东昆仑造山带早古生代的大陆碰撞:来自榴辉岩原岩性质的证据*
2015-03-15孟繁聪崔美慧贾丽辉任玉峰冯惠彬
孟繁聪 崔美慧 贾丽辉 任玉峰 冯惠彬
MENG FanCong,CUI MeiHui,JIA LiHui,REN YuFeng and FENG HuiBin
大陆构造与动力学国家重点实验室,中国地质科学院地质研究所,北京 100037
State Key Laboratory for Continental Tectonics and Dynamics,Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037,China
2015-06-11 收稿,2015-09-08 改回.
1 引言
榴辉岩原岩恢复对认识造山带性质和造山过程具有重要意义(Zheng,2012;Wang et al.,2013)。若其原岩为洋壳性质,则代表了洋壳的俯冲变质,表明存在增生造山作用,如中国的西南天山和北祁连(Gao and Klemd,2003;Zhang et al.,2007);若其原岩为陆壳性质,则代表了大陆地壳的俯冲变质,表明存在陆陆碰撞造山作用,如中国的苏鲁-大别造山带(王式洸等,1995;Zhang et al.,2006;Liu et al.,2007,2008;Zheng,2012)。蛇绿岩、花岗岩和基性麻粒岩的研究表明东昆仑存在早古生代的造山作用(姜春发等,1992;许荣华等,1994;Yang et al.,1996;潘裕生等,1996;李怀坤等,2006),东昆中断裂带被认为是一条早古生代缝合带或者是一个重要的早古生代汇聚板块边界(肖序常等,1986;高延林等,1988;Chen and Wang,1996;陆松年等,2006;李怀坤等,2006)。对于东昆仑的造山性质大部分研究者倾向认为是增生造山(尹安,2001;边千韬等,2002;Pan et al.,2012),但缺少洋壳俯冲变质的岩石学证据。也有学者认为是软碰撞,时间限定在早二叠世(殷鸿福和张克信,1997)或者是元古代的碰撞(陈能松等,1999)。因此,东昆仑早古生代造山带的性质仍需要深入研究(李荣社等,2007)。东昆仑早古生代榴辉岩的发现(Meng et al.,2013;祁生胜等,2014),表明东昆仑昆北地体中的部分金水口岩群曾经历过高压变质作用(Meng et al.,2013),但是榴辉岩代表了俯冲的洋壳还是陆壳仍不清楚。本文依据东昆仑东段温泉榴辉岩的岩石地球化学、Nd 同位素及榴辉岩锆石的微量元素及Hf 同位素组成对榴辉岩原岩进行了讨论,这一结果有助于理解东昆仑早古生代的造山过程和性质。
2 地质背景
东昆仑以昆中断裂带为界可分为昆北地体和昆南地体两部分(图1a;吴功建等,1989;李怀坤等,2006;许志琴等,2006)。
昆北地体出露有金水口群的太古代-古元古代的白沙河岩组和中元古代的小庙岩组(王云山和陈基娘,1987;王国灿等,2004,2007),早古生代浅变质的纳赤台群火山-沉积岩(姜春发等,1992),志留纪-泥盆纪花岗闪长岩和花岗岩侵入体以及泥盆纪的陆相火山岩(莫宣学等,2007;许志琴等,2007;陆露等,2010),大面积印支期的花岗闪长岩和花岗岩侵入体(莫宣学等,2007;许志琴等,2007)和晚三叠世的鄂拉山组活动大陆边缘火山岩(刘红涛,2001)。沿昆中断裂带断续出露有超基性岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩和基性火山岩,它们以岩片或岩块形式混杂在前寒武纪变质岩系和早古生代纳赤台群中,被认为是蛇绿岩(肖序常等,1986;姜春发等,1986;高延林等,1988;古凤宝,1994;潘裕生等,1996;Chen and Wang,1996;王国灿等,1999;Yang et al.,1996;朱云海等,1999,2002;Zhu et al.,2006;冯建赟等,2010;崔美慧等,2011;Meng et al.,2015),主要形成于早古生代(Yang et al.,1996;Zhu et al.,2006;崔美慧等,2011;Meng et al.,2015),是原特提斯洋的残片。
昆南地体由前寒武纪的苦海群和万宝沟群,早古生代纳赤台群火山-沉积岩,晚泥盆世红色磨拉石建造,石炭-中三叠世浅海相地层和晚三叠世-侏罗纪陆相地层组成。其中苦海群由角闪岩相变质的斜长角闪岩-长英质片麻岩及大理岩构成,原岩为碎屑岩-中基性火山岩-碳酸盐岩(Liu et al.,2005);万宝沟群原岩为一套碎屑岩、大理岩和火山岩组合,遭受绿片岩相变质(姜春发等,1992;潘裕生等,1996)。上述地层部分被三叠世花岗岩侵入(莫宣学等,2007)。沿昆南断裂由西向东分布的蛇绿岩有大九坝、黑茨沟、布青山、下大武、玛积雪山和玛沁蛇绿岩(姜春发等,1992;Yang et al.,1996,2009;陈亮等,2000,2001;Bian et al.,2004;杨经绥等,2004,2005;郭安林等,2006),这些蛇绿岩主要形成于晚古生代,代表了古特提斯洋的残片(陈亮等,2001;Konstantinovskaia et al.,2003;Bian et al.,2004;杨经绥等,2004,2005;Yang et al.,2009;刘战庆等,2011)。
2.1 榴辉岩产状
研究区位于昆北地体最东端——昆中断裂与温泉断裂的交汇部位,向西北距都兰县约100km,向东南距温泉约40km(图1a),区内主要有元古代白沙河岩群的各类片麻岩,其中含少量规模不等的超基性岩块(王秉璋等,2001)。石炭-二叠纪甘家组灰岩夹砂岩、板岩,二叠纪的火山弧岩片以及三叠纪的洪水川群。侵入岩有新元古代花岗岩、泥盆纪石英闪长岩和花岗岩(图1b)。
榴辉岩呈透镜状分布在二云二长片麻岩中(图2a),较大者东西长约20m,南北宽约5 ~10m,榴辉岩呈灰黑-灰绿色,块状构造(图2b),条带状构造,局部退变成灰黑色榴闪岩。根据石榴石粒度可分两类,一类为粗粒变晶结构,石榴石粒度可达1 ~3mm(图2b);另一类为细粒变晶结构,石榴石粒度≤1mm,以0.1 ~0.3mm 为主。详细的矿物化学成分见(Meng et al.,2013),估算的榴辉岩的形成温度为590 ~650℃,形成压力大于1.6GPa。榴辉岩的原岩时代为934 ±11Ma,变质时代为450 ~430Ma(Meng et al.,2013;贾丽辉等,2014)。
超基性岩块也呈透镜状分布在二云二长片麻岩中,东西长约1000m,南北宽约200 ~300m,主要由蛇纹石化橄榄岩和透闪石化辉石岩组成,黑绿色,片理发育,片理产状100°∠70°。二云二长片麻岩呈灰-灰黑色,条带状构造,片麻理走向近东西,倾向北,倾角约60°,属于早元古代金水口群白沙河岩组(Pt1b)(Meng et al.,2013)。该岩组是柴达木盆地南缘的变质基底(王云山和陈基娘,1987;王国灿等,2004,2007;陈能松等,2006)。
2.2 样品描述
细粒榴辉岩由石榴石(40% ~50%)+角闪石(15% ~20%)+后成合晶(20% ~25%)+石英(10% ~15%)+金红石(5%)组成;峰期阶段(榴辉岩相)矿物组合为:石榴石+绿辉石+石英+金红石;退变质阶段(角闪岩相)矿物组合为:后成合晶+角闪石+石英+钛铁矿。粗粒蓝晶石榴辉岩由石榴石(35%)+绿辉石(20% ~30%)+蓝晶石(10% ~15%)+后成合晶(20%)+ 石英(15% ~20%)+ 金红石(5% ~10%),不含角闪石,矿物定向-半定向排列(图2c,d)。
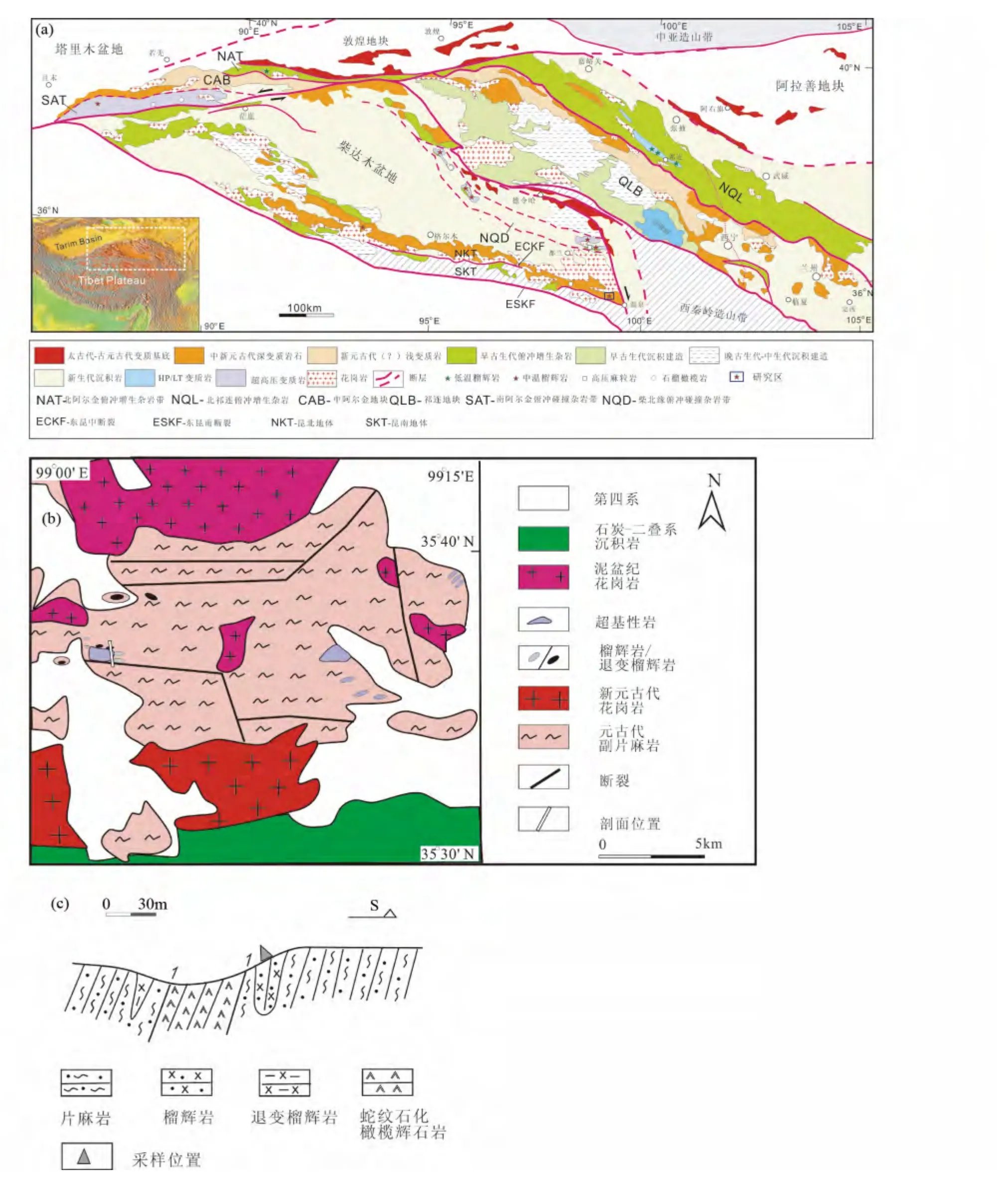
图1 东昆仑及其邻区榴辉岩分布图(a,据张建新等未发表资料修改)、温泉榴辉岩区地质简图(b 据王秉璋等,2001 修改)及榴辉岩产状剖面及采样位置(c)东昆仑温泉榴辉岩(Meng et al. ,2013;贾丽辉等,2014);东昆仑夏日哈木榴辉岩(祁生胜等,2014);邻区榴辉岩(Song et al. ,2003,2006;Zhang et al. ,2008,2010;Yu et al. ,2013 及其参考文献)Fig.1 Distributions of eclogites in the East Kunlun orogen and adjacent area (a),geologic sketch map of the study area (b,modified after Wang et al.,2001)and occurrence and sample location of eclogites in the section (c)Wenquan eclogite (Meng et al. ,2013;Jia et al. ,2014);eclogite from western segment of East Kunlun (Qi et al. ,2014);others eclogite (Zhang et al. ,2008;Yu et al. ,2013,and therein)
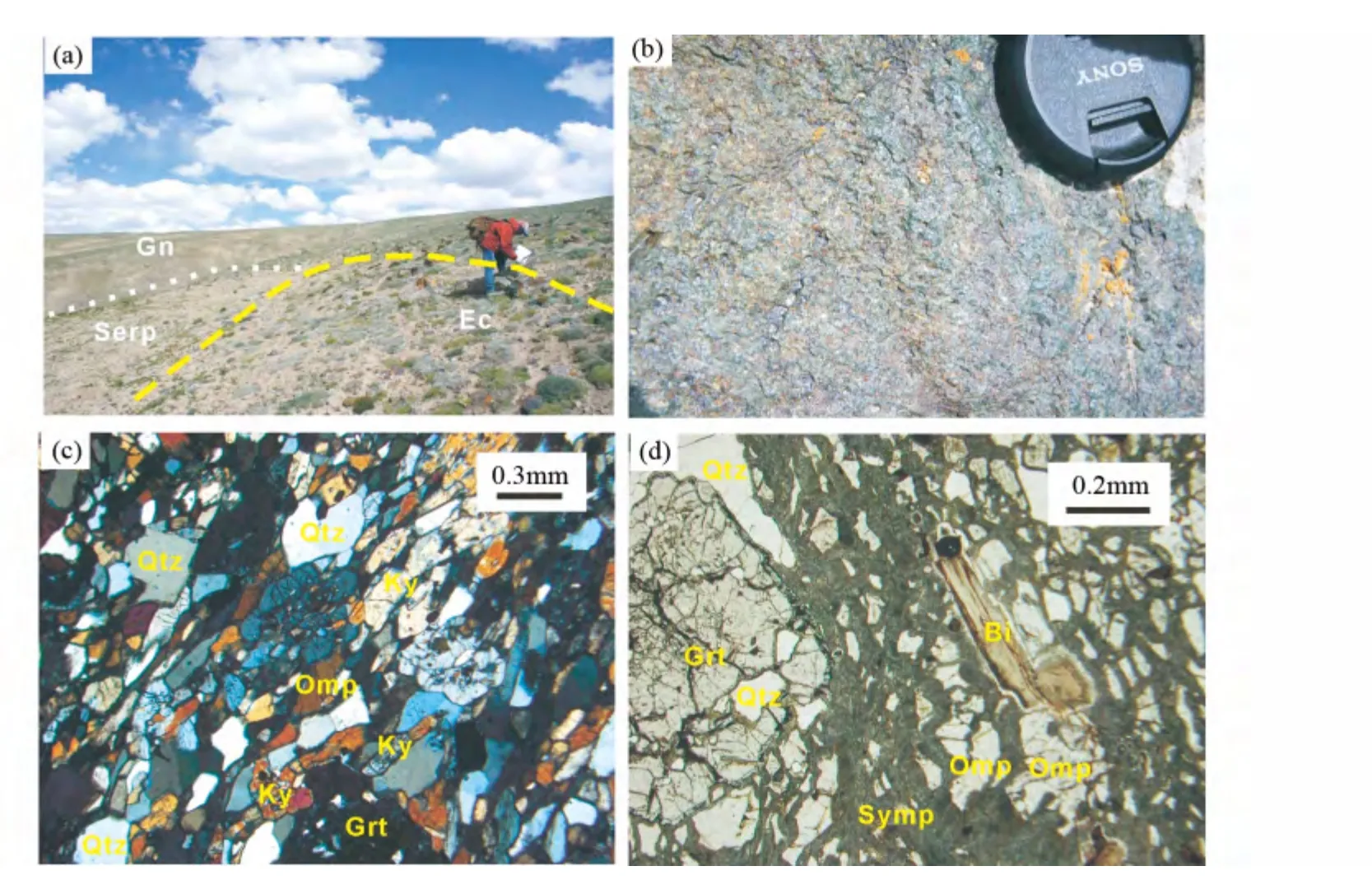

图2 榴辉岩产状及其显微照片(a)榴辉岩(Ec)露头(镜头朝东),在片麻岩(Gn)中呈透镜状,超基性岩(Serp)呈构造岩块分布在片麻岩中,与榴辉岩相邻;(b)粗粒榴辉岩,块状状构造,主要由红色石榴子石(1 ~3mm)和绿色的绿辉石(可退变为透辉石+斜长石后成合晶)组成;(c)蓝晶石榴辉岩(K12-9-5.4),由石榴子石、绿辉石、蓝晶石和石英组成(正交偏光);(d)退变榴辉岩(K11-17-1.8),由石榴子石、绿辉石、石英和后成合晶组成(单偏光). 矿物代号:Grt-石榴子石;Omp-绿辉石;Ky-蓝晶石;Qtz-石英;Symp-后成合晶;Bi-黑云母Fig.2 Occurrence of the eclogites and their mircophotographs(a)eclogite outcrop (camera facing east),eclogites tectonic contact with ultramafic rocks,they as lenses or block occur in paragneiss;(b)coarsegrained eclogite with massiv structure,which consists of red garnet (1 ~3mm)and green omphacite (majority is retrograde symplectite with amphibole and plagioclase);(c)kyanite-eclogite (K12-9-5.4),consisting of garnet,omphacite,kyanite and quartz (CPL);(d)retrograde eclogite (K11-17-1.8),consisting of garnet,omphacite,quartz and symplectite (PPL). Abbreviations:Ec-eclogite;Gn-gneiss;Serp-ultramafic rocks;Grt-garnet;Omp-omphacite;Ky-kyanite;Qtz-quartz;Symp-symplectite;Bi-biotite
2.3 测试方法
全岩分析由国家地质实验测试中心完成,主元素采用X-荧光光谱法(XRF),测试仪器为3080E 型X-荧光光谱仪,其中FeO 采用容量滴定法;稀土元素和微量元素采用等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)。氧化物和微量元素含量大于10 ×10-6的元素的分析误差为5%;小于10 ×10-6的元素分析误差为10%(Zeng et al.,2011)。
Sm-Nd 同位素测试在中国地质科学院地质研究所同位素实验室完成。Sm-Nd 含量测定采用同位素稀释法,测试仪器为MAT262 固体同位素质谱计。Nd 同位素分析仪器为Nu Plasam HR MC-ICP-MS(Nu Instruments),DSN-100 膜去溶;标样为JMC Nd2O3,标样的143Nd/144Nd =0.511126 ±10(2σ);Nd 同位素质量分馏采用146Nd/144Nd =0.7219 校正。详细测试流程见何学贤等(2007)。
锆石Lu-Hf 同位素测试是在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室Neptune多接收等离子质谱和Newwave UP 213 紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA-MC-ICP-MS)上进行的,分析点靠近U-Pb 测定点,且在同一CL 结构位置。εHf(t)计算采用衰变常数λ =1.865 ×10-11year-1,(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR=0.0332,(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR,0=0.282772(Blichert-Toft and Albarède,1997),亏损地幔模式年龄(tDM)计算采用(176Hf/177Hf)DM= 0.0384,(176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325(Griffin et al.,2002)。相关仪器运行条件及详细分析流程见侯可军等(2007)。
3 结果
3.1 全岩地球化学
3.1.1 主元素
对11 件榴辉岩(3 件细粒和8 件粗粒)进行了主元素和微量元素分析(表1)。这些岩石的SiO2含量为46.50% ~59.01%,TiO2含量0.88% ~1.15%,属于拉斑玄武岩系列的基性-中性岩石(玄武岩-安山岩)(图3a,b)。细粒榴辉岩具有低的Al2O3,含量为13.38% ~13.92%,高的FeO 含量,为13.09% ~13.24%,MgO 含量7.59% ~7.97%,Mg#指数为0.47 ~0.48,CaO 含 量 为10.98% ~11.71%,Na2O 含 量1.19% ~1.31%;粗粒榴辉岩的Al2O3较高,含量为15.06%~16.36%,FeO 含量和MgO 含量较低,分别为6.88% ~9.0%和4.30% ~5.59%,Mg#指数为0.45 ~0.51。CaO 含量为5.94% ~7.28%,比细粒榴辉岩低,Na2O 含量4.04% ~5.16%,比细粒榴辉岩高。
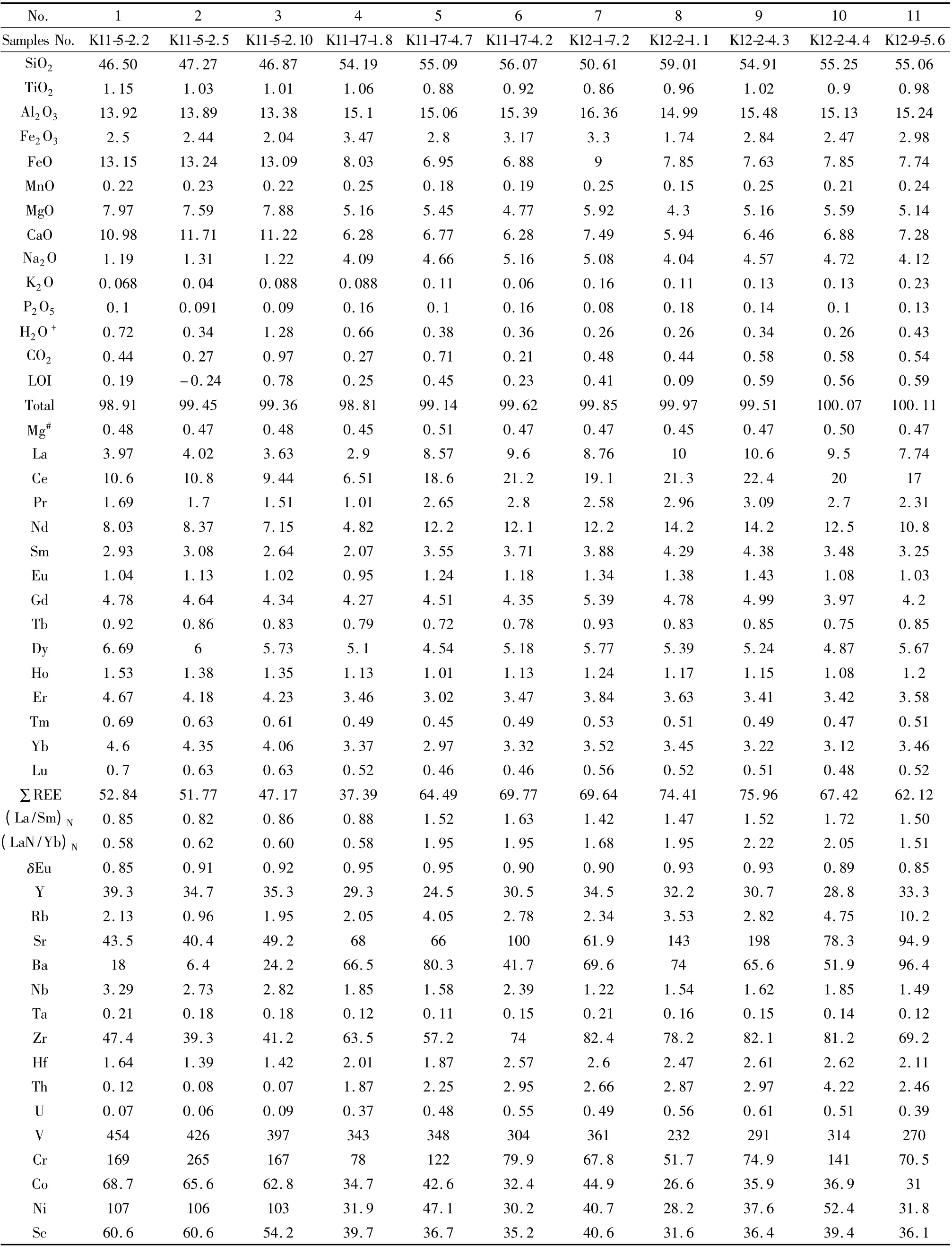
表1 东昆仑温泉榴辉岩的主元素(wt%)和微量元素(×10 -6)Table 1 Major (wt%)and trace elements (×10 -6)concentration of eclogites in Wenquan,East Kunlun
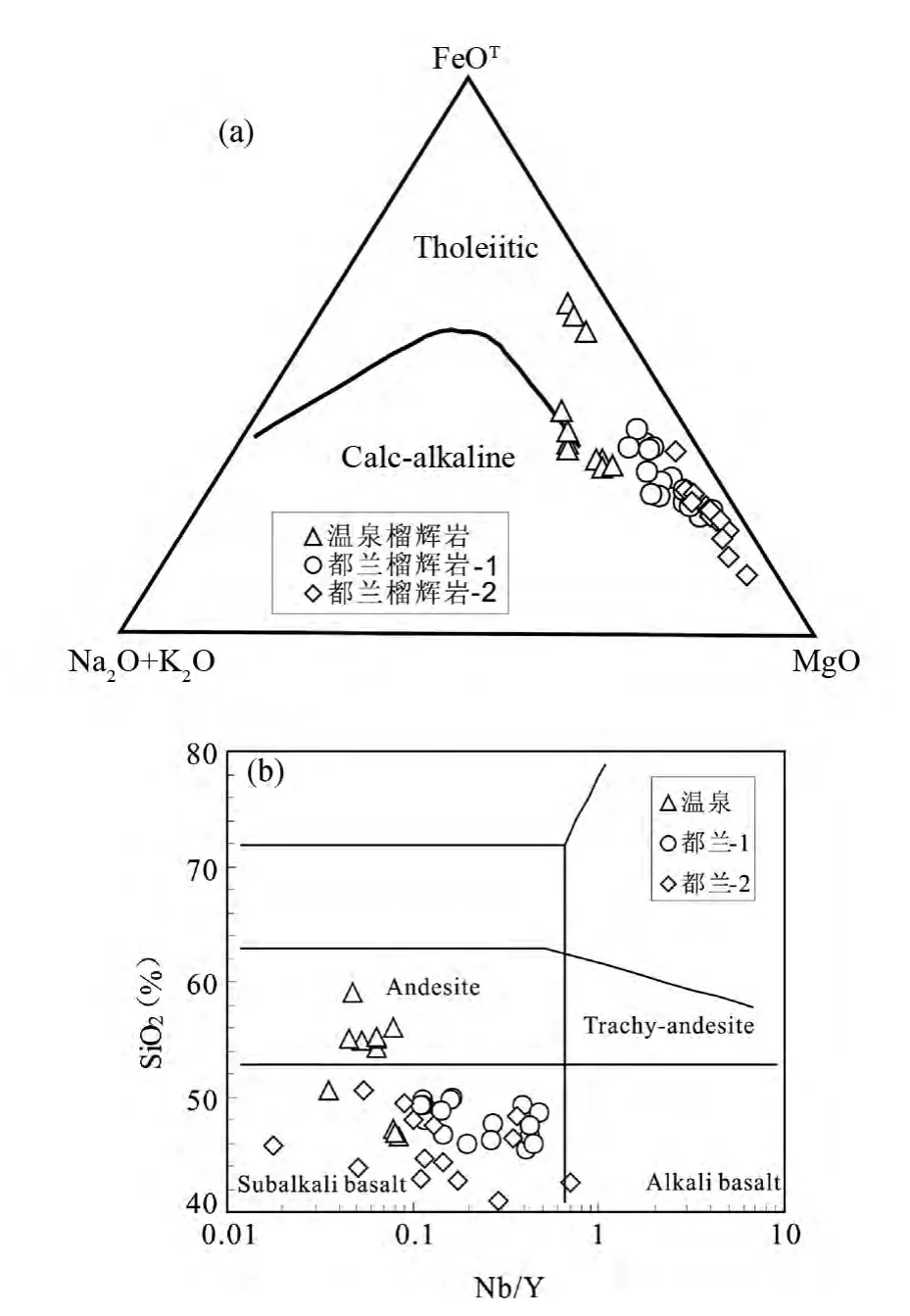
图3 温泉榴辉岩的AFM 图解(a,据Irvine and Baragar,1971)和Nb/Y-SiO2 图解(b,底图据Winchester and Floyd,1977)都兰-1 据Yu et al. ,2013;都兰-2 据Song et al. ,2003;图5、图6同Fig.3 AFM diagram (a,after Irvine and Baragar,1971)and Nb/Y-SiO2 plot (b,after Winchester and Floyd,1977)of eclogites from Wenquan
3.1.2 稀土元素
在球粒陨石标准化图解上(图4),4 件样品显示为轻稀土元素亏损,配分模式类似于N-MORB,(La/Sm)N比值为0.82 ~0.88,(La/Yb)N比值为0.58 ~0.62。其余7 件样品的轻稀土元素略显富集,类似于E-MORB,(La/Sm)N比值为1.42 ~1.72,(La/Yb)N比值为1.51 ~2.22(表1)。所有样品显示Eu 为弱的负异常,δEu 为0.85 ~0.95。
3.1.3 微量元素
在Nb/Yb-Th/Yb 图解上(Pearce,2008),3 件细粒榴辉岩样品显示与N-NORB 有亲缘性,其余样品显示岩浆与地壳反应的趋势(图5)。在Zr-Nb-Y 图上(图6),样品均落入弧玄武岩和洋中脊玄武岩范围。

图4 温泉榴辉岩的稀土元素配分模式(球粒陨石值据Boynton,1984)灰色区域为都兰榴辉岩(Yu et al. ,2013;Song et al. ,2003)Fig.4 Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (REE)patterns of the eclogites from Wenquan (normalization values after Boynton,1984)The gray range for Dulan eclogites (after Yu et al.,2013;Song et al.,2003)

图5 温泉榴辉岩的Nb/Yb-Th/Yb 图解(据Pearce,2008)Fig. 5 Diagram of Nb/Yb vs. Th/Yb for eclogites from Wenquan (after Pearce,2008)

图6 玄武岩的Nb-Zr-Y 图解(据Meschede,1986)Fig.6 Diagram of Nb-Zr-Y for basalts (after Meschede,1986)A (Ⅰ+Ⅱ):basalt within plates;Ⅱ+C:tholeiite within plates;B-P-MORB;C+D:volcanic arc basalt;D:N-MORB and volcanic arc basalts
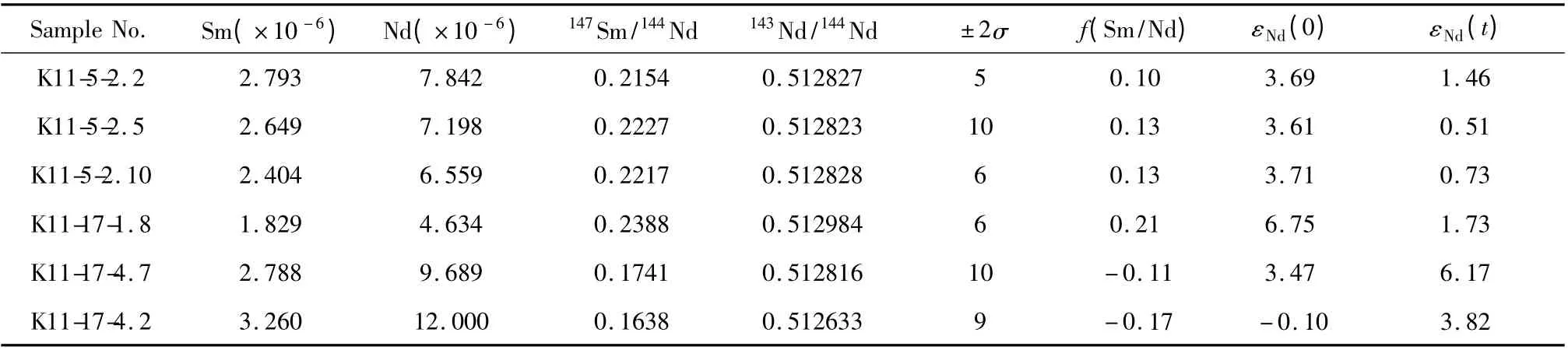
表2 东昆仑温泉榴辉岩的Sm-Nd 同位素组成Table 2 Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of eclogites in Wenquan,East Kunlun

图7 温泉榴辉岩的Sm-Nd 同位素特征都兰榴辉岩据Song et al. ,2003Fig. 7 Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of eclogites from Wenquan
3.1.4 Sm-Nd 同位素
对6 件榴辉岩样品进行了Sm-Nd 同位素分析(表2)。榴辉岩的Sm 含量为1.82 ×10-6~3.26 ×10-6,Nd 含量为4.63 × 10-6~12.0 × 10-6,147Sm/144Nd 比 值 为0.164 ~0.239,143Nd/144Nd 比 值 为0.512633 ~0.512984,计 算 的εNd(0)值为-0.10 ~+6.75,εNd(t)值为0.51 ~+6.17(t =934Ma),变化较大,最大相差6 个εNd单位(图7)。
3.2 锆石矿物化学
3.2.1 锆石微量元素
采用LA-ICP-MS 方法对榴辉岩样品(K11-5-2.18)中21粒测年锆石的18 个测点进行了微量元素分析(表3),稀土元素总量为287 ×10-6~780 ×10-6,重稀土元素(HREE)明显富集,(Lu/Gd)N=31 ~101,δEu=0.12 ~0.24,具有明显的负Eu 异常(表3,图略),表明锆石为火成锆石(Meng et al.,2013)。
东昆仑榴辉岩锆石的U/Yb 比值为0.14 ~0.89,Hf 含量为6610 ×10-6~7917 ×10-6,Y 含量为136 ×10-6~252 ×10-6(表3),在辉长岩锆石的U/Yb-Hf 图解和U/Yb-Y 图解上(图8),均落入陆壳辉长岩锆石的范围内(Grimes et al.,2007),表明这些榴辉岩的原岩形成于大陆环境。

图8 温泉榴辉岩(K11-5-2.18)锆石的Hf-U/Yb 图解(据Grimes et al.,2007)Fig.8 Hf vs. U/Yb diagram of zircons from Wenquan eclogites (after Grimes et al.,2007)

图9 温泉榴辉岩(K11-5-2.18)锆石的Hf 同位素特征都兰榴辉岩锆石Hf 同位素据Yu et al. ,2013Fig.9 Hf isotopic compositions of zircons from Wenquan eclogites
3.2.2 锆石Hf 同位素
对测过年龄的锆石进行了16 个测点的Lu-Hf 同位素分析(表4、图9)。锆石的176Lu/177Hf 比值为0.000540 ~0.001062,176Hf/177Hf 比值为0.282425 ~0.282489,εHf(0)值为-12.26~-10.23,初始的εHf(t)值为+7.5 ~+10(t =934Ma),计算的亏损地幔的模式年龄tDM为1.1 ~1.2Ga。

表3 温泉榴辉岩(K11-5-2.18)锆石的微量元素(×10 -6)组成Table 3 LA-ICP-MS trace element composition (×10 -6)of zircon from Wenquan eclogite (K11-5-2.18)

表4 东昆仑温泉榴辉岩(K11-5-2.18)锆石的Hf 同位素组成Table 4 Hf isotopic compositions of zircons from eclogite (K11-5-2.18)in Wenquan,East Kunlun
4 讨论
4.1 榴辉岩原岩性质
4.1.1 元素地球化学证据
在俯冲的早期阶段(地壳深度)元素的迁移很有限(Zheng,2012),北秦岭榴辉岩的研究表明,在退变质过程中虽然有外部流体活动,如石英脉切割榴辉岩,榴辉岩的HSFE和REE 也没有明显的迁移,只对Rb 和Ba 有一定影响(Wang et al.,2013)。榴辉岩的Mg#值很低(0.45 ~0.51),显然其原岩不是原始玄武岩浆结晶的产物(Mg#= 0.70,Niu,2005),特别是粗粒榴辉岩的SiO2含量达59%(表1),岩石中有大量石英出现(图2c,d),与大别山毛屋榴辉岩类似,表明原岩有可能是分异程度很高的层状侵入体(Jahn et al.,2003)。柴北缘东端都兰榴辉岩的原岩被认为形成于陆壳环境(Song et al.,2003;Yu et al.,2013),与都兰榴辉岩相比,二者均属于拉斑玄武质系列岩石(图3a),但是温泉榴辉岩相对富铁,有部分样品具有安山岩性质;而都兰榴辉岩更富镁,所有样品均属于亚碱性的玄武岩(图3b)。
温泉榴辉岩的稀土元素特征具有N-MORB 型和EMORB 型两种类型(图4),类似于都兰榴辉岩的稀土特征(Song et al.,2003;Yu et al.,2013),也类似于柴北缘鱼卡和锡铁山榴辉岩的稀土特征(孟繁聪等,2003;Zhang et al.,2005,2013;Chen et al.,2009;Song et al.,2010)以及阿尔金榴辉岩的稀土特征(Zhang et al.,2001)。柴北缘的锡铁山榴辉岩和南阿尔金榴辉岩具有轻稀土元素亏损的样品,其原岩被认为形成于大陆裂谷或初始洋盆环境(孟繁聪等,2003;Zhang et al.,2001,2005)。轻稀土元素亏损的榴辉岩也出现在苏鲁超高压变质带中,其原岩被认为形成于大陆裂谷环境(王式洸等,1995)。法国西部华力西带中的榴辉岩也具有轻稀土元素亏损的特征(Bernard-Griffiths and Cornichet,1985),作者认为这些榴辉岩形成于大洋环境。在西班牙具有轻稀土元素亏损特征的榴辉岩,其原岩被认为形成于岛弧环境(Bernard-Griffiths et al.,1985)。而西阿尔卑斯具有N-MORB 稀土特征的榴辉岩原岩被认为形成于减薄的大陆地壳或初始大洋裂谷环境(Paquette et al.,1989)。作为对比,LREE 亏损的大陆拉斑玄武岩常出现在大陆边缘环境,与大陆裂谷环境有关(Cullers and Graf,1984;王式洸等,1995)。另外,玄武岩浆的堆晶相也具有轻稀土元素亏损的特点,如堆晶辉长岩(Coleman,1977)。我们倾向认为这种轻稀土元素亏损的榴辉岩的原岩形成于大陆边缘环境。轻稀土元素富集型的榴辉岩在苏鲁大别造山带分布很广(王式洸等,1995;Chavagnac and Jahn,1996;Jahn et al.,2003;Zhang et al.,2006;Liu et al.,2007,2008),柴北缘及阿尔金也以轻稀土元素富集型的榴辉岩为主(孟繁聪等,2003;Song et al.,2003,2010;Zhang et al.,2001,2005,2008,2013;Chen et al.,2009),多数人认为这些榴辉岩的原岩形成于大陆裂谷环境,轻稀土元素的富集可能与陆壳物质的混染有关(Jahn,1999)。本文榴辉岩轻稀土元素富集的特征类似于大陆拉斑玄武岩(Wilson,1989),其原岩很可能形成于大陆环境。
4.1.2 Sm-Nd 同位素证据
本文榴辉岩原岩形成时代为934Ma,榴辉岩的εNd(t)值为+0.51 ~+6.17(表2),所有样品的147Sm/144Nd 比值为均高于大陆地壳的平均值(0.12),其中4 件样品的147Sm/144Nd比值高于MORB 的平均值(0.22,Jahn,1999)。低的负值和低的正值类似于都兰榴辉岩和碧溪岭榴辉岩。都兰榴辉岩原岩形成时代为828 ±58Ma(Yu et al.,2013),按t =800Ma计算的εNd(t)值为-1.9 ~-0.3(Song et al.,2003),表明原岩岩浆来自富集的大陆岩石圈地幔或者来自亏损的软流圈地幔,但在侵位或喷出地表过程中被陆壳物质强烈混染(Paquette et al.,1989;Jahn,1999;Song et al.,2003)。碧溪岭榴辉岩的εNd(0)值为-2.3 ~ -0.6(Chavagnac and Jahn,1996),其原岩年龄可能为745Ma(郑建平等,2007),重新计算的εNd(t)值为+0.3 ~+2,表明其亏损地幔源区被强烈改造或者岩浆侵位到下地壳时被混染(Chavagnac and Jahn,1996;Jahn et al.,2003)。类似的情形在新生代大陆玄武岩中可以观察到,被认为是软流圈地幔与岩石圈地幔反应的结果(Xu et al.,2005)。榴辉岩高的正值(+6 ~+8)与柴北缘锡铁山榴辉岩和沙柳河榴辉岩Nd 同位素组成类似(分别为+3 ~+9 和+6 ~+8,孟繁聪等,2003;Zhang et al.,2008),在锡铁山地区解释为初始小洋盆或大陆裂谷环境(孟繁聪等,2003;Zhang et al.,2005),在沙柳河地区被认为是变质的洋壳(Zhang et al.,2008)。而具有类似Nd 同位素组成的新生代大陆玄武岩通常被认为来自软流圈地幔(Xu et al.,2005)。东昆仑温泉榴辉岩Nd 同位素组成的不均一性(相差6 个εNd单位)可能是地幔源区不均一或原岩岩浆被陆壳物质不均匀混染所致(Jahn,1999;Jahn et al.,2003)。东昆仑温泉榴辉岩原岩形成于新元古代早期(Meng et al.,2013),同期还有花岗岩形成(孟繁聪等,2013),这一岩浆事件比都兰榴辉岩原岩形成早约100Ma,后者被认为形成于大陆裂谷或初始小洋盆环境(Yu et al.,2013),沙柳河榴辉岩的原岩形成时代为516 ±8Ma(Zhang et al.,2008),但不能排除该年龄为混合年龄(Zhang et al.,2010),如果是这样,其原岩也很有可能形成于新元古代。区域上新元古代早期花岗岩的形成与陆块的汇聚有关(如陆松年等,2002),表明当时环境可能为挤压环境(俯冲或碰撞)。通常活动大陆边缘的地幔楔的Nd 同位素组成不均一(Wilson,1989),俯冲带的交代作用可造成来自地幔楔的基性岩浆具有变化范围较大的εNd值,如东天山白石泉的基性-超基性岩(-0.9 ~+5.6,陈斌等,2013)。东昆仑造山带没有证据显示存在新元古代早期的洋盆及其消亡事件,我们倾向认为榴辉岩原岩是来自亏损地幔的岩浆在侵入地壳或喷出地表过程中遭受了陆壳物质的混染,或者在源区软流圈地幔与岩石圈地幔发生过反应。
4.1.3 锆石证据
东昆仑榴辉岩锆石的U/Yb 比值为0.14 ~0.89,Hf 含量为6610 ×10-6~7917 ×10-6,Y 含量为136 ×10-6~252 ×10-6(表3),在辉长岩锆石的U/Yb-Hf 图解(图8)上,落入陆壳辉长岩锆石的范围内(Grimes et al.,2007),也表明这些榴辉岩的原岩形成于大陆环境。
榴辉岩锆石具有正的εHf(t)值(+8 ~+10,图9、表4),高于柴北缘都兰榴辉岩锆石的εHf(t)值(+3 ~+9,Yu et al.,2013),与苏鲁-大别地区基性超基性岩锆石的εHf(t)值类似,如苏鲁地区斜长角闪岩(退变榴辉岩)的锆石具有正的εHf(t)值(+5.8 ~+11.3,+7 ~+8.5),原岩岩浆被认为来自亏损地幔(Liu et al.,2008),大别山碧溪岭石榴橄榄岩锆石的εHf(t)值+3.6 ~+8.1(Zheng et al.,2007,2008),该岩体的原岩被认为是软流圈地幔上涌形成的岩浆在下地壳形成的基性-超基性堆积体(Zhang et al.,1995;Chavagnac and Jahn,1996;Zheng et al.,2007),也支持榴辉岩的原岩可能是由来自亏损地幔或软流圈地幔的基性岩浆演化形成的。
相比而言,来自洋壳及其有关岩石的锆石通常具有更高的正εHf(t)值,如希腊Tinos 和Syros 岛的变质辉长岩,榴辉岩和硬玉岩及蓝片岩锆石的εHf(t)值为+10 ~+20(Fu et al.,2012),日本Tone 和北危地马拉硬玉岩锆石的εHf(t)值分别为+10 ~+16 和+10 ~+13(Yui et al.,2012),缅甸硬玉岩锆石εHf(t)值为+15 ~+20(Qiu et al.,2009;Shi et al.,2009),西昆仑乌依塔格斜长花岗岩锆石εHf(t)值为+13 ~+20(Jiang et al.,2008),它们同样是亏损地幔部分熔融的产物(Fu et al.,2012;Yui et al.,2012)。
4.2 构造意义
东昆仑榴辉岩的地球化学和Nd 同位素组成以及原岩锆石的特征表明其原岩为大陆拉班玄武质岩石,形成于大陆边缘环境,形成时代为新元古代早期约934Ma(Meng et al.,2013),到早古生代中期(450 ~430Ma)发生陆壳的深俯冲作用形成榴辉岩(Meng et al.,2013;贾丽辉等,2014)。东昆仑祁漫塔格早奥陶世(约480Ma)岛弧型蛇绿岩残片的存在(崔美慧等,2011;Meng et al.,2015)以及布青山467Ma NMORB 型洋壳残片的存在(Bian et al.,2004),均表明该地区曾存在早古生代洋盆(原特提斯洋)。目前还不清楚该洋盆何时打开,但是陆壳型榴辉岩的形成时代可限定该洋盆最终关闭时代(李继亮等,1999),这表明东昆仑早古生代洋盆到晚奥陶世-志留纪已经关闭,早古生代洋壳的俯冲消亡以及安第斯型陆缘弧的形成应发生在榴辉岩形成之前,这对认识东昆仑早古生代花岗岩形成的构造环境有重要意义。
东昆仑西段夏日哈木榴辉岩与本文研究的榴辉岩的特征很类似(祁生胜等,2014;Meng et al.,2013),推测其为陆-陆碰撞的产物(祁生胜等,2014),榴辉岩锆石中有两粒锆石核给出了572Ma 和542Ma 的年龄,根据测点位置和锆石大小判断这些是混合年龄,表明其原岩年龄老于572Ma,很有可能其原岩也形成于新元古代的陆壳环境。虽然作者认为从榴辉岩锆石获得的411 ±2Ma 的年龄代表了榴辉岩相峰期变质时代(祁生胜等,2014),由于缺少可靠的矿物学证据(如锆石中的矿物包裹体),这仍需要进一步确定。祁漫塔格地区的花岗质片麻岩的变质时代为416 ±11Ma(孟繁聪等,2013),可能代表了角闪岩相变质作用发生的时代,我们推测夏日哈木榴辉岩与温泉榴辉岩的峰期变质时代相近。东昆仑榴辉岩的发现给我们提出了新的挑战:它们是昆北地体与昆南地体之间碰撞的产物,还是昆北地体与其他大陆(如东冈瓦纳大陆北缘)碰撞的产物?东昆仑榴辉岩与柴达木盆地北缘榴辉岩的演化有许多相似之处:原岩形成于新元古代陆壳环境,早古生代发生高压变质,虽然目前还没有在榴辉岩中发现超高压变质的矿物学证据。这是否意味着柴达木盆地的基底与盆地南北两侧早古生代造山带的演化历史相似?若果真如此,就需要我们重新认识柴达木地块的性质。
5 结论
东昆仑温泉榴辉岩的SiO2含量较高(可达59%),Mg#指数较低(0.45 ~0.51),表明原岩为分异程度较高的中-基性岩浆;稀土元素显示轻稀土亏损型和轻稀土富集型两种类型,指示原岩形成于大陆边缘环境。榴辉岩的εNd(t)值为+0.51 ~+6.17,变化较大,表明原岩岩浆来自亏损地幔,遭受了不同程度的岩石圈地幔或陆壳物质的混染;锆石具有正的εHf(t)值,也支持榴辉岩原岩岩浆来自亏损地幔。因此,榴辉岩代表了俯冲的陆壳,推测沿东昆中缝合带发生过陆壳的深俯冲作用,从而表明东昆仑经历过陆-陆碰撞造山作用。
致谢 吴祥珂和李云帅两位研究生参加了野外工作;国家地质实验测试中心完成了岩石化学分析;中国地质科学院地质研究所同位素实验室完成Sm-Nd 同位素分析;中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室完成了锆石Lu-Hf 同位素测试;张建新和另一名审稿人对论文初稿提出了中肯的修改意见;在此一并表示衷心感谢。
Bernard-Griffiths J and Cornichet J. 1985. Origin of eclogites from south Brittany,France:A Sm-Nd isotopic and REE study. Chemical Geology,52(2):185 -201
Bernard-Griffiths J,Peucat JJ,Cornichet J,de Léon MIP and Ibarguchi JG. 1985. U-Pb Nd isotope and REE geochemistry in eclogites from the Cabo Ortegal Complex,Galicia Spain:An example of REE immobility conserving MORB-like patterns during high-grade metamorphism. Chemical Geology,52(2):217 -225
Bian QT,Zhao DS,Ye ZR,Chang CF,Luo XQ and Gao SL. 2002. A preliminary study of the Kunlun-Qilian-Qinling suture system. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,23(6):501 - 508 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Bian QT,Li DH,Pospelov I,Yin LM,Li HS,Zhao DS,Chang CF,Luo XQ,Gao SL,Astrakhantsevc O and Chamov N. 2004. Age,geochemistry and tectonic setting of Buqingshan ophiolites,North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,23(4):577 -596
Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,148(1 -2):243 -258
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier,63 -114
Chavagnac V and Jahn BM. 1996. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Bixiling Complex, Dabie Mountains, China: Sm-Nd ages,geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications. Chemical Geology,133(1 -4):29 -51
Chen B,He JB,Chen CJ and Muhetaer Z. 2013. Nd-Sr-Os isotopic data of the Baishiquan mafic-ultramafic complex from East Tianshan,and implications for petrogenesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(1):294-302 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen BW and Wang YB. 1996. Some characteristics of orogenic belts in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences,13(3 -5):237 -242
Chen DL,Liu L,Sun Y and Liou JG. 2009. Geochemistry and zircon UPb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane,the North Qaidam,NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,35(3 -4):259 -272
Chen L,SunY,Liu XM and Pei XZ. 2000. Geochemistry of Derni ophiolite and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica,16(1):106 -110 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen L,Sun Y,Pei XZ,Gao M,Feng T,Zhang ZQ and Chen W.2001. Northernmost paleo-Tethyan oceanic basin in Tibet:Geochronological evidence from40Ar/39Ar age dating of Dur’ngoi ophiolite. Chinese Science Bulletin,46(14):1203 -1205
Chen NS,Zhu J,Wang GC,Hou GJ,Zhang KX,Zhu YH and Bai YS.1999. Metamorohic petrological features of high-grade metamorphic microlithons in Qingshuiquan region,eastern section of Eastern Kunlun orogenic zone. Earth Science,24(2):116 - 120 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen NS,Li XY,Zhang KX,Wang GC,Zhu YH,Hou GJ and Bai YS.2006. Lithological characteristics of the Baishahe Formation to the south of Xiangride Town,eastern Kunlun Mountains and its age constrained from zircon Pb-Pb dating. Geological Science and Technology Information,25(6):1 - 7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Coleman RG. 1977. Ophiolites:Ancient Oceanic Lithosphere?New York:Springer,1 -229
Cui MH,Meng FC and Wu XK. 2011. Early Ordovician island arc of Yaziquan,west of Qimantag Mountain,Eastern Kunlun:Evidences from geochemistry, Sm-Nd isotope and geochronology of intermediate-basic igneous rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(11):3365 -3379 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cullers RL and Graf JL. 1984. Rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust:Predominantly basic and ultrabasic rocks. In:Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry.Amsterdam:Elsevier,237 -267
Feng JY,Pei XZ,Yu SL,Ding SP,Li RB,Sun Y,Zhang YF,Li ZC,Chen YX,Zhang XF and Chen GC. 2010. The discovery of the mafic-ultramafic mélange in Kekesha area of Dulan County,East Kunlun region,and its LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age. Geology in China,37(1):28 -38 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fu B,Paul B,Cliff J,Bröcker M and Bulle F. 2012. O-Hf isotope constraints on the origin of zircon in high-pressure melange blocks and associated matrix rocks from Tinos and Syros,Greece. European Journal of Mineralogy,24(2):277 -287
Gao J and Klemd R. 2003. Formation of HP-LT rocks and their tectonic implications in the western Tianshan Orogen, NW China:Geochemical and age constraints. Lithos,66(1 -2):1 -22
Gao YL,Wu XN and Zuo GC. 1988. The characters and tectonic significance of ophiolite first discovered in the East Kunlun area.Bull. Xi’an Inst. Geol. Min. Res.,Chinese Acad. Geol. Sci.,(21):17 -28 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Griffin WL,Wang X,Jackson SE,Pearson NJ,O’Reilly SY,Xu XS and Zhou XM. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing,SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes,Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos,61(3 -4):237 -269
Grimes CB,John BE,Kelemen PB,Mazdab F,Wooden JL,Cheadle MJ,Hanghøj K and Schwartz JJ. 2007. Trace element chemistry of zircons from oceanic crust:A method for distinguishing detrital zircon provenance. Geology,35(7):643 -646
Gu FB. 1994. Geological characteristics of East Kunlun and tectonic evolution in Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic Era. Geology in Qinghai,(1):4 -14 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo AL,Zhang GW,Sun YG,Zheng JK,Liu Y and Wang JQ. 2007.Geochemistry and spatial distribution of OIB and MORB in A’nyemaqen ophiolite zone:Evidence of Majixueshan ancient ridgecentered hotspot. Science in China (Series D),50(2):197 -208
He XX,Tang SH,Zhu XK and Wang JH. 2007. Precise measurement of Nd isotopic ratios by means of multi-collector magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,28(4):405 -410 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hou KJ,Li YH,Zou TR,Qu XM,Shi YR and Xie GQ. 2007. Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrologica Sinica,23(10):2595 -2604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Irvine TN and Baragar WRA. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences,8(5):523 -548
Jahn BM. 1999. Sm-Nd isotope tracer study of UHP metamorphic rocks:Implications for continental subduction and collisional tectonics.International Geology Review,41(10):859 -885
Jahn BM,Fan QC,Yang JJ and Henin O. 2003. Petrogenesis of the Maowu pyroxenite-eclogite body from the UHP metamorphic terrane of Dabieshan:Chemical and isotopic constraints. Lithos,70(3 -4):243 -267
Jia LH,Meng FC and Feng HB. 2014. Fluid activity during eclogitefacies peak metamorphism:Evidence from a quartz vein in eclogite in the East Kunlun,NW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(8):2339-2350 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang CF,Feng BG,Yang JS,Zhu ZZ,Zhao M,Chai YC,Shi XD and Hu JQ. 1986. An outline of the geology and tectonics of the Kunlun Mts. area. Bull. Inst. Geol. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci.,(15):70 -79 (in Chinese)
Jiang CF,Yang JS,Feng BG,Zhu ZZ,Zhao M,Chai YC,Shi XD,Wang HD and Hu JQ. 1992. Opening-Closing Tectonics of Kunlun Mountains. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 - 224 (in Chinese)
Jiang YH,Liao SY,Yang WZ and Shen WZ. 2008. An island arc origin of plagiogranites at Oytag,western Kunlun orogen,northwest China:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb chronology,elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry and Paleozoic tectonic implications. Lithos,106(3 -4):323 -335
Konstantinovskaia EA,Brunel M and Malavieille J. 2003. Discovery of Paleo-Tethys residual peridotites along the Anyemaqen-KunLun suture zone (North Tibet). Comptes Rendus Geoscience,335(8):709 -719
Li HK,Lu SN,Xiang ZQ,Zhou HY,Guo H,Song B,Zheng JK and Gu Y. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the granulite from the Qingshuiquan area,Central Eastern Kunlun Suture Zone. Earth Science Frontiers,13(6):311 - 321 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li JL,Sun S,Hao J,Chen HH,Hou QL,Xiao WJ and Wu JM. 1999.Time limit of collision event of collision orogens. Acta Petrologica Sinica,15(2):315 -320 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li RS,Ji WH,Zhao ZM,Chen SJ,Meng Y,Yu PS and Pan XP. 2007.Progress in the study of the Early Paleozoic Kunlun orogenic belt.Geological Bulletin of China,26(4):373 -382 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu HT. 2001. Qimantage terrestrial volcanics:Petrologic evidence of active continental margin of Tarim plate during Late Indo-China epoch. Acta Petrologica Sinica,17(3):337 -351 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu YH,Yang HJ,Shau YH,Meng FC,Zhang JX,Yang JS,Xu ZQ and Yu SC. 2007. Compositions of high Fe-Ti eclogites from the Sulu UHP metamorphic terrane,China:HFSE decoupling and protolith characteristics. Chemical Geology,239(1 -2):64 -82
Liu YJ,Genser TJ,Neubauer F,Jin W,Ge XH,Handler R and Takasu A. 2005.40Ar/39Ar mineral ages from basement rocks in the Eastern Kunlun Mountains, NW China, and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics,398(3 -4):199 -224
Liu YS,Zong KQ,Kelemen PB and Gao S. 2008. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole:Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates. Chemical Geology,247(1-2):133 -153
Liu ZQ,Pei XZ,Li RB,Li ZC,Zhang XF,Liu ZG,Chen GC,Ding SP and Guo JF. 2011. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of the two suites of ophiolite at the Buqingshan area of the A’nymaqen orogenic belt in the southern margin of the East Kunlun and its tectonic implication. Acta Geologica Sinica,85(2):185 -194 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu L,Wu ZH,Hu DG,Barosh PJ,Hao S and Zhou CJ. 2010. Zircon U-Pb age for rhyolite of the Maoniushan Formation and its tectonic significance in the East Kunlun Mountains. Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(4):1150 -1158 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu SN,Yu HF,Jin W,Li HK and Zheng JK. 2002. Microcontinents on the eastern margin of Tarim paleocontinent. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,21(4):317 -326 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu SN,Yu HF,Li HK,Chen ZH,Wang HC,Zhang CL and Xiang ZQ.2006. Early Paleozoic suture zones and tectonic divisions in the‘Central China Orogen’. Geological Bulletin of China,25(12):1368 -1380 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Meng FC,Zhang JX,Yang JS and Xu ZQ. 2003. Geochemical characteristics of eclogites in Xitieshan area,North Qaidam of northwestern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,19(3):435 -442 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Meng FC,Zhang JX and Cui MH. 2013. Discovery of Early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun,western China and its tectonic significance. Gondwana Research,23(2):825 -836
Meng FC,Cui MH,Wu XK,Wu JF and Wang JH. 2013. Magmatic and metamorphic events recorded in granitic gneisses from Qimantag,East Kunlun Mountains,Northwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(6):2107 -2121 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Meng FC,Cui MH,Wu XK and Ren YF. 2015. Heishan maficultramafic rocks in the Qimantag area of East Kunlun,China:Remnants of an early Paleozoic incipient island arc. Gondwana Research,27(2):745 -759
Meschede M. 1986. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram. Chemical Geology,56(3 -4):207 -218
Mo XX,Luo ZH,Deng JF,Yu XH,Liu CD,Chen HW,Yuan WM and Liu YH. 2007. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun orogenic belt. Geological Journal of China Universities,13(3):403-414 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Niu YL. 2005. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas:Some basic concepts and new view on the origin of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basaltic volcanism in Eastern China. Geological Journal of China Universities,11(1):9 -46
Pan GT,Wang LQ,Li RS,Yuan SH,Ji WH,Yin FG,Zhang WP and Wang BD. 2012. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,53:3 -14
Pan YS,Zhou WM,Xu RH,Wang DA,Zhang YQ,Xie YW,Chen TE and Luo H. 1996. Geological characteristics and evolution of the Kunlun Mountains region during the Early Paleozoic. Science in China (Series D),39(4):337 -347
Paquette JL,Menot RP and Peucat JJ. 1989. REE,Sm-Nd and U-Pb zircon study of eclogites from the Alpine External massifs (Western Alps):Evidence for crustal contamination. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,96(1 -2):181 -198
Pearce JA. 2008. Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos,100(1 -4):14 -48
Qi SS,Song SG,Shi LC,Cai HJ and Hu JC. 2014. Discovery and its geological significance of Early Paleozoic eclogite in Xiarihamu-Suhaitu area,western part of the East Kunlun. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(11):3345 -3356 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qiu ZL,Wu FY,Yang SF,Zhu M,Sun JF and Yang P. 2009. Age and genesis of the Myanmar jadeite:Constraints from U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of zircon inclusions. Chinese Science Bulletin,54(4):658-668
Shi GH,Jiang N,Liu Y,Wang X,Zhang ZY and Xu YJ. 2009. Zircon Hf isotope signature of the depleted mantle in the Myanmar jadeitite:Implications for Mesozoic intra-oceanic subduction between the Eastern Indian Plate and the Burmese Platelet. Lithos,112(3 -4):342 -350
Song SG,Yang JS,Xu ZQ,Liou JG and Shi RD. 2003. Metamorphic evolution of the coesite-bearing ultrahigh-pressure terrane in the North Qaidam,Northern Tibet,NW China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(6):631 -644
Song SG,Zhang LF,Niu YL,Su L,Song B and Liu DY. 2006.Evolution from oceanic subduction to continental collision:A case study from the northern Tibetan Plateau based on geochemical and geochronological data. Journal of Petrology,47(3):435 -455
Song SG,Su L,Li XH,Zhang GB,Niu YL and Zhang LF. 2010.Tracing the 850-Ma continental flood basalts from a piece of subducted continental crust in the North Qaidam UHPM belt,NW China. Precambrian Research,183(4):805 -816
Wang BZ,Zhang SQ,Zhang ZY and Wang J. 2001. Proterozoic ophiolite in the Zhanahere area in the east section of the East Kunlun.Regional Geology of China,20(1):52 - 57 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GC,Zhang TP,Liang B,Chen NS,Zhu YH,Zhu J and Bai YS.1999. Composite ophiolitic mélange zone in central part of Eastern section of Eastern Kunlun orogenic zone and geological significance of‘fault belt in central part of Eastern section of Eastern Kunlun orogenic zone’. Earth Science,24(2):129 -133 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GC,Wang QH,Jian P and Zhu YH. 2004. Zircon SHRIMP ages of Precambrian metamorphic basement rocks and their tectonic significance in the eastern Kunlun Mountains,Qinghai Province,China. Earth Science Frontiers,11(4):481 - 490 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GC,Wei QR,Jia CX,Zhang KX,Li DW,Zhu YH and Xiang SY. 2007. Some ideas of Precambrian geology in the East Kunlun,China. Geological Bulletin of China,26(8):929 -937 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang H,Wu YB,Gao S,Liu XC,Liu Q,Qin ZW,Xie SW,Zhou L and Yang SH. 2013. Continental origin of eclogites in the North Qinling terrane and its tectonic implications. Precambrian Research,230:13 -30
Wang SG,Tan XR and Zhao YL. 1995. REE geochemistry and origin of eclogite in northern Jiangsu Province. Geological Review,41(5):401 -408 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YS and Chen JN. 1987. Metamorphic Zone and Metamorphism in Qinghai Province and Its Adjacent Areas. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 -248 (in Chinese)
Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis. London:Chapman & Hall,1-466
Winchester JA and Floyd PA. 1977. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chemical Geology,20:325 -343
Wu GJ,Xiao XC and Li TD. 1989. The Yadong-Golmud geoscience section on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica,63(4):285 -296 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao XC,Tang YQ and Gao YL. 1986. Re-exposition on plate tectonics of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,14(3):7 -19 (in Chinese)
Xu RH,Zhang YQ,Xie YW,Chen FK,Vidal P,Arnaud N,Zhang QD and Zhao DM. 1994. A discovery of an Early Paleozoic tectonomagmatic belt in the northern part of West Kunlun Mountains.Scientia Geologica Sinica,29(4):313 - 328 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu YG,Ma JL,Frey FA,Feigenson MD and Liu JF. 2005. Role of Lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction in the genesis of Quaternary alkali and tholeiitic basalts from Datong,western North China Craton. Chemical Geology,224(4):247 -271
Xu ZQ,Yang JS,Li HB and Yao JX. 2006. The Early Paleozoic terrane framework and the formation of the high-pressure (HP)and Ultrahigh pressure (UHP)metamorphic belts at the Central Orogenic Belt(COB). Acta Geologica Sinica,80(12):1793 -1806 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu ZQ,Yang JS,Li HB,Zhang JX and Wu CL. 2007. Orogenic Plateau:Terrane Amalgamation,Collision and Uplift in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 -458 (in Chinese)
Yang JS,Robinson PT,Jiang CF and Xu ZQ. 1996. Ophoilites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their tectonic implications.Tectonophysics,258(1 -4):215 -231
Yang JS,Wang XB,Shi RD,Xu ZQ and Wu CL. 2004. The Dur’ngoi ophiolite in East Kunlun,NE Tibetan plateau:A fragment of paleo-Tethyan oceanic lithosphere. Geology in China,31(3):225 -239(in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang JS,Xu ZQ,Li HB and Shi RD. 2005. The Paleo-Tethyan volcanism and plate tectonic regime in the A’nyemaqen Region of East Kunlun, northern Tibet Plateau. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,24 (5):369 - 380 (in Chinese with English
Abstract)
Yang JS,Shi RD,Wu CL,Wang XB and Robinson PT. 2009. The Dur’ngoi ophiolite in East Kunlun,Northeast Tibetan Plateau:Evidence for a Paleo-Tethyan suture in Northwest China. Journal of Earth Science,20(2):303 -331
Yin A. 2001. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen:Phanerozoic growth of Asia continent. Acta Geosicentica Sinica,22(3):193 -230 (in Chinese)
Yin HF and Zhang KX. 1997. Characteristics of the eastern Kunlun orogenic belt. Earth Science,22(4):339 -342 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu SY,Zhang JX,Li HK,Hou KJ,Mattinson CG and Gong JH. 2013.Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotopic composition of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Dulan area,North Qaidam UHP terrane:New evidence for deep continental subduction. Gondwana Research,23(3):901 -919
Yui TF,Maki K,Wang KL,Lan CY,Usuki T,IIzuka Y,Wu CM,Wu TW,Nishayama T,Martens U,Liou JG and Grove M. 2012. Hf isotope and REE compositions of zircon from jadeitite (Tone,Japan and north of the Motagua fault,Guatemala):Implications on jadeitite genesis and possible protoliths. European Journal of Mineralogy,24(2):263 -275
Zeng LS,Gao LE,Xie KJ and Zeng JL. 2011. Mid-Eocene high Sr/Y granites in the Northern Himalayan Gneiss Domes:Melting thickened lower continental crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,303(3-4):251 -266
Zhang C,Zhang LF,Bader T,Song SG and Lou YX. 2013.Geochemistry and trace element behaviors of eclogite during its exhumation in the Xitieshan terrane,North Qaidam UHP belt,NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,63:81 -97
Zhang GB,Song SG,Zhang LF and Niu YL. 2008. The subducted oceanic crust within continental-type UHP metamorphic belt in the North Qaidam,NW China:Evidence from petrology,geochemistry and geochronology. Lithos,104(1 -4):99 -108
Zhang JX,Zhang ZM,Xu ZQ,Yang JS and Cui JW. 2001. Petrology and geochronology of eclogites from the western segment of the Altyn Tagh,northwestern China. Lithos,56(2 -3):187 -206
Zhang JX,Yang JS,Mattinson CG,Xu ZQ,Meng FC and Shi RD.2005. Two contrasting eclogite cooling histories,North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane,western China:Petrological and isotopic constraints.Lithos,84(1 -2):51 -76
Zhang JX,Meng FC and Wan YS. 2007. A cold Early Palaeozoic subduction zone in the North Qilian Mountains,NW China:Petrological and U-Pb geochronological constraints. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,25(3):285 -304
Zhang JX,Mattinson CG,Yu SY,Li JP and Meng FC. 2010. U-Pb zircon geochronology of coesite-bearing eclogites from the southern Dulan area of the North Qaidam UHP terrane,northwestern China:Spatially and temporally extensive UHP metamorphism during continental subduction. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,28(9):955 -978
Zhang RY, Liou JG and Cong BL. 1995. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphosed talc-magnesite- and Ti-clinohumite-bearing maficultramafic complex,Dabie Mountains,east-central China. Journal of Petrology,36(4):1011 -1037
Zhang ZM,Liou JG,Zhao XD and Shi C. 2006. Petrogenesis of Maobei rutile eclogites from the southern Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt,eastern China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,24(8):727 -741
Zheng JP,Sun M,Griffin WL,Zhong ZQ,Tang HY and Zhang ZH.2007. Study on U-Pb age and Hf isotope of zircons in the Bixiling peridotites,the Dabie ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica,23(2):343 - 350 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng JP,Sun M,Griffin WL,Zhou MF,Zhao GC,Robinson P,Tang HY and Zhang ZH. 2008. Age and geochemistry of contrasting peridotite types in the Dabie UHP belt,eastern China:Petrogenetic and geodynamic implications. Chemical Geology,247(1 -2):282-304
Zheng YF. 2012. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chemical Geology,328:5 -48
Zhu YH,Zhang KX,Pan YM,Chen NS,Wang GC and Hou GJ. 1999.Determination of different ophiolitic belts in eastern Kunlun orogenic zone and their tectonic significance. Earth Science,24(2):134 -138 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu YH,Zhang KX,Wang GC,Bai YS,Chen NS and Hou GJ. 2002.The Ophiolite,Magmatic Rocks and Tectonic Magmatic Evolution of Composite Orogenic Belt of East Kunlun. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,1 -115 (in Chinese)
Zhu YH,Lin QX,Jia CX and Wang GC. 2006. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age and significance of Early Paleozoic volcanic rocks in East Kunlun orogenic belt,Qinghai Province,China. Science in China (Series D),49(1):88 -96
附中文参考文献
边千韬,赵大升,叶正仁,常承法,罗小全,高山林. 2002. 初论秦祁昆缝合系. 地球学报,23(6):501 -508
陈斌,贺敬博,陈长健,木合塔尔·扎日. 2013. 东天山白石泉镁铁-超镁铁杂岩体的Nd-Sr-Os 同位素成分及其对岩浆演化的意义.岩石学报,29(1):294 -302
陈亮,孙勇,柳小明,裴先治. 2000. 青海省德尔尼蛇绿岩的地球化学特征及其大地构造意义. 岩石学报,16(1):106 -110
陈亮,孙勇,裴先治,高明,冯涛,张宗清,陈文. 2001. 德尔尼蛇绿岩40Ar-39Ar 年龄:青藏最北端古特提斯洋盆存在和延展的证据. 科学通报,46(5):424 -426
陈能松,朱杰,王国灿,侯光久,张克信,朱云海,拜永山. 1999. 东昆仑造山带东段清水泉高级变质岩片的变质岩石学研究. 地球科学,24(2):116 -120
陈能松,李晓彦,张克信,王国灿,朱云海,侯光久,拜永山. 2006.东昆仑山香日德南部白沙河岩组的岩石组合特征和形成年代的锆石Pb-Pb 定年启示. 地质科技情报,25(6):1 -7
崔美慧,孟繁聪,吴祥珂. 2011. 东昆仑祁漫塔格鸭子泉早奥陶世岛弧:中基性火成岩地球化学、Sm-Nd 同位素及年代学证据. 岩石学报,27(11):3365 -3379
冯建赟,裴先治,于书伦,丁仨平,李瑞保,孙雨,张亚峰,李佐臣,陈有炘,张晓飞,陈国超. 2010. 东昆仑都兰可可沙地区镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩的发现及其LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄. 中国地质,37(1):28 -38
高延林,吴向农,左国朝. 1988. 东昆仑山清水泉蛇绿岩特征及其大地构造意义. 中国地质科学院西安地质研究所所刊,(21):17-28
古凤宝. 1994. 东昆仑地质特征及晚古生代-中生代构造演化. 青海地质,(1):4 -14
郭安林,张国伟,孙延贵,郑健康,刘晔,王建其. 2006. 阿尼玛卿蛇绿岩带OIB 和MORB 的地球化学及空间分布特征:玛积雪山古洋脊热点构造证据. 中国科学(D 辑),36(7):618 -629
何学贤,唐索寒,朱祥坤,王进辉. 2007. 多接收器等离子体质谱(MC2ICPMS)高精度测定Nd 同位素方法. 地球学报,28(4):405 -410
侯可军,李延河,邹天人,曲晓明,石玉若,谢桂青. 2007. LA-MCICP-MS 锆石Hf 同位素的分析方法及地质应用. 岩石学报,23(10):2595 -2604
贾丽辉,孟繁聪,冯惠彬. 2014. 榴辉岩相峰期流体活动:来自东昆仑榴辉岩石英脉的证据. 岩石学报,30(8):2339 -2350
姜春发,冯秉贵,杨经绥,朱志直,赵民,柴耀楚,施希德,胡金庆.1986. 昆仑地质构造轮廓. 中国地质科学院地质研究所所刊,(15):70 -79
姜春发,杨经绥,冯秉贵,朱志直,赵民,柴耀楚,施希德,王怀达,胡金庆. 1992. 昆仑开合构造. 北京:地质出版社,1 -224
李怀坤,陆松年,相振群,周红英,郭虎,宋彪,郑健康,顾瑛.2006. 东昆仑中部缝合带清水泉麻粒岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 年代学研究. 地学前缘,13(6):311 -321
李继亮,孙枢,郝杰,陈海泓,侯泉林,肖文交,吴继敏. 1999. 碰撞造山带的碰撞事件时限的确定. 岩石学报,15(2):315 -320
李荣社,计文化,赵振明,陈守建,孟勇,于浦生,潘小平. 2007. 昆仑早古生代造山带研究进展. 地质通报,26(4):373 -382
刘红涛. 2001. 祁漫塔格陆相火山岩:塔里木陆块南缘印支期活动大陆边缘的岩石学证据. 岩石学报,17(3):337 -351
刘战庆,裴先治,李瑞保,李佐臣,张晓飞,刘智刚,陈国超,陈有忻,丁仨平,郭俊锋. 2011. 东昆仑南缘阿尼玛卿构造带布青山地区两期蛇绿岩的定年及其构造意义. 地质学报,85(2):185-194
陆露,吴珍汉,胡道功,Barosh PJ,郝爽,周春景. 2010. 东昆仑牦牛山组流纹岩锆石U-Pb 年龄及构造意义. 岩石学报,26(4):1150 -1158
陆松年,于海峰,金巍,李怀坤,郑健康. 2002. 塔里木古大陆东缘的微大陆块体群. 岩石矿物学杂志,21(4):317 -326
陆松年,于海峰,李怀坤,陈志宏,王惠初,张传林,相振群. 2006.“中央造山带”早古生代缝合带及构造分区概述. 地质通报,25(12):1368 -1380
孟繁聪,张建新,杨经绥,许志琴. 2003. 柴北缘锡铁山榴辉岩的地球化学特征. 岩石学报,19(3):435 -442
孟繁聪,崔美慧,吴祥珂,吴久芳,王建华. 2013. 东昆仑祁漫塔格花岗片麻岩记录的岩浆和变质事件. 岩石学报,29(6):2107-2121
莫宣学,罗照华,邓晋福,喻学惠,刘成东,谌宏伟,袁万明,刘云华. 2007. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长. 高校地质学报,13(3):403 -414
潘裕生,周伟明,许荣华,王东安,张玉泉,谢应雯,陈挺恩,罗辉.1996. 昆仑山早古生代地质特征与演化. 中国科学(D 辑),26(4):302 -307
祁生胜,宋述光,史连昌,才航加,胡继春. 2014. 东昆仑西段夏日哈木-苏海图早古生代榴辉岩的发现及意义. 岩石学报30(11):3345 -3356
王秉璋,张森琦,张智勇,王瑾. 2001. 东昆仑东端扎那合惹地区元古宙蛇绿岩. 中国区域地质,20(1):52 -57
王国灿,张天平,梁斌,陈能松,朱云海,朱杰,拜永山. 1999. 东昆仑造山带东段昆中复合蛇绿混杂岩带及“东昆中断裂带”地质涵义. 地球科学,24(2):129 -133
王国灿,王青海,简平,朱云海. 2004. 东昆仑前寒武纪基底变质岩系的锆石SHRIMP 年龄及其构造意义. 地学前缘,11(4):481-490
王国灿,魏启荣,贾春兴,张克信,李德威,朱云海,向树元. 2007.关于东昆仑地区前寒武纪地质的几点认识. 地质通报,26(8):929 -937
王式洸,谭绪荣,赵云龙. 1995. 苏北榴辉岩的稀土元素地球化学及其成因讨论. 地质论评,41(5):401 -408
王云山,陈基娘. 1987. 青海省及毗邻地区变质地带与变质作用. 北京:地质出版社,1 -248
吴功建,肖序常,李廷栋. 1989. 青藏高原亚东-格尔木地学断面. 地质学报,63(4):285 -296
肖序常,汤耀庆,高延林. 1986. 再论青藏高原的板块构造. 中国地质科学院院报,14(3):7 -19
许荣华,张玉泉,谢应雯,陈福坤,Vidal P,Arnaud N,张巧大,赵敦敏. 1994. 西昆仑山北部早古生代构造-岩浆带的发现. 地质科学,29(4):313 -328
许志琴,杨经绥,李海兵,姚建新. 2006. 中央造山带早古生代地体构架与高压/超高压变质带的形成. 地质学报,80(12):1793-1806
许志琴,杨经绥,李海兵,张建新,吴才来. 2007. 造山的高原——青藏高原地体的拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制. 北京:地质出版社,1 -458
杨经绥,王希斌,史仁灯,许志琴,吴才来. 2004. 青藏高原北部东昆仑南缘德尔尼蛇绿岩:一个被肢解了的古特提斯洋壳. 中国地质,31(3):225 -239
杨经绥,许志琴,李海兵,史仁灯. 2005. 东昆仑阿尼玛卿地区古特提斯火山作用和板块构造体系. 岩石矿物学杂志,24(5):369-380
尹安. 2001. 喜马拉雅-青藏高原造山带地质演化——显生宙亚洲大陆生长. 地球学报,22(3):193 -230
殷鸿福,张克信. 1997. 东昆仑造山带的一些特点. 地球科学,22(4):339 -342
郑建平,孙敏,Griffin WL,钟增球,汤华云,张志海. 2007. 大别造山带碧溪岭橄榄岩中锆石U-Pb 年龄和Hf 同位素研究. 岩石学报,23(2):343 -350
朱云海,张克信,Pan YM,陈能松,王国灿,侯光久. 1999. 东昆仑造山带不同蛇绿岩带的厘定及其构造意义. 地球科学,24(2):134 -138
朱云海,张克信,王国灿,拜永山,陈能松,侯光久. 2002. 东昆仑复合造山带蛇绿岩、岩浆岩及构造岩浆演化. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1 -115
