等氮条件下长期有机无机配施对春玉米的氮素吸收利用和土壤无机氮的影响
2015-06-15高洪军张秀芝张卫建
高洪军, 朱 平, 彭 畅, 张秀芝, 李 强, 张卫建
(1 南京农业大学农学院, 南京 210095; 2 中国农业科学院作物科学研究所, 北京 100081;3 吉林省农业科学院, 长春 130033)
等氮条件下长期有机无机配施对春玉米的氮素吸收利用和土壤无机氮的影响
高洪军1,3, 朱 平3, 彭 畅3, 张秀芝3, 李 强3, 张卫建1,2*
(1 南京农业大学农学院, 南京 210095; 2 中国农业科学院作物科学研究所, 北京 100081;3 吉林省农业科学院, 长春 130033)

有机无机配施; 春玉米; 氮肥利用效率; 无机氮
近年来, 有机无机肥配施是肥料应用研究中最活跃的领域之一,也是研究进展最迅速的领域[1]。有机肥与无机肥相结合,在培肥土壤与作物增产方面优于二者单独施用,尤其在等氮量条件下的有机无机配施成了发展有机无机复合肥产业的关键科学与技术问题,是保证作物稳定增产和推动农业持续稳定发展的重要措施[2-3]。
众多研究获得的有机肥和无机肥配施效果结论基本一致,有机无机肥配施有利于作物稳产高产[4-6], 提高土壤肥力[7-8]和氮肥利用率[9-10],这些研究大都是在化肥用量不变的基础上,通过增施有机肥来进行的。但在等养分条件下通过有机肥氮部分替代化肥氮来探讨有机无机配施对作物产量、肥料利用率的影响除在水稻[1,5]和小麦[11]上有一定研究外,在东北春玉米上报道较少。虽然有个别报道,但有机无机肥配施氮利用率较低,其结果与大多数研究不一致,并且此试验有机培肥期限较短[12]。因此,本试验基于国家黑土肥力与肥效长期定位试验,研究等氮条件下长期有机无机配施对春玉米氮养分吸收累积、运移和氮肥利用效率的影响,以期为吉林黑土区春玉米氮肥合理施用和有机无机配施模式提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验区概况

1.2 试验设计
长期土壤肥力监测始于1990年,于2012年选择其中5个处理进行调查分析,即: 1)CK(不施肥); 2)氮肥(N); 3)氮磷钾化肥(NPK); 4)农家肥加化肥(M+NPK); 5)秸秆加化肥(S+NPK)。试验小区面积400 m2,每个小区均匀分成3个亚区,区间由2 m宽过道相隔。有机肥在每年玉米收获后施用,1/3氮肥和磷钾肥在玉米播种前作底肥,2/3氮肥于拔节前追施表土下10 cm处,秸秆在拔节追肥后撒施土壤表面。有机肥为农家肥,养分含量为N 0.5%、 P2O50.4%、 K2O 0.49%; 玉米秸秆N、P2O5、K2O含量为0.7%、0.16%和0.75%。不同处理有机物料和化肥投入量见表1。供试作物为玉米,种植品种为郑单958,于4月末播种,9月末收获,按常规进行统一田间管理,在10月份对土壤进行取样分析测定。
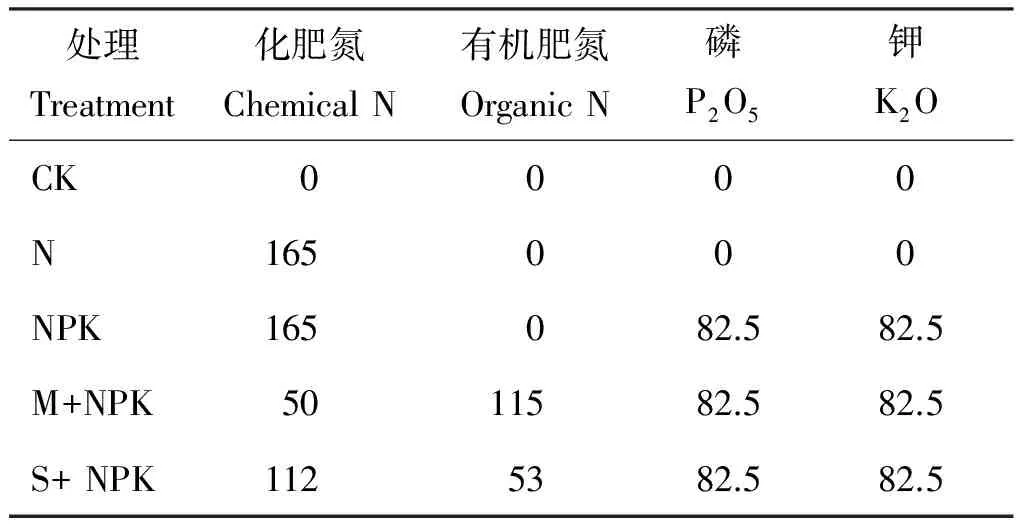
表1 不同处理的施肥量(kg/hm2)
注(Note): M—猪粪Pig manure; S—玉米秸秆Maize straw.
1.3 样品采集和测定
在玉米拔节期(6月19日)、大喇叭口期(7月5日)、抽丝期(7月19日)、灌浆期(8月15日)、成熟期(9月19日)分别采集地上部植株样品,每次在每小区取2株有代表性的玉米植株,将植株分为叶、茎鞘、籽粒、穗轴4部分装入样品袋中,于烘箱105℃杀青30 min,然后于80℃下烘干至恒重,称重,粉碎过0.5 mm筛,用H2SO4-H2O2消煮[13],采用半微量凯氏定氮法测定全氮。
在苗期(6月6日)和上述5个生育期分别采集0—20 cm土壤样品,混匀,风干,过0.85 mm筛。土壤硝态氮含量采用2 mol/L KC1浸提—紫外分光光度法测定[14],铵态氮采用2 mol/L KC1浸提—靛酚蓝比色法测定[13]。
1.4 计算公式及统计方法
氮肥偏生产力(PFP, kg/kg) =施氮处理产量/施氮量[15];
氮收获指数(NHI,%)=籽粒中氮累积量/收获时植株氮素累积量×100[16-17];
氮素转移量(NT, kg/hm2)=抽丝期营养体氮累积量-成熟期营养体氮累积量[18];
氮素转移效率(NTE,%)=氮素转运量/抽丝期营养体氮素累积量×100[18];
转移氮素对籽粒的贡献率(NTC,%) =氮素转移量/籽粒中氮累积量×100[18]。
试验数据采用Excel 2003和SPSS 16.0软件进行统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同施肥处理对氮素吸收累积的影响

2.2 不同施肥处理对氮素各器官转移的影响
籽粒中的养分一部分来源于根系吸收的养分直接输送,另一部分来源于营养器官养分的再转移。养分的转移量和转移效率是营养器官养分向籽粒转输出的重要指标[19]。由表 3 可知,在各施肥处理中,叶和茎鞘总的氮素转移量MNPK、SNPK、NPK和N处理分别为99.0、79.7、87.2和41.8 kg/hm2,MNPK处理显著高于NPK和SNPK处理。 CK和单施N处理氮素转移量最少,且叶片氮素的转移量、转移率和贡献率都显著高于茎秆,表明长期不施肥或不平衡施肥叶片对籽粒养分的贮藏贡献极其重要。

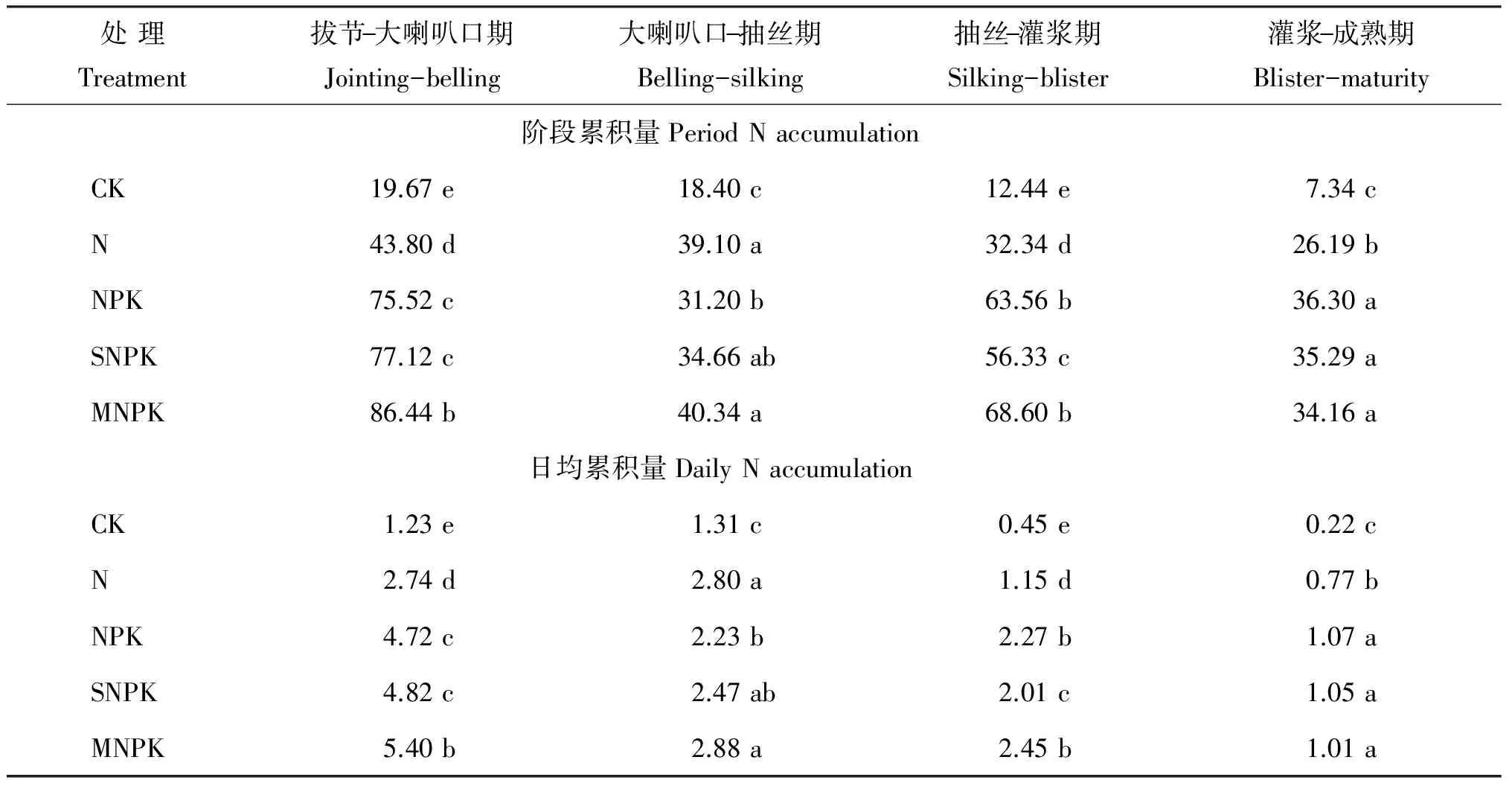
表2 不同施肥处理氮素阶段累积量和日均累积量(kg/hm2)
注(Note): 同列不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平Different letters in a column mean significant difference at the 5% level.
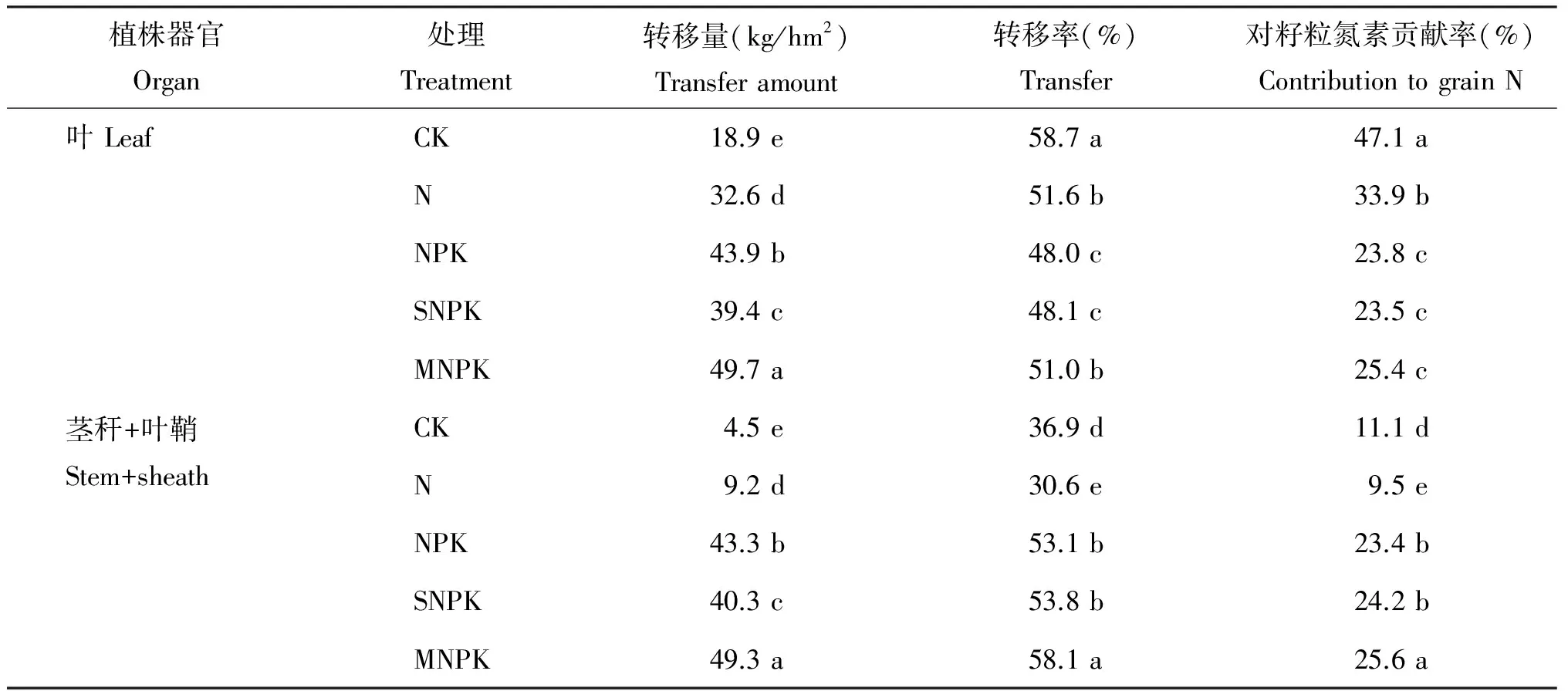
表3 不同施肥处理春玉米各器官氮素的转移量和转移率
注(Note): 同列不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平 Different letters in a column mean significant difference at the 5% level.
2.3 不同施肥处理对氮素利用效率的影响

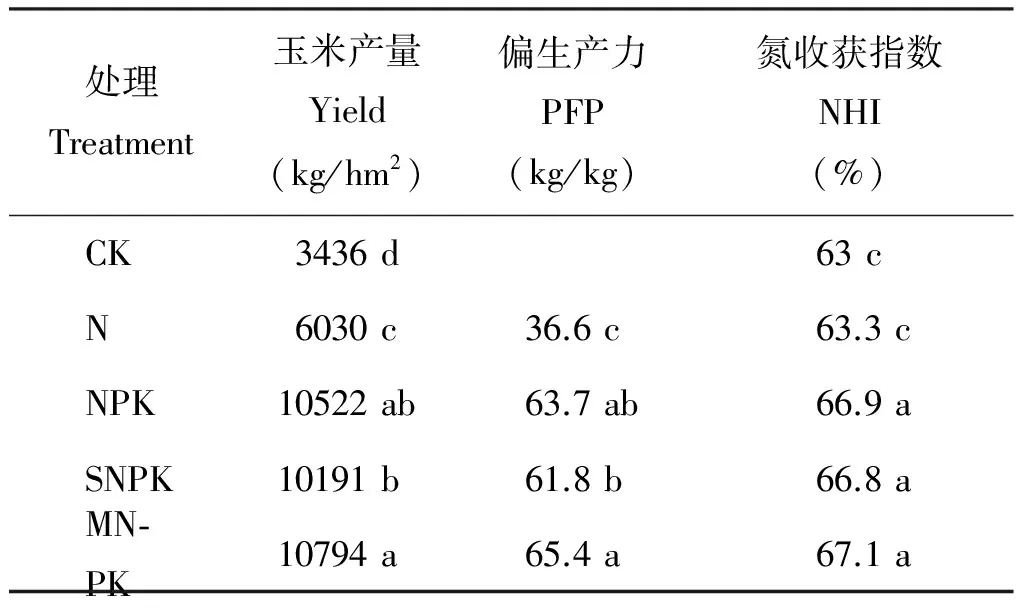
表4 不同施肥处理氮素利用效率的变化
注(Note): PFP—Partial factor productivity; NHI—N harvest index.同列不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平Different letters in a column mean significant difference at the 5% level.
2.4 不同施肥处理耕层土壤无机氮的变化
土壤无机氮(包括硝态氮、铵态氮)含量能够很好地反映植物生长过程中土壤供氮能力。图1表明,各施肥处理的土壤无机氮含量的变化呈现相同的趋势。玉米喇叭口期至灌浆期,土壤矿质氮随着土壤温度的增加而增加,此阶段也是玉米地上部生物量显著增长时期。从玉米喇叭口期至灌浆期,玉米吸收养分急剧增加,土壤无机氮含量下降明显;在喇叭口期由于各施肥处理玉米拔节期追施氮肥,土壤无机氮含量有一个明显的增幅,达到峰值;从灌浆期到成熟期,各处理土壤无机氮含量下降幅度不大。

图1 不同施肥处理耕层(0—20 cm)土壤无机氮含量变化Fig.1 Inorganic nitrogen contents in 0-20 cm soil under different treatments
在各取样时期,不同施肥处理土壤无机氮的含量存在差异,MNPK处理土壤无机氮的含量在玉米整个生育期一直高于其他施肥处理,在大喇叭口期达到60.83 mg/kg,与其他处理达到差异显著,但在其他生育期各施肥处理差异不显著。氮磷钾化肥处理和秸秆加氮磷钾处理差异不显著。因此,NPK配施农家肥比秸秆还田替代部分氮肥和全部使用氮磷钾化肥显著增加表层土壤无机氮含量,有利于土壤无机态氮的长期持续供应。
3 讨论与结论

本试验在长期施肥条件下,化肥配施农家肥的氮肥利用率、农学效率和偏生产力高于化肥处理,并达到差异显著,在其他类型土壤,如潮土[24]、红壤[25]上也有相同的研究结果,红壤上化肥配施农家肥玉米氮肥利用率以每年1.24%个百分点的速率显著增加,施肥18年后达到60%以上,表明不施肥区(空白区)土壤氮素耗竭非常严重;秸秆还田配合NPK和化肥NPK处理对氮肥利用效率的影响基本一致,表明适宜的有机无机配施不仅能提高氮素的生产能力,同时也减少了化肥氮投入,这与众多的研究结果一致[26-28]。适宜的有机肥与化肥配施能提高氮肥利用率的原因可能是有机肥易被微生物利用,更多的氮被固定在微生物体内,从而避免了前期过多的无机氮存在于土壤中而遭受挥发损失;当作物需肥量增加时,土壤中没有更多的能源物质来维持微生物的生命活动,大量的微生物相继死亡,被固持在这些微生物体内的这部分氮素释放出来供作物吸收利用[29-31]。因此,解决有机无机肥配施问题是实现春玉米养分资源高效利用的有效途径之一。
春玉米生长期内土壤无机氮形态以硝态氮为主,铵态氮含量处于较低水平[32]。黄晶等[33]研究表明,与施用NPK 比较,长期有机无机肥配施降低了玉米收获后的表层红壤硝态氮的积累,此试验结果与本试验一致。郝晓辉等[34]研究指出,在等氮量条件下,有机肥与无机肥配施能显著提高稻田土壤无机氮含量。本研究结果表明,在整个生育期,有机无机配施处理表层土壤无机氮含量都高于化肥处理,在喇叭口期达到峰值,土壤无机氮含量达到60.83 mg/kg,较其他处理为作物生长提供了更多的氮素养分,表明长期有机肥与化肥配施是增加土壤氮含量的较好施肥措施。有机肥氮素残效连续叠加,使土壤具有强大而持久的供氮能力,这是施用有机肥产生后效的物质基础和根本原因[35]。长期施用氮肥虽然能够提高土壤供氮能力,但是真正能增加土壤有机氮库、显著提高土壤供氮能力并使土壤在供氮方式上具有渐进性和持续性的只有施用有机肥。这种供氮方式更适合作物根系对氮的吸收利用,这是有机肥优于化肥的原因之一[36],本研究结果也表明,在减施化肥氮的基础上,秸秆还田处理(SNPK)与化肥处理(NPK)的土壤无机氮含量差异不显著,这是连续秸秆还田导致大量的有机氮矿化释放出无机氮的缘故[37]。因此,本试验条件下,长期施用适宜的有机肥氮替代部分化肥氮(用量为N 165 kg/hm2, 并且农家肥氮的替代率在70%或秸秆氮的替代率在30%时)是可行的,既节省化肥氮投入,又能提高土壤肥力。
[1] 孟琳, 张小莉, 蒋小芳, 等. 有机肥料氮替代部分无机氮对水稻产量的影响及替代率研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 290-296. Meng L, Zhang X L, Jiang X Fetal. Effects of partial mineral nitrogen substitution by organic fertilizer nitrogen on the yield of rice grains and its proper substitution rate[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(2): 290-296.
[2] 唐继伟, 林治安, 许建新,等. 有机肥与无机肥在提高土壤肥力中的作用[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2006, (3): 44-47. Tang J W, Lin Z A, Xu J Xetal. Effect of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on soil nutrient[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2006, (3): 44-47.
[3] 索东让. 长期定位试验中化肥与有机肥结合效应研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2005, 23(2): 71-75. Suo D R. Combined fertilization of chemical and organic fertilizers in a long-term position experiment[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2005, 23(2): 71-75.
[4] 高菊生, 徐明岗, 王伯仁, 等. 长期有机无机肥配施对土壤肥力及水稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(8): 211-214, 259. Gao J S, Xu M G, Wang B Retal.. The effects of rational application of long term organic and chemical fertilizers on soil fertility and rice yield[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(8): 211-214, 259.
[5] 刘守龙, 童成立, 吴金水, 蒋平. 等氮条件下有机无机肥配比对水稻产量的影响探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 106-112. Liu S L, Tong C L, Wu J S, Jiang P. Effect of ratio of organic manure/chemical fertilizer in fertilization on rice yield under the same N condition[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 106-112.
[6] 马俊永, 李科江, 曹彩云, 郑春莲. 有机-无机肥长期配施对潮土土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(2): 236-241. Ma J Y, Li K J, Cao C Y, Zheng C L. Effect of long-term located organic-inorganic fertilizer application on fluvo-aquic soil fertility and crop yield[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007, 13(2): 236-241.
[7] 劳秀荣, 孙伟红, 王真, 等. 秸秆还田与化肥配合施用对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, 40(4): 618-623. Lao X R, Sun W H, Wang Zetal. Effect of matching use of straw and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003, 40(4): 618-623.
[8] 刘杏兰, 高宗, 刘存寿, 等. 有机-无机肥配施的增产效应及对土壤肥力影响的定位研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1996, 33(2): 138-147. Liu X L, Gao Z, Liu C Setal. Effect of combined application of organic manure and fertilizers on crop yield and soil fertility in a located experiment[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1996, 33(2): 138-147.
[9] 李菊梅, 徐明岗, 秦道珠, 等. 有机肥无机肥配施对稻田氨挥发和水稻产量影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(1): 51-56. Li J M, Xu M G, Qin D Zetal.. Effects of chemical fertilizers application combined with manure on ammonia volatilization and rice yield in red paddy soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(1): 51-56.
[10] 张娟, 沈其荣, 张亚丽, 等. 施用预处理秸秆的土壤供氮特征及冬小麦吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2004, 10(1): 24- 28. Zhang J, Shen Q R, Zhang Y Letal.. Effects of application of pretreated rice straw on soil nitrogen supply and nitrogen uptake by winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2004, 10(1): 24-28.
[11] 陈志龙, 陈杰, 许建平, 等.有机肥氮替代部分化肥氮对小麦产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(7): 55-57. Chen Z L, Chen J, Xu J Petal.. Effects of partial mineral nitrogen substitution by organic fertilizer nitrogen on the yield of wheat and its use efficiency[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(7): 55-57.
[12] 刘占军, 谢佳贵, 李书田, 等. 不同氮肥管理对吉林春玉米生长发育和养分吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 38-47. Liu Z J, Xie J G, Li S Tetal. Maize growth and nutrient uptake as influenced by nitrogen management in Jilin province[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(1): 38-47.
[13] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M ]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. Bao S D.Analysis of agricultural chemistry in soil[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[14] 宋歌, 孙波, 教剑英. 测定土壤硝态氮的紫外分光光度法与其他方法的比较[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(2): 288-293. Song G, Sun B, Jiao J Y. Comparison between ultraviolet spectrophotometry and other methods in determination of soil nitrate-N[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(2): 288 -293.
[15] 王小燕, 沈永龙, 高春宝, 等. 氮肥后移对江汉平原小麦子粒产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2010, 30(5): 896 -899. Wang X Y, Shen Y L, Gao C Betal. Effects of postponing N application on grain yield and partial factor productivity of wheat in Jianghan Plain[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2010, 30(5): 896 -899.
[16] 王启现. 夏玉米氮肥高效利用机制研究及周年氮素分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学博士学位论文, 2004. Wang Q X. Efficiency usage of nitrogen fertilizer in summer maize and annual soil-plant N balance under wheat-maize system [ D]. Beijing: PhD dissertation, China Agricultural University, 2004.
[17] 刘新宇, 巨晓棠, 张丽娟, 等. 不同施氮水平对冬小麦季化肥氮去向及土壤氮素平衡的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(2): 296-300. Liu X Y, Ju X T, Zhang L Jetal. Effect of different N rates on fate of N fertilizer and balance of soil N of winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(2): 296-300.
[18] 徐祥玉, 张敏敏, 翟丙年, 等. 施氮对不同基因型夏玉米干物质累积转移的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(4): 786 -792. Xu X Y, Zhang M M, Zhai B Netal. Effects of nitrogen application on dry matter accumulation and translocation of different genotypes of summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(4): 786-792.
[19] 杜金哲, 李文雄, 胡尚连, 等. 春小麦不同品质类型氮的吸收、转化利用及与子粒产量和蛋白质含量的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(2): 253 -260. Du J Z, Li W X, Hu S Letal. Nitrogen assimilation, transfer and utilization in relation to grain protein content and yield of spring wheat genotypes differing in quality[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(2): 253-260.
[20] Dobermann A, Dawe D, Roetter R Petal. Reversal of rice yield decline in a long-term continuous cropping experiment[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2000, 92: 633-643.
[21] 何萍, 金继运, 林葆. 氮肥用量对春玉米叶片衰老的影响及其机理研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1998, 31(3): 1-4. He P, Jin J Y, Lin B. Effects of N application rates on leaf senescence and its mechanism in spring maize[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1998, 31(3): 1-4.
[22] 金继运, 何萍. 氮钾营养对春玉米后期碳氮代谢与粒重形成的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 1999, 32(4): 55 -62. Jin J Y, He P. Effect of N and K nutrition on post metabolism of carbon and nitrogen and grain weight formation in maize[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1999, 32(4): 55-62.
[23] 郭瑞英. 设施黄瓜根层氮素调控及夏季种植填闲作物阻控氮素损失研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学博士学位论文, 2007. Guo R Y. The research of nitrogen regulation in root layer with facilities cucumber and control nitrogen loss of planting catch crops in summer[D]. Beijing: PhD disseration, China Agricultural University, 2007.
[24] 蔡祖聪,钦绳武. 华北潮土长期试验中的作物产量、氮肥利用率及其环境效应[J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(6): 885- 891. Cai Z C, Qin S W. Crop yield, N use efficiency and environmental impact of a long-term fertilization experiment in fluvo aquic soil in north China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(6): 885- 891.
[25] 段英华,徐明岗,王伯仁,黄 晶.红壤长期不同施肥对玉米氮肥回收率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(5): 1108- 1113. Duan Y H, Xu M G, Wang B R, Huang J. Effects of long -term different fertilization on nitrogen recovery efficiency of maize in red soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(5): 1108- 1113.
[26] 黄绍敏, 宝德俊, 皇甫湘荣. 长期定位施肥对玉米肥料利用率影响的研究[J]. 玉米科学, 2006, 14(4): 129-133. Huang S M, Bao D J, Huangpu X Retal.. Effect of Long-term fertilization on fertilizer utilization efficiency on maize in fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2006, 14(4): 129-133.
[29] 王艳博, 黄启为, 孟 琳, 沈其荣. 有机无机肥料配施对菠菜生长和土壤供氮特性的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2006, 29(3): 44-48. Wang Y B, Huang Q W, Meng L, Shen Q R. Effect of combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizer application on growth of spinach and soil nitrogen supply[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2006, 29(3): 44-48.
[30] 张亚丽, 张娟, 沈其荣, 王金川. 秸秆生物有机肥的施用对土壤供氮能力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(12): 1575-1578. Zhang Y L, Zhang J, Shen Q R, Wang J C. Effect of combined application of bioorganic manure and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen supplying characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(12): 1575-1578.
[31] 徐阳春, 沈其荣, 冉炜. 长期免耕与施用有机肥对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(1): 89-96. Xu Y C, Shen Q R, Ran W. Effects of zero-tillage and application of manure on soil microbial biomass C, N, and P after sixteen years of cropping[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(1): 89-96.
[32] 戴明宏, 陶洪斌, 王利纳, 等. 华北平原春玉米种植体系中土壤无机氮的时空变化及盈亏[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(3): 417-423. Dai M H, Tao H B, Wang L Netal. Spatial and temporal dynamics of soil mineral nitrogen and balance analysis during maize season[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(3): 417-423.
[34] 郝晓辉,肖宏宇,苏以荣,等. 长期不同施肥稻田土壤的氮素形态及矿化作用特征[J]. 浙江大学学报: 农业与生命科学版,2007,33(5): 544-550. Hao X H, Xiao H Y, Su Y Retal.. Characteristics of nitrogen forms and mineralization in paddy soils of long-term fertilization experiment[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 2007, 33(5): 544-550.
[35] Sommerfeldt T G, Chang C, Entz T. Long-term annual manure applications increase soil organic matter and nitrogen, and decrease carbon to nitrogen ratio[J]. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 1988, 52: 1668-1672.
[36] 杨生茂, 李凤民, 索东让, 等. 长期施肥对绿洲农田土壤生产力及土壤硝态氮积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(10): 2043-2052. Yang S M, Li F M, Suo D Retal. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil productivity and nitrate accumulation in Gansu Oasis[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(10): 2043-2052.
[37] 武际,郭熙盛,鲁剑巍,等. 连续秸秆覆盖对土壤无机氮供应特征和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2012,45(9): 1741-1749. Wu J, Guo X S, Lu J Wetal. Effects of continuous straw mulching on supply characteristics of soil inorganic nitrogen and crop yields[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(9): 1741-1749.
Effects of partially replacement of inorganic N with organic materials on nitrogen efficiency of spring maize and soil inorganic nitrogen content under the same N input
GAO Hong-jun1,3, ZHU Ping3, PENG Chang3, ZHANG Xiu-zhi3, LI Qiang3, ZHANG Wei-jian1,2*
(1CollegeofAgronomy,NanjingAgriculturalUniversity,Nanjing210095,China; 2InstituteofCropSciences,ChineseAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Beijing100081,China; 3JilinAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Changchun130033,China)
【Objectives】 Study on the effect of proper ratio of organic N replacing chemical N on the N use efficiency and soil N content in the long run will provide base support for the efficient fertilization and sustainable soil fertility. 【Methods】 The long-term experiment on black soil fertility and fertilizer efficiency (Gongzhuling City, Jilin Province) was used, and spring maize cultivar, Zhengdan958 was selected. Plant and soil samples were collected from five treatments: no fertilization (CK), fertilizer N (N), fertilizer NPK (NPK), NPK plus pig manure (MNPK) and NPK with straw (SNPK). The nitrogen accumulation, translocation of maize and N use efficiency were studied at six growing stages of maize, seedling, jointing, belling, tasseling, blister and maturity, under the long-term experiment condition. 【Results】 The nitrogen accumulation of maize is increased from the jointing to belling, and the highest daily accumulation is in the belling stage. In MNPK treatment, the value is 86.44 kg/ha, significantly higher than in NPK and SNPK treatments. The total amounts of N transferred from leaves and straw-sheath to grains were 99.0, 79.7 and 87.2 kg/hm2in MNPK, SNPK and NPK treatments, respectively, with the corresponding contribution to grain N of 51.0%, 47.7% and 47.2% respectively. MNPK shows the significantly higher N translocation and contribution than SNPK and NPK treatments. The partial factor productivity of applied N is over 60 kg/kg in the MNPK treatment. Compared to the NPK treatment, SNPK treatment has no obvious differences on PFPs and N harvest index (NHIs). Soil inorganic nitrogen of the MNPK treatment is higher than that of NPK treatment in the whole growing stage, which reaches the highest amount of 60.83 kg/kg at the belling stage. 【Conclusions】 Replacing chemical N with organic N could improve the accumulation and translocation of inputted nitrogen, improve N use efficiency and increase the capacity of soil N supply in the long-run. Replacing 70% of the N 165 kg/ha input with manure fertilizer N or 30% with maize straw N is proved to be a feasible way in nutrient management of spring maize at black soil region in Jilin.
combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers; spring maize; nitrogen use efficiency; inorganic nitrogen
2014-07-17 接受日期: 2014-12-09
吉林省科技支撑重点项目(20110207);公益性行业(农业)科研专项(201203030-04-04)项目资助。
高洪军(1975—),男,吉林省公主岭市人,副研究员,主要从事土壤肥力与农田生态研究。E-mail: ghj-1975@163.com * 通信作者 Tel: 010-62156856,E-mail: zwj@njau.edu.cn
S141.4; S513
A
1008-505X(2015)02-0318-08
