血浆氨基末端脑钠肽前体水平与急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者冠状动脉病变程度的关系研究
2015-02-22陈旭虞
陈旭虞,夏 豪
·论著·
血浆氨基末端脑钠肽前体水平与急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者冠状动脉病变程度的关系研究
陈旭虞,夏 豪
目的 探讨血浆氨基末端脑钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)水平与急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)患者冠状动脉病变程度的关系。方法 选取广西钦州市第二人民医院2012年3月—2015年3月收治的STEMI患者252例,根据血浆NT-proBNP水平分为NT-proBNP正常组(NT-proBNP<800 ng/L)126例和NT-proBNP升高组(NT-proBNP>800 ng/L)126例。所用患者入院后进行全面询问病史、体格检查并记录年龄、性别、冠心病家族史、吸烟史及高血压、高脂血症、糖尿病发病情况,入院后24 h内测定血浆NT-proBNP、肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)、肌红蛋白(MYO)、超敏肌钙蛋白I(ultra-TnI)水平,入院第2天清晨采集空腹静脉血检测血脂,采用Judkins法进行冠状动脉造影检查。比较两组患者一般资料、冠状动脉造影结果,并分析血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分的相关性。结果 NT-proBNP升高组患者高血压发生率、ultra-TnI水平高于NT-proBNP正常组(P<0.05)。两组患者性别、年龄、高脂血症发生率、糖尿病发生率、冠心病家族史和吸烟史阳性率及CK-MB、MYO、总胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。NT-proBNP升高组冠状动脉三支病变发生率高于NT-proBNP正常组,单支病变、双支/左主干病变发生率低于NT-proBNP正常组(P<0.05)。NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉病变支数多于NT-proBNP正常组,Gensini积分高于NT-proBNP正常组(P<0.05)。直线相关分析结果显示,血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分呈正相关(r=0.813,P=0.000)。结论 血浆NT-proBNP水平与STEMI患者冠状动脉病变程度有关,可通过检测血浆NT-proBNP水平来判断冠状动脉病变程度。
利钠肽,脑;冠心病;冠状动脉狭窄
冠心病是冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病和冠状动脉功能性改变的统称,是临床常见病、多发病,尤其是老年人群[1]。脑钠肽(BNP)是一种心脏神经激素,主要由心室肌细胞分泌,当心室肌细胞受到牵拉刺激时就会以脑钠肽前体(proBNP)的形式合成并释放,最后裂解为氨基末端脑钠肽前体(NT-proBNP),其具有利尿、排钠、扩张血管及舒张平滑肌等作用[2]。NT-proBNP在诊断心力衰竭及评价预后方面的重要性已得到证实。近年来,有关NT-proBNP的研究发展迅速,越来越多的证据表明BNP和NT-proBNP是冠心病患者新发心力衰竭和病死的强有力的生物学预测指标,血浆NT-proBNP水平不仅受心脏功能影响,心肌缺血时亦可导致其水平升高[3-4]。本研究旨在探讨血浆NT-proBNP水平与急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)患者冠状动脉病变程度间的关系。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 选取广西钦州市第二人民医院2012年3月—2015年3月收治的STEMI患者252例,均符合美国心脏病学会和美国心脏病协会(ACC/AHA)制定的STEMI诊断标准。根据患者血浆NT-proBNP水平分为NT-proBNP正常组(NT-proBNP≤800 ng/L) 126例与NT-proBNP升高组(NT-proBNP>800 ng/L)126例。排除标准:心功能不全、肝肾功能不全患者;伴有冠心病、心肌梗死病史及其他心脏病如扩张型心肌病、瓣膜性心脏病等患者;伴有严重感染、肿瘤、结缔组织病、甲状腺疾病、肺动脉栓塞等患者。本研究经过本院伦理委员会批准,所有入选患者知情同意并签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 资料采集 所用患者入院后进行全面询问病史、体格检查并记录年龄、性别、冠心病家族史、吸烟史及高血压、高脂血症、糖尿病发病情况。所有患者于入院后24 h内取仰卧位、静息(休息>30 min)状态下抽取肘静脉血3 ml,加入预冷的含抑肽酶(500 U/ml)和10%乙二胺四乙酸30 μl真空抗凝玻璃试管中,30 min内3 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液。采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测血浆NT-proBNP水平,采用化学发光免疫法测定血浆肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)、肌红蛋白(MYO)、超敏肌钙蛋白I(ultra-TnI)水平。入院第2天清晨采集所有患者空腹静脉血检测血脂,检测仪器为HITACH I-7600DP全自动生化分析仪。
1.2.2 冠状动脉造影检查 采用Judkins法,常规左冠状动脉投射6个体位,右冠状动脉投射2个体位,并根据个体病情增加投射体位。以各投射体位中最大狭窄程度作为病变狭窄程度。根据冠状动脉狭窄直径≥50%累及左前降支(LAD)、左回旋支(LCX)、右冠状动脉(RCA)或左主干(LM)分为单支、双支(累及LM为双支病变)及三支病变。冠状动脉狭窄程度:采用Gensini积分对冠状动脉狭窄程度进行定量评分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄25%计1分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄26%~50%计2分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄51%~75%计4分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄76%~90%计8分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄91%~99%计16分,冠状动脉管腔狭窄100%计32分;不同狭窄冠状动脉节段按Gensini积分评分标准乘以相应系数,每例患者冠状动脉狭窄积分为各分支积分之和。
1.3 观察指标 比较两组患者一般资料、冠状动脉造影结果,并分析血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分的相关性。

2 结果
2.1 两组患者一般资料比较 NT-proBNP升高组患者高血压发生率、ultra-TnI水平高于NT-proBNP正常组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者性别、年龄、高脂血症发生率、糖尿病发生率、冠心病家族史和吸烟史阳性率及CK-MB、MYO、总胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1)。
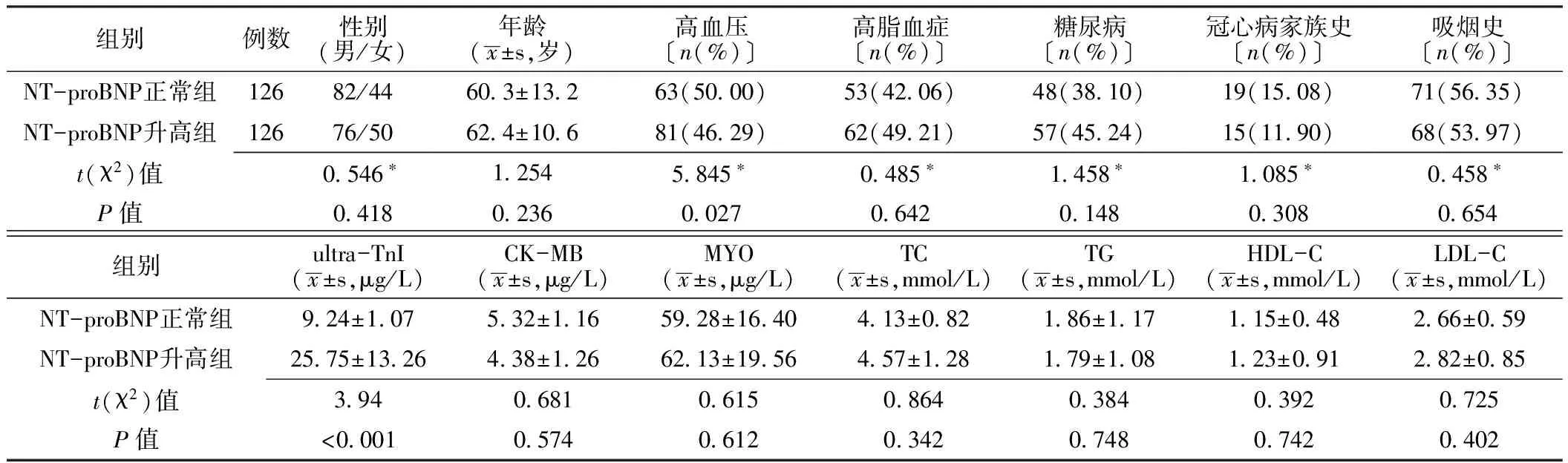
表1 两组患者一般资料比较
注:*为χ2值;NT-proBNP=氨基末端脑钠肽前体,ultra-TnI=超敏肌钙蛋白I,CK-MB=肌酸激酶同工酶,MYO=肌红蛋白,TC=总胆固醇,TG=三酰甘油,HDL-C=高密度脂蛋白胆固醇,LDL-C=低密度脂蛋白胆固醇
2.2 两组患者冠状动脉造影结果比较 NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉病变程度重于NT-proBNP正常组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);其中NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉三支病变发生率高于NT-proBNP正常组(χ2=6.845),双支/LM病变和三支病变发生率低于NT-proBNP正常组(χ2值分为为7.661、34.411),差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉病变支数多于NT-proBNP正常组,Gensini积分高于NT-proBNP正常组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表2)。
表2 两组患者冠状动脉造影结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of coronary angiography results between the two groups

组别例数冠状动脉病变程度(例)单支病变 双支/LM病变 三支病变冠状动脉病变支数(x±s,支)Gensini积分(x±s,分)NT-proBNP正常组1265955121 34±0 6328 58±17 13NT-proBNP升高组1263634562 39±0 7562 38±24 35t(χ2)值4 458∗3 8455 846P值<0 001<0 001<0 001
注:LM=左主干;*为χ2值
2.3 血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分的相关性分析 STEMI患者血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分呈正相关(r=0.813,P=0.000,见图1)。
3 讨论
冠心病是一种严重危害人类健康的常见心血管疾病[5]。BNP属于利钠肽家族中的一员,是在心室容积扩张和压力负荷增加时主要从心室中分泌的一种内分泌激素,具有扩张血管、利尿利钠、抑制交感神经系统及肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS系统)活性等作用[6]。当心脏容量负荷增加时,心室肌细胞受到牵张刺激而产生前BNP前体(pre-proBNP),pre-proBNP随后裂解为32个氨基酸组成的BNP和76个氨基酸组成的NT-proBNP[7]。NT-proBNP的t1/2较BNP长,且无生物活性,因此临床上常通过检测血浆NT-proBNP水平诊断心力衰竭,血浆NT-proBNP水平对心力衰竭患者的治疗效果及预后评估具有指导意义[8]。冠心病患者发生心肌缺血导致心肌损伤及坏死,由于心肌的收缩和舒张功能急剧下降,容量负荷相对过重,导致心室受到明显牵拉而引起血浆BNP水平明显升高,且单纯心肌缺血可以诱导BNP基因的表达,从而促使BNP的合成和释放[9]。目前研究显示,急性冠脉综合征(ACS)患者BNP水平越高,其心血管事件发生率、近期及远期病死率越高,无明确心力衰竭证据的ACS患者BNP水平升高仍然是死亡的独立预测因子,可以为ACS患者的预后提供诊断依据[10]。
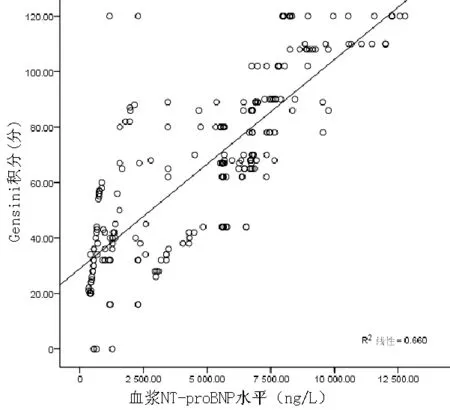
图1 STEMI患者血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分关系的散点图
Figure 1 Scatter diagram of relationship between plasma NT-proBNP level and Gensini score in patients with STEMI
本研究以血浆NT-proBNP水平为800 ng/L作为临界值,将STEMI患者分为NT-proBNP正常组和NT-proBNP升高组。结果显示,NT-proBNP升高组患者高血压发生率高于NT-proBNP正常组,原因可能为高血压患者本身就存在靶器官损害,长期高血压易合并高血压心脏病,当发生ACS时更易发生心力衰竭,导致血浆NT-proBNP水平升高;NT-proBNP升高组患者血浆ultra-TnI水平高于NT-proBNP正常组,血浆ultra-TnI是由心肌损伤后释放入血的一种心肌特异性蛋白质,心肌损伤越重,血浆ultra-TnI水平越高,心肌受损后心脏收缩功能明显减弱,心脏容量负荷过重,易发生心力衰竭而导致NT-proBNP水平升高[11]。
本研究结果显示,NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉三支病变发生率高于NT-proBNP正常组,而单支病变、双支/LM病变发生率低于NT-proBNP正常组,表明冠状动脉病变程度越重患者血浆NT-proBNP水平越高,可能原因为冠状动脉病变越广泛,心肌发生缺血、损伤、坏死越严重,导致心力衰竭发生率越高,一旦发生心力衰竭,血浆NT-proBNP水平就会上升[12]。NT-proBNP升高组患者冠状动脉病变支数多于NT-proBNP正常组,Gensini积分高于NT-proBNP正常组,且相关性分析结果显示,血浆NT-proBNP水平与Gensini积分呈正相关,提示血浆NT-proBNP水平可以预测冠状动脉病变程度,与Kara等[13]研究结果一致。临床研究表明,BNP水平与冠状动脉病变程度、心肌灌注水平有关,BNP水平升高提示心肌梗死面积扩大。Sadanandan等[14]研究表明,罪犯血管狭窄程度越严重、血流灌注不足,BNP水平越高。
本研究尚存在一些局限,首先所选研究对象是连续病例,未能做到随机化,样本量偏小,且是一项回归性研究,因此在解释本研究结果时需慎重;其次冠状动脉造影结果判读因人而异,即使最小地减少人为因素,也会存在一些误差。总之,本研究结果初步表明血浆NT-proBNP水平与冠状动脉病变程度存在一定关系,可以通过检测血浆NT-proBNP水平来判断冠状动脉病变程度。
[1]Mouridsen MR,Sajadieh A,Carlsen CM,et al.Troponin T and N-terminal pro B-Type natriuretic peptide and presence of coronary artery disease[J].Scand J Clin Lab Invest,2015,75 (3):204-212.
[2]Park M,Vittinghoff E,Shlipak MG,et al.Associations of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide with kidney function decline in persons without clinical heart failure in the Heart and Soul Study[J].Am Heart J,2014,168(6):931-939,e2.
[3]Romel SM,Faruque M,Bari MA,et al.Association between elevated B-type natriuretic peptide levels with extent of coronary arterydisease in patients with unstable angina and NSTEMI[J].Mymensingh Med J,2014,23(3):544-551.
[4]Hasegawa T,Asakura M,Eguchi K,et al.Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide is a useful tool for assessing coronary heart disease risk in a Japanese general population[J].Hypertens Res,2015,38(1):74-79.
[5]Goyal BM,Sharma SM,Walia M.B-type natriuretic peptide levels predict extent and severity of coronary artery disease in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome and normal left ventricular function[J].Indian Heart J,2014,66(2):183-187.
[6]Costello-Boerrigter LC,Lapp H,Boerrigter G,et al.Secretion of prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide,proBNP1-108,is increased in heart failure[J].JACC Heart Fail,2013,1(3):207-12.
[7]Dallmeier D,Pencina MJ,Rajman I,et al.Serial measurements of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with coronary heart disease[J].PLoS One,2015,10(1):e0117143.
[8]Wang H, Liu J, Zhao H,et al.Relationship between cardio-ankle vascular index and N- terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in hypertension and coronary heart disease subjects[J].J Am Soc Hypertens,2014,8(9):637-643.
[9]Jefferis BJ,Whincup PH,Lennon LT,et al.Physical activity in older men: longitudinal associations with inflammatory and hemostatic biomarkers,N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide,and onset of coronary heart disease and mortality[J].J Am Geriatr Soc,2014,62(4):599-606.
[10]Nayer J,Aggarwal P,Galwankar S.Utility of point-of-care testing of natriuretic peptides (brain natriuretic peptide and n-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide) in the emergency department[J].Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci,2014,4(3):209-215.
[11]Bassan R,Potsch A,Maisel A,et al.B-type natriuretic peptide:a novel early blood marker of acute myocardial infarction in patients with chest pain and no ST-segment elevation[J].Eur Heart J,2011,26(8):234-240.
[12]Karakas M,Jaensch A,Breitling LP,et al.Prognostic value of midregional pro-A-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-B-typenatriuretic peptide in patients with stable coronary heart disease followed over 8 years[J].Clin Chem,2014,60(11):1441-1449.
[13]Kara K,Gronewold J,Neumann T,et al.B-type natriuretic peptide predicts stroke of presumable cardioembolic origin in addition tocoronary artery calcification[J].Eur J Neurol,2014,21(6):914-921.
[14]Sadanandan S,Cannon CR,Chekuri K,et,al.Association of elevated B-type natriuretic peptide levels with angiographic findings among patients with unstable angina and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,44(3):564-568.
(本文编辑:谢武英)
Correlation between Serum NT-proBNP Level and Severity of Coronary Artery Lesions in Patients with STEMI
CHENXu-yu,XIAHao.TheSecondPeople′sHospitalofQinzhou,Qinzhou535000,China
Objective To explore the correlation between serum NT-proBNP level and severity of coronary artery lesions in patients with STEMI.Methods A total of 252 patients with STEMI were selected in the Second People′s Hospital of Qinzhou from March 2012 to March 2015,and they were divided into groups A(NT-proBNP<800 ng/L)and B(NT-proBNP≥800 ng/L)according to serum NT-proBNP level,each of 126 cases.Age,gender,family history of coronary heart disease,smoking history,and incidence of hypertension,hyperlipidaemia and diabetes were recorded after admission;serum levels of NT-proBNP,CK-MB,MYO,ultra-TnI were detected within 24 hours after admission;fasting venous blood was collected to detect the blood lipid on the second day morning after admission;Judkins method was used to carry out coronary arteriography;linear correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between serum NT-proBNP level and Gensini score.Results The incidence of hypertension,serum ultra-TnI level of B group was statistically significantly higher than that of A group,respectively(P<0.05);while no statistically significant differences of gender,age,CK-MB,MYO,TC,TG,HDL-C,LDL-C,incidence of hyperlipidaemia or diabetes,positive rate of family history of coronary heart disease or smoking history was found between the two groups(P>0.05).The incidence of three-vessel lesions of B group was statistically significantly higher than that of B group,while single-vessel and double-vessel lesions(including left main coronary artery lesions)of B group were statistically significantly lower than those of A group(P<0.05).The number of coronary artery lesions of B group was statistically significantly more than that of A group,and Gensini score of B group was statistically significantly higher than that of A group(P<0.05).Linear correlation analysis showed that,serum NT-proBNP level was positively correlated with Gensini score(r=0.813,P=0.000).Conclusion Serum NT-proBNP level is correlated with the severity of coronary artery lesions in patients with STEMI,and the detection of serum NT-proBNP level is helpful to judge the severity of coronary artery lesions.
Natriuretic peptide,brain;Coronary heart disease;Coronary stenosis
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81270184)
535000广西钦州市第二人民医院(陈旭虞);武汉大学人民医院(夏豪)
夏豪,430060湖北省武汉市,武汉大学人民医院;E-mail:xiahao1966@163.com
R 543.3
A
10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2015.05.002
2015-03-08;
2015-05-16)
陈旭虞,夏豪.血浆氨基末端脑钠肽前体水平与急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者冠状动脉病变程度的关系研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2015,23(5):005-008.[www.syxnf.net]
Chen XY,Xia H.Correlation between serum Nt-proBNP level and severity of coronary artery lesions in patients with STEMI[J].Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease,2015,23(5):005-008.
