血小板衍生生长因子−C对体外培养血管内皮细胞及间充质干细胞的影响
2015-04-21王子婧钱智勇郭希民高德伟
王子婧,钱智勇,郭希民,高德伟
血小板衍生生长因子−C对体外培养血管内皮细胞及间充质干细胞的影响
王子婧,钱智勇,郭希民,高德伟*
(解放军总医院南楼临床部综合外二科,北京 100853)
观察血小板衍生生长因子−C(PDGF-C)对体外培养的血管内皮细胞(VECs)及间充质干细胞(MSCs)的影响。采用培养的大鼠主动脉内皮细胞和MSCs,应用细胞直接计数法、噻唑蓝比色法(MTT法)评价细胞的增殖情况,流式细胞术检测细胞周期,利用Transwell细胞迁移实验和细胞划痕实验测定细胞迁移能力。PDGF-C能明显刺激VECs和MSCs的增殖,增加两种细胞S期细胞的比例,对VECs增殖呈剂量依赖关系,对MSCs的促增殖作用在20μg/L达高峰。同时,PDGF-C促进VECs和MSCs的迁移能力,对MSCs迁移作用强于VECs。PDGF-C可促进培养的VECs、MSCs的增殖与迁移能力。
大鼠;血小板衍生生长因子C;血管内皮细胞;间充质干细胞;细胞增殖;迁移
血管内皮细胞(vascular endothelial cells,VECs)是血管内循环血液与中层平滑肌细胞之间的机械屏障,维持机体重要的生理功能。内皮细胞损伤后脱落,胶原及组织因子暴露,是形成动静脉血栓的重要始动因素。因此,血管内皮损伤后修复可作为血栓性疾病治疗的方法之一。其修复原理主要包括两方面:一是增强成熟内皮细胞的增殖和分化能力,加速内皮的自身修复;二是动员间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)归巢到损伤部位,内皮化后替代修复[1]。血小板衍生生长因子(platelet derived growth factor,PDGF)是正常组织生长和维持的重要生长因子,包括至少PDGF-A,B,C,D 4个成员,其中PDGF-A和B的研究已较成熟,而PDGF-C则是新发现成员之一。研究表明PDGF-C有较强的促进血管新生能力[2.3],其所具有的多重生物学效应是血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF)等其他生长因子所不具备的独特功能[4]。且PDGF-C参与了动脉损伤后修复的过程,机制是促血管平滑肌细胞凋亡或干预血管平滑肌细胞迁移[5],而对内皮细胞和干细胞的作用尚没有明确涉及。为此,我们利用PDGF-C对体外培养的主动脉内皮细胞和骨髓MSCs进行刺激,测定细胞增殖情况,评价细胞的迁移能力,从而了解PDGF-C对VECs及MSCs的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂
PDGF-C(美国Peprotech公司);DMEM细胞培养液(美国Gibco公司);胎牛血清(fatal bovine serum,FBS);流式细胞周期检测试剂盒、Hoechst33258染色试剂盒(碧云天生物技术研究所);噻唑蓝(美国Sigma公司)。
1.2 仪器
超净工作台(苏州市净化设备公司YJ-875);二氧化碳培养箱(美国Shell-Lab2323型);倒置相差荧光显微镜(日本Nikon公司);流式细胞仪(美国Elite SP型);酶标分析仪(美国Bio-RAD Model 550型)、细胞计数仪(美国FJ-2003型)。
1.3 细胞培养
VECs的原代培养和体外增殖:过量1g/L戊巴比妥钠注入SD大鼠(150g)的腹腔内,麻醉致死,75%乙醇浸泡消毒3min后移入超净台,无菌条件下打开胸腔暴露胸主动脉,快速取胸主动脉。用眼科镊夹除动脉外周的结缔组织及脂肪,磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffer solution,PBS)冲洗管腔内面残留血液。眼科剪剪开血管腔,将血管剪成2mm×2mm大小均匀的组织块后转移到25ml的培养瓶中,在含10% FBS的DMEM中培养,待内皮细胞长成典型的铺路石样、细胞融合达到80%~90%,经胰酶消化后传代、取第5~8代细胞用作实验,因子Ⅷ免疫荧光鉴定VECs。将存有MSCs(军事医学科学院提供)的冻存管从液氮中取出,37℃水浴复苏,用含10% FBS的α-MEM培养液常规培养。
1.4 MTT法检测细胞增殖
分别取第5代对数生长期的VECs和MSCs,消化离心后计数,以2×104个/ml密度接种于96孔培养板,常规培养24h后换用2%FBS继续培养24h后,分别加入不同浓度的PDGF-C(10,20,30,40,50μg/L),设对照组,加入等体积PBS。每组设5个复孔,培养24h后加入MTT溶液(5g/L)20μl,继续孵育4h后弃培养基,每孔加入150μl二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide,DMSO),吹匀后492nm波长处测吸光度值(492nm),以时间为横轴,吸光度为纵轴绘制细胞生长曲线。
1.5 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期
取VECs和MSCs,常规培养24h,换含2%FBS的培养基及培养24h后,加入PDGF-C(20μg/L),对照组加入等量的PBS,再孵育24h后,胰酶消化3min,轻轻吹打呈细胞悬液,800r/min离心后,PBS漂洗3遍,重复离心,加入1ml PBS重悬细胞调整细胞密度至1.5×106/ml,过300目细胞筛,去除团聚细胞,加入-20℃预冷的70%乙醇溶液,4℃过夜。PBS充分漂洗离心后加入10μl RNA酶,37℃水浴30min,后加入25μl碘化丙啶染色,避光30min放于4℃冰箱,上样前轻弹试管,流式细胞仪检测细胞周期(激发波长488nm)。
1.6 细胞划痕实验
将两种细胞以2×105/ml的密度接种在6孔培养板中常规培养后,换用含2%FBS细胞培养基培养,细胞融合达到80%后,用20μl无菌枪头在每孔匀速纵向划一道划痕,用PBS轻轻冲洗细胞,加入含浓度为20μg/L的PDGF-C培养基,对照组加入等体积PBS。于0,6,12,24h进行细胞拍照取材,观察各组细胞向空白处迁移的情况。
1.7 Transwell细胞迁移实验
用50mg/L Matrigel稀释8倍后滴加于Transwell小室底部膜的下室面,在超净台内风干后备用。取第5代对数期细胞消化离心后,PBS洗1~2遍,用含10g/L牛血清白蛋白的培养基重悬细胞,调整细胞密度为2×105/ml。在Transwell小室内加200µl细胞悬液,下室加入500µl含20μg/L PDGF-C的培养基,对照组加入等体积PBS。于二氧化碳培养箱中培养24h后,用4%多聚甲醛液4℃固定15min,PBS充分清洗2遍,每次3min。分别加入Hoechst33258染色液,室温静置30min,充分染色后PBS清洗,荧光倒置显微镜下观察并拍照取材。
1.8 统计学处理

2 结 果
2.1 细胞形态及鉴定
原代培养VECs 4d时,显微镜下可见有少量的细胞迁出贴壁生长,细胞呈短梭形或多角形。培养至12d,细胞贴壁生长达到培养瓶面积>2/3,呈现内皮细胞典型的“铺路石”样特征。取第4代生长良好的VECs,经因子Ⅷ抗体进行细胞免疫荧光化学染色鉴定,呈阳性表现;复苏后的MSCs融合单层,细胞形态大多呈长梭形或多角形,符合MSCs的细胞形态(图1)。
2.2 PDGF-C对细胞增殖的影响
观察不同浓度下PDGF-C对VECs和MSCs增殖的影响。结果显示,与对照组相比,加入PDGF-C的实验组细胞增殖能力明显增强,且差异有统计学意义(<0.05)。加入PDGF-C后,两种细胞均在第4天增殖达高峰。随着PDGF-C浓度的增加,VECs的增殖能力逐渐增强,呈现出一种浓度效应关系(图2);而MSCs的增殖在PDGF-C为20μg/L浓度时达高峰(<0.01;图3),当浓度继续增加时,MSCs的增殖能力不再继续增强。

图1 血管内皮细胞与间充质干细胞的细胞培养及鉴定
Figure 1 Cultivation and identification of VECs and MSCs
VECs: vascular endothelial cells; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; A: primary VECs (×100); B: cultured MSCs (×100); C: VECs Dapi nuclear staining (×400); D: positive expression of factor Ⅷ in VECs (×400)
2.3 PDGF-C对细胞周期的影响
实验结果表明,经过PDGF-C的刺激,VECs及MSCs细胞周期各时相的细胞数占细胞总数的百分比与对照组相比有明显不同。其中,MSCs细胞周期中G1期细胞比例明显降低(<0.05),S期细胞比例与对照组相比显著增加(<0.05),G2+M期细胞比例变化不大(>0.05;图4)。
PDGF-C同样增加了VECs增殖期S期细胞比例(<0.05),G1期细胞比例明显降低(<0.05),G2+M期细胞比例有所增加,但差异无统计学意义(>0.05;图5)。
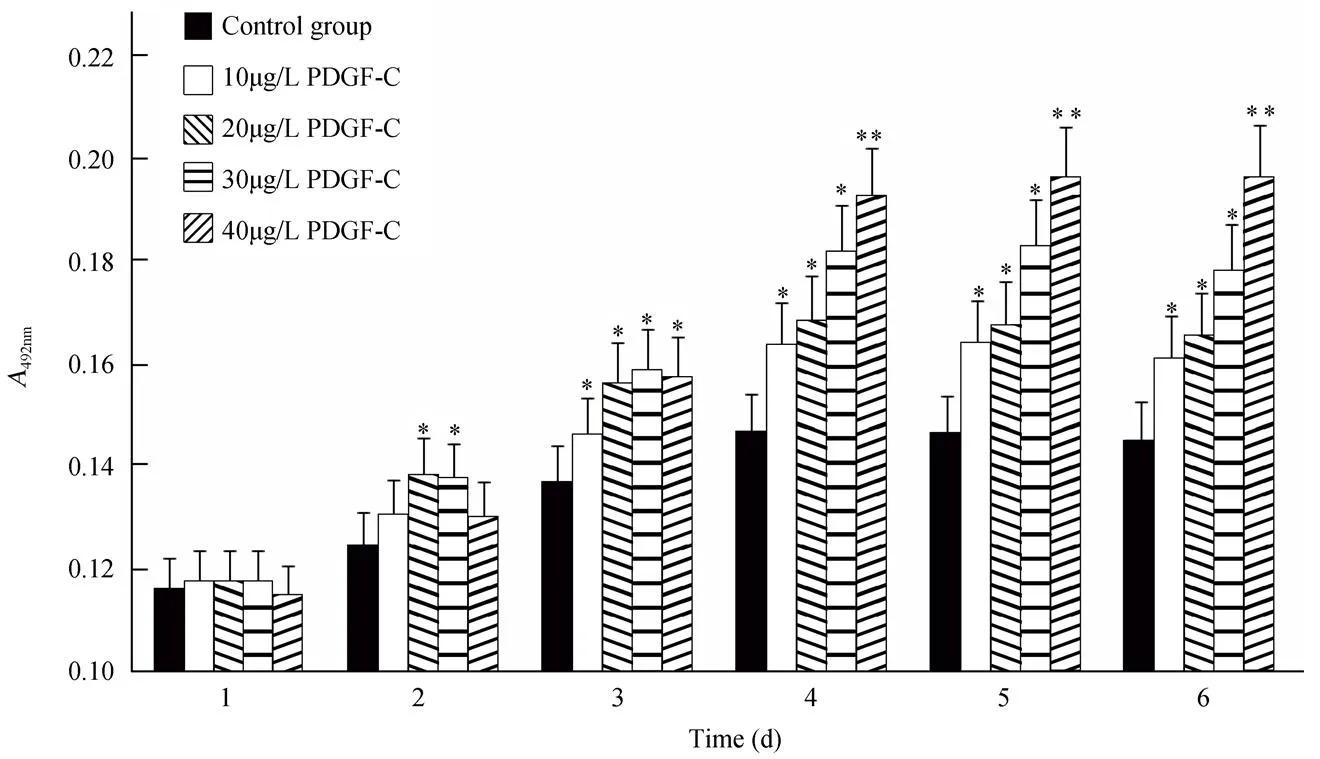
图2 PDGF-C在不同浓度时对血管内皮细胞增殖能力的影响
Figure 2 Effects of PDGF-C in different concentrations on VECs proliferation
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; VECs: vascular endothelial cells. PDGF-C promotes VECs proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Compared with control group,*<0.05,**<0.01

图3 PDGF-C在不同浓度时对间充质干细胞增殖能力的影响
Figure 3 Effects of PDGF-C in different concentrations on MSCs proliferation
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells. PDGF-C promotes MSCs proliferation, and MSCs proliferation reaches peak at 20μg/L concentration of PDGF-C. Compared with control group,*<0.05,**<0.01

图4 PDGF-C对间充质干细胞周期的影响
Figure 4 Effects of PDGF-C on MSCs phases
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells. Compared with control MSCs,*<0.05
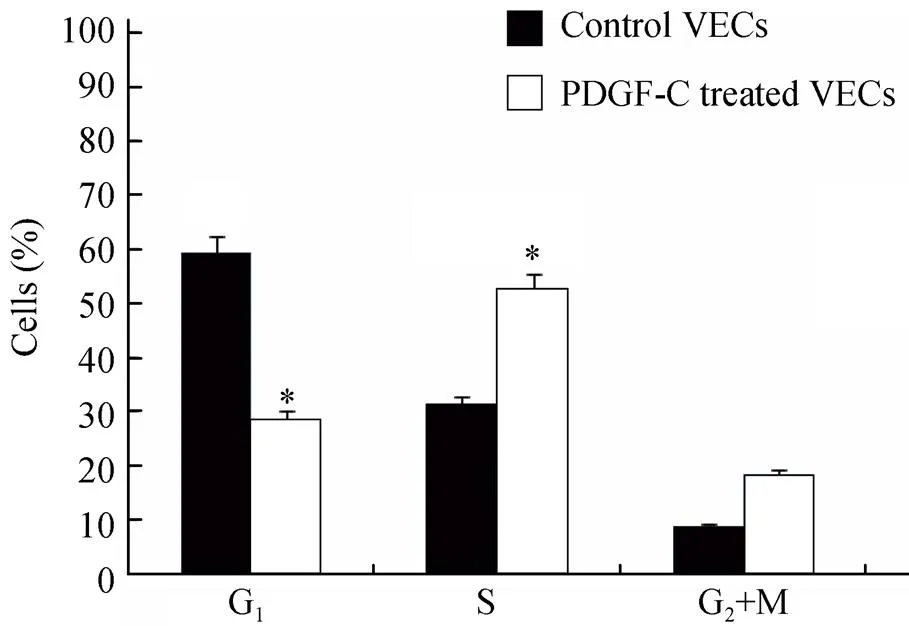
图5 PDGF-C对血管内皮细胞周期的影响
Figure 5 Effects of PDGF-C on VECs phases
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; VECs: vascular endothelial cells. Compared with control VECs,*<0.05
2.4 细胞迁移的划痕实验检测
结果显示,划痕后,加入PDGF-C后的MSCs向空白处迁移的细胞数明显多于对照组(图6);VECs向空白处迁移的细胞有所增加,但迁移能力的增强不如MSCs明显(图7)。
2.5 细胞迁移能力Transwell实验检测
培养24h后,可见VECs及MSCs迁移到小室底部膜的下室面,细胞迁出后,形态呈细长型。加入PDGF-C后,小室膜下室面VECs及MSCs数量都有增加,且对MSCs的迁移能力影响更大(图8)。
3 讨 论
内皮细胞完整性的破坏是导致多种血管性疾病的重要原因,最常见的疾病就是动静脉血栓的形成。因此,保护并维持血管内膜完整性、减轻内皮损伤及加快内皮损伤修复是防治血管性疾病的关键环节。PDGF家族是维持组织正常生长的重要生长因子,PDGF-C是该家族成员之一,在多种正常组织多个阶段都有表达,参与生物体的生长发育。在成熟的组织中,PDGF-C主要表达于肾、睾丸、肝、心及中枢神经系统等[6]。在脉管系统中,PDGF-C主要表达于血管平滑肌细胞[7]。PDGF-C通过结合并活化PDGF受体a(PDGFR-a),使信号传递进入细胞[6],而其活化形式PDGF-CC不仅可和PDGFR-a的同型二聚体PDGFR-aa具有很高亲和力,同时也可与PDGF-a/β异二聚体相结合[3,8],通过激活特异酪氨酸蛋白激酶,能促进细胞DNA合成和分裂增殖[8]。多项实验研究表明PDGF-C有较强的促进血管新生能力[2,3]。有研究显示,灌注PDGF-C可促进缺血心脏的血供重建及诱导缺血肢体的血管新生,这些多重生物学效应是VEGF和bFGF等其他生长因子所不具备的独特功能[4]。Banfi等[10]研究显示PDGF-C能引起VEGF蛋白水平的上调,通过使VEGF蛋白水平上调使血管局部VEGF浓度增高,动员更多内皮祖细胞到达损伤部位,修复损伤的内皮及促进血管的新生[11]。

图6 间充质干细胞细胞迁移能力划痕实验
Figure 6 Cell scratch test for detection of MSCs migration (×100)
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells. A: control MSCs; B: PDGF-C treated MSCs

图7 血管内皮细胞细胞迁移能力划痕实验
Figure 7 Cell scratch test for detection of VECs migration (×100)
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; VECs: vascular endothelial cells. A: control VECs; B: PDGF-C treated VECs

图8 血管内皮细胞及间充质干细胞transwell迁移实验
Figure 8 Transwell assay for detection of VECs and MSCs migration at 24h (×100)
PDGF-C: platelet-derived growth factor-C; VECs: vascular endothelial cells; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells. A: control VECs; B: PDGF-C treated VECs; C: control MSCs; D: PDGF-C treated MSCs
本实验证实PDGF-C能明显促进VECs和MSCs的增殖。流式细胞周期也证实了PDGF-C能刺激停滞于G0/G1期的细胞进入分裂增殖周期,S期细胞比例增大,说明处于活跃的DNA复制与合成期的细胞量有所增加,这也证实了PDGF-C能促进VECs及MSCs内DNA的合成,加快有丝分裂及增殖。
PDGF-C在组织的损伤修复中不仅表现其丝裂原活性,同时能增加细胞的迁移能力。研究表明PDGF-C可促进基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)的上调[12],MMPs通过其酶解能力,减少细胞外基质,从而促使细胞迁移[13],而MMP-2和MMP-9均可刺激局部组织血管的新生[14]。在细胞划痕实验及Transwell细胞迁移实验中,观察到20μg/L的PDGF-C能明显促进VECs及MSCs的迁移,而其对MSCs促进作用更为明显。
综上所述,PDGF-C不但能增强VECs及MSCs的增殖能力,同时也能促进其迁移。以上生物学作用可在血管损伤性疾病的防治中提供新思路,不但有效地增强内皮细胞的增殖修复,也可促进干细胞在体内的归巢与迁移,共同促进内皮损伤后的修复。
[1] Hristov M, Erl W, Weber PC. Endothelial progenitor cells: mobilization, differentiation, and homing[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2003, 23(7): 1185−1189.
[2] Li X, Tjwa M, Moons L,Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PDGF-CCeffects on endothelial cells and their progenitors[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115(1): 118−127.
[3] Cao R, Brokenhielm E, Li X,. Angiogenesis stimulated by PDGF-CC, a novel member in the PDGF family, involves activation of PDGFR-alphaalpha and-alphabeta receptors[J]. FASEB J, 2002, 16(12): 1575−1583.
[4] Leistner DM, Fischer-Rasokat U, Honold J,. Transplantation of Progenitor Cells and Regeneration Enhancement in Acute Myocardial Infarction (TOPCARE-AMI): final 5-year results suggest long-term safety and efficacy[J]. Clin Res Cardiol, 2011, 100(10): 925−934.
[5] Ostan A, Heldin CH. Involvement of platelet-derived growth factor in disease: development of specific antagonists[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2001, 80: 1−38.
[6] Aase K, Abramsson A, Karlsson L,. Expression analysis of PDGF-C in adult and developing mouse tissues[J]. Mech Dev, 2002, 110 (1−2): 187−191.
[7] Uutela M, Lauren J, Bergsten E,. Chromosomal location, exon structure, and vascular expression patterns of the human PDGF-C and PDGF-D genes[J]. Circulation, 2001, 103(18): 2242−2247.
[8] Gilbertson DG, Duff ME, West JW,. Platelet-derived growth factor C(PDGF-C), a novel growth factor that binds to PDGF alpha and beta receptor[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(29): 27406−27414.
[9] Marmur ID, Poon M, Rossikina M,. Induction of PDGF-responsive genes in vascular smooth muscle. Implications for the early response to vessel injury[J]. Circulation, 1992, 86(Suppl 6):Ⅲ53−60.
[10] Banfi A, von Degenfeld G, Gianni-Barrera R,. Therapeutic angiogenesis due to balanced single-vector delivery of VEGF and PDGF-BB[J]. FASEB J, 2012, 26(6): 2486−2497.
[11] Jiang K, Li CY, Meng QY,. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells in the treatment of chronic deep venous thrombosis[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2010, 25(1): 61−63. [姜 坤, 李传勇, 孟庆友, 等. 内皮祖细胞移植治疗慢性深静脉血栓形成的实验研究[J]. 中国普通外科学杂志, 2010, 25(1): 61−63.]
[12] Wagsater D, Zhu C, Bjorck HM,. Effects of PDGF-C and PDGF-D on monocyte migration and MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2009, 202(2): 415−423.
[13] Inkinen K, Turakainen H, Wolff H,. Expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in experimental granulation tissue[J]. APMIS, 2000, 108(5): 318−328.
[14] Collen A, Hanemaaijer R, Lupu F,. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-mediated angiogenesis in a fibrin-collagen matrix[J]. Blood, 2003, 101(5): 1810−1817.
(编辑: 周宇红)
Platelet-derived growth factor-C promotes proliferation and migration of vessel endothelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells
WANG Zi-Jing, QIAN Zhi-Yong, GUO Xi-Min, GAO De-Wei*
(Second Department of Geriatric Comprehensive Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China)
To determine the effect of platelet-derived growth factor-C (PDGF-C) on vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) culturedo.The VECs were isolated from thoracic aorta of SD rats and then cultured. Cryopreserved MSCs were cultured after water bath at 37℃. Cell counting and MTT assay were used to detect the effect of PDGF-C (0, 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50μg/L) on cell proliferation. Flow cytometry was used to detect cell phases. Transwell assay and cell scratch test were used to detect cell migration.PDGF-C significantly promoted the proliferation of VECs and MSCs, and increased the percentage of the cells arrested at S phase. Its effect on the VECs proliferation was found in a dose-dependent manner. PDGF-C of 20μg/L promoted the MSCs proliferation at a summit. PDGF-C also promoted the migration ability of cultured VECs and MSCs, especially on MSCs.PDGF-C promotes the proliferation and migration of cultured VECs and MSCs.
rats; platelet-derived growth factor-C; vascular endothelial cells; mesenchymal stem cells; cell proliferation; migration
R329.2+8
A
10.11915/j.issn.1671-5403.2015.08.142
2015−04−15;
2015−05−07
高德伟, E-mail: gaodw301@sina.com
