Optimizing of Liquid Medium Formula about Medicinal Fungus Phellinus igniarius
2015-01-16XUQian
XU Qian
(Dept. of Life Sci., Heze Uni., Heze 274015)
Optimizing of Liquid Medium Formula about Medicinal Fungus Phellinus igniarius
XU Qian
(Dept. of Life Sci., Heze Uni., Heze 274015)
The influence of liquid medium formula on biomass ofPhellinusigniariusmycelium and the yield of exocellular polysaccharide were studied adopting four factors and three levels orthogonal experiment. The suitable formula for mycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield ofP.igniariuswas A3B1C3D2(wheat bran 10%, peptone 0.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15%), pH 6.The total yield of mycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield was 1.007 7 g/100 mL. The optimized formula can be used in industrial setting in order to get more yield ofP.igniariusmycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide.
liquid medium formula; mycelium biomass; exocellular polysaccharide yield; total yield; orthogonal test;Phellinusigniarius
Phellinusigniarius(L. ex Fr.) Quél. called asSanghuangin Chinese, belongs to the genus pfPhellinusQuél, Hymenochaetaceae, Aphyllophorales, Hymenomycetes, Basidiomycotina. It has been widely used in Asian countries for many years[1-4]. It is a kind of precious mushroom with important medical values. Its natural production is limited and it is called as "woods gold". It is rich in polysaccharide, triterpenoids, flavone etc., these life active substance are used to treat the diseases of cardiovascular, liver, nervous system, kidney and have bioactivities of anticancer, anti-liver fibrosis, anti-lipid peroxidation, immunity enhancement, hypoglycemic action, anti-pneumonia, weight control etc.[5-12]. During the past decades, polysaccharides isolated fromPhellinusspecies have been revealed as some pharmacological activities such as inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis, and low toxicity[13-22].
Traditionally, polysaccharide ofPhellinusigniariuswas extracted from fruit body. It will spend quite a long time in gaining fruit body in nature and artificial cultivation due to its special and complex physiological ecology[23], therefore, liquid culture is employed to developP.igniarius[24]. Liquid culture is a time-saving and high-yield method and mycelium gained through liquid culture has nutrients including polysaccharide similar to fruit body[25-26]. At the same time, quite a lot exocellular polysaccharide yield was got through liquid culture. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize liquid medium formula ofP.igniariusby using the total yield (mycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield) as an index in industry. Wang et al[27]had studied the influence of nutrients onP.igniariusmycelium biomass. He picked ten activated round fungus blocks in outer circle with hole puncher (diameter 0.6 cm), inoculated the ten round fungus blocks to liquid medium including different carbon source or nitrogen source, the biggest mycelium biomass was that 100 mL liquid medium and 10 round fungus blocks could get 1.52 g mycelium, that is to say, 100 mL liquid medium and 2 round fungus blocks (diameter 1 cm) could get about 0.844 4 g mycelium. Li et al[28]had studied liquid fermentation medium ofP.igniariusand got the biggest mycelium biomass (3.56 g/L) by using 10% inoculation quantity. These two studies both got limited mycelium biomass by using a large amount of spawn. This study paid more attention to simplify cultivation process and get more total yield (mycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield) by using a small amount of spawn.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental materials
1.1.1 SpawnP.igniarius(Ph001) was provided by Edible Fungus Institute of Huazhong Agricultural University.
1.1.2 Culture medium PDA culture medium: peeled potatoes 200 g, glucose 20 g, agar 15 g, and water 1 000 mL. Liquid medium (designed by orthogonal test): carbon sources (cornmeal, cotton seed hulls, and wheat bran), peptone, KH2PO4, MgSO4.
1.1.3 Instruments Electronic analytical balance (model: FA1604, Shanghai balance instrument plant), Air temperature oscillator (model: HZQ-C, Harbin city DongLian electronic technology development Co., LTD, China), Automatic control vertical electric steam sterilizer (model: YX40011, Sanshen, Shanghai), Electric drying oven with forced convection (model: 101-2, Beijing Ever Bright Medical Instrument Factory), MJX intelligent mold incubator (Ningbo Jiangnan Instrument Factory), Pointer type electrothermal constant temperature water-bath water pot, Hole puncher (diameter 1 cm), Conical flask (250 mL).
1.1.4 Reagents Glucose (analytical purity, Tianjin Hongyan Reagent Factory), KH2PO4(analytical purity, West Long Chemical Co., LTD), MgSO4(analytical purity, Tianjin Hongyan Reagent Factory), ethanol (95%) (Anhui Antell Biological Chemical Co., LTD), agar (biochemical reagent, Beijing Spiritualizing Star Biological Technology Co., LTD).
1.2 Methods
1.2.1 Preparation of solid medium PDA culture medium (300 mL).
1.2.2 Activating spawnP.igniariusspawn was activated twice on PDA culture medium. The first activation was to pick a little bit of spawn on the slant culture spawn to a PDA plate, and the plate was put in incubator (28 ℃) for 15 days. The second activation was to pick a round fungus block (diameter 1 cm with a hole puncher) from the first activated spawn to the center of another PDA plate and it was put in incubator (28 ℃) for another 15 days.
1.2.3 Formulas of liquid medium The four factors and three levels orthogonal test were used[29]. The four factors were carbon source, peptone, KH2PO4and MgSO4, and each factor had three levels (Table 1). There were nine formulas of the L9(34) orthogonal test (Table 2).
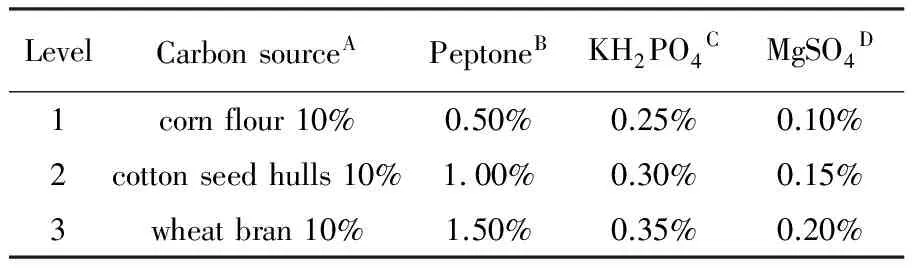
Table 1 Factors and levels of the orthogonal test
1.2.4 Confecting liquid mediums Corn flour, cotton seed hulls, wheat bran were smashed and screened with a 20 mesh screen, and then put into the right amount of water and boiled for 30 min. Flowing filtered by four layers of gauze, other reagents were added into the filtrate. Mediums with carbon source, peptone, KH2PO4and MgSO4were confected according to the formulas designed in Table 2. Each formula was repeated three times with a 150 mL volume of medium, and the medium was placed in 250 mL conical flask and sterilized at 121 ℃ for 30 min.
1.2.5 Liquid culture of spawn Two activated strains bacteria breads in outer circle were picked with hole puncher (diameter 1 cm) and inoculated to liquid medium, and then they were cultured in shake under the condition of 28 ℃, 180 r/min for 15 days. The best medium formula with the highest total yield (g/100 mL) (mycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield) were determined actually or theoretically.
1.2.6 Mycelium biomass assay The mycelium in the conical flask was filtered with eight layers of gauze, and the mycelium was washed with distilled water for three times. They were dried to constant weight in 60 ℃ electric drying oven with forced convection, mycelia dry weight was weighed with electronic analytical balance after being cooled.
Mycelium biomass (g/100 mL) = Mycelia dry weight / Medium volume
1.2.7 Exocellular polysaccharide yield assay 20 mL of filtrate and 60 mL of 95% ethanol were mixed uniformly and placed in 4 ℃ refrigerator for one day (each formula was repeated three times), then the mixture was filtered, the filter residue was exocellular polysaccharide[27], the exocellular polysaccharide was dried to constant weight in 60 ℃ electric drying oven with forced convection and weighed with electronic analytical balance.
Exocellular polysaccharide yield (g/100 mL)=Exocellular polysaccharide dry weight/Medium volume
1.2.8 Total yield assay
Total yield (g/100 mL)=Mycelium biomass+Exocellular polysaccharide yield
1.2.9 Verification Test Corresponding verification tests were done on the base of the orthogonal test’s results. As to the formula which took the total yield as the index, verification test were done with formula 7 (A3B1C3D2) which gained the highest total yield selected through the orthogonal test and the optimal formula theoretically (A3B3C3D2).
2 Results
2.1 Some stages of spawn activation and liquid culture
Fig.1 Pictures of spawn activation and liquid culture
P.igniariusspawn was activated twice on PDA culture medium for 15 days, and then cultured in liquid medium under the condition of 28 ℃, 180 r/min for 15 days
A: the spawn activated on the 6th day;B: was the spawn cultured on the 11th day
Figure 1 showed some stages of spawn activation and liquid culture. While activating spawn, the mycelia were white at the beginning, then became yellow; during the period of liquid culture, the color of mycelia pellet changed from white to yellow too.
2.2 Results of the orthogonal test
The results of the total yield of each formula gained through the orthogonal test were in Table 2.

Table 2 Results of the L9 (34) orthogonal test
Table 2 showed the formula 7 gained the highest total yield, formula 4 gained the lowest total yield, the prominence order of the factors was A (carbon source) > C (KH2PO4) > B (peptone) > D (MgSO4), as to the formula which took total yield as the index, the optimal formula theoretically was A3B3C3D2: wheat bran 10%, Peptone 1.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15%.
Table 3 Analysis of variance of orthogonality of medium formula’s influence on the total yield

SourcesofvariationSSdfMSFSignificancelevelA2.07140521.0357033957.36∗∗B0.05350220.026751102.2136∗∗C0.10218720.051094195.2256∗∗D0.01900420.00950236.30706∗∗e1000.000262e20.00471118
Note: * indicates significant influence, ** indicates very significant influence, blank indicates no significant influence
F1-0.05(2, 18): 3.54, F1-0.01(2, 18): 6.01
Table 3 showed the four factors of medium formula all had significantly higher influence on the total yield ofP.igniarius[29], the prominence order of the factors was A (carbon source) > C (KH2PO4) > B (peptone) > D (MgSO4), and A (carbon source) had the biggest influence on the total yield ofP.igniarius.
2.3 Medium formula’s influence on the total yield
Figure 2 showed the relationship between the total yield and the factors, the optimal formula theoretically was assured: wheat bran 10%, peptone 1.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15% while taking the total yield as the index. The prominence order of the carbon sources three levels was wheat bran>cornmeal>cotton seed hull, the influence of peptone trend on mycelium biomass was polarized, the percentage of KH2PO4still had rising space.
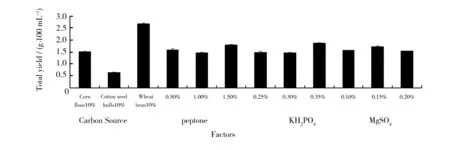
Fig.2 Relationship between factors and the total yield 9 formulas designed with orthogonal test L9 (34) were used to culture P. igniarius by inoculating 2 bacteria breads in each of them for 15 days, 4 factors had different influence on the total yield
2.4 Results of the verification test
Verification test was done with formula 7 (A3B1C3D2) which had the highest total yield gained through the orthogonal test and the optimal formula theoretically (A3B3C3D2), results showed that there were differences in the total yield gained based on the two formulas (Table 4), the optimal formula theoretically gained the largest total yield and there were no significant differences between the influence of two formulas on it (Table 5).
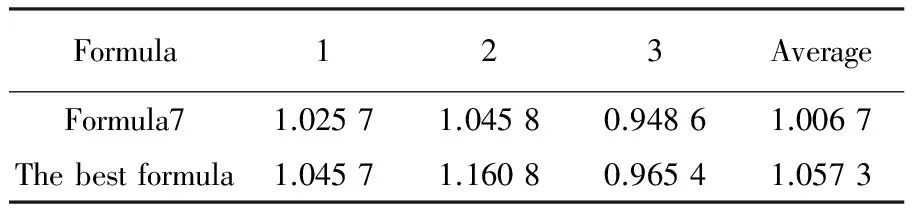
Table 4 Results of the verification test
Table 5 Analysis of variance of formula 7 and the best formula’s influence on the total yield
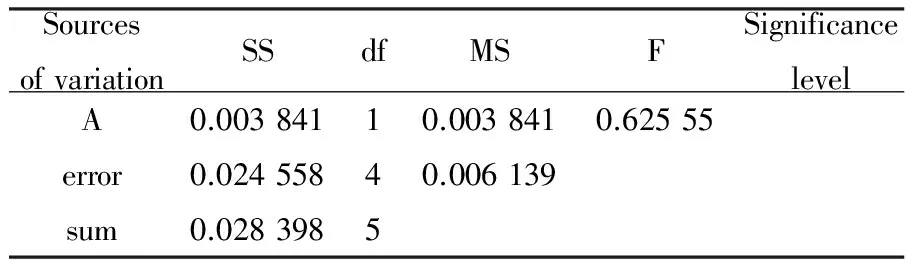
SourcesofvariationSSdfMSFSignificancelevelA0.00384110.0038410.62555error0.02455840.006139sum0.0283985
Note: * indicates significant influence, ** indicates very significant influence, blank indicates no significant influence
F1-0.05(1,4)=6.94 , F1-0.01(1,4)=7.71
3 Discussion
The influence ofP.igniariusliquid medium formula onP.igniariustotal yield was studied through the four factors and three levels orthogonal test. The levels were determined through the former single factor experiment before the orthogonal test. The three levels were the first level in gaining the most total yield and two other levels designed according to the first level (one is higher, another is lower).
The study found that the four factors all had highly significant influence on the total yield and got the best liquid medium formula forP.igniariustotal yield: wheat bran 10%, peptone 1.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15%, pH 6, 1.007 7 g/100 mL total yield could be got by using this formula and 2 round fungus blocks (diameter 1 cm). Verification test proved that there were no significant differences between the influences of the two formulas (formula 7 and the optimal formula theoretically) on the total yield, so in order to save the cost, formula 7 (wheat bran 10%, peptone 0.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15%, pH 6) can be used in industrial settings.
[1] Zou X, Sun M, Guo X. Quantitative response of cell growth and polysaccharide biosynthesis by the medicinal mushroomPhellinuslinteustoNaCl in the medium[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2006, 22(11): 1129-1133.
[2] Yang Y, Zhang JS, Liu YF, et al. Structural elucidation of a 3-O-methyl-D-galactose-containing neutral polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies ofPhellinusigniarius[J]. Carbohydr. Res, 2007, 342(8): 1063-1070.
[3] Dong W, Li N, Lu WD, et al. Tumor-inhibitory and liver-protective effects ofPhellinusigniariusextracellular polysaccharides[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2009, 25(4): 633-638.
[4] Guo X, Zou X, Sun M. Optimization of a chemically defined medium for mycelial growth and polysaccharide production by medicinal mushroomPhellinusigniarius[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2009, 25(12): 2187-2193.
[5] Chi JH, Ha TM, Kim YH, et al. Studies on the main factors affecting the mycelial growth ofPhellinuslinteus[J]. Ko. J Mycol, 1996, 24: 214-222.
[6] Kim DH, Yang BK, Jeong SC, et al. Production of a hypoglycemic, extracellular polysaccharide from the submerged culture of the mushroom [J]. Phellinus linteus. Biotechnology letters, 2001, 23 (7): 513-517.
[7] Hwang HJ, Kim SW, Yun JW. Modern Biotechnology ofPhellinusbaumii-From Fermentation to Proteomics[J]. Food Technol Biotechnol, 2007, 45(3): 306-318.
[8] Zhu T, Kim SH, Chen CY. A medicinal mushroom:Phellinuslinteus[J]. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2008, 15(13): 1330-1335.
[9] Dai HY, Wang P, Feng LY, et al. The molecular mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine ZHENG syndromes on pancreatic tumor growth[J]. Integr Cancer Ther, 2010, 9(3): 291-297.
[10]Noh JR, Lee IK, Ly SY, et al. APhellinusbaumiiextract reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice and absorption of triglyceride in lipid-loaded mice[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food, 2011, 14(3): 209-218.
[11]Li L, Wu G, Choi BY, et al. A mushroom extract Piwep fromPhellinusigniariusameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting immune cell infiltration in the spinal cord[J]. Biomed Res Int., 2014, 2014(1): Article ID 218274. Doi.org/10.1155/2014/218274.
[12]Zhou C1, Jiang SS, Wang CY, et al. Different immunology mechanisms ofPhellinusigniariusin inhibiting growth of liver cancer and melanoma cells[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(8):3659-3965.
[13]Ohtsuka S, Uneo S, Yoshikumi C, et al.Polysaccharides and method for producing same(4051314)[P]. Washington: United States Patent and Trademark Office, 1977: 1-4.
[14]Kim HM, Han SB, Oh GT, et al. Stimulation of humoral and cell mediated immunity by polysaccharide from mushroomPhellinuslinteus[J]. Int J Immunopharmacol, 1996, 18(5): 295-304.
[15]Han SB, Lee CW, Jeon YJ, et al. The inhibitory effect of polysaccharides isolated fromPhellinuslinteuson tumor growth and metastasis[J]. Immunopharmacology, 1999, 41(2): 157-164.
[16]Li G, Kim D, Kim T, et al. Protein-bound polysaccharide fromPhellinuslinteusinduces 2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in SW480 human colon cancer cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2004, 216(2): 175-181.
[17]Kim GY, Lee JY, Lee JO, et al. Partial characterization and immunostimulatory effect of a novel polysaccharide-protein complex extracted fromPhellinuslinteus[J].Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2006, 70(5): 1218-1226.
[18]Sliva D, Kawasaki J, Stanley G, et al.Phellinuslinteusinhibits growth and invasive behavior of breast cancer cells through the suppression of Akt signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2006, 20: 559-560.
[19]Moradali MF, Mostafavi H, Ghods S, et al. Immunonodulating and anticancer agents in the realm of macromycetes fungi (macrofungi)[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2007, 7(6): 701-724.
[20]Zhang M, Cui S W, Cheung P C K, et al. Antitumor polysaccharides from mushrooms: a review on their isolation process, structural characteristics and antitumor activity[J]. Trends Food Sci Technol, 2007, 18(1): 4-19.
[21]Yang Y, Ye LB, ZHang JS, et al. Structural analysis of a bioactive polysaccharide Structural Analysis of a Bioactive Polysaccharide, PISP1, from the Medicinal MushroomPhellinusigniarius[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2009, 73(1): 134-139.
[22]Chen L, Pan J, Li X, et al. Endo-polysaccharide ofPhellinusigniariusexhibited anti-tumor effect through enhancement of cell mediated immunity[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2011, 11(2):255-259.
[23]Li GJ, Wu GY, Cui JC, et al.Phelinuslinteushyphae training and applications[J]. Edible Fungi China, 1998, 17(5): 27-28. (in Chinese)
[24]Song L, Sun PL, Guo BB, et al. The research progress ofPhellinusIgniarius[J]. Edible Fungi China, 2005, 24(3): 7-10. (in Chinese)
[25]Xiao JH, Chen DX, Wan WH,et al. Enhanced simultaneous production of mycelia and intracellular polysaccharide in submerged cultivation of Cordyceps jiangxiensis using desirability functions[J]. Process Biochem, 2006, 41(8): 1887-1893.
[26]Hu GQ. The production of edible fungi liquid spawn and application[J]. Edible Fungi,1998, 20(1): 17-18. (in Chinese)
[27]Wang ZH, Wu ZW, Zhao XF. Nutrients’influence onPhellinusigniariusmycelium biomass and exocellular polysaccharide yield[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Res, 2009, 28(1): 37-41. (in Chinese)
[28]Li CC,Wei YX,Guo LZ. Preliminary study on liquid fermentation medium ofPhellinusigniarius[J]. Edible Fungi China , 2009, 28(2):46-48. (in Chinese)
[29]Zhuang CQ, He CX. Applied Mathematical Statistical Basis[M].Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
药用真菌桑黄液体培养基配方的优化
许 谦
(菏泽学院 生命科学系,山东 菏泽 274015)
研究液体培养基配方对桑黄菌丝体生物量和胞外多糖产量的影响。采用四因素三水平的正交试验方法。适宜于菌丝体生物量和胞外多糖产量的配方为A3B1C3D2(麦麸 10%, 蛋白胨 0.5%, KH2PO40.35%, MgSO40.15%), pH 6,菌丝体生物量和胞外多糖总产达到1.007 7 g /100 mL。优化的配方可以用于工业生产获得更多的菌丝体生物量和胞外多糖。
液体培养基配方;菌丝体生物量;胞外多糖产量;总产量;正交试验;桑黄
Q939.11
A
1005-7021(2015)04-0029-06
10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2015.04.006
Found Projecd:Supported by Projects of Heze City Science and Technology Development (2012N002)
Brief introduction to the writer: XU Qian, female, master, associate professor. Research Area: Development and utilization of
edible-medicinal fungi, microbial genetics and breeding.E-mail: xq710301@163.com
Draft accepted date:2015-05-03;Revision returned date:2015-05-16
