一种基于人工磁导体的低剖面螺旋天线研究
2015-05-30朱雨薇
朱雨薇
【摘要 】 移动互联网影响移动网络服务以“语音”为中心到“数据”为中心的转变,导致整个电信产业结构发生巨大变化。特别是定位技术的大规模使用,使得系统对天线的要求趋于高增益、小型化、圆极化[1-3]。本文提出一种半球形螺旋天线具有低剖面、圆极化的特点,用人工磁导体做反射面。经优化,该天线的中心频率在2.81GHz,波瓣宽度BW=105°,轴比AR=0.493满足圆极化条件。此外,天线峰值增益高达9.725dBi,证明了该天线的可行性。
【关键字】 圆极化 低剖面 螺旋天线 人工磁导体
This research investigates a low profile circularly hemispherical helical antenna above an artificial magnetic conducting surface. The hemispherical helical antenna gives a wider bandwidth than other antennas, for example micro strip antenna. When compare with that antenna over perfectly electrical conducting, its radiation is better. This thesis researched 3-turns and 5-turns helix above AMC and PEC surface, the result shows AMC ground plane could increase antenna radiation pattern, power gain and optimise the axial ratio.
The simulation software CTS (Computer simulation Technology) MICROWAVE STUDIO (CST MWS) will be used to design and simulate the hemispherical antenna structure, which will carry out the required results. Last but not least, optimization is a vital procedure, the performance will be better after this stage.
KEY WORDS: helical antenna,low profile, circularly polarization, Artificial electromagnetic materials
由于移动互联网的大势发展,使得用户对通信质量的要求越来越高。更为重要的是“4G时代移动互联网的时间、地点、流量、应用差异化会带来愈发明显的流量突发性,一个基站,早、中、晚,甚至每时每刻负载量都存在巨大差异。”康普无线解决方案部销售总监王胜说。而作为基站的一部分,天线也将随之发生变化。虽然说,天线的成本不及基站的百分之三,但是天线的性能好坏直接影响着基站的性能。传统天线用理想电导体(PEC)做反射材料,但根据镜像原理,反射场会产生180°相位差[4]。这要求天线与反射面距离大于? λ。无法满足低剖面的要求。
人工磁导体(AMC Artificial Magnetic Conductor)具有零相位反射特性,可以满足天线的低剖面。并且由于反射场与入射场叠加使天线增益提高3dB[5]。本文研究设计出一款半球面螺旋天线可以满足小型化,宽频带,圆极化的要求。
一、单元设计分析
本文采用的半球形螺旋半径a=1.95cm,天线材料自身半径与馈电的同轴电缆的内导体半径相同,均为=0.05cm,同轴电缆的外导体半径为=0.225 cm。离理想电导体高度h=0.8cm,频率为2.94GHz。如图1。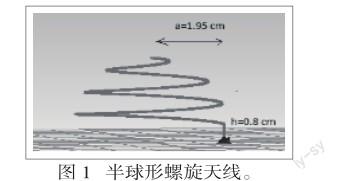
(环绕圈数N=3,半径a=1.95cm,离地高度h=0.8cm)
人工磁导体选用无过孔结构,具有零相位反射特性而且比过孔接口结构简单[6]。本文用方形单元的AMC结构,如图2。像一块夹心饼干一样,方形贴片被2层介质板夹在中间。介质板的介电常数2.5,单层厚度==1.5748 mm,边长L=13.3mm。贴片边长W=0.192*0.192=12.8 mm(其中)。
理论上这种结构的AMC具有较为优良的反射相位特性,因为反射场相位在±90°之间的频带是AMC单元的带宽[7]。图3给出了其反射相位曲线。显然,此单元的中心频点是4.5GHz。反射场相位±90°之间带宽0.73GHz。
为了与天线的2.94GHz匹配,需要改变AMC单元尺寸使中心频点到2.94GHz,,其中单层厚度==1.4606 mm,边长L=25.6mm。贴片边长W=24.6mm,带隙间隔g=0.5mm。更改后得到的反射相位曲线如图5,显示其中心频点为2.94GHz。可以与天线匹配,使天线的性能达到最佳。
二、天线设计与仿真
在各种类型的天线中,螺旋天线具有更宽的带宽,更是广泛应用在卫星通信和定位系统中。[8]而半球形螺旋天线与之相比具有更低的剖面,更小的轴比,而且同样有较好的圆极化特性[9]。理论上,AMC单元组成的反射面为无限大的结构。但在实际中,AMC反射面不可能无限增大。故本文采用4×4的结构模型来代替无限大的反射面。图5显示了基于AMC反射面的半球形螺旋天线,参数设置如下:绕线圈数N=5,天线半径a=1.85cm,离地高度h=0.4cm,天线自身半径=0.05 cm, AMC反射面用的之前改良后的单元组成的4×4的结构模型(但在仿真中必须作为一个整体构成,不能由16块小的AMC单元拼凑。不然会有误差)。由图6、图7可知,在C/λ=1.13时,即频率f=2.81GHz时,远场轴比具有接近0的最小值AR=0.493,极化方式为圆极化,波瓣宽度达到105°。且此时的增益最大,为G=9.725dBi。较普通天线而言性能更优化。


三、结论
半球形螺旋天线的由来已久,但基于人工磁导体平面使得该天线的性能发挥到最优。通过数值仿真,证明与PEC理想电导体相比,人工磁导体具有更宽的带宽。经过仿真优化,改变天线环绕圈数,离地高度,馈电位置等参数,得到合成天线极化方式为圆极化,增益达到9.725dBi,高于普通圆极化天线。
参 考 文 献
[1]Constantine A. Balanis. (c1982) Antenna theory: analysis and design, Cambridge, Mass.; London: Harper & Row, c1982
[2] Robert S. Elliott (Robert Stratman). (c2003) Antenna theory and design Author,RevisedEd,Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, c2003, pp. 361
[3] Jeffrey R. Clark,(2004)Multifilar Hemispherical Helical Antennas,IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society Symposium, 2004, June 2004, Vol.3, pp.3333-3336
[4]Alexandros P. Feresidis; George Goussetis;Shenhong Wang, and John (Yiannis) C. Vardaxoglou.(2005) Artificial Magnetic Conductor Surfaces and Their Application to Low-Profile High-Gain Planar Antennas, Ieee translations on antennas and propagation,vol. 53, No. 1, Jan. 2005
[5]Maisarah Abu, M. K. A. Rahim, S. A. Hamzah (2010) A Meandered Triple-band Dipole Antenna with 920 MHz Artificial Magnetic Conductor, Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, July 2010, pp.1-4
[6] Goussetis, G. ; Feresidis, A.P. ; Vardaxoglou, J.C. (2006) Tailoring the AMC and EBG characteristics of periodic metallic arrays printed on grounded dielectric substrate, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2006, Vol.54(1), pp.82-89 [Peer Reviewed Journal]
[7] Kretly, L.C. ; Silva, A.M.P.A.(2003) The influence of the height variation on the frequency bandgap in an AMC, artificial magnetic conductor, for wireless applications: an EM experimental design approach, Proceedings of the 2003 SBMO/IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference - IMOC 2003, Sept. 2003, Vol.1, pp.219-223
[8] Hui, H.T. ; Chan, K.Y. ; Yung, E.K.N. (2003) The low-profile hemispherical helical antenna with circular polarization radiation over a wide angular range, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, June 2003, Vol.51(6), pp.1415-1418
[9] Chan, K.Y. ; Hui, H.T. ; Yung, E.K.N. (2001) Central-fed hemispherical helical antenna, IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, July 2001, Vol.4, pp.545-548
[10]Safaai-jazi, A. (1996) Radiation characteristics of a spherical helical antenna
,IEEE Proceedings - Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 1996, Vol.143(1), pp.7
[11]杨奋华;汤炜.一种新型的高增益低剖面天线[J].通信技术.2013.01.PP.35-41
[12]Grange, F. ; Delaveaud, C. ; Madhjoubi, K. (2010) Miniaturization of artificial magnetic conductors, Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, July 2010, pp.1-4
