蕨麻多糖对小鼠脾淋巴细胞上清液IFN-γ和可溶性LAG-3分子水平的影响
2015-06-24何多谊白德成张倩倩
魏 慧, 何多谊, 白德成*, 程 菊, 沈 蓉, 张倩倩
1.兰州大学基础医学院, 兰州 730000;
2.甘肃省武威职业学院, 甘肃 武威 733000
蕨麻多糖对小鼠脾淋巴细胞上清液IFN-γ和可溶性LAG-3分子水平的影响
魏 慧1, 何多谊2, 白德成1*, 程 菊1, 沈 蓉1, 张倩倩1
1.兰州大学基础医学院, 兰州 730000;
2.甘肃省武威职业学院, 甘肃 武威 733000
为了观察蕨麻多糖对急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠脾淋巴细胞上清液中IFN-γ和可溶性LAG-3(soluble LAG-3,sLAG-3)分子水平的影响。将试验小鼠一次性腹腔注射氯化镉溶液(1 mg/kg)染毒,观察24h即造模成功后,腹腔注射低、中、高剂量蕨麻多糖治疗一周,于实验终末测各组小鼠脾脏、胸腺指数,ELISA法测IFN-γ、sLAG-3含量;免疫荧光法观察CD3+、CD4+、CD8+T淋巴细胞。结果表明蕨麻多糖低、中、高剂量组中,IFN-γ、sLAG-3的含量较空白对照组和单纯镉染阳性对照组均增高,以高浓度组增高明显(P<0.05);CD3+、CD4+T淋巴细胞较空白对照组和单纯镉染阳性对照组均增多,仍以高浓度组增多明显,CD8+T变化不显著。蕨麻多糖能促进急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠脾淋巴细胞分泌IFN-γ和sLAG-3,CD3+、CD4+T淋巴细胞亦相应增加。
蕨麻多糖;IFN-γ;sLAG-3
镉是一种广泛存在的工业级环境毒物,主要通过职业接触和被污染的空气、水、食物等进入人和动物体内并蓄积,导致机体急慢性中毒和多器官受损[1]。它能产生细胞、体液等的免疫抑制, 抑制T淋巴细胞增殖从而引起其亚群的改变[2],并有强致癌性。
蕨麻多糖(PAP)是藏药蕨麻的活性成分,具有提高机体免疫力、抗疲劳和耐缺氧等作用[3]。LAG-3是广泛存在于动物和人体内的免疫负调节分子, 具有维持内环境稳定和参与免疫调节的功能,其表达与IFN-γ相关[4]。PAP可通过改变IFN-γ等的水平,增强机体的免疫功能[5];因此PAP对机体中的IFN-γ和LAG-3有直接影响,但PAP对镉抑制的影响尚缺乏资料。本实验旨在通过小鼠急性低剂量腹腔注射镉,观察蕨麻多糖对脾淋巴细胞IFN-γ和sLAG-3分子的影响,以期为研究蕨麻多糖干预镉引起的免疫抑制提供实验依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
清洁级昆明系小鼠,雌雄各半,体重20 g左右,由兰州大学医学院实验动物科提供;蕨麻多糖,由本试验室经乙醇提取保存,采用硫酸-苯酚法[5]测得蕨麻多糖含量2%,用蒸馏水分别配成所需浓度的蕨麻多糖溶液,无菌滤器过滤备用;免疫荧光抗体(CD4-Phycoerythrin、CD8-Phycoery-thrin、CD3-FITC)、LAG-3酶联免疫试剂盒、IFN-γ酶联免疫试剂盒购于南京建成生物公司;小鼠淋巴细胞分离液购自深圳达科为公司;氯化镉(CdCl2)、台盼兰染色剂等试剂均为国产分析纯。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 动物分组及给药 清洁级昆明系小鼠,8周龄,60只,雌雄各半,随机分为6组,具体操作:第1组为空白对照组(C1),每只小鼠分别于第1 d、3 d、5 d、7 d腹腔注射0.9%的生理盐水;第2组为PAP阳性对照组(C2),分别于第1 d、3 d、5 d、7 d腹腔注射PAP 50 mg/kg;第3组为镉染毒模型组(C3),每只小鼠实验前一天一次性腹腔注射氯化镉1 mg/kg,24 h后按第1 d、3 d、5 d、7 d腹腔注射同体积的生理盐水;第4、5、6组为PAP低(L)、中(M)、高(H)治疗组,每只小鼠实验前一天一次性腹腔注射氯化镉1 mg/kg,24 h后各组分别按50 mg/kg、100 mg/kg、200 mg/kg剂量于第1 d、3 d、5 d、7 d腹腔注射PAP;治疗后观察48 h,所有供试小鼠断椎处死。
1.2.2 测脾脏指数和胸腺指数、脾淋巴细胞上清液IFN-γ、sLAG-3及CD3+、CD4+、CD8+T淋巴细胞[6,7]各组小鼠扑杀后称重,分别取脾脏、胸腺称重,计算脾脏指数和胸腺指数(mg/g)。无菌取脾脏,小鼠淋巴细胞分离液分离脾淋巴细胞,加5 mL RPMI-1640培养液,用吸管吹打均匀,细胞计数调节细胞密度至2×106~5×106/mL,台盼兰染色检测细胞存活率大于85%,RPMI-1640完全培养基铺板,将细胞悬液加到96孔细胞板中,100 μL/孔,5% CO2、37℃、95% 湿度孵箱中,培养48 h,并随时观察细胞情况。48 h后,用毛细玻璃管将培养物移入无菌离心管中,2 500 r/min离心20 min,仔细收集上清,按照ELISA检测试剂盒说明书操作,进行脾脏淋巴细胞上清液中IFN-γ和sLAG-3分子水平的测定(测定时间不超过24 h)[8]。收集完脾脏淋巴细胞上清液,将细胞用PBS稀释成细胞悬液,细胞浓度达到2×106~5×106/mL,24孔细胞板铺板,1 mL/孔,再分别加入稀释的Anti-Mouse CD3c-FITC、Anti-Mouse CD4-Phycoerythrin、Anti-Mouse CD8-Phycoerythrin荧光素标记抗体,室温避光反应1 h,荧光显微镜拍照观测。
采用三色直接免疫荧光标记法,观察PAP对小鼠脾脏CD3+、CD4+、CD8+T淋巴细胞的影响[7]。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同剂量 PAP 对小鼠胸腺指数及脾脏指数的影响
经方差分析,结果显示:PAP阳性对照组胸腺、脾脏指数高于空白对照组,说明PAP能提高正常小鼠的脾脏指数和胸腺指数;中、高剂量组脾脏指数高于镉染毒模型组(P<0.05),低剂量组差异不显著;低、中、高剂量组胸腺指数与生理盐水组和镉染毒模型组相比均无统计学差异(P>0.05);不同剂量PAP组的脾脏指数均高于生理盐水组和镉染毒模型组(P<0.05),表明PAP能提高急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠的脾脏指数,说明造模成功,但PAP对急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠的胸腺指数无明显恢复和提升作用,具体结果见表1。
注: 同一列内不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
2.2 不同剂量PAP对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞培养上清液中IFN-γ水平和sLAG-3分子水平的影响
经方差分析,结果显示:PAP阳性组IFN-γ、sLAG-3高于空白对照组和镉染毒模型组(P<0.05);低剂量组IFN-γ、sLAG-3与PAP阳性组相比差异不显著(P>0.05);中、高剂量组IFN-γ、sLAG-3高于空白对照组和镉染毒模型组,以高剂量组差异显著(P<0.05)。表明PAP能够促进正常小鼠和急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠脾淋巴细胞分泌IFN-γ和sLAG-3,且与剂量相关,具体结果见表2。
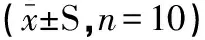
表2 不同剂量PAP对小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞培养上清液中IFN-γ水平和sLAG-3分子水平的影响
注: 同一列内不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
2.3 不同剂量PAP对小鼠脾脏CD3+、CD4+、CD8+ T淋巴细胞的影响
荧光显微镜结果显示(图1,彩图见封三图版):高剂量组中CD3+、CD4+T细胞荧光标记数目较空白对照组和镉染毒模型组有增高趋势;低、中剂量组与空白对照组和镉染毒模型组相比增多不显著,表明PAP能增加正常小鼠和急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠CD3+、CD4+T细胞数目,以高剂量200 mg/kg组明显;CD8+T细胞变化不显著。
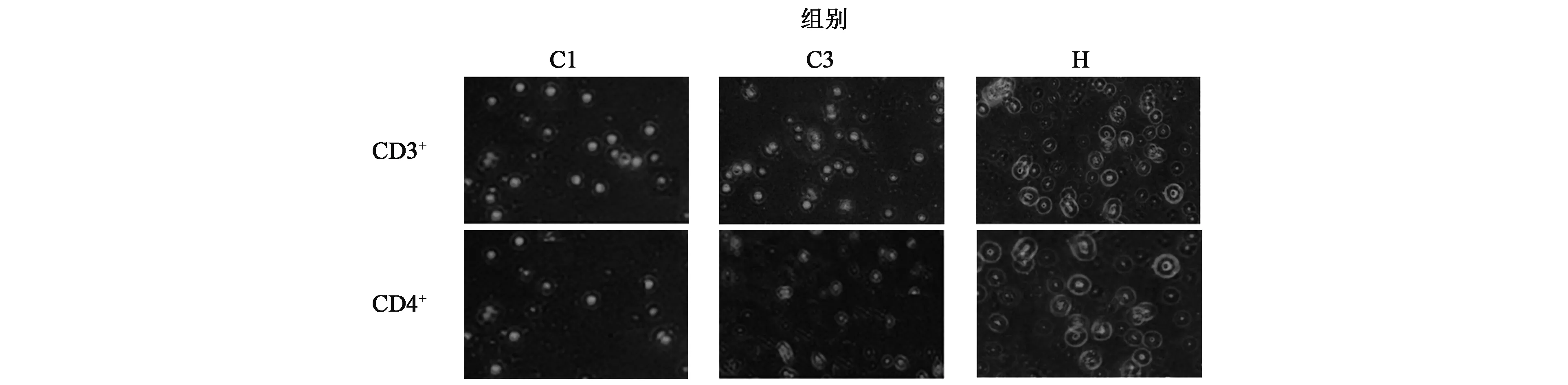
图1 不同剂量PAP对小鼠脾脏CD3+、CD4+ T淋巴细胞影响的荧光显微镜图片Fig.1 Effect of PAP with different content on CD3+、CD4+ T in spleen lymphocytes.(彩图见封三图版)
3 讨论
研究认为重金属镉暴露可引起人类的免疫抑制,目前许多急、慢性镉中毒仍只能采取对症支持治疗[1],为此研究者不断探究镉损伤的保护剂,寻找既能排镉,又能提高机体免疫力的药物,故中药对抗镉抑制的研究变得很有意义。随着PAP的免疫研究不断深入,它对镉抑制的干预机制将引起越来越多的学者的重视。本实验通过对急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠采用PAP治疗后,中、高浓度组的IFN-γ和sLAG-3水平,与镉染毒模型组比较有所上升,表明PAP可以增强急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠的免疫力。
免疫系统中IFN-γ和LAG-3由机体免疫器官活化后的T细胞等产生,当抗原、PHA或ConA刺激后T细胞分泌IFN-γ[9],IFN-γ能诱导单核细胞、树突状细胞等MHC-Ⅱ类抗原的表达,MHC-Ⅱ与LAG-3结合后负调控T细胞功能[10]。LAG-3参与调控记忆性T细胞池和树突状细胞[11],它只表达于活化的淋巴细胞和类浆细胞性树突状细胞(pDC)[9]。在金属蛋白酶的作用下,LAG-3分子的连接肽发生断裂,形成可溶性的部分(包括D1-D3域)和跨膜-胞质部分;LAG-3的可溶性单体最先在炎症性疾病患者体内发现,治疗有效时,其表达水平增高,sLAG-3分子与MHC-Ⅱ分子作用可诱导DC成熟并迁移到次级淋巴器官[5]。另外sLAG-3分子可以明显抑制肿瘤细胞的生长,人LAG-3抑制作用更加显著[12]。
实验表明蕨麻多糖能增强急性低剂量镉染毒小鼠的免疫力,使活化T淋巴细胞产生IFN-γ增多;它能直接作用于脾淋巴细胞,促进其分泌IFN-γ,使sLAG-3的水平发生相应变化;本 研 究 中 得 出 的IFN-γ和sLAG-3均低于以往文献[6]报道中的数据,考虑可能与标本量较少有关,下一步需扩大样本量加以佐证;蕨麻多糖可以干预镉的抑制作用,其具体机制有待进一步研究证实。
[1] 陈建忠,赵锋利,蔡婷峰,等.健脾泻浊方对亚急性镉染毒大鼠肾毒性影响的实验研究[J].中国职业医学,2010,37(4):283.
[2] 谢黎虹,许梓荣. 重金属镉对动物及人类的毒性研究进展[J].浙江农业学报,2003,15(6) :376-380.
[3] 韦 薇,李广策,龚海英,等.蕨麻多糖抗缺氧作用研究[J].武警医学院学报,2010,19(5):345.
[4] Poirier N, Haudebourg T, Brignone C,etal.. Antibody-mediated depletion of lymphocyte-activation gene-3 (LAG-3+)-activated T lymphocytes prevents delayed-type hypersensitivity in non-human primates[J].British. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2011,164: 265-272.
[5] 陈炅然,胡庭俊,程富胜,等.蕨麻多糖的免疫药理实验研究[J].兽药与饲料添加剂, 2005,5(10):1-2.
[6] 江 露,吴昌平,徐 斌,等.胃癌患者血清中可溶性LAG-3分子的水平及意义[J].临床检验杂志,2014, 32 (1):39-40.
[7] 张志远,王海莉,苗明三.扶正中药复方对环磷酰胺所致免疫功能低下小鼠免疫器官和肠黏膜 CD3+、CD4+、CD8+的影响[J]. 中医研究,2008, 21(12):19.
[8] 王少敏,张 洁,马 丽. 30例女性SLE患者淋巴细胞培养上清液中IL-2、 TNF-α、IFN-γ、IL-4水平测定[J].中国妇幼保健,2008, 23 (7) : 982-983.
[9] 金伯泉.细胞与分子免疫学[M].西安:第四军医大学免疫学教研室,1997,203-204.
[10] 龚洪立,陶 磊,周 梁. LAG-3分子在免疫系统的研究进展[J].复旦学报:医学版,2010,37(4):495-497.
[11] Maria B, Andrea L,Szymczak W,etal.. Accelerated autoimmune diabetes in the absence of LAG-3[J].J. Immunol.,2012,187(7):1-2.
[12] 田晓玲,仇 超,徐建青.LAG-3分子与免疫调节[J].中华微生物学与免疫学杂志,2013,3(33):231-235.
·Nature系列期刊导读·
研究发现控制水稻粒形和稻米品质的重要基因
近日,中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所傅向东研究员领导的团队从优质杂交水稻不育系泰丰A中成功分离并克隆了一个控制水稻粒形和提升稻米品质的重要基因GW7。这一基因能通过改变细胞分裂模式,让稻米变得更为细长,有效地减少垩白率和垩白面积,从而提高稻米在外观、口感等方面的品质。该研究还表明将GW7和GS3基因的优异等位变异聚合并应用到我国高产籼稻中,可明显提高稻米品质,同时还可提高产量。该项研究为水稻高产优质分子模块设计育种提供了具有重要应用价值的新基因,也为揭示水稻品质和产量协同遗传改良的分子奥秘提供了新线索。
论文链接: Wang S,etal.. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nature Genetics, 2015, doi: 10.1038/ng.3352. Published online: 06 July, 2015.
Abstract: The deployment of heterosis in the form of hybrid rice varieties has boosted grain yield, but grain quality improvement still remains a challenge. Here we show that a quantitative trait locus for rice grain quality, qGW7, reflects allelic variation of GW7, a gene encoding a TONNEAU1-recruiting motif protein with similarity to C-terminal motifs of the human centrosomal protein CAP350. Upregulation of GW7 expression was correlated with the production of more slender grains, as a result of increased cell division in the longitudinal direction and decreased cell division in the transverse direction. OsSPL16 (GW8), an SBP-domain transcription factor that regulates grain width, bound directly to the GW7 promoter and repressed its expression. The presence of a semidominant GW7TFAallele from tropical japonica rice was associated with higher grain quality without the yield penalty imposed by the Basmati gw8 allele. Manipulation of the OsSPL16-GW7 module thus represents a new strategy to simultaneously improve rice yield and grain quality.
水稻氮利用效率改良研究取得重大突破
植物主要以铵态氮和硝态氮为主要氮源,中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所储成才研究员领导的团队研究表明,籼稻品种利用硝酸盐的能力显著高于粳稻品种,该团队通过图位克隆技术从籼稻中克隆出高氮利用效率基因NRT1.1B,NRT1.1B编码一个硝酸盐转运蛋白,在籼、粳稻间只有一个氨基酸的差别,且籼稻与粳稻呈现出显著的分化,各种证据表明,籼稻型具有更高的硝酸盐吸收及转运活性。尤为重要的是,籼稻中的硝酸盐同化过程的关键基因也被显著上调,这种结果导致籼稻具有更高的氮肥利用能力,说明NRT1.1B在粳稻氮肥利用效率改良上具有巨大应用价值。
论文链接: Hu B,etal.. Variation in NRT1.1B contributes to nitrate-use divergence between rice subspecies. Nature Genetics, 2015,47(7):834-838. doi: 10.1038/ng.3337. Published online: 08 June, 2015.
Abstract: Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) consists of two main subspecies, indica and japonica. Indica has higher nitrate-absorption activity than japonica, but the molecular mechanisms underlying that activity remain elusive. Here we show that variation in a nitrate-transporter gene, NRT1.1B (OsNPF6.5), may contribute to this divergence in nitrate use. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that NRT1.1B diverges between indica and japonica. NRT1.1B-indica variation was associated with enhanced nitrate uptake and root-to-shoot transport and upregulated expression of nitrate-responsive genes. The selection signature of NRT1.1B-indica suggests that nitrate-use divergence occurred during rice domestication. Notably, field tests with near-isogenic and transgenic lines confirmed that the japonica variety carrying the NRT1.1B-indica allele had significantly improved grain yield and nitrogen-use efficiency (NUE) compared to the variety without that allele. Our results show that variation in NRT1.1B largely explains nitrate-use divergence between indica and japonica and that NRT1.1B-indica can potentially improve the NUE of japonica.
科学家发明单碱基分辨率测序技术:CeU-Seq
近日,北京大学生命科学学院伊成器研究组报道了一种通过化学标记和富集手段实现全转录组水平上假尿嘧啶RNA修饰的单碱基分辨率测序技术CeU-Seq,并绘制了人和小鼠细胞转录组中假尿嘧啶RNA修饰的谱图。该研究进一步确定了多个可以作用于mRNA上的假尿嘧啶合成酶(其中PUS1、DKC1两种酶之前被发现与线粒体肌病、先天性角化不良等人类疾病相关),并且发现转录组中假尿嘧啶的含量与分布均会受到各种环境刺激的调控,呈现出“刺激条件特异性”的诱导修饰。该研究为假尿嘧啶转录后修饰参与基因表达调控的研究提供了重要工具,为近年来兴起的“RNA表观遗传学”领域提供了崭新的研究方向。
论文链接: Li X,etal.. Chemical pulldown reveals dynamic pseudouridylation of the mammalian transcriptome. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1836. Published online: 15 June, 2015.
Abstract: Pseudouridine (Ψ) is the most abundant post-transcriptional RNA modification, yet little is known about its prevalence, mechanism and function in mRNA. Here, we performed quantitative MS analysis and show that Ψ is much more prevalent (Ψ/U ratio~0.2~0.6%) in mammalian mRNA than previously believed. We developed N3-CMC-enriched pseudouridine sequencing (CeU-Seq), a selective chemical labeling and pulldown method, to identify 2 084 Ψ sites within 1 929 human transcripts, of which four (in ribosomal RNA and EEF1A1 mRNA) are biochemically verified. We show that hPUS1, a known Ψ synthase, acts on human mRNA; under stress, CeU-Seq demonstrates inducible and stress-specific mRNA pseudouridylation. Applying CeU-Seq to the mouse transcriptome revealed conserved and tissue-specific pseudouridylation. Collectively, our approaches allow comprehensive analysis of transcriptome-wide pseudouridylation and provide tools for functional studies of Ψ-mediated epigenetic regulation.
Crispr-Cas9技术获重大新成果
来自麻省总医院的一个研究小组找到了一种新方法来扩大强大基因编辑工具——Crispr-Cas9 RNA引导核酸酶的使用及提高其精确性。相比于迄今为止使用的自然形式的Cas9,演化版本的Cas9能够识别前者无法靶向的不同范围的核酸序列。采用该小组设计改进的新的Cas9变体,可以靶向过去用野生型Cas9无法改造的人类和斑马鱼基因。这将使得研究人员能够靶向各种基因组中更大范围内的一些位点,这个新方法可以用于需要高度精确靶向DNA序列的研究。该研究第一次证实了可以通过定向的蛋白质演化来改变SpCas9的活性,通过相似的方法还可以改变Cas9酶其他的有用特性,使得定制化一些重要特性成为可能。
论文链接: Kleinstiver B P,etal.. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities. Nature, 2015,doi: 10.1038/nature14592. Published online: 22 June, 2015.
Abstract: Although CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases are widely used for genome editing, the range of sequences that Cas9 can recognize is constrained by the need for a specific protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). As a result, it can often be difficult to target double-stranded breaks (DSBs) with the precision that is necessary for various genome-editing applications. The ability to engineer Cas9 derivatives with purposefully altered PAM specificities would address this limitation. Here we show that the commonly used Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 (SpCas9) can be modified to recognize alternative PAM sequences using structural information, bacterial selection-based directed evolution, and combinatorial design. These altered PAM specificity variants enable robust editing of endogenous gene sites in zebrafish and human cells not currently targetable by wild-type SpCas9, and their genome-wide specificities are comparable to wild-type SpCas9 as judged by GUIDE-seq analysis. In addition, we identify and characterize another SpCas9 variant that exhibits improved specificity in human cells, possessing better discrimination against off-target sites with non-canonical NAG and NGA PAMs and/or mismatched spacers. We also find that two smaller-size Cas9 orthologues, Streptococcus thermophilus Cas9 (St1Cas9) and Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 (SaCas9), function efficiently in the bacterial selection systems and in human cells, suggesting that our engineering strategies could be extended to Cas9s from other species. Our findings provide broadly useful SpCas9 variants and, more importantly, establish the feasibility of engineering a wide range of Cas9s with altered and improved PAM specificities.
科学家开发出简单便宜的组织蛋白分析新技术
近日,来自瑞典乌普萨拉大学的研究人员开发了一种蛋白质分析技术,利用这种技术不需要高级设备、专门的实验室以及昂贵的试剂就可对组织蛋白进行分析。该技术以两个抗体对同一蛋白两个不同位点或两个定位很近的不同蛋白的结合为基础,将两个抗体分别与一段含发卡结构的DNA链连接,当两个抗体靠得非常近的时候,其带有的DNA链会结合形成一个起始序列。当这种情况发生时,通过杂交链式反应(hybridization chain reaction)将带有荧光标记并具有发卡结构的寡聚核苷酸连接到起始序列上,这样扩增出的每一条DNA链上都连接有荧光底物,实现了信号扩增,当使用特定波长的光进行激发,DNA链上连接的荧光底物会发射出荧光。当链式反应进行到一定程度,便可以在荧光显微镜下观察到明亮的点状荧光,点状荧光越多,蛋白就越多。除此之外,这种链式反应不需要任何酶的催化,在室温情况下就可进行反应。这项技术将给基础研究和医学诊断带来极大便利。
论文链接: Koos B,etal.. Proximity-dependent initiation of hybridization chain reaction. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7294. doi:10.1038/ncomms8294.
Abstract: Sensitive detection of protein interactions and post-translational modifications of native proteins is a challenge for research and diagnostic purposes. A method for this, which could be used in point-of-care devices and high-throughput screening, should be reliable, cost effective and robust. To achieve this, here we design a method (proxHCR) that combines the need for proximal binding with hybridization chain reaction (HCR) for signal amplification. When two oligonucleotide hairpins conjugated to antibodies bind in close proximity, they can be activated to reveal an initiator sequence. This starts a chain reaction of hybridization events between a pair of fluorophore-labelled oligonucleotide hairpins, generating a fluorescent product. In conclusion, we show the applicability of the proxHCR method for the detection of protein interactions and posttranslational modifications in microscopy and flow cytometry. As no enzymes are needed, proxHCR may be an inexpensive and robust alternative to proximity ligation assays.
研究发现检测血液中miRNA的简便技术
最近,密歇根大学的研究人员开发出一种有效的方法,能在血液中检测到癌变肿瘤脱落的microRNAs。这种方法可通过一种廉价的血液测试,同时对多种类型的癌症进行筛选——最终可能超过100种不同的类型。在实验中,研究人员用称为“捕获探针” 的分子包覆一个载玻片,这些探针分子可紧紧抓住在其附近的microRNAs。这种方法的独特之处在于,DNA和RNA结合太弱,因此它们不能停留。虽然之前有研究人员已经在血清中检测到microRNA,但是本研究中的这种方法更为直接,并且几乎没有假阳性。
论文链接: Johnson-Buck A,etal.. Kinetic fingerprinting to identify and count single nucleic acids. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(7):730-732. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3246. Published online: 22 June, 2015.
Abstract: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as promising diagnostic biomarkers. We introduce a kinetic fingerprinting approach calledsingle-molecule recognition through equilibrium Poisson sampling (SiMREPS) for the amplification-free counting of singleunlabeled miRNA molecules, which circumvents thermodynamic limits of specificity and virtually eliminates false positives. We demonstrate high-confidence, single-molecule detection of synthetic and endogenous miRNAs in both buffer and minimally treated biofluids, as well as >500-fold discrimination between single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Influence of PAP on the IFN-γ and Soluble LAG-3 Molecule Level of Spleen Lymphocyte Supernatant in Mice
WEI Hui1, HE Duo-yi2, BAI De-cheng1*, CHENG Ju1, SHEN Rong1, ZHANG Qian-qian1
1.SchoolofBasicMedicalSciences,LanzhouUniversity,Lanzhou730000,China;
2.WuweiOccupationalCollege,GansuWuwei733000,China
To observe the influence of PAP on the IFN-γ and soluble LAG-3 molecule level of spleen lymphocyte supernatant in mice which acute exposured to low doses of cadmium. The solution of cadmium chloride were injected into the intraperitoneal of the test mice with 1 mg/kg. After 24 h, the model had been successfully made, PAP of low, medium and high doses were injected into the intraperitoneal for a week, spleen index and thymus index were measured at the end of the experiment, the content of IFN-γ and sLAG-3 were measured by ELISA. The cells of CD3+,CD4+,CD8+in spleen lymphocytes was observed by immunofluorescence. The results showed that, compared with the blank control and the cadmium stained positive control, the content of IFN-γ and sLAG-3 were increased among the different doses of PAP groups. The high concentration group increased the most obvious(P<0.05), the amount of CD3+, CD4+cells were also correspond to the number of rising but CD8+cells were not increased significantly. It was still the most significant increase in the high dose group. PAP could increase the content of IFN-γ and soluble LAG-3 of the mice acute exposuring to low doses of cadmium, and CD3+,CD4+lymphocytes were in a corresponding increase.
PAP; IFN-γ; sLAG-3
2015-03-27; 接受日期:2015-04-09
魏慧,硕士研究生,主要从事中西医结合基础研究。E-mail:1159300949@qq.com。*通信作者:白德成,教授,研究生导师,主要从事基础医学研究。E-mail:bdc@lzu.edu.cn
10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2015.04.12
