On Income Distribution Mechanism of Farmer Cooperatives in the Context of Membership Heterogeneity
2015-02-05XiangzhiKONGDongLOUChanjuanFANG
Xiangzhi KONG,Dong LOU,Chan juan FANG
1.School of Agricultural Economics and Rural Development,Renmin University of China,Beijing 100872,China;2.Wuyi University,Wuyishan 354300,China
1 Introduction
Since the implementation ofLaw of the People’s Republic of China on Specialized Farmer Cooperativesin 2007,China's farmer cooperatives have been developing rapidly.According to statistics of State Administration for Industry and Commerce,by the end of December,2014,there were 1.2888 million specialized farmer cooperatives in the whole country,31.18%more than the previous year,with total contribution up to 2730 billion yuan,growing about 44.15%.At the same time of rapid increase in number,there is outstanding problem of membership heterogeneity,mainly manifested in difference between large farmers and small farmers,core and non-core members,full members and non-full members.The differences mainly lie in degree of cooperation participation,rights and duties,and income distribution.
It should be specially noted that the membership heterogeneity still increases with development of cooperatives[1].In the context of membership heterogeneity,the unequal income distribution between large and small farmers in cooperatives attracts attention of academic circle.On the one hand,some scholars stress protecting rights and interests of small farmers in income distribution[2-3],while some scholars stress enhancing incentive to rights and interests of large farmers(especially the director of cooperative)in income distribution[4-7],and more scholars are devoted to considering both rights and interests of small and large farmers in the context of membership heterogeneity[8-14].In this paper,we will study the standard for building income distribution mechanism of farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneity and how to build such income distribution mechanism.
In the context of membership heterogeneity,farmer cooperatives generally consist of a large farmer(or enterprise)and a group of small farmers or several large farmers and a group of small farmers[15].Discussing income distribution needs discussion of cooperation of many people,which will involve coalition of small alliances,thus the situation will become very complicated.For the convenience of analysis,we made personification of large farmer group and small farmer group in cooperatives.In this way,income distribution of cooperatives is simplified into large and small farmer cooperation model and this satisfies the purpose of this paper,namely,analyzing how to distribution income between large and small farmers.
2 Literature review of income distribution between two subjects
Many scholars have studied income distribution of two subject cooperation.For example,Rubinstein(1982)[16]proposed bargaining game of alternating offers,but this analysis framework is not suitable in practice[17].The bargaining analysis framework of Nash(1950)[18]introduced using game balance to define solution and use axiom to describe this solution.He proved that there exists a unique solution to symmetric(S),Pareto(P),independence of irrelevant alternatives(IIA),and independence of the utility origin(IUO)and independence of the utility units(IUU),and this solution is the product of two subject utility function,namely,Nash solution.Although Nash solution is generally recognized to a certain extent,there still exits certain drawbacks,particularly in whether it satisfies IUU and IIA[17].
Rubinstein,Safra and Thomson(1992)[19]clearly expounded economic significance of Nash solution and stated that Nash solution is based on no objection of two parties;if either party is not satisfied at this solution,the other party can rebut,till both parties have no objection.According to ideas of Nash(1950),equalization solution can meet requirement of S,P,IIA and IUO[17].At the same time,Kalai and Smorodinsky(1975)[20]found that there exists a unique solution to P,S,IUO,IUU,and Monotonicity(M),namely,the Kalai-Smorodinsky solution.
Some scholars also discussed unique solution to Nash bargaining solution.For example,Border and Segal(1997)[21]stated that theoretically,there are several solutions to Nash bargaining issue and some people may have preference to these solutions.Under the premise of the preference to these solutions satisfying continuity,monotonicity,disagreement indifference),and mixture symmetry,it can be proved that Nash solution is a unique solution to Nash bargaining issue.There are also the above problems in these conclusions.In other words,it is difficult to prove hypotheses of the preference.At present,in the context of membership heterogeneity,there exist many models of income distribution in farmer cooperatives.But the problem can be traced back to the income distribution of large and small farmers.To a certain extent,this can be deemed as Nash bargaining issue.
3 Income distribution models of farmer cooperatives and theoretical analysis in the context of membership heterogeneity
3.1 Four accumulation point solutions to income distribution of two subject cooperationCombining the above literature review and analysis of Huang Shaoanet al(2003)[17]on residual cooperation mechanism in the condition of two subject cooperation,we can obtain the accumulation point solution to income distribution of two subject cooperation.The accumulation point theory was firstly introduced by Schelling(1960)[22].Theoretically,there may be several Nash equalization points in a game.Then,in real life,an actor will find a point which is a common interest.This point will become a final solution to game in real life.This point becomes the accumulation point because culture and experience of game parties make them believe that this point is easy to be thought and selected.Through accumulation point analysis,there are at lest following four accumulation point solutions to income distribution of two subject cooperation.
(i)Equalization solution:it refers to the solution with equal utility of two cooperation parties.This is an equal distribution idea.The reason for this solution lies that the cooperation parties believe that cooperation income is jointly created by them.In other words,if there exists a third party trusted by both parties and letting this third party to distribute cooperation income,equalization solution means the third party will distribute income equally.Applying the development reality of farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneity,equalization solution means equal distribution of cooperation income between large and small farmers without considering heterogeneity of contribution of large and small farmers.Such distribution method will be partial to protecting rights and interests of small farmers to a certain extent.
(ii)Pure utility solution:Cooperative parties jointly increase the sum of respective utility,rather than considering respective income.This is a typical collective distribution method.To a certain extent,this solves the problem with the idea of development.Cooperative members firstly make the"cake"bigger.The point making the"cake"bigger will be the basis of income distribution.In practice,such distribution method will be partial to encouraging large farmers in cooperatives,increasing income of large farmers,and bringing into play functions of large farmers in cooperatives,and income of small farmers may not be guaranteed.To a certain degree,this is a distribution method of"efficiency coming first".
(iii)Nash solution:It is a solution to which cooperative parties have no objection and it is the bargaining result of the parties.In other words,if either party is not satisfied with distribution method of Nash solution and proposes new distribution method,and threatens to terminate the cooperation if the new distribution method is refused.At this time,the other party sticks to Nash solution distribution method considering the risk of cooperation termination.In practice of cooperatives,if cooperation income follows Nash solution distribution method,large and small farmers fail to propose other feasible method.If income distribution is partial to large farmers,small farmers will withdraw from cooperation;if income distribution is partial to small farmers,large farmers will lose enthusiasm for operating cooperatives,then the cooperatives will exist only in name.
(iv)Kalai-Smorodinsky solution:the cooperative parties distribute the cooperation income according to respective effort.To a certain extent,this solution contains the idea of distributing income according to element input.It will distribute cooperation income with full consideration of respective effort and respective input proportion.In the practice of farmer cooperatives,if using Kalai-Smorodinsky solution to distribute cooperation income,it will consider large volume of manpower and materials and social capitals of large farmers.Besides,large farmers undertake a larger portion of operating risk.Thus,it is reasonable that they will receive higher cooperation income.
3.2 Income distribution models of farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneityWe use A1and A2to represent large and small farmers in farmer cooperatives separately.Assume cost of large farmers for establishing the cooperatives is C1.C1is a constant and the cost of large farmers for sending the cooperation invitation.In practice,costs for establishing cooperatives are generally undertaken by large farmers.Obviously,no matter the cooperative is established or not,such costs have to be paid.
When A1and A2bargain about distribution of cooperation income,there can be new quotation.Certainly,in the practice of cooperation,A1generally makes no direct quotation.As long as A2has such expectation,in other words,the distribution mechanism proposed by A1is not responded by A2,it will need quotation again,science of A2is like voting by foot.If it exceeds certain time limit,A2still keeps silent and does not cooperate with A1,it is deemed that the cooperation breaks.Besides,we need assuming other costs for cooperation C2,mainly including transaction cost between A2and cooperative(such as time cost,learning cost,opportunity cost,transportation allowance,and communication ex-penses for A2participating in cooperatives).Such costs are undertaken by A2and will be paid only when the cooperation is successfully established.Assume the utility of cooperation to A1is V1and the utility of cooperation to A2is V2,V1and V2are constants.Assume cooperation income promised by A1to distribute to A2is X,once A2accepts X,A1must honor his promise.However,in the practice of farmer cooperatives,moral constraint of rural acquaintance society is more effective than laws.
For the convenience of calculation,we assume that both parties can make random combination between cooperation breaking and establishment point,but can not make random combination between cooperation establishment points.In other words,once cooperation is established,the utility function is ordinary instead of expected form.In sum,if the cooperation is established in the condition that the cooperation income X promised by A1to distribute to A2,and the utility function of A1and A2is U”1=V1-xa-C1and U2=xb-C2,where 1≤a≤+∞,0≤b≤1,a and b signify equitable distribution criteria expected by A1and A2respectively.According to this logic,the bigger a and the smaller b,the negative utility of this distribution method to A1will be greater,while the positive utility to A2will be smaller.There are two extreme cases:when a=1 and b=1,small farmers incline to ask cooperation income from large farmers and it is deemed reasonable no matter the amount of asking;when a= +∞and b=0,the cooperative inclines to encourage large farmers and considers that large farmers are the key for development of the cooperative,and small farmers need not obtain more income distribution.
When the cooperation breaks,the utility of A1is U1'=-C1,and the utility of A2'is U2'=0,i.e.S=(-C1,0).This is because the cooperation will be established only when the cooperation is more beneficial than non-cooperation.Thus,it requires U1-U1'>0 and U2-U2'>0.Huang Shaoan(2003)held that it is difficult to work out solution to a and b in this constraint condition.Therefore,we have to use the accumulation point solution to study the income distribution mechanism in the context of membership heterogeneity:when a is smaller and b is bigger,the income distribution inclines to protect small farmers and use equalization solution;when a is bigger and b is smaller,the income distribution inclines to encourage large farmers and use pure utility solution or Kalai-Smorodinsky solution;when intermediate condition appears,there generally occurs typical bargaining Nash solution.
3.3 Factors influencing income distribution mechanism of farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneitySchelling(1960)[22]and Huang Shaoan(2003)[17]stated that factors influencing people selecting accumulation point are mainly social conventions,including value concept,ideology,cultural character,experience and practice.In the practice of cooperation income,usually the conviction of members determines income distribution mechanism,while the conviction generally comes from local social conventions.Since there are great differences in social conventions in the whole country,these accumulation point solutions will exist in the income distribution of different farmer cooperatives.It should be noted that even in the same farmer cooperative,at different development stages,there will be changes in the above four solutions to the income distribution.
In farmer cooperatives,large and small farmers will make choice of cooperation income distribution mechanism according to information brought by social conventions.In other words,specific income distribution mechanism is the result of rational choice of large and small farmers.For example,when large farmers propose pure utility solution,Nash solution or Kalai-Smorodinsky solution,they must base on their conviction consistent with that of small farmers.Otherwise,blindly adopting income distribution mechanism will lead to small farmers quitting from cooperation and accordingly the cooperation breaks.At this time,large farmers will observe daily action of small farmers and respect their choice according to information brought by social conventions.If they found that small farmers only care about improving services for small farmers(especially the problem of difficult sales for small farmers),but do not care income distribution,large farmers generally propose using pure utility solution;if they found small farmers have impulse to directly participate in income distribution and propose designing more reasonable income distribution mechanism,large farmers may adopt Nash solution;if they found small farmers admit their contribution to farmer cooperative is limited and recognize resource contribution of large farmers,large farmers may adopt Kalai-Smorodinsky solution.Naturally,if local social convention is still following no difference between people,cooperation income should be equally distributed,then equalization solution will become common choice of large and small farmers.In other words,because information can be disseminated,knowledge can be accumulated,and people are good at summarizing experience,large and small farmers will learn local distribution rules to select the income distribution mechanism suitable for local social conventions.
To a certain extent,we can use saving transaction cost to explain income distribution mechanism according social conventions.Making decisions according to social conventions can effectively save transaction cost,so this is a rational choice.In the same region,social conventions are the same,and people's understanding of equal standard is similar.Thus,there will appear the income distribution solution most suitable for local equal standard.Of course,the changes of solution will also influence social conventions.For example,if Kalai-Smorodinsky solution appears in a place where equalization solution is stressed,people may not accept in the beginning.However,if people are slowly realizing benefit of Kalai-Smorodinsky solution,local areas will change their understanding of equal standard,accordingly the local social conventions will gradually change,but this is a long process.It should be specially noted that not all social conventions are conforming to moral standards.As long as they suit equal standard believed by majority people,they can be deemed locally moral.From development process of cooperatives in the world,principles of cooperatives are constantly modified,especially in the income distribution.Besides,the above four solutions are based,to a certain extent,on the same negotiation ability of large and small farmers.If a party has stronger negotiation ability,the distribution solution will be inclined to this party.For example,in China's farmer cooperatives,large farmers generally have stronger negotiation ability,the income distribution solution may be probably inclined to pure utility solution and Kalai-Smorodinsky solution which are favorable for large farmers.
4 Case analysis
According to the above literature review and theoretical analysis,there is inherent theoretical basis for diversified trend of income distribution mechanism of farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneity.In farmer cooperatives,large and small farmers will rationally select equalization solution,pure utility solution,Nash solution,and Kalai-Smorodinsky solution,and reach common understanding of cooperation to realize win-win.In this process,large and small farmers also imbed local social conventions and equal standard into the income distribution mechanism,to reduce transaction cost.Now,we selected five cases to make empirical analysis.
4.1 Equalization solution:Shandong DX Fruit and Vegetable Farmer CooperativeThe predecessor of Shandong DX Fruit and Vegetable Farmer Cooperative is DX Fruit Association.At the early period of establishment,DX Fruit Association had common reserve fund,public welfare fund,and profit return project,and had good reputation in local areas.After the implementation ofLaw of the People’s Republic of China on Specialized Farmer Cooperativesin 2007,Director Mr.Sun took the lead in transforming the association into farmer cooperative,and founded the board of directors and board of supervisors,and Mr.Sun served as the president.At that time,there were 112 members,but there appears significant heterogeneity in capital contribution,as listed in Table 1.
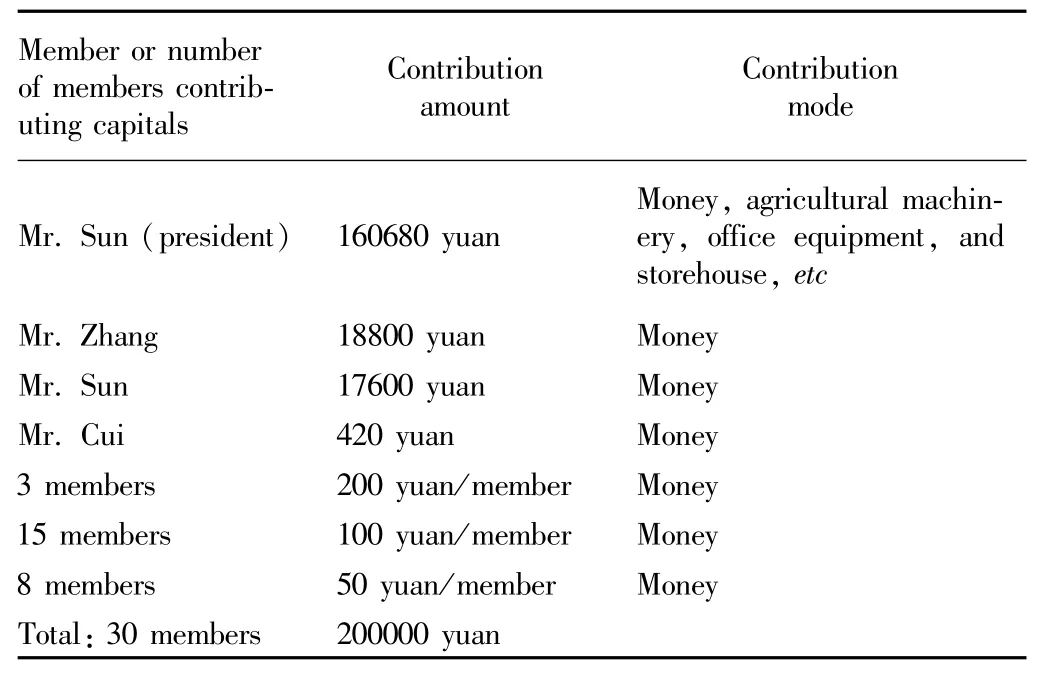
Table 1 Capital contribution of DX Fruit and Vegetable Farmer Cooperative at the time of registration
Although there is significant heterogeneity in members of DX Fruit and Vegetable Cooperative,its income distribution mechanism still follows relatively fair income distribution mechanism specified inLaw of the People’s Republic of China on Specialized Farmer Cooperatives.The income is distributed mainly through transaction volume with the cooperative.The distributable income of the cooperative,after deducting current year production,operation and management service costs,making up for losses,drawing 25%public reserve fund and 5%public welfare fund,can be distributed according to following sequence based on decisions of the member assembly.Firstly,the income will be returned according to transaction volume of members with cooperative,and the total amount of return should not be lower than 60%of distributable profit.Secondly,the remainder after allocating as per the preceding provision will be distributed as per the contribution amount and share of public reserve fund recorded in the member account plus state finance subsidy and donation of other people.For example,the cooperative sold 420 tons of fruits for cooperative members in 2007,realizing total operating income of 1.02 million yuan and the profit of 21000 yuan.After drawing the public reserve fund and public welfare fund of 6300 yuan,the distributable profit was 14700 yuan.The return of8820 yuan as per transaction volume of members with the cooperative accounts for 60% (namely,1 kg fruit transaction with the cooperative can obtain return of 0.021 yuan profit);the remainder 5880 yuan accounts for 40%and is distributed as per contribution amount.For100 yuan contribution,members can obtain 2.94 yuan bonus.Such method of dealing with matters is popular with cooperative members.In the driving of the cooperative,in addition to rise of fruit price,it greatly increased income of members.In that year,the net income per capita of cooperative members reached 9672 yuan,34.03%higher than other farmers(7216 yuan)in local areas.
From the income distribution mechanism of DX Fruit and Vegetable Farmer Cooperative,we can find that it is based on equalization solution.Although there is significant membership heterogeneity,the income distribution still follows the equalized income distribution principle which is advocated by theLaw of the People’s Republic of China on Specialized Farmer Cooperatives.This is because Mr.Sun has been the local village branch secretary and director of village committee and inclines to care about income of small farmers,and also because this cooperative is developed through an association that is inclined to protect benefits of small farmers and has the social conventions of equalization solution to income distribution.
4.2 Pure utility solution:Sichuan JY Fruit Farmer CooperativeSichuan JY Fruit Farmer Cooperative founded in 2008 is engaged in helping cooperative members to sell oranges.Now,its existing total assets are 0.87million yuan.It owns38000mu fruit orchard,covering 33 townships in 3 counties,and 1680 member households,accounting for 1/3 of local fruit farmers.In the year of establishment,the sales revenue reached 36 million yuan and the total profit reached 0.33million yuan.Members purchased low price production means from the cooperative and sold oranges at high price,realizing increase of income up to 3000 yuan on average.Membership heterogeneity of the cooperative is significant,funds mainly came from 7 directors and supervisors with amount fro 20000 yuan to 120000 yuan.Besides,the cooperative also attracted 38 orange operators in other places to join in.They purchased shares with their information advantage and marketing network converting to price,about2000 yuan each person.Directors,supervisors and operators form large farmer group of the cooperative,while ordinary fruit farmers(small farmers)join in the cooperative by means of their orchards,enjoy various services and also undertake the responsibility of ensuring fruit supply for the cooperative.
Since the purpose of establishing the cooperative is to solve the difficulty of selling oranges,maximizing utility and encouraging large farmers to bring into play their marketing ability fully become a common choice for large and small farmers.Manifested in design of income distribution mechanism,this reflects high compensation for marketing ability,using pure utility solution,namely,operating profit is obtained by operators responsible for sales,while ordinary fruit farmers can sell products at price higher than market price,to obtain benefit from preferential price.In actual operation of the cooperative,large farmers(operators)input greater market development costs,and assume higher market risks,so it is reasonable to make them possess control power of the cooperative.Income of the cooperative inclines to large farmers,small farmers can increase orange price,which can protect their benefits.Small farmers will be satisfied if they can purchase means of agricultural production at low price and sell oranges at high price.In this way,large and small farmers reach common understanding in income distribution and take selling oranges at high price as objective to make distribution of income.
Our survey found that social conventions including individual contract,more pay for more work,and developed individual and private economy influence formation of pure utility solution income distribution mechanism to a certain extent.As mentioned by a local grass-roots cadre,the earliest agricultural industrialized association in China was established in Sichuan.However,due to excessive concern about equity,skills of some rural able people fail to be brought into play in associations.Now,people gradually realize function of clear property right and individual operation.The precondition for cooperation is individual operation.To bring into play real function of the cooperative,it is required to make effort to establish household operation and individual operation based cooperation.According to introduction,local individual and private economy is well developed,and there is certain gap in income of farmers.Some farmers have annual income up to 100000 yuan.They are recognized as able and wise and hardworking.Just because of such social conventions,large farmers will make effort to increase their income,and small farmers will also strive to participate in cooperative activities.Small farmers will not be envious of large farmers' high income.Accordingly,it forms pure utility solution income distribution mechanism in the cooperative.
4.3 Nash solution:Zhejiang XJ Free-range Egg CooperativeEstablished in May 2003,Zhejiang XJ Free-range Egg Cooperative is a farmer cooperative professionally engaged in free range egg production,purchase,and sales and has members of 1245 households in township B,T,and P.Since the foundation,its operating scale is constantly expanding.By 2007,the annual breeding amount exceeded 200000 chicken and annual free-range eggs up to 150 tons,and annual sales income up to 8.6 million yuan.In the process of operation,this cooperative undertakes the duty of providing chicks,special feed,and technical service and ensures to purchase free-range eggs at certain price,while members make management of raising and sell all eggs to the cooperative.In fact,members play the role of free-range chicken raiser in the cooperative,while the cooperative obtains stable and high quality eggs.In this cooperative,the membership heterogeneity is prominent,the leading entity is a company founded in 2001 and can be considered as large farmer,and the rest members are small farmers.Before the founding of the cooperative,enterprise and farmers are connected with orders.After founding of the cooperative,the income distribution mechanism is that members provide labor,sell free-range eggs to enterprise,and get more pay with more work,while enterprise obtains all remaining profit of selling eggs.
Such income distribution mechanism is the result of bargaining between large and small farmers.Member C recalled that in the time of made-to-order farming,chick and skills are ours,we can bargain with enterprises;when the market is in high demand,enterprises have to raise price,but we also have high risks,including risk of chick disease and market price fluctuation.Now,there is minimum price guarantee and also technical guidance,so our risks are lower and our income becomes stable and we have no need of bargaining.The former enterprise president and now the cooperative president stated that the rate of violation in original made-to-order farming was high,and supply of goods can not be guaranteed;if including farmers into enterprise and paying them salary,we are afraid of their laziness.Now,there is the cooperative.Although the cooperative assumes certain risk,the cooperative can operate with guaranteed supply of goods and quality.Thus,in the existing income distribution mechanism,large farmers obtain cooperation remainder and assume risk,while small farmers lose cooperation remainder and are relieved from assuming risks.Both parties accept such Nash solution distribution mechanism and accordingly the cooperation continues.
Nash solution income distribution mechanism is greatly influenced by made-to-order agriculture to a great extent.The made-to order agriculture is wide applied in local areas,and local farmers also have social conventions of bargaining with purchasers.Therefore,members will see clearly benefits and shortfalls brought by the cooperative,and make bargaining with large farmers in the cooperative,to form Nash solution income distribution mechanism acceptable to both parties.As introduced by its president,the cooperative is operating smoothly and has high profit.Members are satisfied with their income.Thus,there will be no big change in the income distribution mechanism and members do not want changes.
4.4Kalai-Smorodinsky solution:Liaoning HS Traditional Chinese Medicinal Materials CooperativeLiaoning HS Traditional Chinese Medicinal Materials Cooperative,founded in 2008,mainly supplies services of planting,processing,sales and related information of traditional Chinese medicinal materials.By August 2010,number of members reached 209,covering 8 villages in 5 townships,and the cooperative develops in good trend.Membership heterogeneity in the cooperative is outstanding:large farmers are mainly the president(having high social capitals,funds,and land),large planting households(having funds and land),and share purchasers(having much funds),while small farmers are generally small farmer households(He Anhuaet al,2012).
The income distribution mechanism of this cooperative follows the principle of Kalai-Smorodinsky solution,namely,it distributes income according to efforts of large and small farmers.For example,in the respect of large farmers,the president uses his social capital to raise funds for obtain government support.In the development of the cooperative,large farmers and share purchasing members provide funds and obtain share profit according to contribution(60%for share profit according to contribution,20%for public reserve funds,and 20%for public welfare funds).If large and small farmers deliver their land to the cooperative for trust,the profit will be distributed in 2:8 ratio,namely,80%profit is turned to the cooperative,and 20%is turned to farmer households.If large and small farmers join in the cooperative with their land and labor,the profit will be distributed in the ratio of50%,and large farmers and small farmers can obtain 30%more profit than trust.Finally,if some small farmers are just working for the cooperative,they can obtain wages.
The Kalai-Smorodinsky income distribution mechanism of this cooperative is also influenced partly by local social conventions.Traditional Chinese medicinal material industry is an industry requiring social capital,funds,forest land,and labor.Before founding of the cooperative,individuals plant medicinal materials separately.When they need capital,they have to borrow money through social relations;when they need labor,they have to employ local labor;when they need land,they have to contract land and pay land rent.In this situation,local areas have formed the social convention of providing remuneration for these elements,and then the demand and supply parties may make effort to work.After founding of the cooperative,these elements participate in cooperation,so the income distribution mechanism also changes to distribution according to element contribution,which is equivalent to distribution according to respective effort.
4.5 Evolution from Nash solution to Kalai-Smorodinsky solution:Heilongjiang RF Agricultural Machinery Cooperative
Heilongjiang RF Agricultural Machinery Cooperative was established by branch secretary Mr.Li and other 6 villagers of Village RF in October2009.Mr.Li contributed 5.5million yuan and other 6 villagers contributed 0.5million yuan separately,and the total registration amount was8.5million yuan.By August2013,total assets of the cooperative had reached 30 million yuan and the number of cooperative members reached 2400 households.Besides,it owned 72 sets of modern large agricultural machinery and the radiating area was up to 500000 mu.The membership heterogeneity of the cooperative is prominent.Except the 7 starters,most other members join in the cooperative through transferring land.From 2011 to 2013,the income distribution mechanism of RF Agricultural Machinery Cooperative realized evolution from Nash solution to Kalai-Smorodinsky solution.
From 2011 to 2012,RF Agricultural Machinery Cooperative adopted Nash solution income distribution mechanism.To establish such distribution mechanism,core members made certain concession to cater to non-core members and bring into play functions of bargaining mechanism.Specifically,before 2011,the transaction between the cooperative and local farmers was a zero-sum game.The cooperative provided farming service and collected certain service charges.In zero-sum game,each participant's gain(or loss)of utility is exactly balanced by the losses(or gains)of the utility of the other participant.In this situation,farmers were still separate operation and land was not developed into centralized and large-scale operation,so the cooperative benefit was not good.In view of this,the cooperative started to make a concession.It not only guaranteed greatly increasing land income of participating farmers(implementing land minimum price),equalized huge financial supporting funds to the newly joined members,but also promised to make secondary sharing of bonus as per amount of stocks converted by land.Such measures effectively catered to farmers' mentality of fearing risks and caring about benefits,and accordingly broke original low efficiency balance state.As a result,many farmers directly delivered their land to the cooperative.And Nash solution income distribution mechanism was established.By 2013,the cooperative can celled the"land minimum price",improved the matching of income with risk in members,and made clear the income distribution proportion of buying shares in the form of funds and in the form of land.Besides,in order to fully bring into play working enthusiasm of management personnel,the cooperative drew 2%from the annual total profit to pay out annual wages of the president and other management personnel.Then,such elements as fund,land,enterpriser talent would need to be benefited from the cooperative,and it accordingly realized the Kalai-Smorodinsky solution income distribution mechanism according to respective effort.
The income distribution mechanism of RF Agricultural Machinery Cooperative is also greatly influenced by local social conventions.At first,to attract farmers to participate in cooperation,the cooperative catered to local social conventions and adopted Nash solution income distribution mechanism.When it developed to certain level,most members realized functions of funds and enterpriser talent,the cooperative gradually adopted Kalai-Smorodinsky solution to distribute the income.
5 Conclusions and recommendations
With reference to several possible solutions to the issue of two subject allocation,using the Accumulation Point analysis method in Game Theory,we analyzed the income distribution mechanism between large-scale farmers and small-scale farmers in farmer cooperatives in the context of membership heterogeneity.We found that,in the practice of the income distribution in farmer cooperatives,there possibly exists equalization solution,pure utility solution,Nash solution and Kalai-Smorodinsky solution and it will be affected by social conventions.
From these conclusions,we came up with following recommendations:
(i)In the context of membership heterogeneity,large and small farmers of the cooperatives will rationally select suitable income distribution mechanism according to local social conventions and equitable standard.There is no income distribution mechanism valid everywhere.
(ii)In the process of guiding farmer cooperatives to establish income distribution mechanism,it is recommended to respect opinions of large and small farmers,respect creative initiative of grass-roots people,bring into play their subjective initiative,and attach importance to administration function of rules and regulations of the cooperatives.As long as the cooperatives can promote increase of farmers' income,agricultural development,and rural prosperity,it is required to support their development,rather than suppress them due to imperfect income distribution mechanism.
(iii)In the context of membership heterogeneity,no matter the equalization solution,Kalai-Smorodinsky solution,pure utility solution,and Nash solution,the income distribution mechanism easily leads to the conflict between weak incentive and insufficient protection for small farmers.Therefore,it is necessary to make further pertinent study to bring into play functions of large farmers and protection of small farmers' rights and interests,rather than briefly stating that the income distribution is not perfect yet.
[1]CUI BY,LI XM.Study of constraints on endogenous capital supply in heterogeneous cooperatives:Based on Linhai Fengyi cooperative in Zhejiang Province[J].Finance and Trade Research,2008,19(4):35-42.(in Chinese).
[2]WEN TJ.Governments&capital re-entry rural areas and development of specialized cooperative economic organizations of farmers[J].Economic Theory and Business Management,2009(7):5-12.(in Chinese).
[3]TONG ZH,LOUD.The logic formation and continuation of farmers' professional cooperative[J].China Co-Operation Economy,2010(4):60-61.(in Chinese).
[4]ZHANG XS.An analysis of the developing trend of rural cooperatives[J].Management World,2009(5):89-96.(in Chinese).
[5]XU XC,WU B.The effects of governance mechanism on the performance of farmers' professional cooperative[J].Chinese Rural Economy,2010(5):43-55.(in Chinese).
[6]HUANG ZH,GAO YL.The service function of farmers' professional cooperatives in China,and the influencing factors thereof[J].Chinese Rural Economy,2012(7):4-16.(in Chinese).
[7]HUANG JK,DENG HS,XU ZG.The service function of farmers’special cooperative economic organization in China and its influencing factors[J].Management World,2010(5):75-81.(in Chinese).
[8]FENG KW.On establishing and perfecting the cooperative distribution system[J].Management and Administration on Rural Cooperative,2005(11):17-19.(in Chinese).
[9]ZHOU LY.A brief analysis on farmers' professional co-operatives distribution system and cases[J].China Collective Economy,2009(2):38-41.(in Chinese).
[10]HONG XZ,JIANG CC.Heterogeneity among members influencing the governance mechanism of a cooperative[J].Rural Economy,2010(9):8-11.(in Chinese).
[11]ZHENG D.Exploration on the distribution of earnings of farmers' professional co-operatives[J].Chinese Rural Economy,2011(4):74-80.(in Chinese).
[12]CAI R.Surplus creation,division of earning and the future of farmers' professional cooperatives[J].Reform,2012(5):88-93.(in Chinese).
[13]TIAN YL,XIU CB.Building the benefit allocation mechanism of Herdsmen' specialized cooperatives in China from the perspective of life cycle[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2012(9):70-76.(in Chinese).
[14]HE AH,SHAO F,KONG XZ.The difference of resource endowment and the distribution of cooperation benefits[J].Jianghuai Tribune,2012(1):11-18.(in Chinese).
[15]GUO HD.A theoretical and empirical study on the development of Chinese farmers’professional cooperative[M].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University Press,2011.(in Chinese).
[16]Rubinstein A.Perfect equilibrium in a bargaining model[J],Econometrica:Journal of the Econometric Society,1982.
[17]HUANG SA,GONG MB.The allocation of cooperative surplus under the situation of two subjects[J].Economic Research Journal,2003(12):78-85.(in Chinese).
[18]Nash JF.The bargaining problem[J].Econometrica:Journal of the Econometric Society,1950.
[19]Rubinstein A,Safra Z,Thomson W.On the interpretation of the Nash bargaining solution and its extension to non-expected utility preferences[J].Econometrica:Journal of the Econometric Society,1992.
[20]Kalai E,Smorodinsky M.Other solutions to Nash's bargaining problem[J].Econometrica:Journal of the Econometric Society,1975.
[21]Border KC,Segal U.Preferences over solutions to the bargaining problem[J].Econometrica:Journal of the Econometric Society,1997.
[22]Schelling TC.The strategy of conflict[M].Cambridge,Mass,1960.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Study on Circulation and Management of Rural Land Use Right
- Construction of Rural Grass-roots Water Conservancy Service System in the Context of Institutional Changes
- Preliminary Study on Management of Agricultural Scientific Research Projects in the New Situation
- Review and Prospect of Development Capability of New Generation Farmers
- Multiscale Regional Formula Fertilization Considering Environment Information Incompleteness
- Empirical Study on Grow th of Evil Forces in Land Requisition and Relocation in City G of Hubei Province Based on Social Network Analysis
