睾丸肿瘤中β-catenintenin的表达及其意义*
2015-08-04邹沙沙宋平平陈婷婷朱王柱清胡洪亮上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院泌尿外科上海200001
邹沙沙 平 萍 宋平平 陈婷婷朱 勇 王柱清 刘 勇 李 铮 胡洪亮上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院泌尿外科(上海 200001)
睾丸肿瘤中β-catenintenin的表达及其意义*
邹沙沙 平 萍 宋平平 陈婷婷
朱 勇 王柱清 刘 勇 李 铮 胡洪亮
上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院泌尿外科(上海 200001)
摘要目的 初步研究β-catenin蛋白在不同类型睾丸肿瘤中的表达特性,并探讨β-catenin分子的表达与睾丸肿瘤的关系,为临床诊断或治疗睾丸肿瘤提供一定依据。方法 随机收集我院于2012年1月至2012年12月期间确诊的21例睾丸肿瘤组织和1例梗阻性无精子症(OA)患者的睾丸活检组织(作为正常对照,其睾丸生精功能正常);同时,选取5只9周龄的ICR小鼠作为实验补充。采用了免疫组化、Western blots 和RT-qPCR等方法来检测β-catenin的表达情况。结果 在梗阻性患者中,β-catenin在精原细胞的胞膜和胞浆中呈现低表达;在小鼠中,β-catenin也仅表达在精原细胞的胞浆和胞膜上。在睾丸肿瘤组织中,睾丸孤立性纤维肿瘤中可检测到β-catenin的mRNA和蛋白的高表达,分别为OA患者的9.4倍和17倍,且其β-catenin主要异位表达在细胞核中,可检测到磷酸化的β-catenin的表达。然而,β-catenin在睾丸精原细胞肿瘤和间质细胞肿瘤中不表达或低表达。结论 本研究初步表明β-catenin与正常的睾丸生精过程及病理的睾丸孤立性纤维肿瘤发生发展相关,而与睾丸精原细胞肿瘤和间质细胞肿瘤之间无明显相关性。但仍需扩大样本数量进行研究,或采用动物实验深入研究。
关键词睾丸肿瘤; β连环素
Key woorrddss Testicular neoplasms; beta-catenin
睾丸肿瘤虽是一种临床少见的生殖细胞系肿瘤,但近年来其全球发病率呈逐渐增加的趋势,是5~45岁青年男性常见的肿瘤之一[1, 2],睾丸肿瘤约占男性癌症患者的1%~2%[3]。根据2004年WHO标准可将睾丸肿瘤分为3类,包括生殖细胞瘤、性索/性腺间质肿瘤及其他非特异性间质肿瘤[4, 5]。其发病机制尚不清楚,环境及遗传因素均可致睾丸肿瘤的形成[6-8]。β-catenin已被证实是Wnt信号通路中的核心蛋白分子,且大量研究发现其不仅在胚胎期器官发育中具有重要的作用;还与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[9]。基因突变或外界因素均可导致β-catenin的异常活化,促使肿瘤的发生[10, 11]。本实验旨在检测不同类型睾丸肿瘤中β-catenin的表达差异,探讨β-catenin的异常表达与睾丸肿瘤之间的关系。
材料与方法
一、临床资料
收集我院于2012年1月至2012年12月间的睾丸肿瘤及其癌旁组织标本21例,诊断根据其组织病理学特征。其中,生殖细胞瘤15例(病理类型均为精原细胞肿瘤),性索/性腺间质肿瘤6例(间质细胞肿瘤4例,睾丸纤维性肿瘤2例)。同时,获取1例梗阻性无精子症患者(obstructive azoospermia,OA,输精管梗阻,病理诊断其睾丸生精功能正常)的睾丸活检组织作为正常对照。9周龄的ICR小鼠(来源于上海交通大学Bio-X中心实验室)饲养于SPF环境中,给予其12h(8:00~20:00)光照。
二、免疫组化与免疫荧光检测β-catenintenin表达水平
取出石蜡包埋的组织切片,脱蜡后用4%多聚甲醛(paraformaldehyde,PFA)固定15min,PBT冲洗min×3次,3%H2O2浸泡30min,PBT冲洗,羊血封闭30min,一抗(兔抗人β-catenin,ABI公司)4℃过夜孵育,PBT冲洗,二抗(羊抗兔抗体IgG,Vector公司)37℃孵育1h,PBT冲洗,DAB显色5~15min,BT冲洗,苏木素复染30s,乙醇脱水及二甲苯透明处理后用中性树胶封片。对免疫组化结果采用mage J及SPSS 17.0软件进行图像处理及统计分析。
免疫荧光操作过程与免疫组化过程相似,其中,荧光二抗避光孵育,细胞核染色用DAPI显色。
三、RT-qPCR-qPCR检测β-catenintenin分子mRNA表达水平
用Trizol法提取总RNA,然后进行反转录RTPCR反应:使用ABI公司的Taqman®universal PCR master mix试剂和7500仪器进行检测,荧光染料是SYBR GREENⅠ荧光染料,内标基因采用β-actin。RT-qPCR的产物可采用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行分析。所有引物采用primer 5.0分析软件设计(见表1),由上海生工生物公司合成。
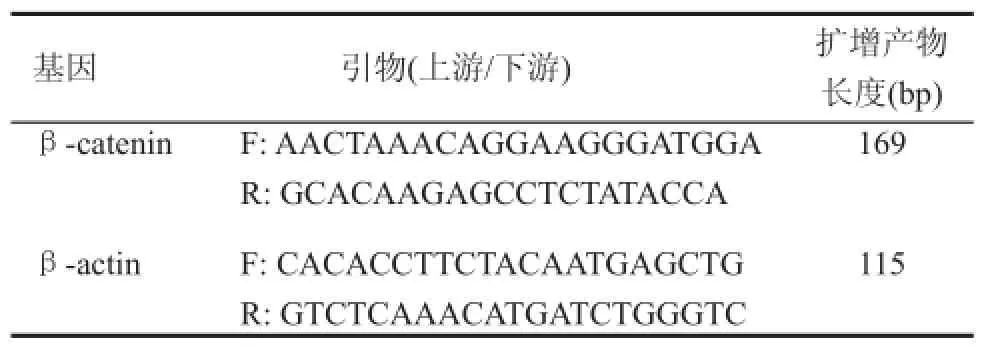
表1 PCR引物序列
四、Western blots lots检测β-catenintenin蛋白表达水平
首先,分别使用promega公司的蛋白裂解液离心收集蛋白。进行western blots检测β-catenin蛋白的表达:先配置好10%分离胶和5%浓缩胶,取等量提取的蛋白液加入6×Loading buffer,98℃水浴5min,上样后电泳(恒压,90V,30min;120V,60min)。电泳结束后取出胶,切掉浓缩胶部分,按照吸水垫、3层滤纸、凝胶、PVDF膜、3层滤纸、吸水垫的顺序夹好转膜夹,4℃进行电泳,1.5h(恒流,350mA)。转膜后,配置封闭液,室温孵育1h。洗膜液清洗,加入Flag一抗稀释液,置于摇床上,室温反应2h,洗膜液TBST洗3次,每次5min。加入羊抗兔IgG二抗,摇床上室温下反应2h,洗膜液TBST洗3次,每次5min。配置发光底物,溶液 A和B等体积混合。在暗室中进行下列操作:将发光底物均匀滴在保鲜膜上,PVDF膜正面朝下放于发光底物上,3 min后包好,放于压片盒中,上面放一张胶片,反应10 min后显影、定影。蛋白显影图片结果采用Image J及SPSS 17.0软件进行图像处理及统计分析。
结 果
一、β-catenintenin蛋白在梗阻性无精子症患者及睾丸肿瘤患者中的表达差异
在梗阻性无精子症患者睾丸生精小管中,精原细胞的细胞膜和细胞质见有少量棕黄色颗粒(见图1A1A,图1B1B);同时,9周龄小鼠的睾丸生精小管免疫荧光结果显示,β-catenin蛋白特异性强表达于小鼠精原细胞的细胞膜和细胞质上(见图1C1C-图1E1E)。这也就表明,β-catenin蛋白在正常睾丸发育过程中可能特异性表达于精原细胞上,并且β-catenin仅表达在细胞膜和细胞质上,细胞核中未表达,说明Wnt/ β-catenin通路在成年睾丸精子发生过程中尚未被激活,而β-catenin是通过其他调控方式参与精原细胞的增殖分化。
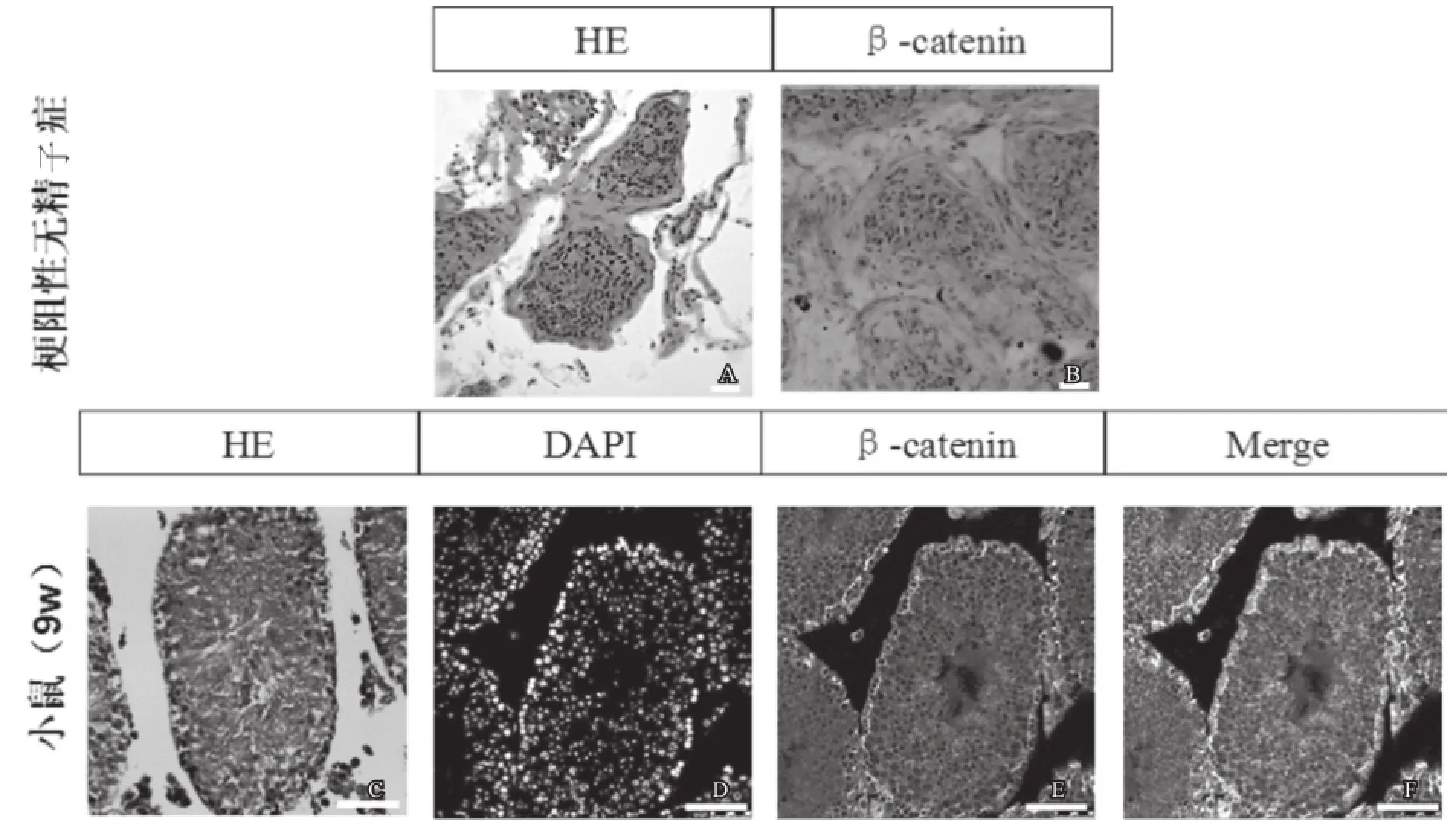
图1 β-cateninn 在梗阻性无精子症患者(免疫组化)及正常小鼠(免疫荧光)睾丸中表达于精原细胞胞膜和胞浆中
对睾丸肿瘤组织及其癌旁组织进行β-catenin免疫组化染色检测发现,β-catenin在所检测的精原细胞肿瘤与间质细胞肿瘤中没有出现高表达,与梗阻性无精子症相比较发现无明显差异。β-catenin蛋白在睾丸纤维性肿瘤中出现异常高表达的情况,且主要表达在肿瘤细胞的细胞核中;同时,在其癌旁组织中也呈现出高表达状态(见图2A2A,图2L2L)。采用图像处理软件分析、定量免疫组化图片中的阳性表达部位,睾丸纤维性肿瘤组织及其癌旁组织中β-catenin阳性部位的面积分别是梗阻性无精症的9.4 和7.2倍(见图3)。
二、睾丸肿瘤中β-catenintenin分子mRNAmRNA与蛋白表达差异的定量分析
采用Western blot与RT-qPCR方法进行半定量分析β-catenin在不同类型的睾丸肿瘤中的表达情况,发现β-catenin基因mRNA高表达于睾丸纤维性肿瘤及其癌旁组织,表达量分别为梗阻性无精子症组织的17倍和5倍(见图4A4A),结果与上述免疫组化相一致。Western blot结果也显示β-catenin高表达于睾丸纤维性肿瘤及其癌旁组织,并且可检测到β-catenin磷酸化蛋白的表达(见图4B4B)。这表明,在睾丸纤维性肿瘤中Wnt通路被激活,即Wnt/β-catenin通路可能参与了睾丸纤维性肿瘤的发生及发展过程。
讨 论
在此次实验研究中,采用了免疫组织化学方法(图像分析技术)和Western blot、RT-PCR等方法来检测分析β-catenin在不同类型睾丸肿瘤中的表达情况。上述结果表明, 在所收集的睾丸生殖细胞肿瘤中,在精原细胞肿瘤和间质细胞肿瘤中β-catenin的表达量均较低。这表明,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可能不参与睾丸生殖细胞肿瘤的形成;但在睾丸纤维性肿瘤中检测到β-catenin的该信号通路的异常高表达,而Wnt/β-catenin信号转导通路的激活水平是由细胞中β-catenin蛋白的表达水平所决定的,因此,我们推测Wnt/β-catenin信号通路参与了睾丸纤维性肿瘤的发生、发展。
在睾丸发育中,李毅等[12]发现可通过上调 c-myc基因表的达来激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,从而促进成人睾丸支持细胞的增殖、分裂。虽然,目前已有一些学者已指出,β-catenin分子的异常可能会导致生殖系统的肿瘤形成,卵巢癌的发生就被证实与Wnt/ β-catenin信号通路的失调有关[13],但是,β-catenin与睾丸肿瘤的相关研究还很少,且国内在这方面的研究几乎是空白。Chang等[14]发现在小鼠睾丸发育中,β-catenin的过度活化可导致支持细胞肿瘤的形成;此外,最近的一篇研究也表明在支持细胞肿瘤患者中可检测到β-catenin基因的突变及其在支持细胞的细胞核中的异位表达(即β-catenin的磷酸化)[15]。
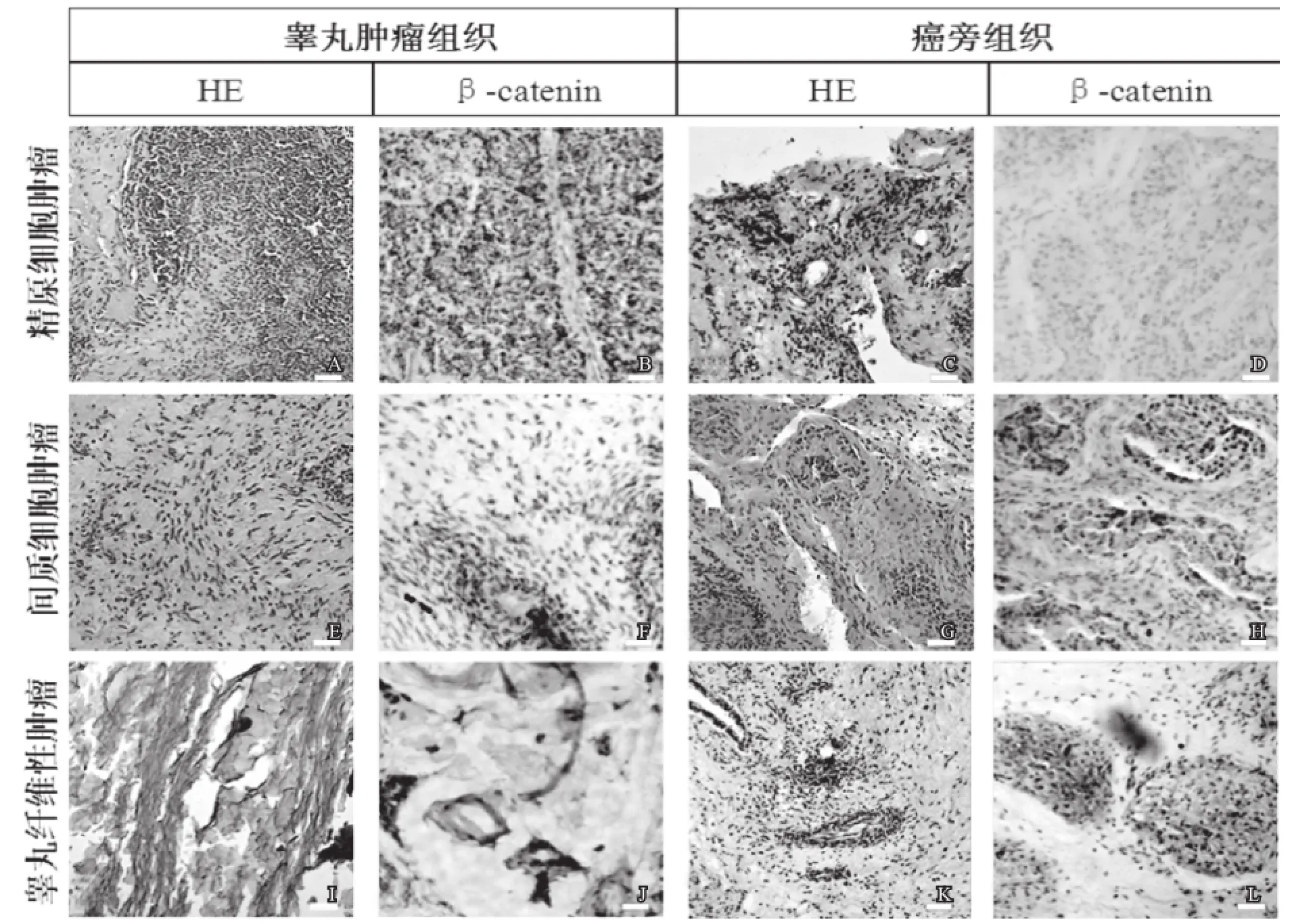
图2 β-cateninn 在睾丸肿瘤组织及其癌旁组织中的表达

图3 图像处理软件定量分析免疫组化β-catenintenin阳性细胞面积
在本研究中,仅在睾丸纤维性肿瘤检测到了β-catenin的异常强表达,而其在睾丸生殖细胞肿瘤上的表达很弱。与本研究相似的是,已有一些国内外学者报道了β-catenin在纤维性肿瘤中的表达情况,Rakheja等[16]报道在孤立性纤维性肿瘤中检测到β-catenin的阳性率高达100%;在肠系膜纤维瘤、韧带样型纤维瘤病等都可检测到β-catenin的异常表达。由于Wnt信号通路参与调控着细胞的生长、运动和分化,已被确认是与肿瘤相关的一个关键性信号通路。
β-catenin在人类肿瘤发生发展中的作用机制的相关研究备受关注[17];有研究证实,通过抑制β-catenin的表达可控制肿瘤细胞的增殖,促进其凋亡[18]。随之,药物研发者们以该分子作为抗肿瘤治疗靶点,进一步研究有效的抗肿瘤药物治疗方案,这些候选抗肿瘤治疗方案的主要机理是从不同水平阻断β-catenin信号转导通路[19, 20]。因而,深刻理解Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控机制,对于以β-catenin信号转导通路为靶点的抗肿瘤药物的研究具有重要意义。
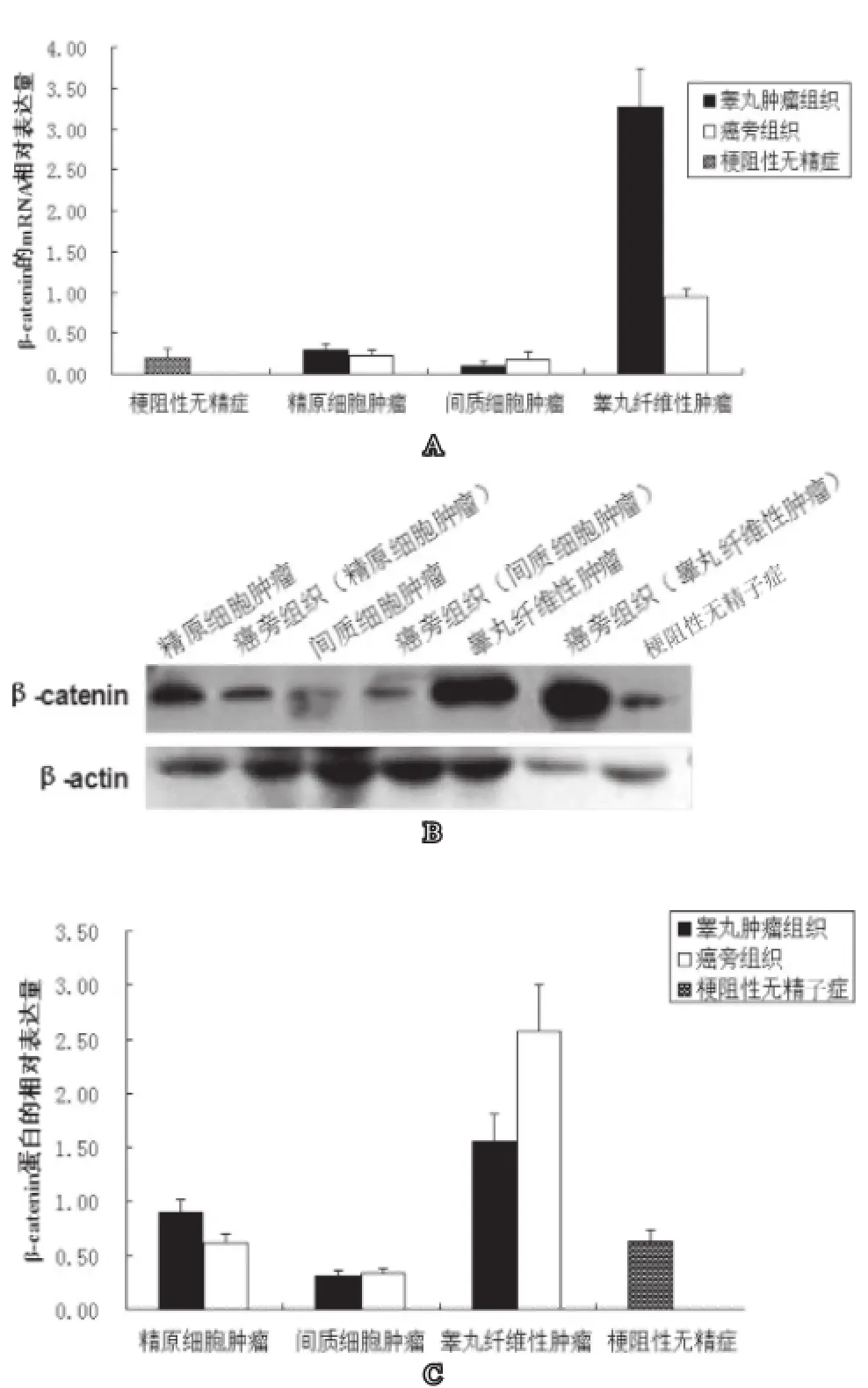
图4 RT-qPCRR 和Western blloottss检测睾丸肿瘤组织与梗阻性无精子症患者睾丸组织中Shh分子的表达
参 考 文 献
1 张宏艳, 刘端祺. 睾丸肿瘤流行病学研究进展. 解放军医学杂志 2007; 32(3): 274-275
2 Shanmugalingam T, Soultati A, Chowdhury S, et al. Global incidence and outcome of testicular cancer. Clin Epidemiol 2013; 5: 417-427
3 罗文彬, 姜昊文, 吴忠. 睾丸癌的研究进展. 国际泌尿系统杂志 2007; 27(6): 820-822
4 Huyghe E, Matsuda T, Thonneau P. Increasing incidence of testicular cancer worldwide: a review. J Urol 2003; 170(1): 5-11
5 Bosl GJ, Motzer RJ. Testicular Germ-Cell Cancer. N Engl J Med 1997; 337 (4):242-254
6 Heidenreich A, Knüchel-Clarke R, Pfi ster D. Importance of pathology for therapy planning of testicular germ cell tumors. Pathologe 2014; 35(3): 266-273
7 Goddard NC, McIntyre A, Summersgill B, et al. KIT and RAS signaling pathways in testicular germ cell tumours: new data and a review of the literature. Int J Androl 2007; 30(4): 337-348
8 Bartek J, Bartkova J, Lukas J. DNA damage signaling guards against activated oncogenes and tumour progression. Oncogene 2007; 26(56): 7773-7779
9 Fodde R, Brabletz T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19(2): 150-158
10 Espada J, Calvo MB, Díaz-Prado S, et al. Wnt signalling and cancer stem cells. Clin Transl Oncol 2009; 11(7): 411-427
11 Rosenbluh J, Wang X, Hahn WC.Genomic insights into WNT/β-catenin signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2014; 35(2): 103-109
12 Honecker F, Kersemaekers AM, Molier M, et al. Involvement of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in germ cell tumours and in normal male fetal germ cell development. J Pathol 2004; 204(2): 167-174
13 Rosanò L, Cianfrocca R, Masi S, et al. Beta-arrestin links endothelin A receptor to beta-catenin signaling to induce ovarian cancer cell invasion andmetastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106(8): 2806-2811
14 Chang H, Guillou F, Taketo MM, et al. Overactive betacatenin signaling causes testicular sertoli cell tumor development in the mouse. Biol Reprod 2009; 81(5): 842-849
15 Perrone F, Bertolotti A, Montemurro G, et al. Frequent mutation and nuclear localization of β-Catenin in sertoli cell tumors of the testis. Am J Surg Pathol 2014; 38(1): 66-71
16 Rakheja D, Molberg KH, Roberts CA, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of beta-catenin in solitary fibrous tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005; 129(6): 776-779
17 MacDonald BT1, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-cateninsignaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009; 17(1): 9-26
18 Galuppo R, Maynard E, Shah M, et al. Synergistic inhibition of HCC and liver cancer stem cell proliferation by targeting RAS/RAF/MAPK and WNT/β-catenin pathways. Anticancer Res 2014; 34(4): 1709-1713
19 Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, et al. WNT and betacatenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5(9): 691-701
20 Maruyama K, Ochiai A, Akimoto S, et al. Cytoplasmic beta-catenin accumulation as predictor of hematogenesis metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Oncology 2000; 59(4): 302-309
(2014-08-08收稿)
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0848.2015.01.002
中图分类号R 737.21
*基金项目资助: 国家自然科学基金面上项目(30973069);上海交通大学医学院属仁济医院科研种子基金培养计划(RJZZ14-017)
Expression analysis of β-catenin in testicular cancer*
Zou Shasha, Ping Ping, Song Pingping, Chen Tingting,
Zhu Yong, Wang Zhuqing, Liu Yong, Li Zheng, Hu Hongliang Department of Urology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai 200001, China
AbstractObjective To study and analyzes the expression pattern and association of β-catenin in testicular cancer, and explore the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the mechanism of testicular cancer occurrence, thus provide evidence for clinical diagnosis and therapy of testicular cancer. Metthhooddss We randomly collected 21 cases of testicular cancer biopsy tissue and the testicular biopsy tissue of one obstructive azoospermia patient (OA, as healthy control, due to the completely normal spermatogenic function) in Hospital, from 2012.01 to 2012.12. Five 9w ICR mices were also used in the additional experiments. Expression of β-catenin in the process of spermatogenesis and testicular cancer was detected and quantifi ed by using immunohistochemical, Western blot and RT-qPCR. Ressuullttss In the obstructive azoospermia patient, β-catenin is weakly expressed in the cell membrane and cytoplasm of spermatogonia. Moreover, in the testis of 9w ICR mices, β-catenin is expressed in the cytoplasm and cell membrane of spermatogonia. However, the results of testicular cancer showed obviously high protein and mRNA expression levels of β-catenin in testicular solitary fi brous tissue, 9.4 folds and 17 folds, respectively, but not in other testicular tumours. β-catenin is ectopicly expressed in the cellular nucleus of testicular solitary fi brous tissue, and we also detected the phosphorylation β-catenin by western blot. Concluussiioonn The results suggested β-catenin may be associated with the process of spermatogenesis and testicular tumor, but not other testicular tumours. However, Considering the limit of sample size, future validating studies in more samples and mechanism study in animal experiments are strongly suggested.
