建差生的误差以及定位方法和过程.传感器节点在进行通信时其物理层的传播模式可以任意,其公式为[7,8]:
图11表示3DCCD算法的开销在不同测量误差时都要比SV及COLA算法的开销要小,这是由于3DCCD采用的迭代次数少的缘故.
6结束语
本文研究复杂3D平面的定位机制,该策略首先将复杂三维平面进行逻辑水平分层,然后在水平层进行子区域的划分及合并处理,最后用大气压传感器测距进行计算未知节点的坐标从而得到3D复杂平面的定位.该思路为不规则复杂三维平面提供了新的思路.该策略尤其适用于不确定节点的定位.
参考文献
ZHAO Y,WU H,JIN M,et al.Localization in 3D surface sensor networks: Challenges and solutions[C]//The 31st Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (IEEE INFOCOM 2012).Orlando, Florida,USA,2012:55-63.
〖LL〗[2]LIU Q,REN P,ZHOU Z. Threedimensional accurate positioning algorithm based on wireless sensor networks[J].Journal of Computers, 2011, 6(12): 2582-2589.
[3]LIU C,JIANG H,ZENG L D.Unitary matrix pencil algorithm for rangebased 3d localization of wireless sensor network nodes[J]. Journal of Networks, 2012, 7(9):1384-1390.
[4]赵德鑫,李婷,黄芝平,等.无人潜航器舷侧阵声呐匹配场被动定位方法研究[J].湖南大学学报:自然科学版,2013,40(8):76-82.
ZHAO Dexin,LI Ting,HUANG Zhiping,et al.Matchedfield source localization using the flank array of unmanned under water vehicle[J].Journal of Hunan University:Natural Sciences, 2013,40(8):76-82. (In Chinese)
[5]STOLERU R,HE T,MATHIHARAN S S,et al.Asymmetric eventdriven node localization in wireless sensor networks[J]. Parallel and Distributed Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 2012,23(4): 634-642.
[6]杨高波,吴潇,张兆扬,等.基于过渡像素的视频图像文本检测与定位[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版,2011,38(6):69-74.
YANG Gaobo,WU Xiao,ZHANG Zhaoyang,et al.A transition pixels based text detection and localization for video images[J]. Journal of Hunan University:Natural Sciences, 2011,38(6):69-74.(In Chinese)
[7]CUI H,WANG Y.Fourmobilebeacon assisted localization in threedimensional wireless sensor networks[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2012, 38(3): 652-661.
[8]WANG R J,QIN Z G.A weighted 3D localization algorithm based on partial hopsize in wireless sensor network[J]. International Journal of Advancementsin Computing Technology,2012, 4(9): 504-513.
[9]WANG Y,LIU Y,GUO Z.Threedimensional ocean sensor networks: A survey[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2012, 11(4): 436-450.
[10]王小平,罗军,沈昌祥.无线传感器网络定位理论和算法[J].计算机研究与发展, 2011,48(3):353-363.
WANG Xiaoping,LUO Jun,SHEN Changxiang. Theory and algorith mson localization in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2011,48(3):353-363. (In Chinese)
