紫云英与化肥配施对安徽沿江双季稻区土壤生物学特性的影响
2015-06-15万水霞朱宏斌郭熙盛王允青
万水霞, 朱宏斌, 唐 杉, 郭熙盛, 王允青*
(1 安徽省农业科学院土壤肥料研究所, 合肥 230031;2 安徽养分循环与资源环境省级实验室, 合肥 230031)
紫云英与化肥配施对安徽沿江双季稻区土壤生物学特性的影响
万水霞1,2, 朱宏斌1,2, 唐 杉1,2, 郭熙盛1,2, 王允青1,2*
(1 安徽省农业科学院土壤肥料研究所, 合肥 230031;2 安徽养分循环与资源环境省级实验室, 合肥 230031)

紫云英; 土壤微生物量碳; 土壤微生物量氮; 土壤酶活性
土壤微生物和土壤酶是土壤生物学特征的重要指标。土壤微生物通过参与土壤生态系统的能量流动和物质循环,在农业生态系统物质能量转化过程中起着重要作用,是农业土壤生态系统中极其重要和最为活跃的部分[1-2]。土壤酶参与土壤中一切复杂的生物化学过程,包括各种有机化合物的分解、养分固定与释放以及各种氧化还原反应等,是土壤中物质转化方向和动力的枢纽[3]。土壤中碳、氮转化的主要过程都受微生物控制,土壤微生物是土壤氮的源和库,是土壤碳、氮转化的驱动力,土壤养分有效性又反作用于微生物群落结构、活性及生理状态[4-5]。施肥是影响土壤质量及其可持续利用最深刻的农业措施之一,它通过改变土壤微生物活性、数量(微生物生物量碳、氮)和群落结构,改变土壤碳、氮养分转化速率和途径,影响土壤供氮能力和碳贮备能力,进而影响土壤质量。研究不同施肥措施对土壤微生物特性以及土壤酶活性的影响,对于相关物种的种植生产以及区域农业生态系统健康的维持具有重要的理论和实践意义。
绿肥具有良好的改土培肥作用,绿肥还田不仅能够改善土壤矿质养分状况,有利于后茬作物的生长,还可减少化肥投入,降低农业生产成本[6]。近年来对旱地绿肥翻压还田土壤的微生物学特性已经进行过很多研究[7-8],对水稻田土壤的微生物学特性的研究也有一些报道[9-10]。但在水稻-绿肥轮作模式下化肥与绿肥配施对土壤微生物特性影响的深入系统研究鲜见报道。因此,本研究针对安徽沿江地区现行的主要冬季绿肥-双季稻的种植制度,通过田间定位试验研究紫云英与化肥配施条件下,紫云英不同施用量对土壤微生物量及酶活性的影响,为安徽双季稻区稻田土壤肥力培育及紫云英合理施用提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验设计
试验开始于2008年,安排在安徽省桐城市吕亭镇新店村,成土母质为河流冲积物发育的水稻土,作物体系为紫云英—早稻—晚稻。土壤主要农化性状: pH 6.2,有机质17.5 g/kg,全氮1.34 g/kg,碱解氮75 mg/kg,速效磷(P)6 mg/kg,速效钾(K) 78 mg/kg,缓效钾(K)246 mg/kg。早稻品种为早籼7038,2008年开始早稻每年3月28日左右播种,播种密度大约为每公顷30 万丛,4月28日左右移栽。紫云英为弋江籽,在晚稻收获后播种,第二年早稻移栽前两星期收割还田。小区面积20 m2,4次重复,随机区组排列。小区埂宽30 cm,高20 cm,用薄膜覆盖,防止小区间串水串肥。每小区在灌排小沟一端设灌排水口。
试验设5个处理: 1)不施紫云英和化肥(对照,CK);2)100%化肥,不施紫云英(T1);3)70%化肥,施紫云英7500 kg/hm2(T2);4)70%化肥,施紫云英15000 kg/hm2(T3);5)70%化肥,施紫云英30000 kg/hm2(T4)。其中,100%化学肥料用量(N、 P2O5、 K2O分别为165、 75、 90 kg/hm2)。除对照外,各处理均施硫酸锌15 kg/hm2。试验中的磷肥、钾肥、锌肥全部作基肥一次施用,氮肥按基肥50%、 蘖肥30%、 穗肥20%施用。
1.2 样品采集与分析方法
2013年早稻生长季内采集0—20 cm 土样,具体为: 紫云英施用前、早稻移栽后15、30、50、80 d 随机选取0—20 cm土层采集5个土样,混匀。样品带回实验室后手工拣去植物残体、砾石等,过2 mm 筛,将一部分土样保存在4℃冰箱用于测定土壤微生物量碳、氮,剩余部分风干过1 mm 筛和0.15 mm 筛测定土壤酶活性和土壤养分。
土壤微生物量碳、氮的测定采用氯仿熏蒸浸提法[11],其含量计算用熏蒸和未熏蒸样品碳含量之差除以回收系数(KC=0.45,KN =0.45)。土壤酶活性的测定根据关松荫的方法[12],脲酶采用苯酚钠比色法;酸性磷酸酶用磷酸苯二钠比色法;过氧化氢酶活性采用高锰酸钾滴定法;土壤化学性质采用常规土壤农化分析方法[11]。
1.3 数据处理
本研究所有数据的基本统计采用Microsoft Excel 2003软件完成,方差分析及相关性分析采用SPPS 17.0统计软件进分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 对稻田土壤微生物量的影响


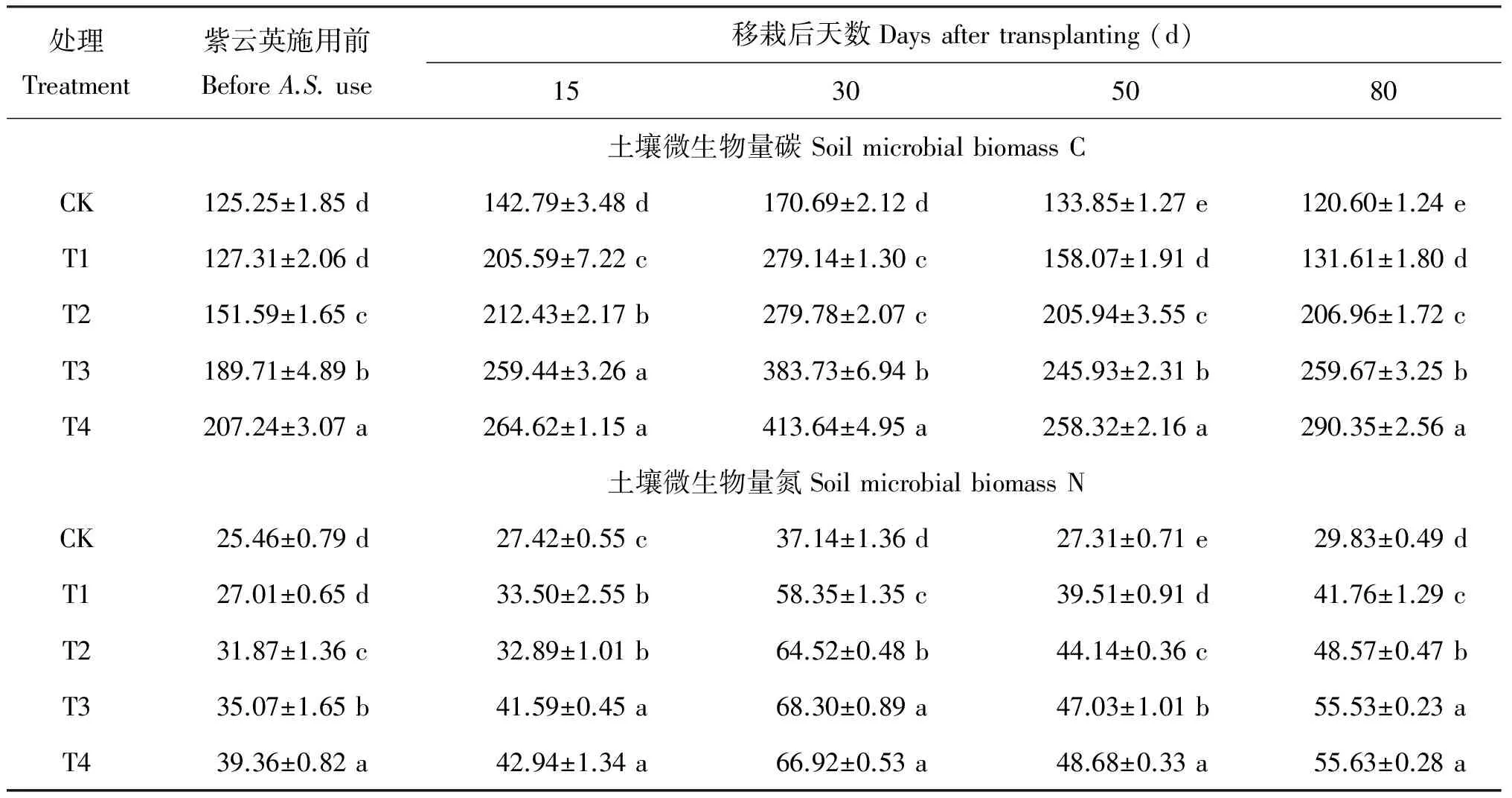
表1 不同施肥处理稻田土壤微生物生物量
注(Note):A.S.—Astragalussinicus; 表中数据为平均数±标准差 Data in the table are Mean±SD; 同列数值后不同字母表示处理间差异达到5%显著水平Values followed by different letters with in the same column are significant among treatments at the 5% level.
2.2 对稻田土壤酶活性的影响


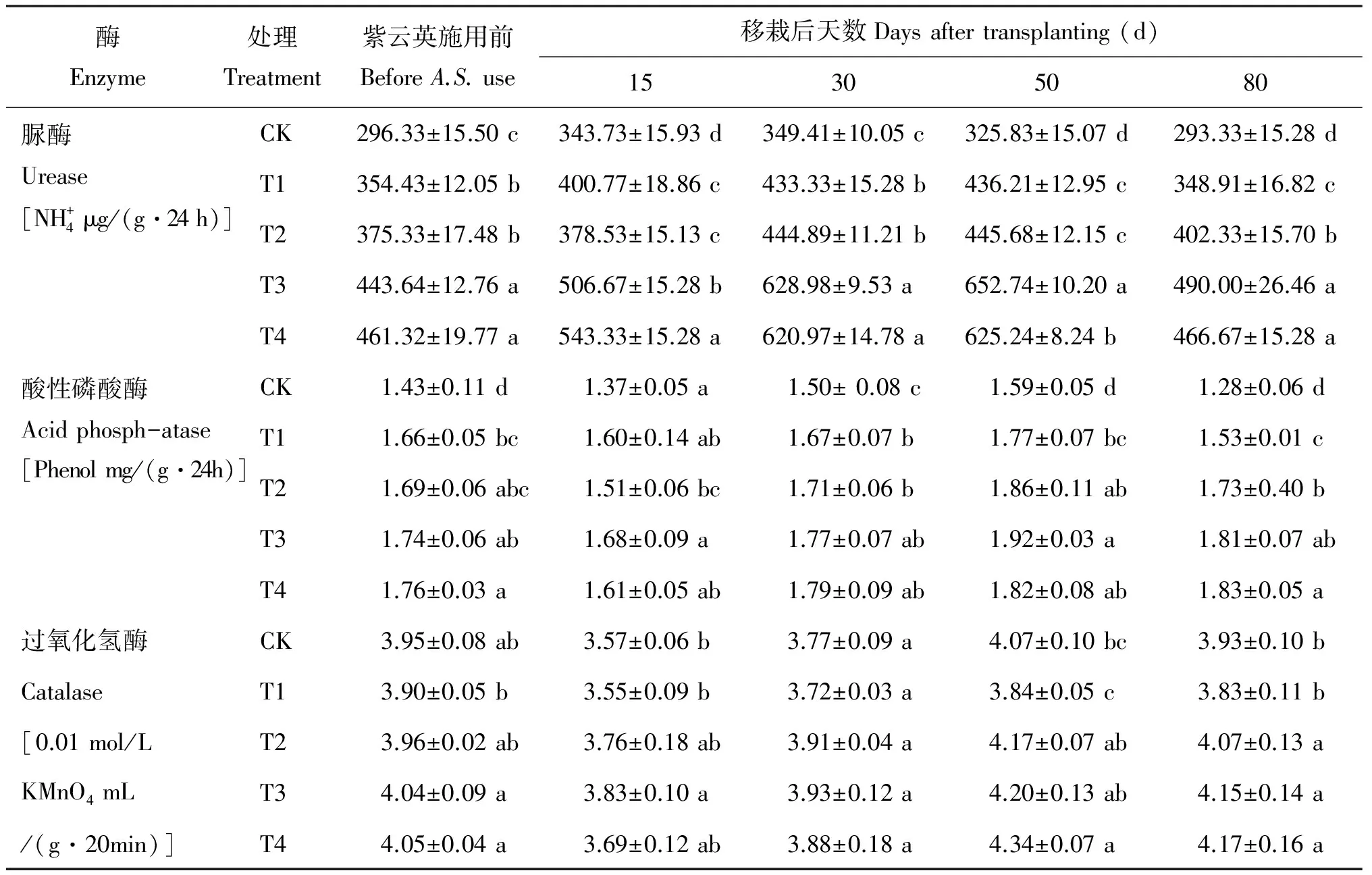
表2 不同处理土壤酶活性
注(Note):A.S.—Astragalussinicus; 同列数值后不同字母表示处理间差异达到5%显著水平Values followed by different letters with in the same column are significant among treatments at the 5% level.

2.3 对水稻产量的影响

2.4 土壤化学肥力因素与土壤微生物量及酶活性的关系
由表4可以看出,土壤微生物量碳、氮与土壤有机质、全氮、碱解氮均存在极显著或显著相关性。脲酶、酸性磷酸酶含量与土壤有机质、全氮、碱解氮显著相关,酸性磷酸酶与速效磷相关显著。而在水稻成熟期过氧化氢酶活性与土壤各养分之间无明显相关性。pH值与土壤微生物量及土壤酶活性均呈负相关性。说明紫云英还田在一定程度上降低了土壤pH,提高了土壤有机质及氮含量。这与刘国顺等[14]的研究结果基本一致。但这只是一年的试验结果,具体施用紫云英多年的效果比较还需进一步研究。
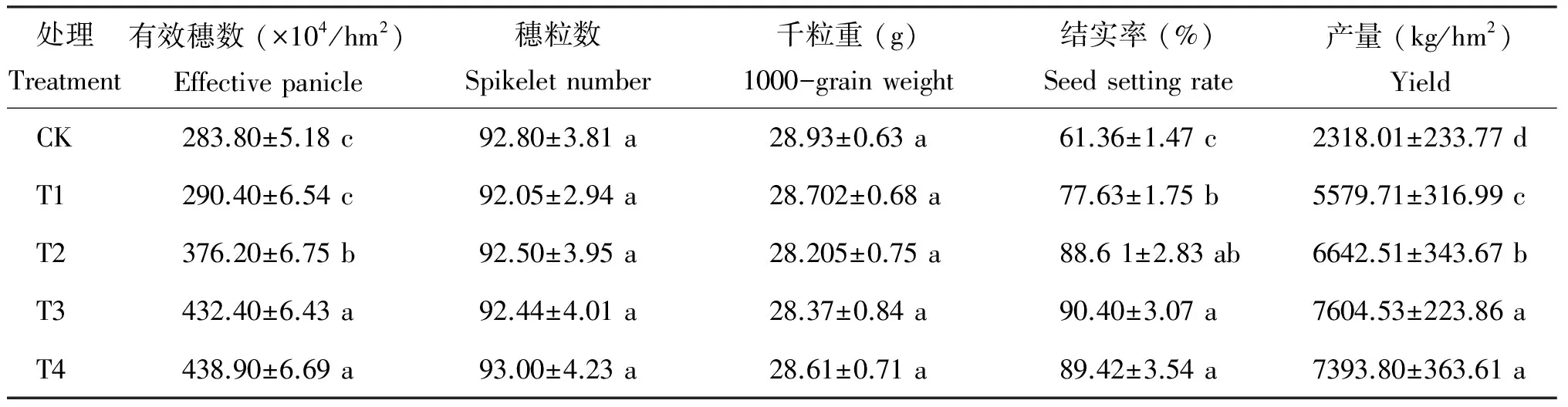
表3 不同施肥处理对水稻产量及其构成要素的影响
注(Note): 同列数值后不同字母表示处理间差异达到5%显著水平Values followed by different letters with in the same column are significant among treatments at the 5% level.
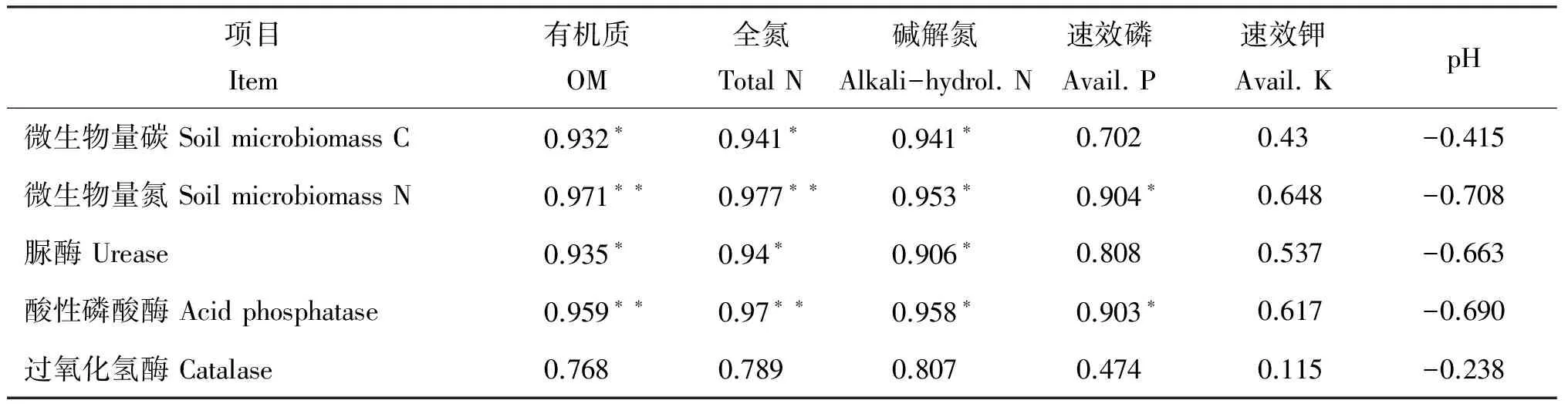
表4 土壤化学性质、微生物量碳氮以及酶活性之间的线性相关系数
注(Note): *—P<0.05; **—P<0.01.
3 讨论与结论

土壤微生物量的大小与气候条件、土壤状况有关[19],但在相同的自然条件下,相同的耕作管理下,施肥是土壤微生物量大小的主要影响因素之一。本研究结果表明,施肥处理均不同程度地提高了土壤微生物量碳、氮含量;紫云英与化肥配施处理明显高于单施化肥处理,并且土壤微生物量随着紫云英施用量的增大而提高。究其原因,一方面,施入化肥后水稻生长加快,水稻根系生物量及根系分泌物增加,同时化肥也为微生物提供大量矿质元素,促进土壤微生物生长,表现为土壤微生物量得以提高;另一方面,紫云英还田后在土壤微生物的作用下分解迅速,释放出大量可溶性有机物如氨基酸、有机酸以及无机养分[20],而这些养分又为微生物提供了充足碳源和氮源,促进微生物的大量繁殖,相应地也促进了土壤微生物活性的提高,表现为土壤微生物量的提高。上述结果与秸秆及绿肥还田对土壤微生物生长的影响是一致的[21-22]。
本研究还发现,在水稻不同生育时期,土壤微生物量碳、氮的动态变化呈现出相似的规律性,这与李正等[23]研究结果相一致,但与武雪萍等[24]研究芝麻饼肥结果有差异。紫云英还田前,各处理土壤微生物量碳、氮均处于较低值的状态,随着化肥基肥的施入,紫云英的施用,土壤微生物量碳、氮含量开始上升,其中T3、T4上升幅度最大,并于水稻移栽30 d左右达到最大。紫云英施入土壤后腐解,微生物利用其腐解产物作为碳源大量繁殖,将紫云英中的碳同化为微生物体碳[25],进而使微生物量碳含量提高。土壤微生物活性增强促进了紫云英有机物质的转化与养分的释放,并转化为较为稳定的微生物碳氮等物质,土壤中的氮素营养积累增多。水稻前期养分需求量相对较小,多余的氮素被微生物同化固定起来,从而使微生物量氮含量不断升高。水稻生长进入拔节期后,养分需要量增加,土壤中碳、氮养分被大量消耗,部分微生物碳、氮又被释放出来,进而土壤微生物量碳、氮开始降低。移栽80 d左右,水稻生长成熟,此时水稻生命活动减弱,需肥量减少,施用紫云英的处理土壤中残存的有机物继续腐解,土壤中微生物将再次被激活,微生物活性又有所增强,土壤微生物量碳、氮含量有所回升。这也说明施用紫云英使土壤保肥性能提升。

土壤生物学性状与土壤养分相关性分析表明,紫云英与化肥配施有助于增加土壤有机碳含量,对土壤氮素供应能力具有重要影响。施用紫云英促进微生物量提高及酶活性的增强,而微生物量及酶活性的提高又促进土壤氮素的固定、转化、保存和释放,也即提高了土壤的氮素供应水平。另外,紫云英的固氮作用也促进土壤碱解氮及全氮的提高。紫云英施用与土壤速效磷、钾无显著相关性,这可能与水稻的吸肥规律及磷、钾元素的运输特征有关。

[1] 庞新, 张福锁, 王敬国. 不同供氮水平对根系微生物量氮及微生物活度的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2000,6(4): 476-480. Pang X, Zhang F S, Wang J G. Effect of different nitrogen levels on SMBON and microbial activity[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2000, 6(4): 476- 480.
[2] 林先贵, 胡君利. 土壤微生物多样性的科学内涵及其生态服务功能[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 892-898. L in X G, Hu J l. Scientific connotation and ecological service function of soil microbial diversity[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(5): 892-898.
[3] 何念祖. 浙江省几种水稻土的酶活性及其与土壤肥力的关系[J]. 浙江农业大学学报, 1986, 12(l): 43-47. He N Z. Enzymatic activities in paddy soils in Zhejiang province and the correlation between enzymatic activities in soils and soil fertility[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1986,12(l): 43-47.
[4] 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 冉炜. 长期免耕与施用有机肥对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(1): 89-96. Xu Y C, Shen Q R, Ran W. Effects of zero-tillage and application of manure on soil microbial biomass C,N and P after Sixteen years of cropping[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(1): 89-96.
[5] 沈宏, 曹志洪, 徐本生. 玉米生长期间土壤微生物量与土壤酶变化及其相关性研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1998, 10(4): 471-474. Shen H, Cao Z H, Xu B S. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and soil enzyme activity and their relationships during maize growth[J]. Chinese journal of applied ecology, 1999, 10(4): 471-474.
[6] 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2009, (4): 1-3. Cao W D, Huang H X. Ideas on restoration and development of green manure s in China[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences In China, 2009, (4): 1-3.
[7] 郭晓霞, 刘景辉, 张星杰, 等. 免耕对旱作燕麦田耕层土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(3): 575-580. Guo X X, Liu J H, Zhang X Jetal.Effects of non-tillage on soil microbial C, N and P in plough layer of oat field[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(3): 575-580.
[8] 马晓霞,王莲莲,黎青慧,等. 长期施肥对玉米生育期土壤微生物量碳氮及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(17): 5502-5511. Ma X X, Wang L L, Li Q Hetal. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities during maize growing season[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(17): 5502-5511.
[9] 王丽宏, 曾昭海, 杨光立, 等. 冬季作物对水稻生育期土壤微生物量碳、氮的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报2009, 15(2): 381- 385. Wang L H, Zeng Z H, Yang G Letal. Effects of winter crops on microbial biomass C and N during rice growth[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(2): 381- 385.
[10] 张英, 褚秋华, 邱多生, 等. 11年连续肥料处理对水稻土碳、氮及微生物量的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2001, 24(4): 112-114. Zhang Y, Zhu Q H, Qiu D Setal. Effect of 11-year continuous fertilizer application on soil carbon, nitrogen and microbial biomass of paddy soil[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2001, 24 (4): 112- 114.
[11] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1981. Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1981.
[12] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. Guan S Y. Soil enzyme and study method[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1986.
[13] 张成娥, 梁银丽, 贺秀斌. 地膜覆盖玉米对土壤微生物量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(4): 508-512. Zhang C E,Liang Y L,He X B. Effects of plastic cover cultivation on soil microbial biomass[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2002,22(4): 508-512.
[14] 刘国顺, 罗贞宝, 王岩, 等. 绿肥翻压对烟田土壤理化性状及土壤微生物量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2006, 20(1): 95-98. Liu G S, Luo Z B, Wang Yetal. Effect of green manure application on soil properties and soil microbial biomass in tobacco field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(1): 95-98.
[15] 杨滨娟, 黄国勤, 王超, 等. 稻田冬种绿肥对水稻产量和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(10): 1209-1216. Yang B J, Huang G Q, Wang Cetal. Effects of winter green manure cultivation on rice yield and soil fertility in paddy field[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(10): 1209-1216
[16] 王璐, 吴建富, 潘晓华, 等. 紫云英和稻草还田免耕抛栽对水稻产量和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010,26(20): 299-303. Wang L, Wu J F, Pan X Hetal. Effects of no-tillage and cast-transplanting with milk vetch and straw incorporation on rice yield and soil fertility[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(20): 299-303.
[17] 肖恕贤. 双季稻田冬季不同复种轮作方式的增产效果及对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 1980, 13(2): 59-66. Xiao S X. Effect of the increase of production by different multiple cropping and crop rotation pattern of double cropping rice field in winter and its influence to soil fertility[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1980, 13(2): 59-66.
[18] 周兴, 谢坚, 廖育林, 等. 基于紫云英利用的化肥施用方式对水稻产量和土壤碳氮含量的影响[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 39(2): 189-193. Zhou X, Xie J, Liao Y Letal. Effect of fertilizer management on rice yield, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen based on utilizing the milk vetch[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2013, 39(2): 189-193.
[19] Insam H, ParkinsonD, Domsch K H. Influence of macroclimate of soil microbial biomass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1989, 21(2): 211-221.
[20] 代静玉, 周江敏, 秦淑平. 几种有机物料分解过程中溶解性有机物质化学成分的变化[J]. 土壤通报,2004, 35(6): 724-727. Dai J Y, Zhou J M, Qin S P. Dynamic changes of chemical composition of dissolved organic matter during decomposition of organic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 35(6): 724-727.
[21] Okautz T, Wirth S, Ellner F. Microbial activity in a sandy arable soil is governed by the fertilization regine[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2004, 40(2): 87-94.
[22] 李贵桐, 张宝贵, 李保国. 秸秆预处理对土壤微生物量及呼吸活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(12): 2225-2228. Li G T, Zhang B G, Li B G. Effect of straw pretreatment on soil microbial biomass and respiration activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(12): 2225-2228.
[23] 李正, 刘国顺, 敬海霞, 等. 翻压绿肥对植烟土壤微生物量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(3): 225- 232. Li Z, Liu G S, Jing H Xetal. Effects of green manure application on the microbial biomass C and N contents and of the enzyme activity of tobacco-planting soil[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(3): 225- 232.
[24] 武雪萍, 刘增俊, 赵跃华, 等. 施用芝麻饼肥对植烟根际土壤酶活性和微生物碳、氮的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(4): 541- 546. Wu X P, Liu Z J, Zhao Y Hetal. Effects of sesame cake fertilizer on soil enzyme activities and microbial C and N at rhizosphere of tobacco[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(4): 541- 546.
[25] 肖嫩群, 张洪霞, 成壮, 等. 紫云英还田量对烟田土壤微生物及酶的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(4): 711-715. Xiao N Q, Zhang H X, Cheng Zetal. Effect of incorporation of astragalus sinicus on microbe and enzyme dynamics in tobacco cultivated soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(4): 711-715.
[26] Dick R P. Soil enzyme activities as integrative indicators of soil health[A]. Pnkrst Cetal(Eds). Biological Indicators of Soil Health[M]. Wallingford, Oxon, UK: CAB International, 1997. 121-157.
[27] 王树起, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等. 长期施肥对东北黑土酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2008, 19(3): 551-556. Wang S Q, Han X Z, Qiao Y Fetal. Effects of long-term fertilization on enzyme activities in black soil of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(3): 551-556.
[28] 孙瑞莲, 赵秉强, 朱鲁生, 等. 长期定位施肥对土壤酶活性的影响及其调控土壤肥力的作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2003, 9(4): 406-410. Sun R L, Zhao B Q, Zhu L Setal. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil enzyme activities and its role in adjusting-controlling soil fertility[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2003, 9(4): 406-410.
[29] 邱现奎, 董元杰, 万勇善, 等. 不同施肥处理对土壤养分含量及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 2010, 42(2): 249-255. Qiu X K, Dong Y J,Wan Y Setal. Effects of different fertilizing treatments on contents of soil nutrients and soil enzyme activity[J]. Soils, 2010, 42(2): 249-255.
Effects ofAstragalussinicusmanure and fertilizer combined application on biological properties of soil in Anhui double cropping rice areas along the Yangtze River
WAN Shui-xia1,2, ZHU Hong-bin1,2, TANG Shan1,2, Guo Xi-sheng1,2, WANG Yun-qing1,2*
(1SoilandFertilizerResearchInstitute,AnhuiAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Hefei230031,China; 2AnhuiProvincialKeyLaboratoryofNutrientRecycling,ResourcesandEnvironment,Hefei230031,China)
【Objectives】Astragalussinicus-rice rotation system has been extended in rice production in order to prevent the ever growing areas of fallow fields. The effects of incorporation ofAstragalussinicuscombined with chemical fertilize of rice production and soil microbial properties were studied in order to provide a theoretical support for improving soil biochemical environment and soil quality, insuring high and steady yield of crops. 【Methods】 Based on the vetch-rice-rice experiment which was set by theSoil and Fertilizer Institute, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences in 2008, microbial biomass C and N contents, soil enzymatic activities and correlation between biological characteristics of the soil and soil nutrients of paddy topsoil (0-20 cm) were analyzed. The soil productivity was evaluated with yield and agricultural traits of rice. The experiment included five treatments: no fertilizer (CK), 100% fertilizer, incorporatingAstragalusinicusof 7500, 15000, 30000 kg/ha with 70% of normal amount of chemical fertilizers. 【Results】 1)Application ofAstragalusinicuscan significantly improve grain yield of rice, increase the effective panicles and seed setting rate, especially in treatment applicationAstragalusinicus15000 kg/ha with 70% amounts o f chemical fertilizers, in which the highest yield of 7604.53 kg/ha was obtained, the effective panicles and seed setting rates are about 228.06% and 36.29% higher than those in CK and 100% fertilizer treatment. 2) Compared with the control, soil microbial biomass carbon(SMBC), soil microbial biomass nitrogen(SMBN), enzyme activities of soil acid phosphatase and urease are increased in chemical fertilizer treatments while the catalase activity decreased. Compared with the treatments of chemical fertilizer and CK, application ofAstragalussinicuscombined with 70% chemical fertilizer significantly increased SMBC, SMBN, and soil enzyme activities. Which increased with the increasing amount ofAstragalussinicusapplication, and the treatment with 15000-30000 kg/ha ofAstragalussinicusreturning with 70% amounts of chemical fertilizer had better comprehensive effects. During the whole growth period, the contents of soil microbial biomass C and N were increased by 21.03%-142.33% and 19.97%-83.91%, and the activities of soil urease, acid phosphatase, catalase by 10.12%-100.33%,10.22%-43.23%,0.14%-7.28% after turnover ofAstragalussinicus, compared with CK. All the soil microbial biomass, activities of urease, and acid phosphatase had positive and significant relationship with soil organic matter, total N, alkalitic N (P<0.05,P<0.01), but the correlation between hydrogen peroxidase activityand soil nutrients content was not obvious. 【Conclusions】 Long-term application ofAstragalussinicuscombined with chemical fertilizer can significantly increase the rice yield, soil microbial biomass and soil enzyme activity, improve paddy soil micro-ecological environment. Within the test area and on the condition of appropriate amount of fertilizer 70%, the incoporation of 15000-30000 kg/haAstragalussinicusis appropriate. This combination ratio of Astragalus sinicus and chemical fertilizer is conducive to improve soil productivity, and it is an effective way to improve crop yield and soil fertility in double-cropping paddy field areas along the Yangtze River in Anhui Province.
Astragalussinicus; soil microbial carbon; soil microbial nitrogen; enzyme activity
2014-01-10 接受日期: 2014-05-09
公益性行业(农业)专项(201103005,201203032);安徽省农业成果转化项目(12040302003);安徽省科技厅项目(1406c085025)资助。
万水霞(1978—),女,安徽东至人,硕士,主要从事农业微生物和农业废弃物资源化研究。 * 通信作者 E-mail: yunqingw@126.com
S154.37; S551+.9
A
1008-505X(2015)02-0387-09
