Study on Dryland Weed Species under Different Land Use Patterns in Southwest of Guangxi Province——A Case Study of Longzhou County
2015-01-18QiujinTANZhenshiQINHaishengCHENDongyingXUDaxuanZHAOXianyangHEXiyunHUANG
Qiujin TAN,Zhenshi QIN,Haisheng CHEN,Dongying XU,Daxuan ZHAO,Xianyang HE,Xiyun HUANG
Agricultural Science Research Institute of South Subtropics of Guangxi,Longzhou 532415,China
Responsible editor:Yingchun YANG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Weed includes all the kinds of plants which were disadvantageous to human activities or deleterious to production spots.It strongly inhibits the growth and development of crops,and it can promote the spread of diseases and pests[1].The size,structural features and dynamic change of the potential weed communities in dryland decide the harm conditions in the future[2-3].In recent years,with the change of cropping system,adjustment of cropping structure,improvement of the integration of water and fertilizer and the long period using of chemical herbicides,the dominant populations of weed in farmland and the community structures had been changed obviously.Dryland weeds have serious damages and effects on the yield and quality of crops[4-5].In abroad,in order to maintain the balance of farmland ecosystem under the condition of changed cultivation system,species,density,distribution and dominant population of weed were widely investigated[6-8]including scientific fertilization,regulation of weed seed bank,reasonable control of weed and reduction the use of chemical herbicide[9-11].In order to master weed community structure,diversity,other dynamic characteristics,occurrence and damage conditions in dryland under different land use patterns in southwest of Guangxi and provide theoretical foundation for scientific prediction of community succession patterns of weeds,scientific and reasonable application of chemical herbicides and efficient control of agroecological system,the writer investigated weed species,density,distribution and dominant population in corn,sugarcane,pineapple,banana and mango fields in Longzhou County during 2013 to 2014.
General Situation in Study Area and the Study Method
General situation in study area
The study area is Binqiao village,Longzhou County,Guangxi Province and belongs to southwest Guangxi,which is located at 22°8′- 22°44′ N and 106°33′-107°12′ E.The highest altitude of the area is 1 045 m and the general altitude is 200 m.It is famous as a basin and belongs to subtropical monsoon climate area.The annual average temperature is 22.3-23.0 ℃;the extremely high temperature is 41.6 ℃and the lowest air temperature is -3.0℃.The sunshine duration is 1 582.7 h and the frost-free period is more than 350 d.The average annual precipitation is 1 304.1 mm and the precipitation period is mainly between June and September.The annual average relative humidity of air is 81%-87%.The northwest of the area is high while the middle-of-south is low.It is mainly consisted of karstic feature stone mountains.There are many small,independent and steep peaks,which belongs to limestone soil weathered from rock during Permian period.
Study method
On the basis of field survey in study area,representative corn,sugarcane,pineapple,banana and mango fields with basically consistent site conditions were selected and fields of each pattern were no less than five.The 0.5 m × 0.5 m square iron wires were adopted for investigation.Weed species,number,height,breadth and cover degree were investigated according to the sampling methods of inverted W-pattern.The density,frequentness and growth condition were investigated with quadrat method[12].The abundance,important value Shannon-Wiener,Simpson and Pielou uniformity of the dominant species of dryland weed were calculated[13].
Results and Analysis
Weed species
According to the investigation results of the five survey points,11 weed species of Gramineae and ten species of Compositae were the main species among the 27 families 54 species(Table1) appeared in the sampling fields.According to the different land use patterns and cultivated crops in the drylands,weeds could be classified into corn field weed,sugarcane field weed,pineapple field weed,banana field weed and mango field weed.There were 20 weed species in sugarcane field,18 weed species in pineapple field,11 weed species in banana field,14 weed species in mango field and 13 weed species in corn field.
Dominant weed species in the dryland under different land use patterns
The dominant weed species and degree of dominance in various drylands were different because of the different planting patterns and ecological environments[14].According to the investigation results,the dryland in Longzhou County formed weed populations with Gramineae,Compositae and Oxalidaceae as the main families(Table2).Bidens bipinnata,Oxalis corniculata,Urena lobata,Roegneria kamoji,etc.were the main weeds in corn fields.The relative abundance,Shannon-Wiener and Simpson of Oxalis corniculata were 0.313,0.294 and 0.026,respectively,which were the biggest.Stellaria media,Emilia sonchifolia and Stenotaphrum helferi were the main weeds in sugarcane fields.The relative abundance,Shannon-Wiener and Simpson of Stellaria media were 0.145,0.255 and 0.014,respectively,which were the biggest.Bidens bipinnata,Oxalis corniculata,Eupatorium odoratum and Silene conoidea were the main weeds in pineapple fields.The relative abundance,Shannon-Wiener and Simpson of Oxalis corniculata were 0.151,0.268 and 0.018,respectively,which were the biggest.Bidens bipinnata,Roegneria kamoji,Oxalis corniculata and Galium aparine were the main weeds in banana fields.The relative abundance of Roegneria kamoji was 0.216,which was the biggest.The Shannon-Wiener and Simpson of Bidens bipinnata were 0.277 and 0.020,respectively,which were the biggest.Oxalis corniculata,Viola inconspicua,Euphorbia prostrata and Bothriochloa bladhii were the main weeds in mango fields.The relative abundance,Shannon-Wiener and Simpson of Oxalis corniculata were 0.200,0.300 and 0.028,respectively,which were the biggest.The relative abundance of the dominant species and dominant populations of weeds in drylands under different land use patterns were relatively high[15].The Pielou uniformity under the five land use patterns were 0.967,0.964,0.947,0.969 and 0.962,respectively.The number and damage degree of the dominant species and populations were over other weeds.It might because of the low drug delivery level or the misuse of herbicides that resulted in the rapid growing of Compositae weeds,Gramineous weeds and other swart weeds.The prevention and treatment are difficult.It could not be controlled by one-time drug delivery while the cost of two times drug delivery was high,which resulted in serious damages of Compositae weeds,Gramineous weeds and other swart weeds which should be treated as the key objects of weed control in Longzhou County.
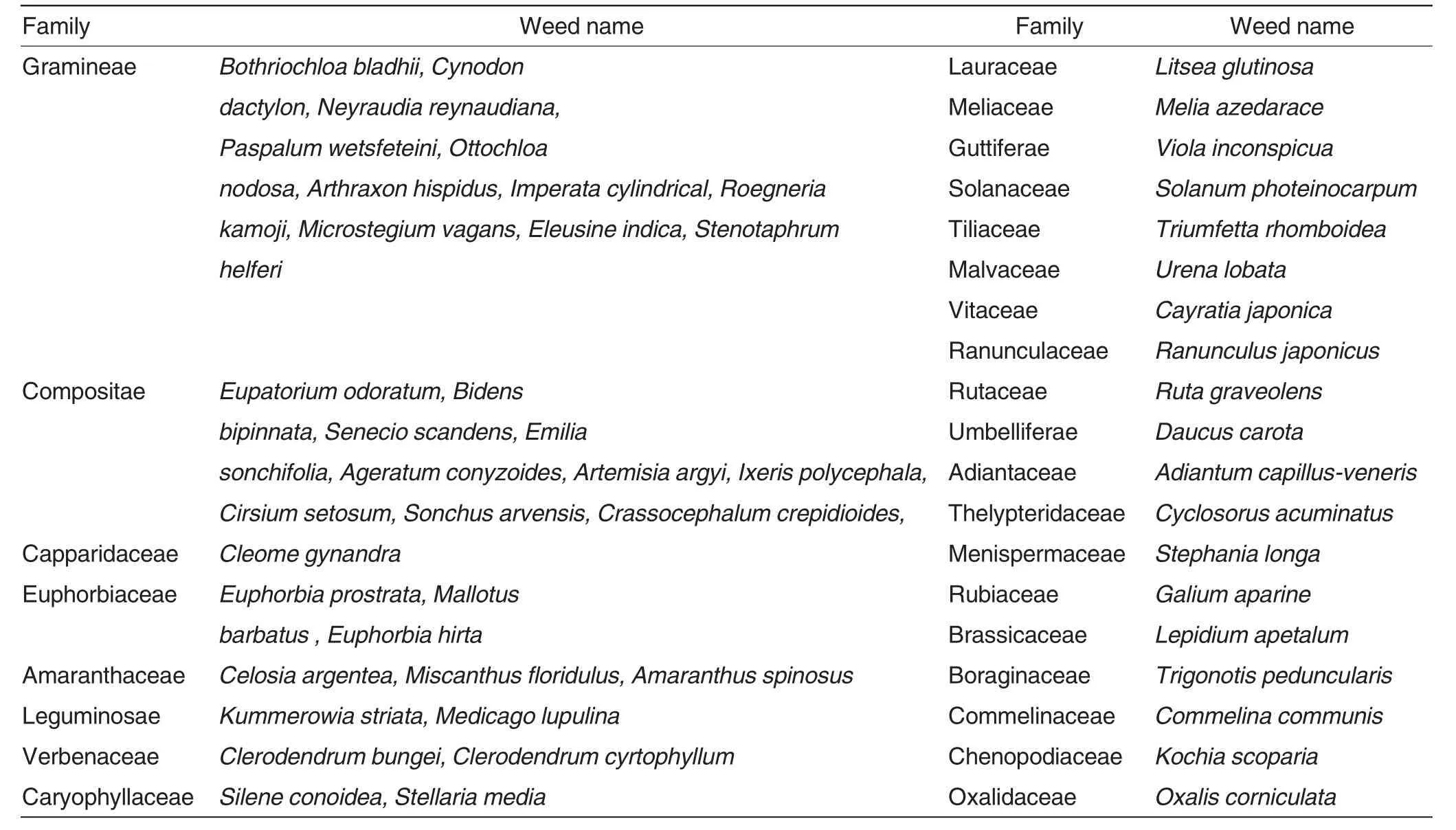
Table1 Weed species in dry land under different land use patterns in southwest Guangxi
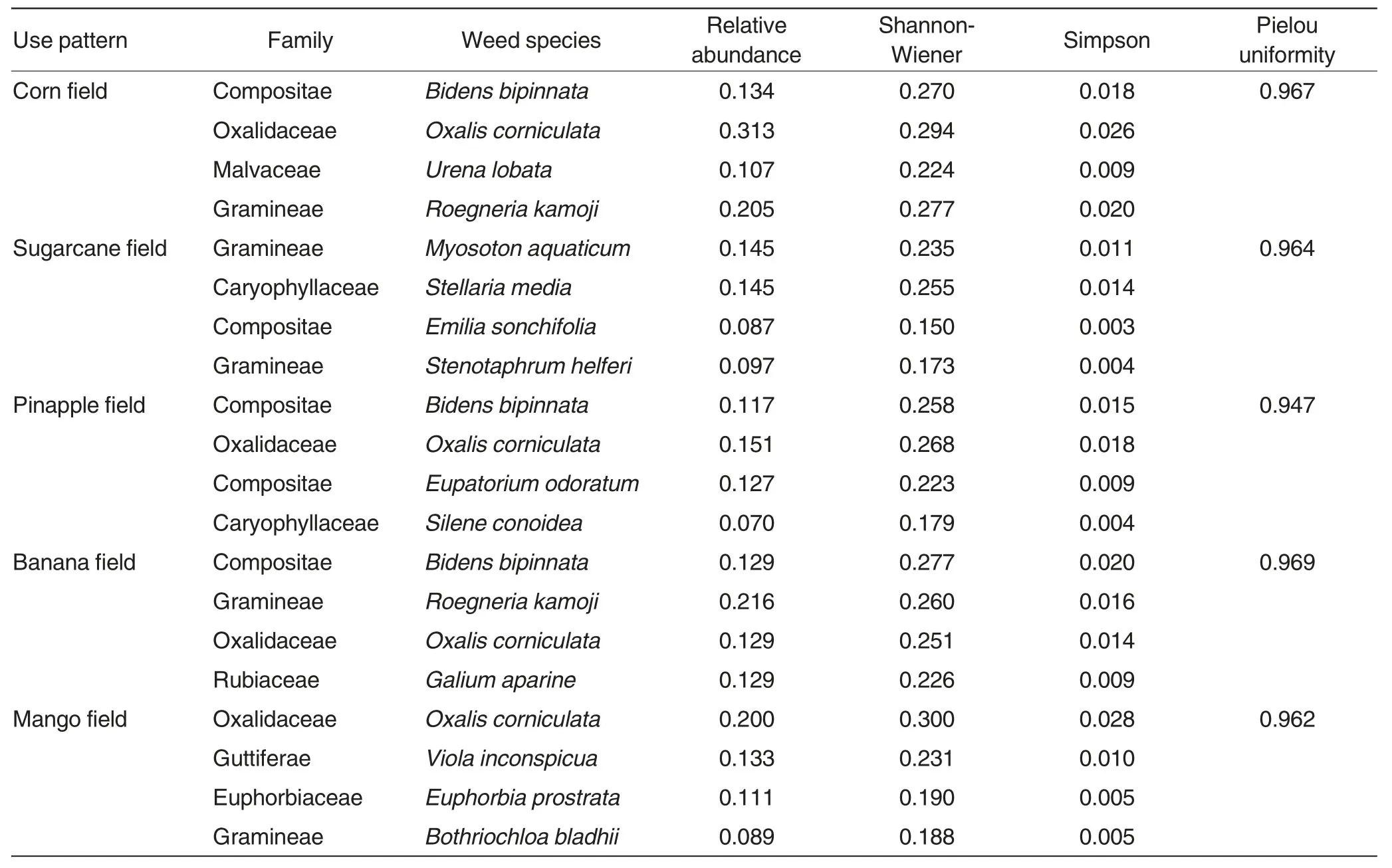
Table2 The dominant species and diversity indexes of dry land weeds
Discussion
Sugarcane was basically planted in the dryland in Longzhou County,southwest Guangxi.In recent years,the income of sugarcane industry decreased under the continuous influences of years of drought.The positivity of farmers was not high.Currently,partial cropping structures were drastically adjusted and the cultivation system was changed.Weeds fight for nutrient,moisture,sunshine and space and produce inhibiting substances to impede crop growth,which not only decrease crop yield and influence the quality of agricultural products but also hamper farm operation and seriously influence agricultural production[16-17].Weed investigation is helpful to construct integrated forecasting system for dryland weeds,to scientifically perform the reform of cultivation system,to implement crop rotation,to increase the input for the basic construction of dryland,to perform deep tillage roundly,to improve ecological environment of dryland and to decrease cardinal number of weeds on the basis of effectively control of weed damage[15].Suggestions were proposed as follows:①Herbicides should be used scientifically; new medicaments with high efficiency,low toxicity and low residual should be studied and developed; the weeding effect of herbicides should be improved to restraint drug resistance of weeds.A certain degree of weed biodiversity should be kept while the weed damage is controlled.②Correlations among the germination of weed seeds,feature of soil seed bank and weed populations under the condition of fertilization should be studied to construct database of weed seed in dryland soil,forecast the population dynamics and community succession of weeds and construct the comprehensive control system of weeds.③Cultivation system should be reformed scientifically;crop rotation should be implemented; ecological and disciplinary management measures for weeds should be formulated;ecological environment of dryland should be improved; the base of weeds should be decreased and weed management should be improved.
Reference
[1]WANG SB(王淑彬),HUANG GQ(黄国勤),LIU LW(刘隆旺).The effect of paddy-upland rotation (the second year)on weed growth in paddy fields (稻田水旱地轮作(第2年度) 对农田杂草的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2002,24(1):20-23.
[2]CARDINA J,HERMS CP,DOOHAN DJ.Crop rotation and tillage system effects on weed seed banks[J].Weed Science,2002,50:448-460.
[3]BARBERI P,CASCIO BL,CASCIO B.Long-term tillage and crop rotation effects on weed seed bank size and composition [J].Weed Research,2001,41(4):325-340.
[4]GU QZ (古巧珍),YANG XY (杨学云),SUN BH(孙本华),et al.Weed biodiversity in winter wheat field of loess soil under different fertilization regimes(不同施肥条件下黄土麦地杂草生物多样性)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报),2007,18 (5):1038-1042.
[5]MA CZ(马承忠).Identification and Control of Farmland Weeds (农田杂草识别及防除)[M].Beijing (北京):China Agriculture Press (中国农业出版社),1999:92-96.
[6]ZHANG HM(张红梅),BAI RL(白容霖),ZHANG HL (张慧丽),et al.Studies on Weed Bank in Dry Farmland of Changchun Suburb(长春市郊区旱田土壤杂草种子库的研究)[J].Journal of Jilin Agricultural University(吉林农业大学学报),2002,24(1):42-46.
[7]WILES L,SCHWEIZERB E.Spatial dependence of weed seed banks and strategies for sampling [J].Weed Science,2002,50:595-606.
[8]YANG YS,WANG H,TANG JJ,et al.Effects of weed management practices on orchard soil biological and fertility properties in southeastern China[J].Soil&Tillage Research,2007,93 (1):179-185.
[9]NAN WG(南维鸽),LI SQ(李世清),HOU HQ(侯红乾),et al.Effect of different nitrogen application levels and weeding time on the nitrogen utilization and yield in semi-humid area(不同施氮水平和杂草清除时间对半湿润地区农田氮素利用及产量的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica(西北农业学报),2007,16(5):124-130.
[10]TANG LL(汤雷雷),WAN KY(万开元),CHEN F (陈防).Advances in studies on weeds biodiversity and genetic evolution in farmland in relation to nutrient management (养分管理与农田杂草生物多样性和遗传进化的关系研究进展)[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences (生态环境学报),2010,19(7):1744-1749.
[11]WAN KY,TAO Y,LI RH,et al.Influences of long-term different types of fertilization on weed community biodiversity in rice paddy fields [J].Weed Biology and Management,2012,12(1):12-21.
[12]HAN HF (韩惠芳),NING TY (宁堂原),TIAN SZ (田慎重),et al.Effect of soil cultivation and straw turnover on the biodiversity of weeds in summer maize field (土壤耕作及秸秆还田对夏玉米田杂草生物多样性的影响)[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报),2010,30(5):1140-1147.
[13]ZHANG Y(张怡),CHEN HH(陈宏灏),ZHANG HP (张华普).Population dynamic and eco-niches of major weeds in watermelon fields in arid area of central Ningxia (宁夏中部干旱带压砂西瓜田主要杂草的消长动态及生态位)[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica (西北农业学报),2010,19(10):78-81.
[14]GAO XT(高先涛),SHEN MZ(申慕真),YAO JY (姚景勇),et al.Species and occurrence regularity of dry farmland weeds in Southwestern Shandong (鲁西南地区旱田杂草种类及发生规律初探)[J].Weed Science (杂草科学),2001(3):5-7.
[15]ZHA SQ (查顺清),DAI PB (戴蓬博),FENG BL (冯佰利),et al.Composition and community characteristics of weeds in broom corn millet field in Northern Shaanxi area (陕北地区糜子田杂草组成及群落特征)[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica(西北农业学报),2014,23 (5):164-170.
[16]ZHANG YY(张玉玉),TIAN JJ(田净净),LIU ZY(刘志英),et al.investigation on weed species in alfalfa field in Qingdao(青岛苜蓿田杂草种类调查研究)[J].Shandong Agricultural Sciences (山东农业科学),2013,45(7):102-105.
[17]YE ZC (叶照春),YANG YH (杨雨环),ZHU F (朱峰),et al.Investigation on weed occurrence in Guizhou maize field(贵州省玉米地杂草发生情况调查)[J].Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences(西南农业学报),2014(4):1488-1493.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- On Genetic Parameter Estimation of Xinjiang Brown Cattle’s Main Economic Characters
- Effect of Flooding and Air-drying on Nutrition Content of Soil in Embankment WLFZ of Chaohu Lake
- Influences of Nitrogen-phosphorus Ratio on the Growth and Competition of Chlorella vulga and Anabaena sp.strain PCC
- Fatty Acid Composition and Seed Quality Traits of the Transgenic Rapeseed W-4(Brassica napus L.)with Down-regulated Expression of fad2 Gene
- Research on the Construction of Remote Plant and Animal Hospital in Omnimedia Era
- Study on Physical Properties and Related Spectral Characteristics of Composited Soil with Different Ratio of Feldspathic Sandstone and Sand
