PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中的传输特性
2015-03-18胥克涛袁扬胜
胥克涛,袁扬胜,冯 霞,屈 军
(安徽师范大学物理与电子信息学院,芜湖241000)
引 言
激光在大气遥感、目标追踪、远距离光通信等领域得到了广泛的应用[1-12],光束在传输过程中,湍流会导致光束质量变差。近年来,很多学者研究发现,相对于完全相干光,部分相干光束或特殊轮廓光束受湍流影响小[13-16]。WU等人利用高斯-谢尔模型部分相干光以及WANG和LÜ等人利用部分相干扭曲各向异性高斯-谢尔模型光束和部分相干厄米-余弦高斯光束进行传输的研究都证实了这一结论[13,17-20]。最近,激光光束阵列在大气中的传输特性相继得到研究。ZHOU等人研究了高斯光束阵列和部分相干平顶(partially coherent flat-topped,PCFT)光束阵列在大气湍流中的传输特性[21-23],EYYUBOGLU等人研究了激光光束阵列在大气湍流中的闪烁特性[24]。
特殊轮廓激光束在大气湍流中的传输同样也得到广泛研究,CAI等人研究了各种空心光束在大气湍流中的传输特性[25];WANG等人分析了部分相干拉盖尔-高斯矢量光束在大气湍流中偏振变化特性[26];JI等人探究了部分相干厄米-高斯光束在大气湍流中的扩散特性[27]。从调研的文献看,只有 KOROTKOVA等人研究了电磁光束在海洋湍流中的偏振特性[28],HANSON等人研究了激光光束在水下湍流的传输特性[29],TANG等人研究了径向偏振环状光束在湍流海洋中的光谱密度、方均根束宽、偏振度和桶中功率[30-33],但PCFT光束阵在海洋湍流中的传输特性相对较少。
鉴于此,假设光束在传输过程中没有发生吸收和散射现象,且随光束传输距离的增加,海洋湍流的强弱不发生变化,本文中基于惠更斯-菲涅耳原理和魏格纳分布函数的二阶矩理论得到了部分相干平顶光束阵列在均匀的各向同性的海洋湍流中传输因子、有效曲率半径和瑞利长度的解析表达式,数值计算并简要分析了它们与光束的相干长度、海水温度与盐度起伏、动能耗散率、温度方差耗散率等参量的关系。得到相对于部分相干高斯光束、部分相干平顶光束、部分相干高斯光束阵列,PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中传输时受海洋湍流的影响相对更小。所得结果对研究光通信和激光实际传输有一定的参考价值。
1 理论模型
在直角坐标系中,PCFT光束阵列在源平面(z=0)的电场表达式为[16]:
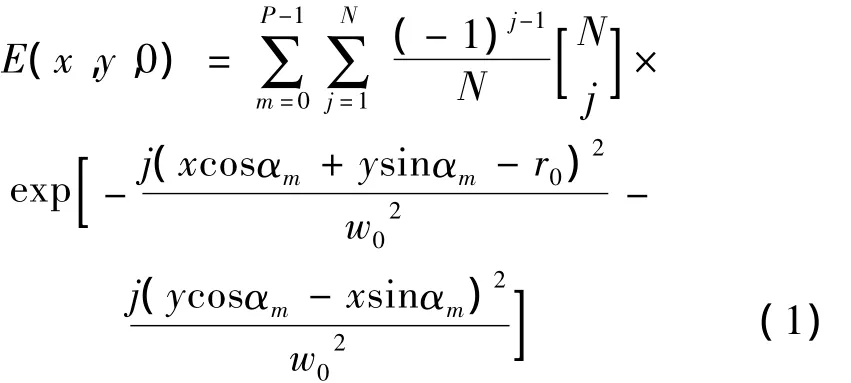
式中,j表示光束的阶数,j=0,1,2,…,N;m 表示光束阵列中小光束的个数,m=0,1,2,…,P-1;w0为源场中高斯光束的束腰宽度;r0为光束阵列的半径;αm表示小光束与x轴所成的角度,αm=mα0,α0=2π/P。
在源平面上交叉谱密度函数可以表示为:
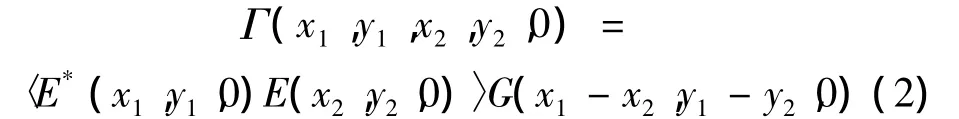
式中,

式中,(x1,y1),(x2,y2)为源平面任意两点,〈〉表示求平均值,*表示复共轭,σl表示光束横向相干长度[34]。
在近轴近似下,根据广义惠更斯-菲涅耳原理,PCFT光束阵列经相应坐标变化后通过湍流介质的交叉谱密度可表示为[35]:
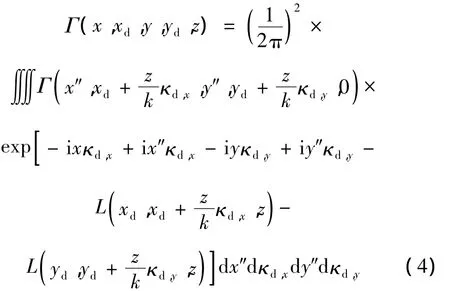
式中,k=2π/λ 为波数。(x,y),(xd,yd)为距离光源面z处接收面上的两点,κd=(κd,x,κd,y)表示空间频率域的位置矢量。exp[-L(xd,xd′,z)],exp[-L(yd,yd′,z)]项表示湍流介质对光束传输的影响,其表达式为:
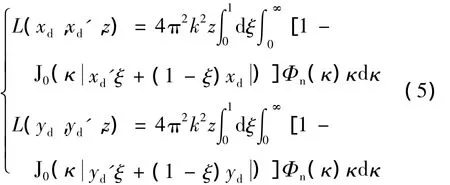
式中,J0为0阶贝塞尔函数,ξ为距离的归一化积分变量,Φn为折射率指数波动的空间功率谱,κ为空间频率,光束经过湍流介质传输距离z后,其交叉谱密度的魏格纳分布函数可以表示为[35]:
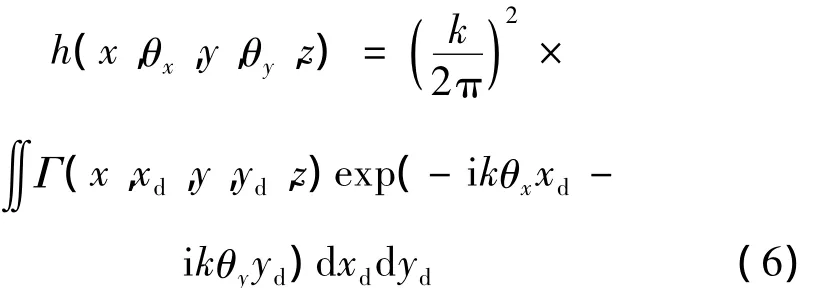
式中,→θ=θx,θ()y表示光束传输角度。kθx,kθy分别表示沿x方向和y方向的波数。将(1)式、(2)式、(4)式代入(6)式,经过运算可得:
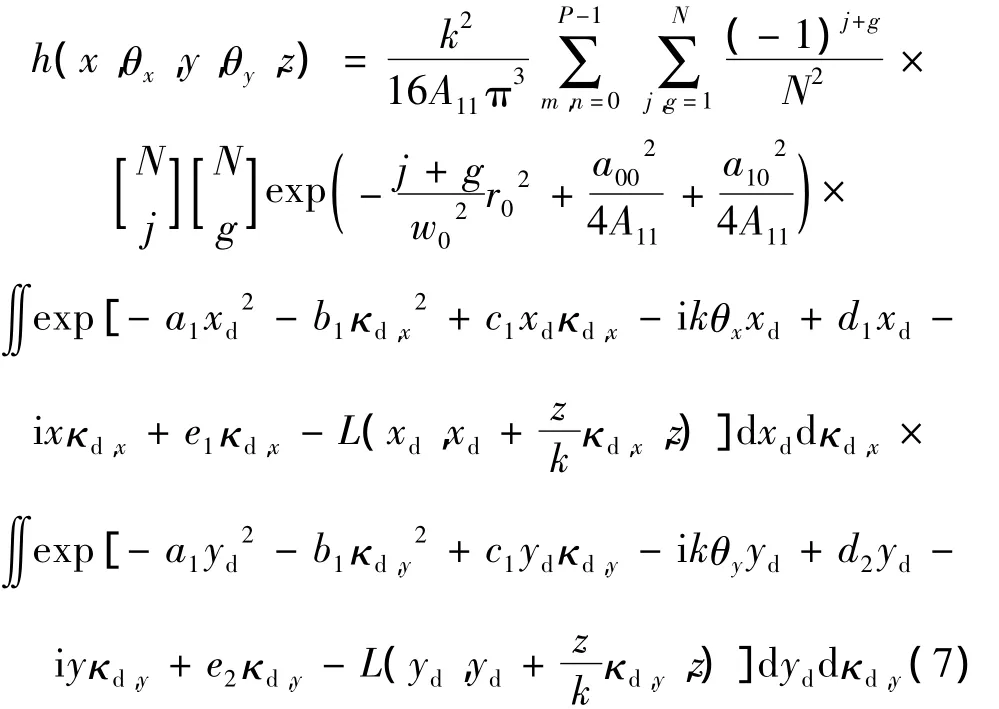
式中,j,g和m,n是为了说明在交叉谱密度中任意两点间的相互关系时所对应的光束阶数和光束阵列中小光束的个数。

根据定义,维格纳分布函数的(n1+n2+m1+m2)阶矩可以表示为:
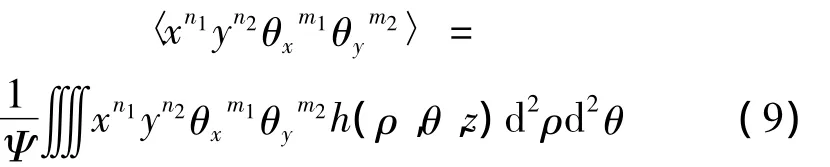
式中,Ψ表示光束总功率:
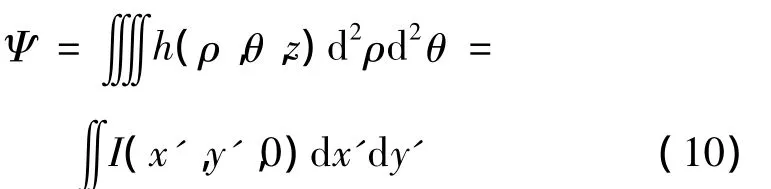
将(1)式、(2)式带入(10)式,经过运算可得:
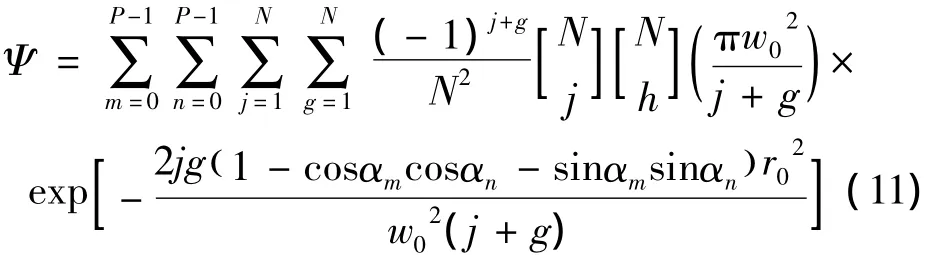
将(7)式带入(9)式可得:
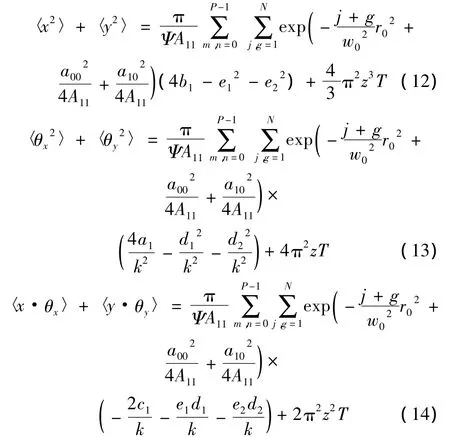
式中,
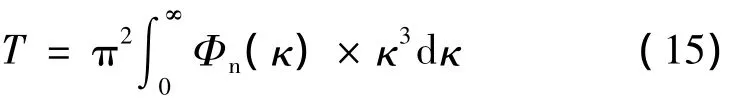
其中,海洋湍流的空间功率谱函数[36-37]为:
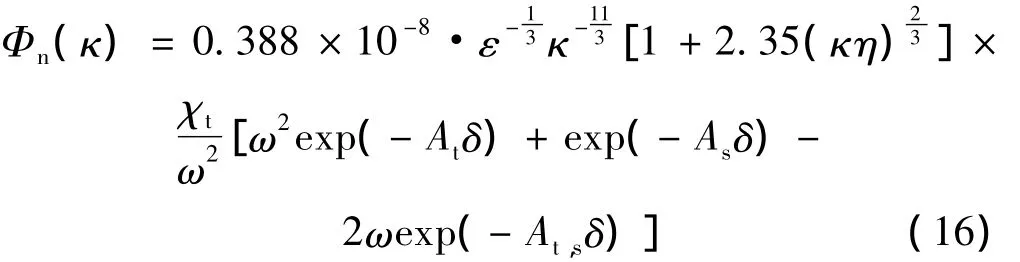
式中,χt为温度方差耗散率,从海洋表面到深水层的取值范围为10-10K2·s-1~10-2K2·s-1;ε为单位质量湍流动能耗散率,取值范围为10-10m2·s-3~10-4m2·s-3;η表示柯尔莫哥诺夫海洋湍流内尺度,一般取值为η=10-3m;ω表示温度起伏和盐度起伏相对强弱的关系,其在海水中变化范围是-5~0,-5表示由盐度起伏占主导地位引起的光学湍流,0表示由温度起伏占主导地位引起的光学湍流[36-37]。参量 At=1.863 ×10-2,As=1.9 × 10-4,At,s=9.41 × 10-3,δ=8.284(κη)4/3+12.978(κη)2。
在上述运算过程中,用到了以下关系式[35]:
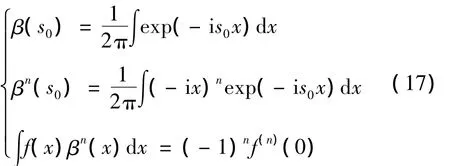
式中,β(s0)为参考文献[35]中给出的积分公式,用这个积分关系得到β函数,(17)式中第3个公式为本文中用到的积分关系。
1.1 PCFT光束阵列传输因子
光束M2的表达式可用(9)式中的二阶矩定义为[35]:
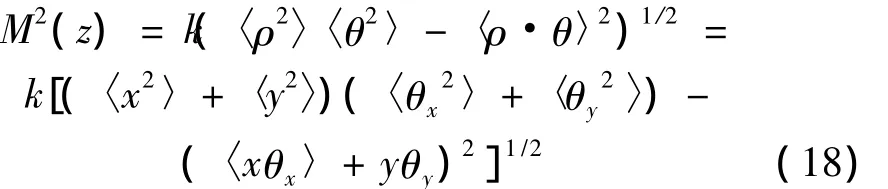
将(12)式~(14)式代入(18)式,可得在湍流介质中PCFT光束阵列的传输质量因子为:
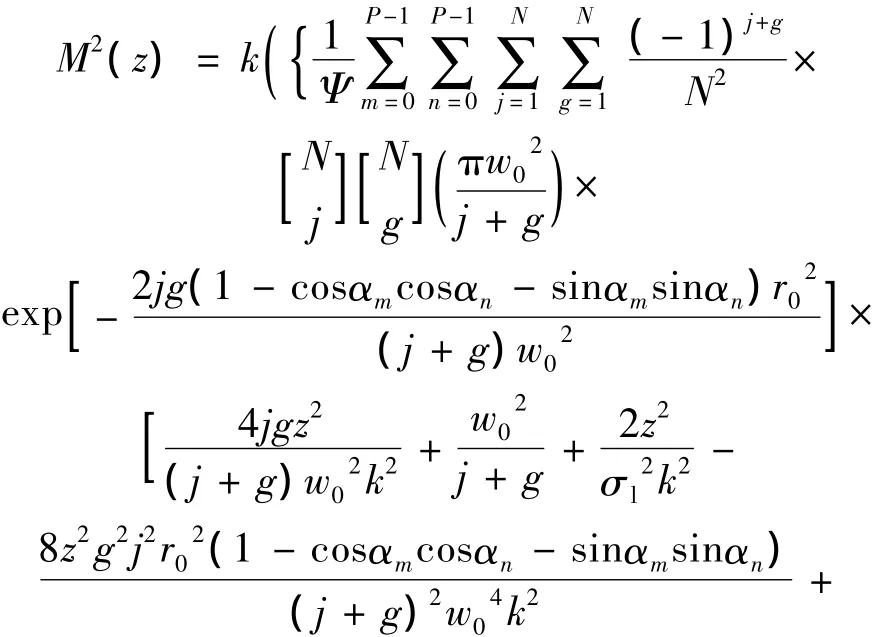
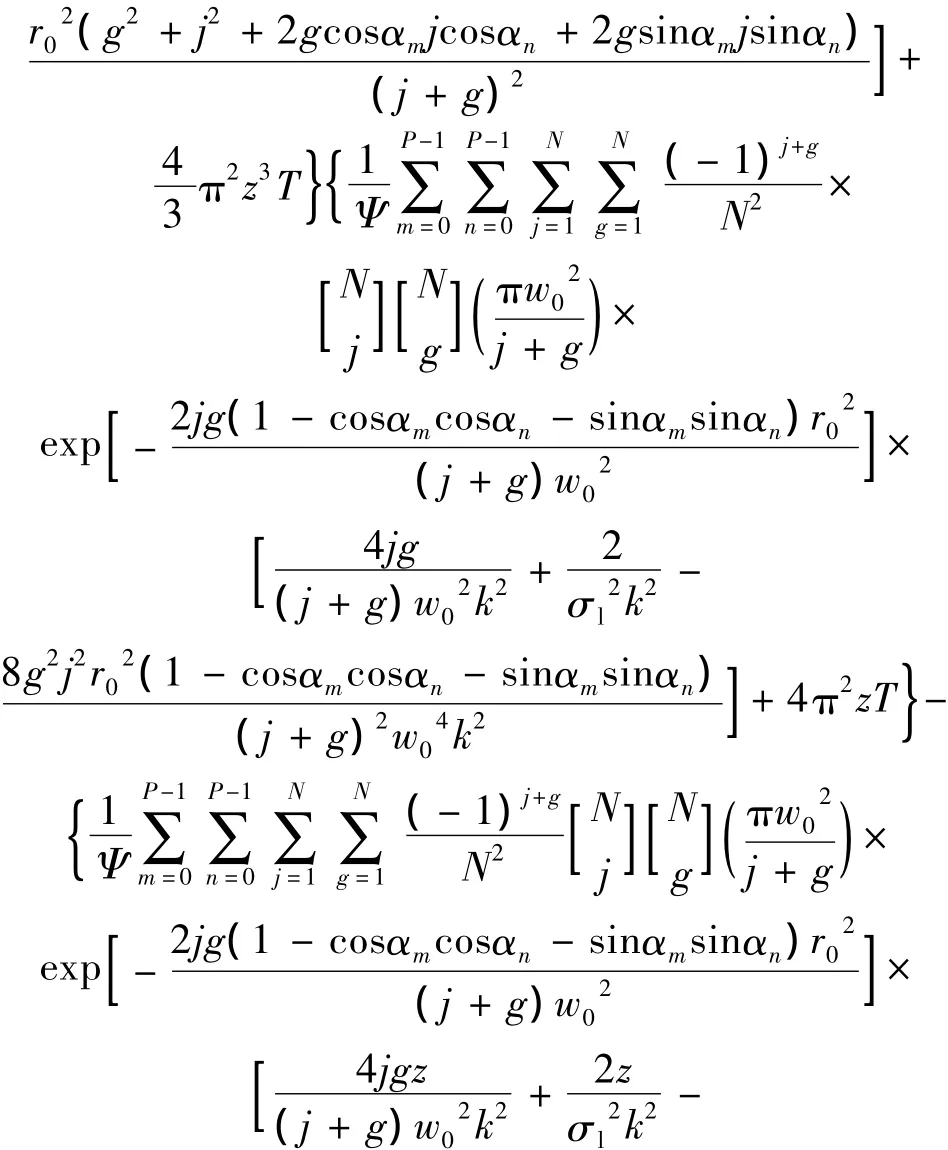
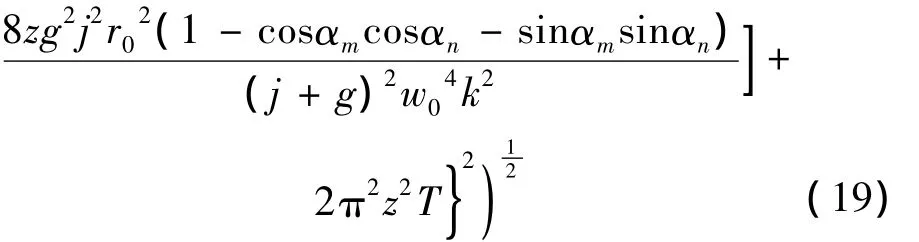
在Φn(κ)=0时,(19)式表示PCFT光束阵列在自由空间中的质量传输因子。(19)式可用来探究部分相干高斯光束(P=1,N=1,r0=0),部分相干平顶光束(P=1,N >1,r0=0)、部分相干高斯光束阵列(P >1,N=1,r0>0)和 PCFT光束阵列(P >1,N >1,r0>0)在海洋湍流中的光束质量传输特性。
1.2 PCFT光束阵列的有效曲率半径
光束有效曲率半径定义为二阶矩〈→r(z)2〉与〈→r(z)·→θ(z)〉的比值[38-39]:

将(12)式、(14)式代入(20)式,可得PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中的有效曲率半径表达式:
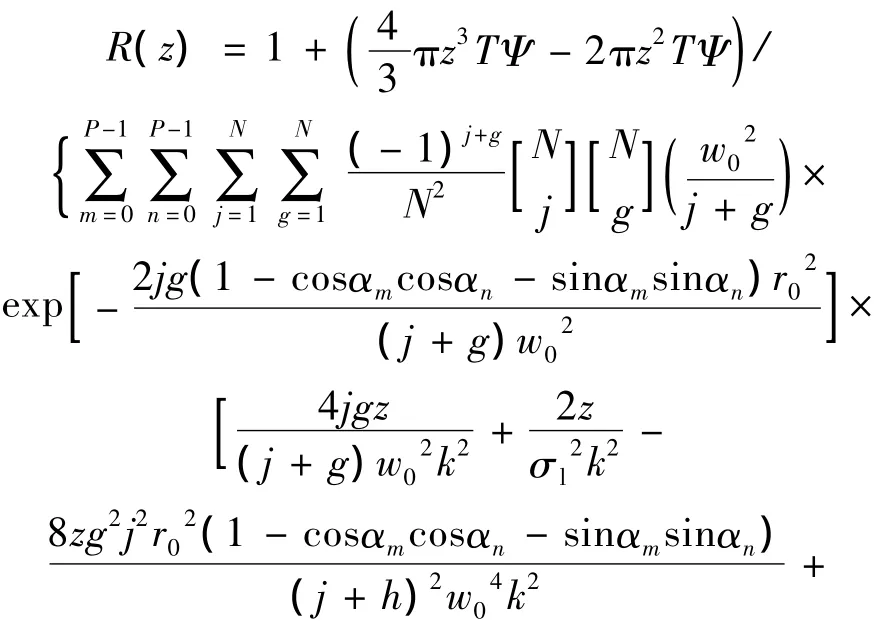

从(21)式可以看出:PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中的有效曲率半径受束宽、相干宽度、波长、海洋湍流参量的影响。(21)式可以实现部分相干高斯光束、部分相干平顶光束、部分相干高斯光束阵列、PCFT光束阵列等不同种光束在海洋湍流中的有效曲率半径的比较,探究它们在不同海洋湍流强度下有效曲率半径大小的演变趋势。
1.3 PCFT光束阵列的瑞利尺寸
光束瑞利尺寸以及最小有效曲率半径尺寸可表示为[40]:
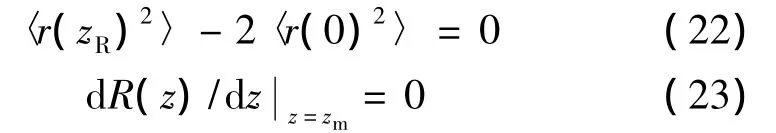
分别将(12)式代入(22)式、(21)式代入(23)式,经过运算后可得:
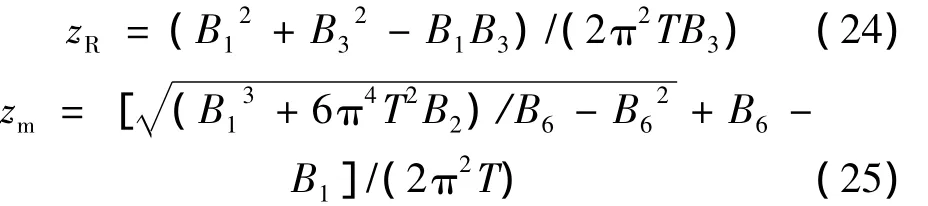
式中,

在自由空间中,瑞利尺寸zR和最小有效曲率半径尺寸zm是相等的[18]。从(24)式、(25)式可以看出,与在自由空间中不同,PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中传输的瑞利尺寸zR与最小有效曲率半径尺寸zm不再相等,这是受海洋湍流的影响所造成的,具体关系将在下面进一步讨论。
2 数值计算与分析

Fig.1 a—curve of normalized M2factors of four different beams propagating through oceanic turbulence with the transverse coherence width σl=8mm b—curve of normalized M2factors of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different the transverse coherence widths

Fig.2 a—curve of normalized M2factors of four different beams through oceanic turbulence with the ratio of temperature to salinity ω=-4.5 b—curve of normalized M2factors of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different ratios of temperature to salinity
图1a、图2a、图3a、图4a中给出了4种不同光束归一化M2在海洋湍流中的传输特性曲线(参量λ=632.8nm,w0=0.01m,ω =-3,ε =1.0 ×10-4m2·s-3,χt=1.0 ×10-10K2·s-1)。从图 1a、图 2a、图 3a、图 4a可以看出,各光束归一化M2随传输距离增加而增加,当传输距离z>400m时,相比其它光束,PCFT光束阵列的归一化 M2更小。图1b、图2b、图3b、图4b中描绘了在不同相干长度、温度起伏和盐度起伏相对强弱的关系、湍流动能耗散率、温度方差耗散率下,PCFT光束阵列归一化M2的传输特性曲线,从图1b、图2b、图3b、图4b可以看出,当相干长度越小,ω越小,湍流动能耗散率越大,温度方差耗散率越小时,光束归一化M2越小。

Fig.3 a—curve of normalized M2factors of four different beams through oceanic turbulence with ε =1.0 ×10-4m2·s-3 b—curve of normalized M2factors of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different ε
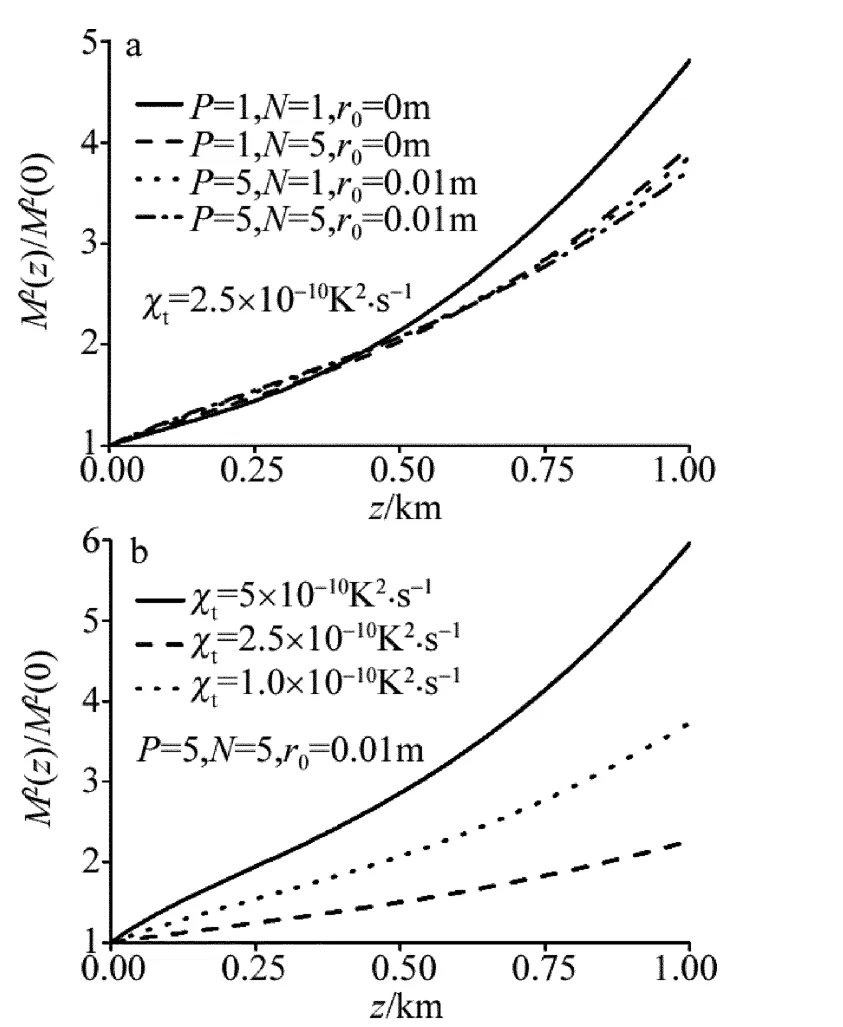
Fig.4 a—curve of normalized M2factors of four different beams through oceanic turbulence with χt=1.0 ×10-10K2·s-1 b—curve of normalized M2factors of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different χt
图5 、图6中分别给出了不同光束有效曲率半径在海洋湍流中的传输特性曲线(参量σl=8mm,w0=0.01m,ε =1.0 ×10-4m2·s-3,χt=1.0 ×10-10K2·s-1),从图5、图6可以看出,较其它光束,PCFT光束阵列的有效曲率半径发散更小。图7、图8中分别给出了在不同相干长度、温度起伏和盐度起伏相对强弱的关系下PCFT光束阵列有效曲率半径与传输距离的变化特性曲线,从图7、图8可以看出,当光束相干长度更小、ω更小时,PCFT光束阵列的有效曲率发散特性更小,这个结论与图1b、图2b中所得到的结论是一致的。
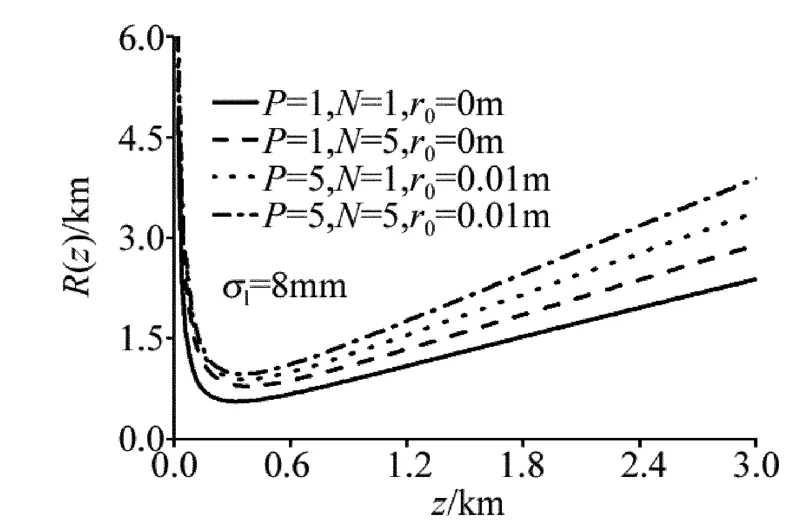
Fig.5 Curve of effective radius of curvature of four different beams through oceanic turbulence with σl=8mm

Fig.6 Curve of effective radius of curvature of four different beams through oceanic turbulence with ω=-4.5
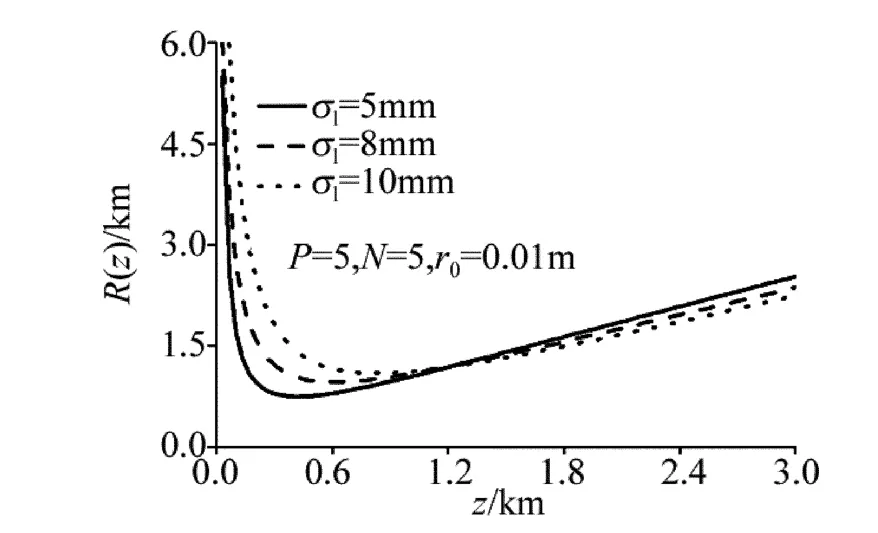
Fig.7 Curve of effective radius of curvature of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different σl
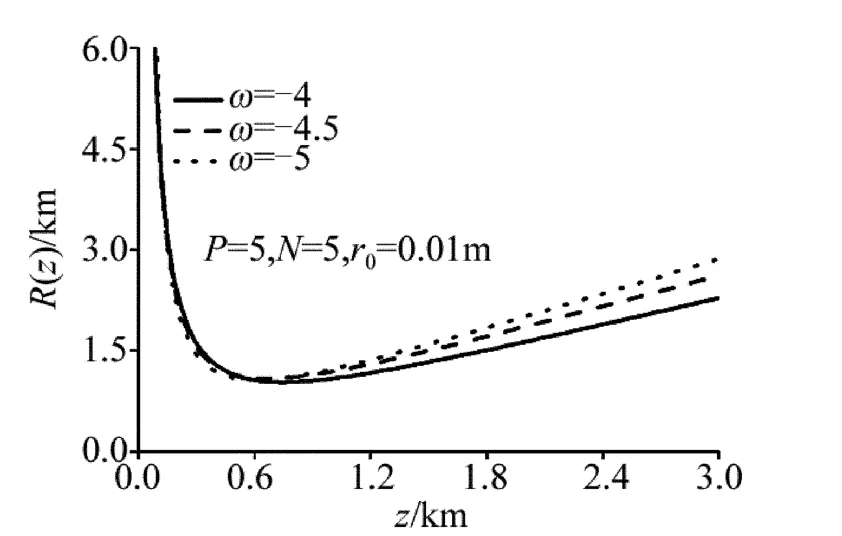
Fig.8 Curve of effective radius of curvature of PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence with different ω
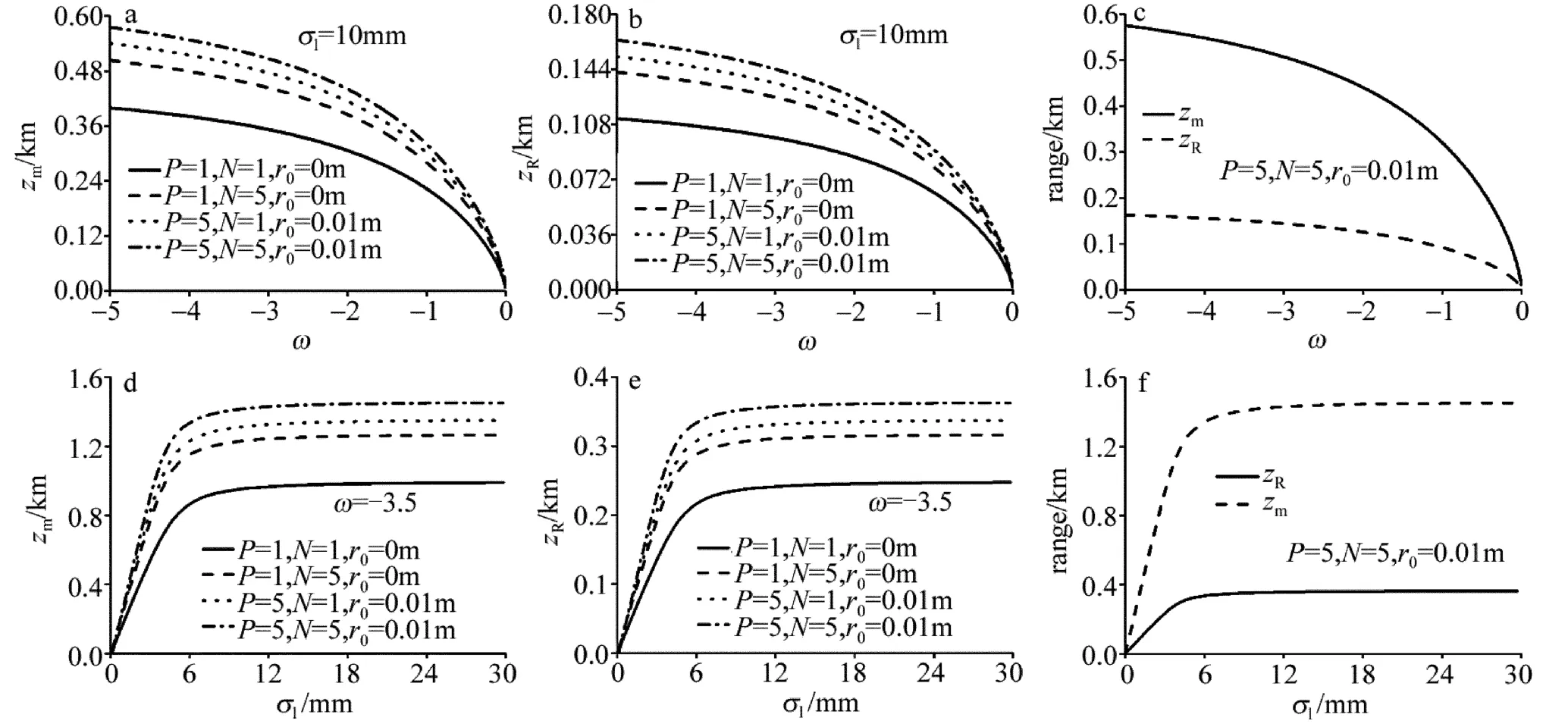
Fig.9 Curve of zm,zRof four different beams propagation through oceanic turbulence versus the ratio of temperature to salinity with the transverse coherence width σl=8mm,the transverse coherence width with the ratio of temperature to salinity ω =-4.5 and zm,zRof PCFT laser beam array propagating through oceanic turbulence
图9a、图9b中给出了不同光束最小有效曲率半径尺寸zm、瑞利尺寸zR与ω的曲线(参量λ=632.8nm,w0=0.01m,σl=10mm,ε =1.0 × 10-4m2·s-3,χt=1.0×10-9K2·s-1),从图9a、图9b可以看出,各光束的zm与zR随ω增加而减小,相对其它光束,PCFT光束阵列zm与zR最大。图9d、图9e中给出了不同光束zm和zR与相干长度的特性曲线(参量λ=632.8nm,w0=0.01m,ω =-3.5,ε =1.0 × 10-4m2·s-3,χt=1.0 ×10-9K2·s-1),从图9d、图9e可以看出,各光束的 zm与zR随相干长度增加而增加,当相干长度达到一定值时,各光束的zm与zR不变,且较其它光束,PCFT光束阵列的zm与zR最大。图9c、图9f中分别描绘了PCFT光束阵列的zm和zR与相对比值及相干长度的特性曲线,从图9c、图9f可以看出,与在自由空间中不同,PCFT光束阵列zm与zR不再相等,且zm的值大于zR的值,这主要是受海洋湍流的影响所造成的。
3 结论
给出了PCFT光束阵列在海洋湍流中的M2因子、有效曲率半径、瑞利尺寸的解析表达式,分析了相干长度、温度变化、盐度变化、湍流动能耗散率、温度方差耗散率等参量对它们的影响。此结果不仅可以研究PCFT光束阵列的光束传输特性,同时还可以研究部分相干高斯光束、部分相干平顶光束、部分相干高斯光束阵列在海洋湍流中的光束传输特性。与在大气湍流中各光束传输特性的演变趋势相似,但在海洋湍流的干扰下,光束传输质量的衰减更为严重,通过选择合适的光束参量,可以减小海洋湍流的强度,探究光束在海洋弱湍流中的传输特性。此结果对于激光光束在海洋中传输特性的研究具有一定的理论参考价值。
[1] EYYUBOGLU H T.Propagation and coherence properties of higher order partially coherent dark hollow beams in turbulence[J].Optics& Laser Technology,2008,40(1):156-166.
[2] ZHU Z W,XU J C,CANG J.Propagation properties of J0-correlated partially coherent flt-topped beams in a turbulent atmosphere[J].Laser Technology,2010,34(4):565-568(in Chinese).
[3] RODRIGO J N M,JULIO C G V.Rytov theory for Helmholtz-Gauss beams in turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics Express,2007,15(25):16328-16341.
[4] FEI J C,CUI Z F,WANG J S,et al.Propagation characteristics of elegant Laguerre-Gaussian beam passing through a circular aperture in turbulent atmosphere[J].Laser Technology,2011,35(6):849-853(in Chinese).
[5] CHU X.The relay propagation of partially coherent cosh-Gaussian-Schell beams in turbulent atmosphere[J].Applied Physics,2010,B98(2/3):573-579.
[6] ZHOU P,MA Y,WANG X,et al.Average spreading of a Gaussian beam array in non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J].Optics Letters,2010,35(7):1043-1045.
[7] WANG B,FEI J Ch,CUI Zh F,et al.Research of degree of polarization of PCELG beam propagating through a circular aperture[J].Laser Technology,2013,37(5):672-678(in Chinese).
[8] CHEN Z,LI C,DING P,et al.Experimental investigation on the scintillation index of vortex beams propagating in simulated atmospheric turbulence[J].Applied Physics,2012,B107(2):469-472.
[9] ALAYINEJAD M,GHAFARY B,KASHANI F D.Analysis of the propagation of flat-topped beam with various beam orders through turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics and Lasers in Engineering,2008,46(1):1-5.
[10] ZHANG R,WANG X Z,CHENG X.Far-zone polarization distribution properties of partially coherent beams with non-uniform source polarization distributions in turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics Express,2012,20(2):1421-1435.
[11] ZHAO T J,PU Z C.Effects of the aperture on the on-axis polarization properties of partially coherent light[J].Laser Technology,2008,32(4):424-433(in Chinese).
[12] JI X L,SHAO X L.Influence of turbulence on the propagation factor of Gaussian Schell-model array beams[J].Optics Communications,2010,283(6):869-873.
[13] WU J.Propagation of a Gaussian-Schell beam through turbulent media[J].Journal of Modern Optics,1990,37(4):671-684.
[14] PAN L Zh.Far-field behavior of partially polarized Gaussian Schellmodel beams diffracted through an aperture[J].Acta Optica Sinica,2006,26(8):1250-1255(in Chinese).
[15] WANG F,CAI Y J,KOROTKOVA O.Partially coherent standard and elegant Laguerre-Gaussian beams of all orders[J].Optics Express,2009,17(25):22366.
[16] ZHONG Y L,CUI Z F,SHI J P,et al.Propagation properties of partially coherent flat-topped beam array in a turbulent atmosphere[J].Laser Technology,2010,34(4):542-547(in Chinese).
[17] WU J,BOARDMAN A D.Coherence length of a Gaussian-Schell beam in atmospheric turbulence[J].Journal of Modern Optics,1991,38(7):1355-1363.
[18] WANG F,CAI Y J.Second-order statistics of a twisted Gaussian Schell-model beam in turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics Express,2010,18(24):24661-24672.
[19] LÜ B D,LUO Sh R.Beam propagation factor of aperture super-Gaussian beams[J].Optik,2001,112(11):503-506.
[20] LÜ B D,MA H.A comparative study of elegant and standard Hermite-Gaussian beams[J].Optics Communications,2000,174(1):99-104.
[21] ZHOU P,MA Y,WANG X,et al.Average spreading of a Gaussian beam array in non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J].Optics Letters,2012,35(7):1043-1045.
[22] ZHOU P,LIU Z,XU X,et al.Propagation of coherently combined flattened laser beam array in turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics & Laser Technology,2009,41(4):403-407.
[23] ZHOU P,LIU Z,XU X,et al.Propagation of phase-locked partially coherent flattened beam array in turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics and Lasers in Engineering,2009,47(1):1254-1258.
[24] EYYUBOGLU H T,BAYKAL Y,CAI Y J.Scintillations of laser array beams[J].Applied Physics,2008,B91(2):265-271.
[25] CAI Y J,HE S.Propagation of various dark hollow beams in a turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics Express,2006,14(4):1353-1367.
[26] WANG H T,LIU D,ZHOU Z.The propagation of radially polarized partially coherent beam through an optical system in turbulent atmosphere[J].Applied Physics,2010,B101(12):361-369.
[27] JI X L,CHEN X W,LÜ B D.Spreading and directionality of partially coherent Hermite-Gaussian beams propagating through atmos-phere turbulence[J].Journal of the Optics Society of America,2008,A25(1):21-28.
[28] KOROTKOVA O,FARWELL N.Effect of oceanic turbulence on polarization of stochastic beams[J].Optics Communication,2011,287(7):1740-1746.
[29] HANSON F,LASHER M.Effects of underwater turbulence on laser beam propagation and coupling into single-mode optical fiber[J].Applied Optics,2010,49(16):3224-3230.
[30] TANG M M,ZHAO D M.Propagation of radially polarized beams in the oceanic turbulence[J].Applied Physics,2013,B111(4):665-670.
[31] ZHOU Y,CHEN Q ,ZHAO D M.Propagation of astigmatic stochastic electromagnetic beams in oceanic turbulence[J].Applied Physics,2013,B114(4):475-482.
[32] ZHOU Y,HUANG K,ZHAO D M.Changes in the statistical properties of stochastic anisotropic electromagnetic beams propagating through the oceanic turbulence[J].Applied Physics,2012,B109(2):289-294.
[33] TANG M M,ZHAO D M.Spectral changes in stochastic anisotropic electromagnetic beams propagating through turbulent ocean[J].Optics Communications,2014,312(3):89-93.
[34] MANDEL L,WOLF E.Optical coherence and quantum optics[M].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,1995:100-125.
[35] DAN Y Q,ZHANG B.Beam propagation factor of partially coherent flat-topped beams in a turbulent atmosphere[J].Optics Express,2008,16(20):15563-15575.
[36] FARWELL N,KOROTKOVA O.Intensity and coherence properties of light in oceanic turbulence[J].Optics Communication,2012,285(6):872-875.
[37] LU W,LIU L R,SUN J F.Influence of temperature and salinity fluctuations on propagation behaviour of partially coherence in oceanic turbulence[J].Journal of Optics,2006,A8(12):1052-1058.
[38] JI X L,EYYUBOGLU H T,BAYKAL Y.Influence of turbulence on the effective radius of curvature of radial Gaussian array beams[J].Optics Express,2010,18(7):6922-6928.
[39] EYYUBOGLU H T,BAYKAL Y,JI X L.Radius of curvature variations for annular,dark hollow and flat topped beams in turbulence[J].Applied Physics,2010,B99(4):801-807.
[40] GBUR G,WOLF E.The Rayleigh range of Gaussian Schell-model beams[J].Journal of Modern Optics,2010,48(11):1735-1741.
