Research on Rooting Cuttings of Hard Branch ofHippophae rhamnoides
2015-02-05DengmingLANZhiweiXINGJuxiangXING
Dengming LAN,Zhiwei XING,Juxiang XING
1.College of Ecology and Environment,Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,Hohhot 010019,China;
2.Chifeng City Songshan Forestry Bureau 024005,China
3.Inner Mongolia Technical College of Mechanics and Electrics,Hohhot 010070,China;
Research on Rooting Cuttings of Hard Branch ofHippophae rhamnoides
Dengming LAN1,Zhiwei XING2,Juxiang XING3*
1.College of Ecology and Environment,Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,Hohhot 010019,China;
2.Chifeng City Songshan Forestry Bureau 024005,China
3.Inner Mongolia Technical College of Mechanics and Electrics,Hohhot 010070,China;
[Objective]In order to improve the survival rate of Hippophae rhamnoides hardwood cuttings,cultivate high-quality sea buckthorn seedlings.[Method]This paper took hard branches of Russian big fruit H.rhamnoides as material.The days of striking roots,rate of striking roots,root length and number of adventitious root were determined.[Result]The cuttings collected from upper treetops were obviously inferior to the lower ones.Three years cutting is obviously better than one or two years. Cuttings from lower branches were not so good as the cuttings from upper branches.Base oblique incisions were clearly superior to paper-cover incision.The optimal length of cuttings was 20-25 cm.The rooting rate of cuttings was the highest by fast dipping with NAA of 50 mg/L.[Conclusion]The study provides theoretical basis for H.rhamnoides artificial cultivation.
Hippophae rhamnoides;Rooting cuttings of hard branch;Cutting wood
H ippophae rhamnoidesis a species of flowering plant in the family Elaeagnaceae,native to temperate zones in the north of 10℃isotherm of Eurasian continent in January.It is a spiny deciduous shrub or mesophanerophytes that the male and female flowers grown on different shrubs,with wide application[1].It is an ideal tree for preventing winds and sands,conserving water and soil,and improving eco-environment,which can be used as health-care food,beverage,and liquor,as well as a medical resource performing excellently in ecological,economic and social benefits.In China,the development and use of Hippophae rhamnoides resources is a large-scale ecological and economic project[2].With increasingly development of the products and demands of ecological afforestation, people’s demand on seedlings of Hippophae rhamnoides keeps growing[3]. Therefore,it is important to swiftly resolve the issue of cultivating Hippophae rhamnoides seedlings.
The method of rooting cuttings of hard branch refers to a vegetative propagation cultivating a part of lignified shoots into an individual and complete plant with roots and branches[2]. With extension of clonal forests,the method of rooting cuttings of hard branch has become an important way for cultivating clonal forests and widely applied[4].The research select ed the optimal branch age,matrix, growth environment and the best concentration and time of growth regulators for the cultivation by analyzing the effects of different branch ages,matrixes,environment,and growth regulators on rooting cuttings of hard branch,providing theoretical references for artificial cultivation.
Natural Condition of Test Zones
The test zones are located in Horinger County,Huhhot,Mongolia, which is 36 km away from Huhhot.It belongs to the region of Manhan Mountain,Yinshan Moun-
Materials and Methods
Test materials
The test materials were collected from a planting base of Yuhangren High-tech Industrial Co.,Ltd.in Horinger County,Mongolia.The test species was Hippophae rhamnoides and branches were collected from healthy and well-grown plants as cuttings.
Research method
The branches were cultivated in a plastic greenhouse with micro-jet equipment.Specifically,a water pipe was equipped on the location 15 cm above of every seedbed and a shower nozzle was equipped every 40 cm away.Furthermore,the temperature of the greenhouse should be set in 21-33℃and relative humidity of 55%-76%.Before cuttage,soils were sterilized with 0.5%potassium permanganate solution.
The cuttage time was determined in middle April,and the cuttings were cut into the required cutting slips which can be immerged in water for 24 h to reduce the effects of inhibitor on rooting.It is notable that the test used completely randomized block design and every test treatment included 50 cutting slips,with three repetitions.After cuttage process,the samples should be collected every day to research rooting and record the specific time.After 50 dm,the seedlings can be collected to make statistic work of rooting rate,the number of adventitious root,the diameter of adventitious root and growth location of adventitious root.
Test content
The test of the length of cutting slipThe three-year old branches(middle and down parts)were sampled and cutting slips with lengths of 10-15,15-20 and 20-25 were prepared.It is notable that down-cuttings with 150 beveling cuts and 150 truncation cuts. Furthermore,for down-cuttings with beveling cuts,average diameter of 10-15 cm cutting slips was 0.73 cm,of 15-20 cm slips was 0.79 cm and of 20-25 cm clips was 0.75 cm.In contrast,for down-cuttings with truncation cuts,average diameter of 10-15 cm cutting slips was 0.77 cm,of 15-20 cm slips was 0.76 cm and of 20-25 cm clips was 0.77 cm.
The test of cutting slips at different ages in varied crown partsSpecifically,150 cuttings at one year old,two years old and three years old were sampled from upper,middle and down parts of crowns to prepare cutting slips and record rooting.
The test with different matrixes
The branches at three years old were collected from middle and down parts of crowns to prepare cutting slips with average diameter of 0.77 cm.Besides, the matrix was collected from local areas,including matrix 1 with nursery soil-to-residues of Hippophae rhamnoides at 2:1,matrix 2 with nursery soil-to-sands at 2:1,and matrix 3 with nursery soil-to-charcoal ash at 2:1. The treatment with nursery soil as matrix was taken as control group, with two repetitions,and every repetition involved 50 cutting slips.In addition,rooting of seedlings was observed by sampling after 50 d.
The contrast test in and out of greenhousesIn the test,300 three years old branches were collected from middle and down parts of crowns to prepare cutting slips,with diameter of 0.8-1.2 cm.Subsequently,the cuttage proceeded in and out of a greenhouse and every treatment included 150 branches.
The test with drugsThree years old branches were collected from middle and down parts of crowns to prepare cutting slips with diameters of 0.8-1.2 cm.Subsequently,cutting slips were treated with NAA with concentrations of 50,100 and 200 mg/L and the treatment time included swift treating,3,6 and 12 h,respectively.Besides,the treatment with water was taken as a control(CK).All branches were conducted as per straight cutting,with the depth of 5 cm and row spacing of 5 cm×10 cm.The matrix was nursery soils and rooting should be observed in the treatment periods.
Except of the test of the length of cutting slip,the length of cutting slip in rest tests was all in 15-20 cm with beveling cuts.Except of the test with drugs,cutting slips were immerged with 100 mg/L NAA for 3 h.Except of the test with different matrixes,the rest tests were all conducted in a greenhouse.Moreover,truncation cuts were all in the location 1 cm of upper lateral buds and the base parts were stuck onthe matrixes vertically,with depth of 5 cm and planting spacing of 5 cm×10 cm.
Results and Analysis
The relationship between root length and root diameter
Root diameter and length were measured from samples after 50 d, and the scatter diagram was mapped with Excel.
As shown in Fig.1,root diameter was of positive correlation with root length.The longer root,the larger diameter.The prediction model was y= 0.033 14+0.010 64x(y refers to root diameter and x refers to root length).
Effects of the distance of rooting location and down cuts on rooting
After 50 d of cuttage,samples were collected randomly to explore the distance of rooting location and down cuts.The cut location was given 0 cm, and the interval was set at 0.5 cm,totaling 10 levels.As shown in Fig.2, more roots grew from the locations 1.5-3.5 cm away from the down cuts, representing 65.08%,which suggested that Hippophae rhamnoides rooted from the location 1.5-3.5 cm from down cutting cuts.
Effects of crown locations and cuttage age on rooting
As shown in Table 1,it showed rooting days of three years old branch<rooting days of two years old branch<rooting days of one year old branch,which incorporated that the older the branch,the shorter rooting days.Furthermore,it showed that rooting rate of three years old branch>rooting rate of two years old branch>rooting rate of one year old branch, which suggested that the older branch, the higher rooting rate.As for the number of adventitious root,Table 1 showed that the number of three years old adventitious root>the number of two years old adventitious root>the number of one year old adventitious root,which indicated that the older branches,the more the number of adventitious root.Additionally,it can be concluded that the length of three years old adventitious root>the length of two years old adventitious root>the length of one year old adventitious root,suggesting that the older branch, the longer roots.
On the other hand,Table 1 showed that for one year old rooting crowns,the number of adventitious root in upper parts of rooting crowns>the number of adventitious root in middle parts of rooting crowns>the number of adventitious root in down parts of rooting crowns.For two years old rooting crowns,the number of adventitious root in middle parts>the number of adventitious root in upper parts>the number of adventitious root in down parts.As for three years old rooting crowns,the number of adventitious root in down parts>the number of adventitious root in middle parts>the number of adventitious root in upper parts.Besides,for one year old rooting crowns,it showed the length of adventitious root of upper parts>the length of adventitious root of middle parts>the length of adventitious root of down parts.For two years old rooting crowns,it showed the length of adventitious root of middle parts>the length of adventitious root of upper parts>the length of adventitious root of down parts.For three years old rooting crowns,it showed the length of adventitious root of upper parts>the length of adventitious root of middle parts>the length of adventitious root of down parts.
Effects of different cutting methods and cutting slip length on rooting
As shown in Table 2,rooting days showed little differences upon cutting methods and cuttage length.Specifically,the length of cuttage slips were as follows:rooting rate with length of 20-25 cm>rooting rate with length of 15-20 cm>rooting rate with length of 10-15 cm;the number of adventitious roots with length of 20-25 cm>the number of adventitious roots with length of 15-20 cm>the number ofadventitious roots with length of 10-15cm;the length of adventitious root with length of 20-25 cm>the length of adventitious root with length of 15-20 cm>the length of adventitious root with length of 10-15 cm.
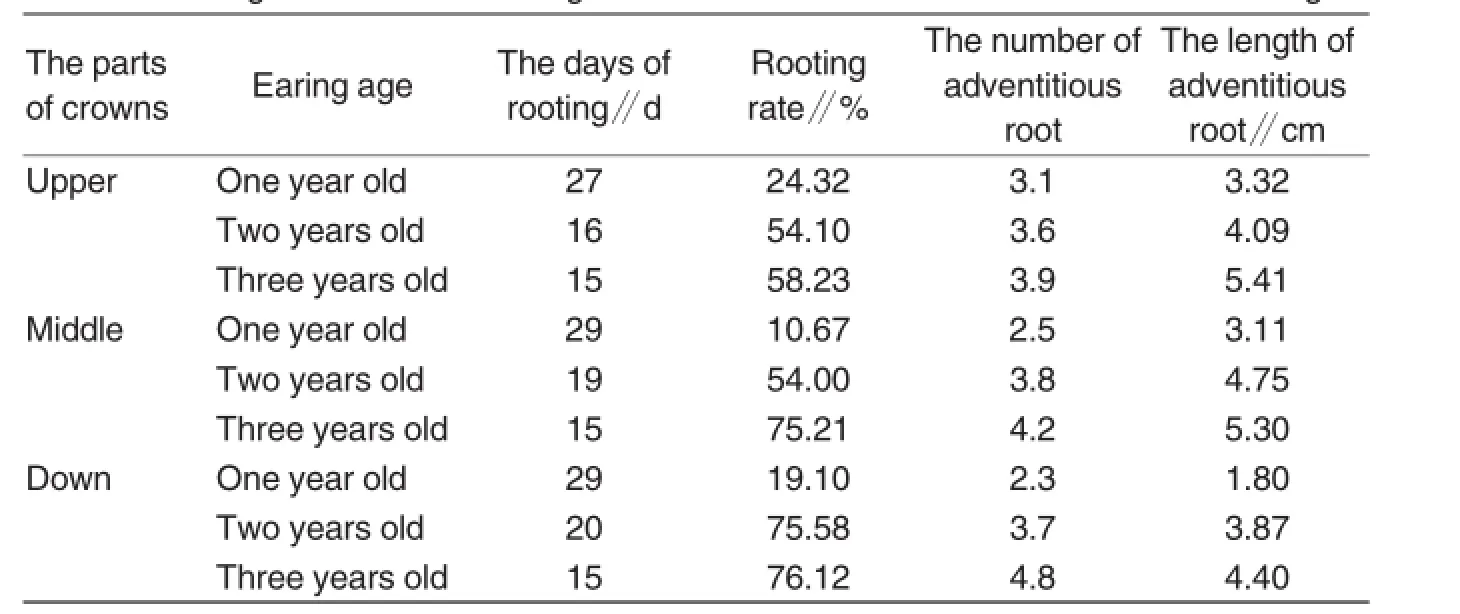
Table 1Rooting of branches at cuttage from different crown locations and at different ages
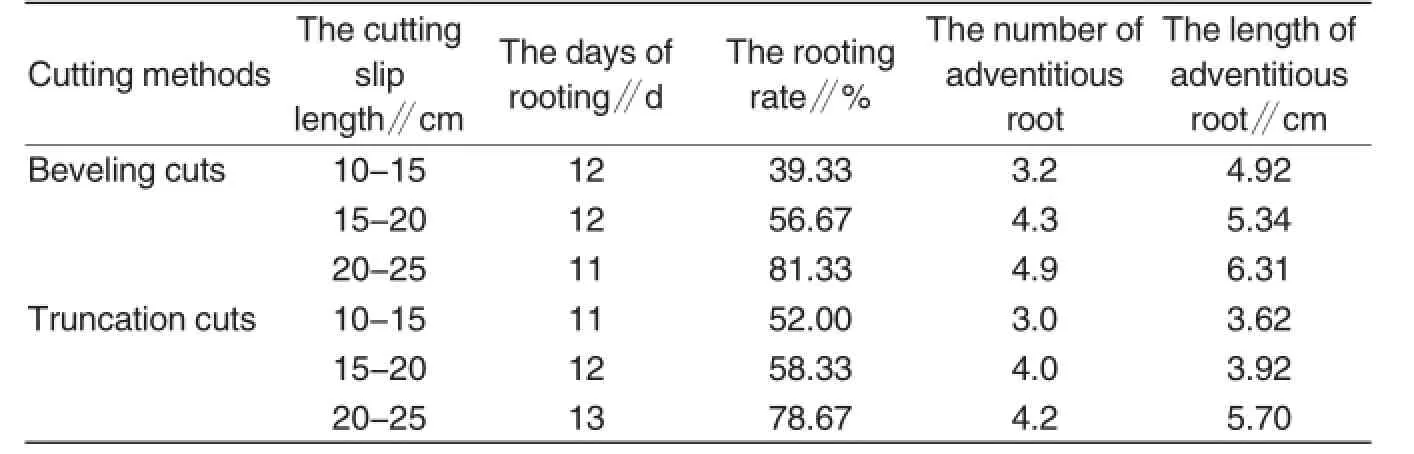
Table 2Effects of different cutting methods and cutting slip length on rooting
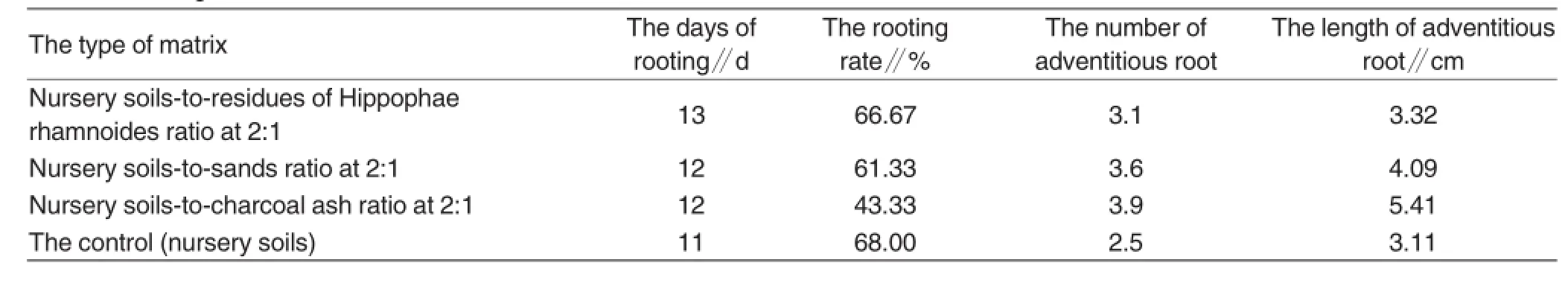
Table 3Rooting in treatments with different matrixes
Effects of matrixes on rooting
As shown in Table 3,the effects of matrixes on rooting days showed insignificant differences.It showed that rooting rate in control>the rooting rate in the treatment with residues of Hippophae rhamnoides>the rooting rate in the treatment with river sands>the rooting rate in the treatment with charcoal ash.Furthermore,the number of adventitious root was as follows:the treatment with charcoal ash>the treatment with river sands>the treatment with residues of Hippophae rhamnoides>the control group.As for the length of adventitious root,it showed the treatment with charcoal ash>the treatment with river sands>the treatment with residues of Hippophae rhamnoides>the control group.
Results of contrast test in and out of greenhouses
As shown in Table 4,the rooting day of branches in a greenhouse was significantly shorter compared with that out of a greenhouse;the rooting rate in the greenhouse also kept higher;the number of adventitious roots was higher;the length of adventitious roots was longer.
Effects of medical drugs on rootingIt can be concluded from Table 5 that the rooting day was the shortest in 9 d in the treatments with 50 mg/L NAA for 12 h,with 100 mg/L NAA for 12 h,and 200 mg/L NAA for 12 h.In contrast,the rooting day in the treatment with 100 mg/L NAA for 6 h maintained the longest in 13 d.In addition to that,the rooting rate reached the highest at 80.67%in the treatment with 50 mg/L NAA swiftly and the least in the treatment with water for 6 h at 38.12%.
Conclusions
The test indicated that the rooting day was the shortest of three years old branch,with high rooting rate,more and long adventitious root.Therefore, the branches(>three years old)should be a priority in production.
For cutting slips with the same length,rooting rate,the number and the length of adventitious roots all kept higher in down-cuttings with beveling cuts compared with down-cuttings with truncation cuts.Therefore,down-cutting should be conducted as per beveling cuts.
With the cutting method the same, rooting rate,the number and the length of adventitious roots of cuttage slips of 20-25 cm performed higher compared with the cuttage slips of 15-20 cm and 10-15 cm.Hence,the cuttage slips of 20-25 cm are recommended in production.
Based on matrixes available,rooting rate in the treatment with nursery soils reached the highest and the lowest in the treatment with nursery soilto-charcoal ash at 2:1;the number of adventitious roots in the treatment with nursery soil-to-charcoal ash at 2:1 achieved the highest and the lowest in the treatment with only nursery soils; adventitious roots in the treatment with nursery soil-to-charcoal at 2:1 was the longest and the shortest in control group.
The rooting rate reached the peak at 80.67%in the treatment with NAA at 50 mg/L by swiftly treating.
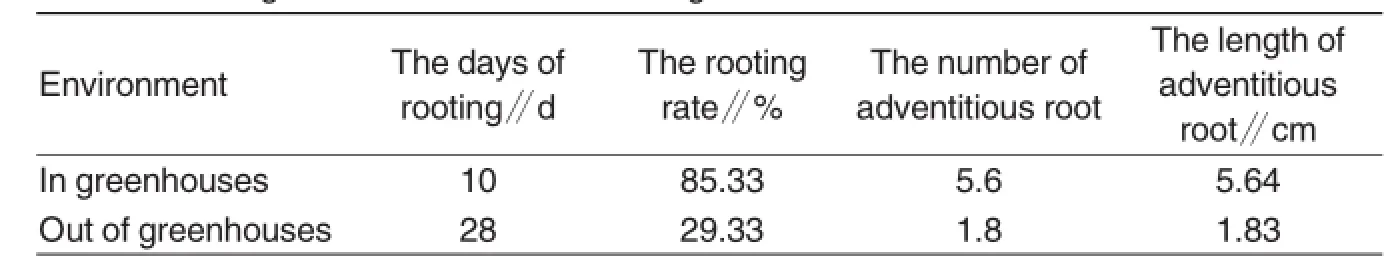
Table 4Rooting of branches in and out of a greenhouse
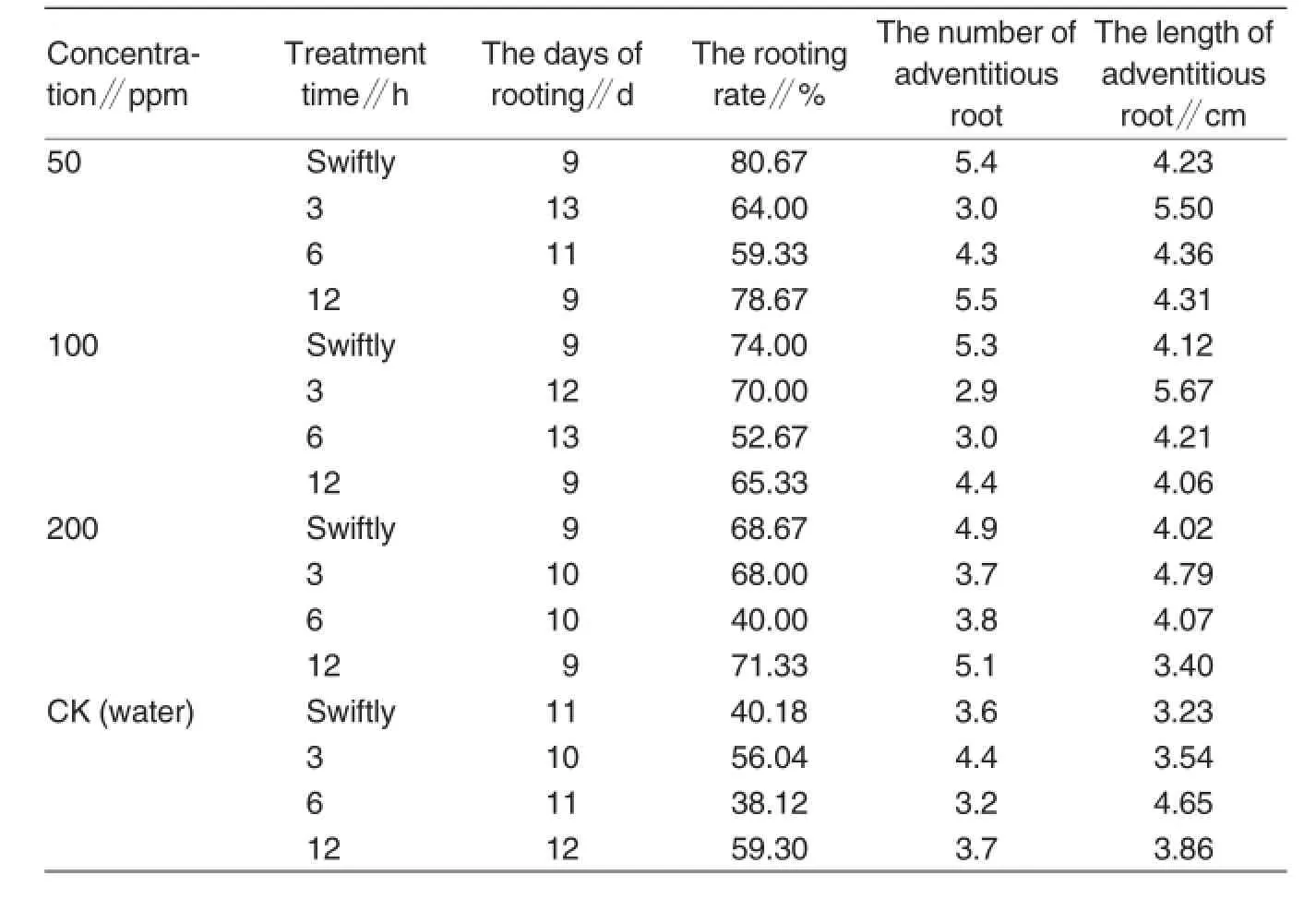
Table 5Rooting in treatments with NAA at different concentrations in different periods
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG
[1]LIU HZ(刘洪章),HAO R(郝瑞),WEN LK(文连奎).Research progress of Hippophae resources(沙棘属植物种质资源研究进展)[J].Forest by Product and Speciality in China(中国林副特产), 1995,33(2):39-42.
[2]SUN SX(孙时轩).Silviculture(造林学) [M].the 2ndedition(2版).Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House(北京:中国林业出版社),1995.
[3]GAO ZY(高志义),ZHANG YS(张玉胜). Observation and research of Hippophae rhamnoides roots(沙棘根系特性的观察与研究)[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University(北京林业大学学报),1989, 11(4):53-59.
[4]CHENG SY(程水源),WANG Y(王燕). The relationship of rooting with enzyme and endogenous hormone of gingko at rooting cuttings(银杏插穗生根与酶及内源激素的关系)[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica(园艺学报),1996(4):407-408.
[5]LUO JZ(骆建中),WANG XL(王秀丽), WANG SF(王塞峰).Wind-breaking and desert-control and effects in Horinger County(和林格尔县防风治沙的措施及其效益分析)[J].Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design(内蒙古林业调查设计),2010,33(1):43-44.
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
沙棘硬枝扦插生根情况研究
蓝登明1,邢志传2,邢菊香3*
(1.内蒙古农业大学生态环境学院,内蒙古呼和浩特010019;2.赤峰市松山区林业局,内蒙古赤峰024005;3.内蒙古机电职业技术学院,内蒙古呼和浩特010070)
[目的]提高沙棘硬枝扦插成活率,培育优质沙棘苗木。[方法]以俄罗斯大果沙棘硬枝为材料,设计不同采条部位、插穗年龄、插穗长度、下切口方式、扦插基质、药剂等处理进行沙棘硬枝扦插试验,测定和分析了不同处理的硬枝插穗生根天数、生根率、不定根长度、不定根数量4个指标。[结果]采自树冠上部的插穗生长明显劣于来自树冠中、下部插穗,3年生插穗明显优于1、2年生插穗,枝条下部不及枝条上部插穗,插穗基部斜切口优于平切口,20~25 cm插穗较优用50 mg/L NAA速蘸,插穗生根率最高,达80.67%。[结论]该研究为大果沙棘人工栽培提供理论依据。
沙棘;硬枝扦插;插穗tain,at 39°58′11″-40°41′31″N, 111°26′52″-112°18′11″E,with elevations of 1 050-1 110 m,and area of 343 638.8 hm2[5].Horinger County is dominated by flatlands,and ground water is abundant.Besides,annual mean temperature reaches 6.3℃;accumulated temperature(>10℃)totals 2 916℃;frost-free period lasts for 120-140 d;annual sunshine hour reaches 2 700-3 000 h.It has a Eurasian continent semi-arid climate, with west wind as a dominant wind and predominant wind direction and annual mean precipitation of 376.4 mm[5].
国家科技支撑计划课题(2011BA107B05-2)。
蓝登明(1961-),男,呼和浩特人,教授,从事植物资源保护与利用方面的研究。*通讯作者,邢菊香,从事水土保持的教学与科研工作。
2015-04-03
修回日期 2015-05-16
Supported by Key Projects in the National Science&Technology Pillar Program (2011BA107B05-2).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:13171090919@163.com
Received:April 3,2015 Accepted:May 16,2015
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Analysis and Discussion on Some Problems of the Edible Fungi Production in Asmara Area
- The Control Research Progress ofLiberobacter asiaticumin Taizhou City
- Application of Genetically Modified Technology in Maize Breeding
- Breeding of Indica Rice CMS Line Renong 1A with Virescent-yellow Leaf
- Breeding and Application of Indica PTGMS Line Yan 161S and Its Hybrid Yanliangyou 1618 in Rice
- Thoughts on the Sustainable Development of the Fava Bean Industry in Chongqing
