Comprehensive Evaluation on Drought Resistance of Different Flue-cured Tobacco Cultivars in Bijie Tobacco Growing Area
2015-02-05XinyanFUXinZHAIXueCHENGongCHENGHongchenLIQiweiYUXiaoquanZHANGTiezhaoYANG
Xinyan FU,Xin ZHAI,Xue CHEN,Gong CHENG,Hongchen LI,Qiwei YU,Xiaoquan ZHANG,Tiezhao YANG*
1.College of Tobacco Science,Henan Agricultural University,Henan 450002,China;
2.Bijie Subsidiary of Guizhou Tobacco Company,Bijie 551700,China;
3.Xuchang Tobacco Monopoly Bureau,Xuchang 461000,China
Comprehensive Evaluation on Drought Resistance of Different Flue-cured Tobacco Cultivars in Bijie Tobacco Growing Area
Xinyan FU1,3,Xin ZHAI2,Xue CHEN2,Gong CHENG3,Hongchen LI1,Qiwei YU2,Xiaoquan ZHANG1,Tiezhao YANG1*
1.College of Tobacco Science,Henan Agricultural University,Henan 450002,China;
2.Bijie Subsidiary of Guizhou Tobacco Company,Bijie 551700,China;
3.Xuchang Tobacco Monopoly Bureau,Xuchang 461000,China
Based on pot experiments,major agronomic traits,biomass accumulation, leaf water-holding capacity,relative water content,root MDA content,root proline content and other physiological indicators of four different flue-cured tobacco cultivars under drought stress were investigated,and drought resistance in various fluecured tobacco cultivars was comprehensively analyzed with subordinate function method,aiming at clarifying the differences in drought resistance among various flue-cured tobacco cultivars.The results indicated that under drought stress,major agronomic traits,fresh and dry mass accumulation,and leaf relative water content of four different flue-cured tobacco cultivars were reduced significantly;the decreasing range of Yunyan 87 reached the minimum,followed by Bina 1,while Qianxi 1 demonstrated the maximum decreasing range.Leaf water-holding capacity of various flue-cured tobacco cultivars showed a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Qianxi 1>Jiucaiping 2.MDA content and proline content in roots of various fluecured tobacco cultivars increased significantly;to be specific,Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 exhibited a slight increase in root MDA content and a significant increase in root proline content,while Jiucaiping 2 and Qianxi 1 showed an opposite trend.According to the results of comprehensive analysis with subordinate function method, drought resistance in various flue-cured tobacco cultivars showed a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Jiucaiping 2>Qianxi 1.
Flue-cured tobacco;Cultivar;Drought resistance;Subordinate function
I n recent years,global climate deterioration is becoming increasingly evident,which shortens the drought cycles,thereby posing a serious threat to crop production.As an important cash crop in China,tobacco grows best in warm and humid climate,with high water requirements during the whole growth period.Bijie tobacco growing area is located in southwest China.Due to lack of necessary irrigation facilities,water deficiency has become a major factor restricting the cultivation and quality formation of flue-cured tobacco[1].Therefore,strengthening the theoretical research of drought resistance in fluecured tobacco cultivars and breeding high-quality drought-resistant fluecured tobacco cultivars has become one of the issues to be solved in tobacco science and technology in Bijie tobacco growing area.
At present,a large number of studies have been conducted on drought resistance in flue-cured tobacco cultivars.Ren et al.[2]comprehensively evaluated drought resistance in flue-cured tobacco cultivars with subordinate function method and found that highly drought-resistant flue-cured tobacco cultivars exhibited relatively high leaf water-holding capacity,net photosynthetic rate,
Materials and Methods
Materials
Four flue-cured tobacco cultivars in Bijie tobacco growing areas were selected as experimental materials, including Yunyan 87,Bina 1,Qianxi 1 and Jiucaiping 2.Tobacco seeds were provided by the tobacco breeding laboratory in Henan Agricultural University. Potting soils was collected from from the plough horizon in the field,which belonged to loam soils and contained 0.87 g/kg total nitrogen,11.96 g/kg organic matter,54.12 mg/kg rapidly available phosphorus,126.41 mg/kg rapidly available potassium and 53.72 mg/kg alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen,pH 7.8.
Experimental design
The experiment was carried out under plastic sheeting in the Science Garden of Henan Agricultural University in 2013.The potted seedlings were planted under limited water condition,and the relative soil water content was controlled with weighing method.After forcing of germination,flue-cured tobacco seeds were sown on seedbed for seedling raising.After emergence of 6-7 true leaves,flue-cured tobacco seedlings with uniform growth were selected,transplanted into plastic pots and cultivated under plastic sheeting.One tobacco seedling was planted in each pot;each cultivar was planted in 45 pots.NH4NO3, KH2PO4and KNO3were applied as nitrogen fertilizer,phosphate fertilizer and potassium fertilizer,respectively.The application amount of nitrogen fertilizer (pure nitrogen)and phosphate fertilizer(P2O5)was 2.5 g/plant;N∶P2O5∶K2O= 1∶1∶2.Fertilizers and soils were mixed evenly and loaded into the pots,16.5 kg soil/pot.The moisture content was measured every 3 d with weighing method to maintain relatively water holding capacity at about 75%.Droug-ht stress experiment was carried out at 40 d post-incubation.Three treatments were designed, including normal water supply treatment,mild drought stress treatment and severe drought stress treatment,in which relative soil water content was 80%,60% and 40%,respectively.At 20 d post-treatment,the fifth leaf from the top of fluecured tobacco seedling was collected as the experimental material(avoiding the main vein)to determine physiological indicators.Each indicator was measured three times.
Determination items and methods
Leaf water-holding capacity was determined in accordance with the method proposed by Zhang et al.[8];leaf relative water content was determined in accordance with the method proposed by Bajji et al.[9];root MDA content was determined with thiobarbituric acid(TAB)colorimetric meth-od[10];proline content was determined in accordance with the method proposed by Zou et al.[11];drought resistance was evaluated comprehensively with subordinate function method[12]as follows:
(1)Subordinate function values of different physiological indicators of various flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Where,X indicates the ratio of indicator value to control value under drought conditions.When indicator value was negatively correlated with drought resistance,Xij=1-(X-Xjmin)/(Xjmax-Xjmin),where Xijindicates the subordinate function value of physiological trait j of flue-cured tobacco cultivar i;Xjminindicates the minimum value of physiological trait j of each cultivar;Xjmaxindicates the maximum value of physiological trait j of each cultivar.
(2)Subordinate function value Xijmildunder mild drought conditions and subordinate function value Xijsevereunder severe drought conditions.(Xijmild+Xijsevere)/2 represents the average subordinate function value of physiological trait j of cultivar i under mild and severe drought conditions,denoted by Ui.The average value Uiwas calculated to represent the level of drought resistance.Greater Uivalue indicates higher drought resistance.
Data analysis
Variance analysis and mean significant difference test of experimental data were performed using SPSS17.0 statistical software.
Results and Analysis
Effects of drought stress on major agronomic traits of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Under drought conditions,flue-cured tobacco plants exhibit retarded growth and development,poor root development,inhibited stem elongation,reduced leaf size and plant height[13].As could be seen from Table 1,drought stress affected significantly major agronomic traits of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars.The analysis of variance showed extremely significant differences among different flue-cured tobacco cultivars(F0.05=4.07;F0.01=7.59).Under normal water supply and drought stress conditions,Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 exhibited better growth than Jiucaiping 2 and Qianxi 1.With the increase of drought stress level,plant height,stem circumference,maximum leaf length,maximum leaf width and root volume of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars showed varying degrees of decrease.To be specific,plant height and root volume were significantly affected by drought stress.
Effects of drought stress on biomass accumulation of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Biomass accumulation is the final performance of plant growth and development.Under drought conditions, the amount and reduction of biomass can be used as indicators to identify drought resistance[2,14-15].As shown in Fig.1,with the increase of drought stress level,dry and fresh mass accumulation of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars declined significantly compared with that in normal water supply treatment.Under normal water supply conditions,dry and fresh mass accumulation of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars demonstrated a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Jiucaiping 2>Qianxi 1.Under mild drought conditions,Qianxi 1 was the most sensitive,exhibiting a significant reduction in dry and fresh mass accumulation(26.02%,29.22%),followed by Jiucaiping 2(24.48%,25.93%); Yunyan 87 exhibited the minimum reduction in dry and fresh mass accumulation(17.33%,19.36%).Under severe drought conditions,the growth of tobacco plants was further inhibited,and the reduction in dry and fresh mass accumulation increased significantly. Qianxi 1 exhibited the maximum reduction in dry and fresh mass accumulation(52.21%,66.00%),while Yunyan 87 exhibited the minimum reduction in dry and fresh mass accumulation (34.43%,46.28%).Therefore,Yunyan87 and Bina 1 were insensitive to drought stress,which were more resistant to drought stress compared with Qianxi 1 and Jiucaiping 2.
Effects of drought stress on leaf water-holding capacity and relative water content of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Leaf water-holding capacity is positively correlated with plant drought resistance.Higher leaf water-holding capacity indicates stronger drought resistance;conversely,drought resistance is poorer[16-17].As shown in Fig. 2(A),leaf water-holding capacity of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars varied significantly,which demonstrated a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Qianxi 1>Jiucaiping 2.Although there was no significant difference between Yunyan 87 and Bina 1, these two flue-cured tobacco cultivars varied extremely significantly compared with Qianxi 1 and Jiucaiping 2,respectively.

Table 1Effects of drought stress on major agronomic traits of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
The change in leaf relative water content is an adaptive response of tobacco plants to drought stress,which can to some extent reflect the level of drought resistance[2,18].As shown in Fig.2(B),under the same conditions, leaf relative water content of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars demonstrated a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Jiucaiping 2>Qianxi 1. With the increase of drought stress level,relative water content of tobacco leaves declined remarkably and varied significantly among different flue-cured tobacco cultivars.Compared with normal water supply conditions,leaf relative water content of Yunyan87 was reduced by 2.17%and 7.61%with the minimum variation,exhibiting strong anti-dehydration capacity;leaf relative water content of Qianxi 1 was reduced by 6.98%and 20.93%with the maximum variation,exhibiting weak antidehydration capacity.
Effects of drought stress on root MDA content and proline content of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Malonaldehyde(MDA)is a product of membrane lipid peroxidation. Under drought stress,the increase of MDA content can be used as an important physiological indicator to evaluate plant resistance[19-20].As shown in Fig.3(A),under normal water supply conditions,MDA content in roots of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars exhibited no significant difference.Under mild drought conditions,MDA content in roots of Qianxi 1 and Jiucaiping 2 was significantly higher than that in roots of Bina 1 and Yunyan 87.Compared with normal water supply conditions,MDA content in roots of Jiucaiping 2,Qianxi 1,Bina 1 and Yunyan 87 was improved by 23.83%,20.94%, 16.67%and 12.01%,respectively.Under severe drought conditions,MDA content in roots of Qianxi 1,Jiucaiping 2,Bina 1 and Yunyan 87 was improved by 66.07%,60.44%,40.23% and 31.28%,respectively.Therefore, Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 could maintain relatively high activities of endogenous protective enzymes,remove excess free radicals,and reduce lipid-membrane peroxidation damage under drought conditions.
The accumulation of a large amount of free proline is an adaptive biochemical metabolic response of plants to drought stress that can enhance osmotic adjustment ability of plants,resist external osmotic stress and improve the stability of protoplasmic colloid as a determinant of stable material metabolism[20-21].As shown in Fig.3(B),under normal water supply conditions,root proline content exhibited no significant difference among different flue-cured tobacco cultivars. Under mild drought conditions,root proline content of Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 was significantly higher than that of Qianxi 1 and Jiucaiping 2.Under severe drought conditions,differences in root proline content further increased among different flue-cured tobacco cultivars.Under mild and severe drought conditions,root proline content of Bina 1 and Yunyan 87 was improved by 219.30%,486.76%and 188.91%,406.39%,respectively,indicating that these two flue-cured tobacco cultivars had strong osmotic adjustment ability and high drought resistance;root proline content of Jiucaiping 2 and Qianxi 1 was improved by 94.42%,177.93%and 78.67%,134.63%, respectively,indicating that these two flue-cured tobacco cultivars had weak osmotic adjustment ability and could be remarkably affected by drought stress.
Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of different fluecured tobacco cultivars
Subordinate function method is a commonly used comprehensive evaluation method in the evaluation of plant drought resistance.The droughtresistance of four different flue-cured tobacco cultivars under drought stress was shown in Table 2.Based on comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance,subordinate function values of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars demonstrated a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Jiucaiping 2>Qianxi 1.Therefore,Yunyan 87 had the highest drought resistance,followed by Bina 1;Qianxi 1 had the lowest drought resistance.
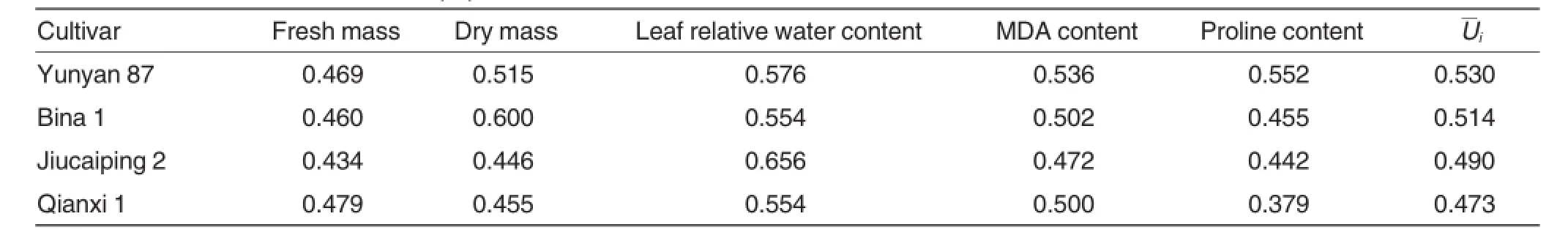
Table 2Subordinate function values(Ui)of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars
Conclusion and Discussion
Different flue-cured tobacco cultivars vary significantly in the sensitivity and tolerance to drought stress. Drought stress leads to photosynthetic metabolism disorder,reduction in photosynthetic products,poor plant growth and significant decline in leaf biomass accumulation(especially for sensitive varieties)[20],thereby remarkably affecting tobacco yield and quality.In this study,under drought conditions,major agronomic traits and fresh and dry mass accumulation of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars were inhibited to varying degrees.To be specific,plant height and root volume were significantly inhibited.Yunyan 87 exhibited the minimum reduction in biomass accumulation,showing relatively high drought resistance.Qianxi 1 exhibited the maximum reduction in biomass accumulation,showing high sensitivity to drought stress and low drought resistance.
Wang et al.[17]and Ni et al.[22]reported that leaf relative water content of highly drought-resistant flue-cured tobacco cultivars declined slightly and slowly,maintaining good water balance;conversely,lowly drought-resistant flue-cured tobacco cultivars exhibited poor water balance,and leaf growth was inhibited significantly.In this study,Yunyan87 has strong leaf water-holding capacity,with the minimum reduction in leaf relative water content under drought conditions, showing high drought tolerance; Qianxi 1 has poor leaf water-holding capacity,with the maximum reduction in leaf relative water content under drought conditions,showing low drought tolerance.
MDA content and proline content of tobacco plants increase under drought conditions.Large amounts of MDA will destroy the structure and function of cell membranes,thereby remarkably affecting normal physiological metabolism of tobacco plants. As an osmotic adjustment substance, proline accumulated in tobacco plants can not only maintain intracellular water balance,but also protect the stability of proteins.In this study,under drought conditions,MDA content in roots of Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 increased slightly;proline content in roots of Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 was significantly higher compared with Jiucaiping 2 and Qianxi 1,indicating that Yunyan 87 and Bina 1 can maintain relatively high activities of endogenous protective enzymes to remove oxygen free radicals under drought conditions. In addition,the accumulation of a large amount of proline is conducive to reducing osmotic potential and enhancing the ability to resist drought stress.
The drought resistance of crops is related to crop species,genotype, morphological characters,physiological and biochemical responses,which can also be affected by the level,occurrence period and duration of drought stress[23-24].The drought resistance of flue-cured tobacco is a complex quantitative trait that is affected by genetic and environmental factors, which should be comprehensively evaluated based on various indicators. In this study,under three treatments (normal water supply,mild drought stress and severe drought stress), drought resistance-related physiological indicators of shoots and roots of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars were determined,and the drought resistance of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars was comprehensively evaluated with subordinate function method. According to the results,the drought resistance of four flue-cured tobacco cultivars demonstrated a descending order of Yunyan 87>Bina 1>Jiucaiping 2>Qianxi 1.
[1]ZHOU JH(周冀衡),SHANGGUAN KP (上官克攀),QIU BR(邱标仁),et al. Physiological evaluation on drought resistance of introduced flue-cured tobacco cultivars(引进烤烟品种的抗旱性生理评价)[J].Tobacco Science&Technology(烟草科技),2002,(5):3-7.
[2]REN QC(任庆成),CHEN XH(陈秀华), YANG TZ(杨铁钊),et al.Comparison of drought resistance characteristics of different flue-cured tobacco varieties(不同烤烟品种抗旱生理特征比较研究)[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica(西北植物学报),2009,29(10):2019-2025.
[3]SHANG XY(尚晓颖),LIU HB(刘化冰), YANG TZ(杨铁钊),et al.Growth and physiological characteristics of roots in different flue-cured tobacco varieties under drought stress(干旱胁迫对不同烤烟品种根系生长和生理特性的影响) [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica(西北植物学报),2010,30(2): 357-361.
[4]MA WG(马文广),CUI HW(崔华威),LI YP(李永平),et al.Physiological characteristics of 20 tobacco cultivars under drought stress and assessment of their drought tolerance at germination and seedling stages(20个烟草品种干旱胁迫下发芽和苗期生理特性及耐旱性评价)[J].Seed(种子),2012,31(2).
[5]ZHANG H(张慧),HE YJ(何玉杰),CHEN TS(陈铁山),et al.Effect of the physiological characters on the different genotype tobaccos under a long period of water stress(长期水分胁迫对不同基因型烟草生长旺盛期生理特性的影响)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica(西北农业学报),2009,18(2):144-148.
[6]HU W(胡玮),KANG J(康君),LIU Y(刘阳),et al.The effect of drought stress on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of the different tobacco varieties(干旱胁迫对不同烟草品种光合生理特性的影响)[J].Chinese TobaccoScience(中国烟草科学),2013,34(2).
[7]NONG ML(农梦玲),LIU YX(刘永贤),LI FS(李伏生),et al.Advances in study on effects of drought stress on the physiological and biochemical properties of tobacco(干旱胁迫对烟草生理生化特征影响的研究进展)[J].Guangxi Agricultural Sciences(广西农业科学),2008,39(2).
[8]ZHANG ZL(张志良).Experimental Guide for Plant Physiology(植物生理学实验指导)[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press(北京:高等教育出版社),1993:3-4.
[9]BAJJI M,LUTTS S,KINET JM,et al. Water deficit effect on solution contribution to osmotic adjustment as a function of leaf ageing in three durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf)cultivars performing differently in arid conditions[J]. Plant Science,2001,160:669-681.
[10]WANG XK(王学奎).Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment(植物生理生化实验原理和技术)[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press(北京:高等教育出版社),2006:280-281.
[11]ZOU Q(邹琦).The Instruction of Experiment on Plant Physiology(植物生理学试验指导)[M].Beijing:China A-griculture Press(北京:中国农业出版社),2003:161-162.
[12]ZHUANG L(庄丽),CHEN YN(陈亚宁), CHEN M(陈明),et al.Evaluation on the drought-resistant capability of the riparian desert vegetation along the Tarim River,Xinjiang(模糊隶属法在塔里木河荒漠植物抗旱性评价中的应用) [J].Arid Land Geography(干旱区地理),2005,28(3):367-372.
[13]LUO ZC(罗占春),DU W(杜伟), ZHANG WX(张卫星),et al.The progress on the effect of soil water on growth and development and physiological metabolism of tobacco(土壤水分与烟草生长发育和生理代谢的相关研究进展)[J].Journal of Mountain A-griculture and Biology(山地农业生物学报),2009,28(5):446-451.
[14]MA XL(马新蕾),FANG Y(房燕), WANG YJ(王玉军),et al.The evaluation of drought resistance of ten tobacco cultivars(十个烤烟品种的抗旱性鉴定)[J].Acta Tabacaria Sinica(中国烟草学报),2005,11(5):26-30.
[15]WANG YF(汪耀富),ZHANG FS(张福锁).Effects of drought stress and nitrogen on dry matter accumulation and concentration of mineral elements in flue-cured tobacco(干旱和氮用量对烤烟干物质和矿质养分积累的影响)[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica(中国烟草学报), 2003,9(1):19-23.
[16]LIU H(刘浩),ZHANG ZS(张宗山).A preliminary study on drought resistance in potato cultivars in southern mountainous area of Ningxia(宁夏南部山区马铃薯主栽品种抗旱性研究初报)[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology(现代农业科技), 2008,16:18-20.
[17]WANG DM(汪邓民),WU FR(吴福如), YANG HJ(杨红娟),et al.Effect of drought on physiology and growth vigor of different flue-cured tobacco cultivars(干旱对不同烤烟品种的生理及其烟株生长势的影响)[J].Tobacco Science&Technology(烟草科技), 2001,10.
[18]ZHANG HY(张海燕),JIAO BC(焦碧婵),LI GQ(李贵全),et al.Study on selecting targets in drought-resistant breeding of soybean(大豆抗旱性鉴定指标评价的研究)[J].Soybean Science (大豆科学),2005,24(3).
[19]ZHANG HP(张红萍),NIU JY(牛俊义), XUAN CX(轩春香),et al.Effects of drought stress and rewatering on content of proline and malondiadehyde in pea leaves(干旱胁迫及复水对豌豆叶片脯氨酸和丙二醛含量的影响)[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University(甘肃农业大学学报),2008(5):50-54.
[20]ZHAO SJ(赵世杰),LIU HS(刘华山), DONG XC(董新纯),et al.Experimental Guide of Plant Physiology(植物生理学实验指导)[M].Beijing:China A-gricultural Science and Technology Press(北京:中国农业科技出版社), 1998,98-151.
[21]ZHOU JH(周冀衡),HU XW(胡希伟), ZHOU XS(周祥胜),et al.Study on drought-resistant physiology of tobacco(烟草抗旱生理的研究)[J].Chinese Tobacco Science(中国烟草科学), 1988(2):37-41.
[22]NI Y(倪郁),LI W(李唯).The status and recent development in crop droughtresistant mechanism and index(作物抗旱机制及其指标的研究进展与现状) [J].Journal of Gansu Agricultural University(甘肃农业大学学报),2001(1): 14-22.
[23]LUO LJ(罗利军),ZHANG QF(张启发). The status and strategy on drought resistance of rice(Oryza sativa L.)(栽培稻抗旱性研究的现状与策略)[J].Chinese Journal of Rice Science(中国水稻科学),2001,15(3):209-214.
[24]WANG HZ(王贺正),MA J(马均),LI XY (李旭毅),et al.Screening identification indexes of drought resistance at flowering stage in rice(水稻开花期抗旱性鉴定指标的筛选)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2005,31(11):1485-1489.
Responsible editor:Xiaohui FAN
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
毕节特色烤烟品种抗旱性评价
符新妍1,翟欣2,陈雪2,程功3,李洪臣1,喻奇伟2,张小全1,杨铁钊1*(1.河南农业大学烟草学院,河南郑州450002;2.贵州省烟草公司毕节地区公司,贵州毕节551700;3.许昌市烟草专卖局,河南许昌461000)
采用盆栽试验,研究了4个烤烟品种在干旱胁迫条件下的主要农艺性状、生物量积累、叶片保水力、相对含水量、根系丙二醛、脯氨酸含量等生理指标,并通过隶属函数法对各品种的抗旱性进行综合分析,以期明确烤烟品种间抗旱性的差异。结果表明:在干旱胁迫条件下,4个烤烟品种的主要农艺性状、干鲜重积累量及叶片相对含水量均显著下降,云烟87下降幅度最小,毕纳1号次之,黔西1号下降幅度最大;叶片保水力表现为云烟87>毕纳1号>黔西1号>韭菜坪2号;各烤烟品种根系丙二醛含量和脯氨酸含量均显著增加,云烟87和毕纳1号丙二醛含量增加量较少,脯氨酸含量增加量较大,韭菜坪2号和黔西1号则相反;隶属函数法综合分析发现抗旱性由强到弱顺序为云烟87>毕纳1号>韭菜坪2号>黔西1号。
烤烟;品种;抗旱性;隶属函数biomass and ABA content,and relatively low MDA content,with slight changes in most of the indicators(except ABA content).Shang et al.[3]found that highly drought-resistant flue-cured tobacco cultivars could maintain relatively high total root absorption area,active absorption area, root vitality and protective enzyme activity under drought stress.Currently, many studies have been carried out about the effects of drought stress on different tobacco varieties[4],growth stages[5],photosynthetic physiological characteristics[6]and physiological and biochemical characteristics[7].In this study,drought conditions were simulated with artificial water-control method to determine the drought resistance-related physiological and biochemical indicators of four different flue-cured tobacco cultivars in Bijie tobacco growing area and comprehensively analyze the drought resistance in different flue-cured tobacco cultivars with subordinate function method, aiming at clarifying the differences in drought resistant capacity among different flue-cured tobacco cultivars, selecting appropriate varieties for fluecured tobacco cultivation under drought conditions,and providing theoretical guidance for the identification of drought resistance in flue-cured tobacco.
贵州省烟草公司毕节市公司科技项目“毕节特色烤烟品种的深度挖掘与配套技术研究”。
符新妍(1988-),女,河南南阳人,硕士研究生,从事烟草遗传育种研究,E-mail:fxy1988fxy@163.com。*通讯作者,杨铁钊,博士生导师,教授,主要从事烟草遗传育种研究,E-mail:yangtiezhao@126.com。
2015-04-27
修回日期 2015-05-18
Supported by Science and Technology Project of Bijie Subsidiary of Guizhou Tobacco Company"Study on In-depth Searching and Supporting Techniques of Distinctive Fluecured Tobacco Cultivars in Bijie".
*Corresponding author.E-mail:yangtiezhao@126.com
Received:April 27,2015 Accepted:May 18,2015
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Analysis and Discussion on Some Problems of the Edible Fungi Production in Asmara Area
- The Control Research Progress ofLiberobacter asiaticumin Taizhou City
- Application of Genetically Modified Technology in Maize Breeding
- Breeding of Indica Rice CMS Line Renong 1A with Virescent-yellow Leaf
- Breeding and Application of Indica PTGMS Line Yan 161S and Its Hybrid Yanliangyou 1618 in Rice
- Thoughts on the Sustainable Development of the Fava Bean Industry in Chongqing
