核桃楸皮多糖的分离纯化及抗癌活性研究
2015-01-11梁启超邹桂华沈广志吴宜艳
梁启超,邹桂华,刘 爽,沈广志,吴宜艳
1 牡丹江医学院药学院;2 牡丹江市心血管病医院,牡丹江 157011
Introduction
Juglans mandshurica,one of rare species of trees for pharmacy resources native to many Asian countries.Its leaves,barks,roots and seeds have been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of cancer in Asia and Europe[1].Recent scientific investigations have focused on its cytotoxic activity,antioxidant activity and anti-complement activity[2-4].These biological effects maybe due to the fact that it contains similar chemical components,including glucosides,naphthoquinones,naphthalenyl and galloyl glycosides[5-7],but they cannot account for all the effects mentioned above.In recent years,as more and more polysaccharides have been reported to exhibit a variety of biological activities,including antitumor[8],antiviral[9],anti-oxidation[10],etc.,which have emerged as an important class of bioactive natural products.There are few reports on polysaccharides from the bark of J.mandshurica(JMPS).Therefore,the objective of this work was to extract water-soluble JMPS and to study preliminary characterization and molecular weight of purified polysaccharide fractions.Moreover,the anticancer activities of JMPS were also investigated in vitro.
Materials and Methods
Plant materials and chemicals
The bark of J.mandshurica was collected in a mountain area of Mudanjiang,Heilongjiang Province.The material was confirmed taxonomically by Professor Liu Juan,at College of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Jia Musi University,China.The sample was pulverized into powder and passed through a 40-mesh sieve.SMMC-7721 cells were obtained from the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The monosaccharide standards of rhamnose,arabinose,fructose,glucose,galactose and the T-series Dextran(T-2000,T-500,T-110,T-70,T-40,and T-10)were purchased from Pharmacia.DEAE-52(Shanghai Jinhui).MTT was purchased from Sino-American Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.RPMI-1640 medium was obtained from Gibco.Fetal bovine serum(Hangzhou Sijiqing).Propidium iodide(KeyGen Biotech Corporation).All other chemical reagents were analytical reagent grade.
Instruments
Rotary vacuum evaporator(RE-52AA,Shanghai Yarong Biochemical Instrument Factory,China),UVvisible spectrophotometer(Cary100,Varian,USA),High-performance liquid chromatography(Agilent 1100,Agilent,USA),Gas chromatograph(Agilent 6890N,Agilent,USA),Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer(Scimitar FTIR-640,Varian,USA),Flow Cytometer(BD FACS Calibur,BD Biosciences,USA).
Extraction of JMPS
The powder of J.mandshurica bark(850 g)was preextracted two times with 95% aqueous ethanol(v/v)in a ratio(material to ethanol solution)of 1∶15(g/mL)at room temperature for 12 h each,and the supernatant was removed,in order to remove the pigments.The resulting residues were dried and extracted three times with distilled water in a ratio of material to water 1∶20(g/mL)at 90 ℃for 3 h each,filtered through the gauze and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min.The supernatants were combined and concentrated by a rotary vacuum evaporator at 50 ℃to a proper volume,and then deproteinized with Sevag regent[11].The resulting concentrate was mixed with three times volume of anhydrous ethanol,stirred vigorously and kept overnight at 4 ℃.The precipitates were then collected by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 15 min,and washed twice with acetone and ether,respectively,dissolved in distilled water,dialyzed against distilled water to remove small molecules and lyophilized,and the brown product was obtained as crude JMPS.
Separation and purification of JMPS
The crude JMPS was dissolved in distilled water,and filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter.The resulting solution of crude JMPS was loaded onto a DEAE-52 column(5 cm×60 cm)[12].The column was firstly eluted with distilled water followed by 0.1 M and 0.3 M NaCl at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min,respectively.The eluate was collected automatically(10 mL/tube),and the presence of carbohydrate in each tube was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method.As a result,three fractions were obtained.They were pooled,concentrated,dialyzed against deionized water and lyophilized,respectively,affording four purified fractions.
Determination of molecular weight
The homogeneity and molecular weight of the purified polysaccharides were determined by high-performance gel-permeation chromatography(HPGPC)[13]using an Agilent1100 instrument with a Shodex KS-805(8.0 mm×300 mm,17 μm)column.Mobile phase:distilled water,flow rate of 1.0 mL/min,temperature of 60℃,injection volume of 20 μL,and the elution was monitored by ELSD detector.Standard dextrans T-2000,T-500,T-110,T-70,T-40,and T-10 were passed through a Shodex KS-805 column,and elution volumes were plotted against the logarithms of their respective molecular weights.All samples were prepared as 2%(W/V)solutions and 20 μL of solution was injected in each run,and eluted with distilled water at a fixed flow rate(1 mL/min).Elution volume of the polysaccharide was then plotted in the same graph,and the average molecular weight of JMPS was measured.
Analysis of monosaccharide composition
The monosaccharide compositions of polysaccharides were analyzed by GC-FID method[14].Briefly,the polysaccharide sample(2.0 mg)was hydrolyzed with 4 mL trifluoroacetic acid in a sealed-tube at 110 ℃for 2 h.The hydrolyzate was repeatedly evaporated with methanol to dryness.Then the hydrolyzed products were prepared for acetylation.The acetylation was carried out with 0.5 mL of pyridine by getting heated in a water bath for 30 min at 90 ℃.After incubation,the mixture was cooled at room temperature,and then 0.5 mL of acetic anhydride was added and mixed thoroughly by vortexing.The tube was sealed and incubated in a water bath for another 30 min at 90 ℃.The acetylate was repeatedly evaporated with methanol to dryness.In a similar manner,the monosaccharide standards of rhamnose,arabinose,fructose,glucose and galactose were acetylated.Then,all the derivatives were analyzed by a HP6890N GC equipped with flame ionization detector(FID)and a HP-5 capillary column(30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm).The operation conditions of GC were as follows:flow rates of N2,H2and air were 45,30 and 300 mL/min,respectively.Column temperature programmed from 170 to 215 ℃at 2 ℃/min,then increased to 250 ℃at 8 ℃/min.Detector temperature:250 ℃.Inositol was used as the internal standard.The injection volume was 1 μL aliquot for each run.
Infrared spectral analysis of the polysaccharides
The structural characteristics of the JMPS fractions were determined using a Fourier transform infrared(IR)spectrophotometer(Scimitar FTIR-640,Varian,USA)[15]equipped with Varian Resolutions software.The purified polysaccharides sample(1 mg)were ground with KBr powder(100 mg)and then pressed into pellets for transform IR spectral measurement in the frequency range of 4000 to 400 cm-1.
Assay of anticancer activity in vitro of JMPS
Cell culture and treatment
The SMMC-7721 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum,100 units/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin at 37 ℃under a humidified 5% CO2atmosphere.The medium was changed every other day.The cells were split every 4-5 days by trypsinization and centrifugation,followed by aspiration of the culture medium.Exponentially growing cells were used for the experiments.Inhibition activity on SMMC-7721 cells of JMPS
The inhibition activities in vitro of JMPS on the SMMC-7721 cells were determined using a MTT colorimetric assay[16].Briefly,the SMMC-7721 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were collected and resuspended in RPMI-1640 medium at a density of 1×104cells/mL,100 μL the cell suspension were pipetted into each well of 96-well flat-bottomed microtiter plates.After that,50 μL fresh medium(control group)and test sample(purified JMPS at a final concentration of 25,50,100 and 200 μg/mL)was added to each well,and the cells were incubated for 48h,respectively.Three replicate wells were used for each data point in the experiments.After incubation for the indicated intervals,20 μL of MTT(5 mg/mL in PBS)solution was added to each well and plates were then incubated for 4 h at 37 ℃.After the logarithmic growth phase of cells was reached,the supernatant was discarded.Intracellular formazan crystals were dissolved by adding 150 μL of DMSO to each well,and the plates were shaken for 10 min.The absorbance was read at 490 nm with a microplate reader.The inhibition rate was calculated according to the formula below:
Inhibition rate(%)=(1-Abssample/Abscontrol)×100
DNA content and cell cycle analyzed
The DNA content and cell cycle of the SMMC-7721 cells were detected using FCM[17].The SMMC-7721 cells in logarithmic growth phase(3×105cells/mL)were plated at 1 mL/well in 6-well plates and allowed to attach overnight.After 24 h,the various JMPS-1 were added to the wells in a volume of 1mL per well to a final concentration of 50,100 and 200 μg/mL.An equal volume of medium was added to the wells in control group.The plates were incubated in 5% CO2at 37 ℃for 48 h.Then,cells were harvested.Cells harvested with 0.25% trypsinization were sedimented by centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature.After the supernatant was removed,70% icecold ethanol was added.Finally,cells were incubated in PI/RNase Staining Buffer,according to the manufacturer’s instructions and the cell cycle was analyzed with a BD FACS Calibur Flow Cytometer(BD Biosciences,USA).The percentage of cells in different cell cycle phases(G0/G1,S,and G2/M phase)was calculated using MultiCycle AV DNA Analysis DEMO.
Results and Discussion
Isolation and purification of polysaccharides
The crude JMPS was obtained in an overall yield of 0.81% through a series procedure of defatting,hot water extraction,ethanol precipitation,deproteiniation,dialysis and lyophilization.Furthermore,the crude JMPS was fractionated by a column of DEAE-52 cellulose to afford four polysaccharide fractions as shown in Fig.1.The four fractions were concentrated,dialyzed and lyophilized,affording JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3,respectively(Fig.1).
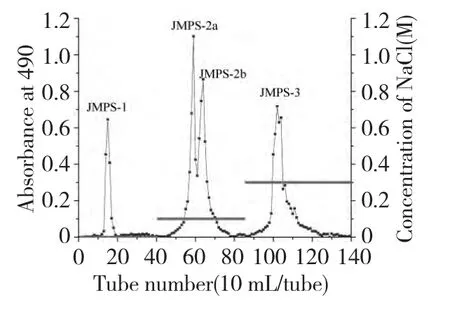
Fig.1 Chromatogram of eluted JMPS on DEAE-52 column
Molecular weight and monosaccharide compositions of JMPS
The HPGPC-ELSD analysis showed that the average molecular weight(Mw)of JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3 were approximately 227.9 kDa,28.6 kDa,23.1 kDa,and 12.7 kDa,respectively.The monosaccharide compositions JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3 determined by GC-FID analysis showed that the four polysaccharides were composed of monosaccharide(Table 1).JMPS-1 was composed of rhamnose(Rha),arabinose(Ara),xylose(Xyl),mannose(Man),glucose(Glc)and galactose(Gal)in a molar ratio of 1.00∶1.64∶2.12∶11.31∶7.46∶26.58,respectively.JMPS-2a and JMPS-2b were composed of Rha,Man and Glc in a molar ratio of 1.00∶1.19∶9.50 and 1.00∶2.07∶37.02,respectively.JMPS-3 was composed of Man,Glc and Gal in a molar ratio of 1.38∶3.67∶1.00.
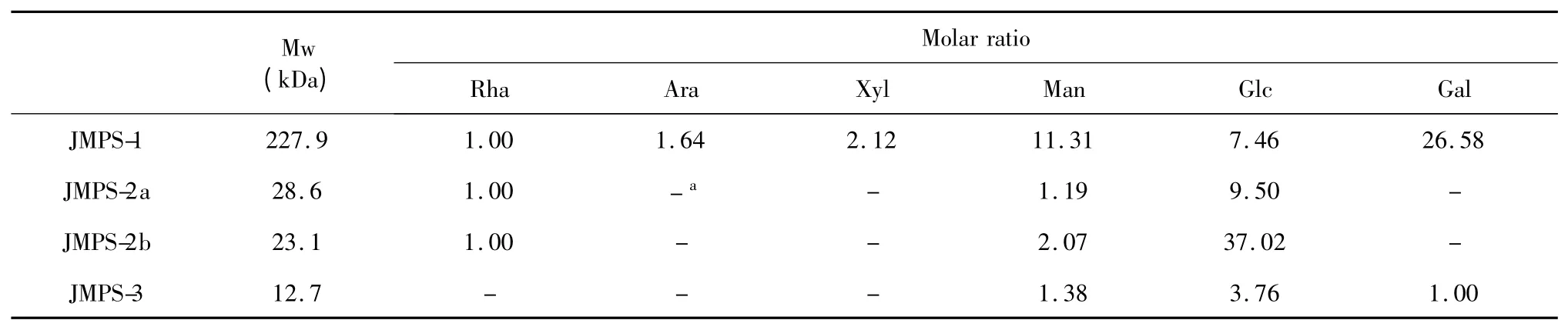
Table 1 Molecular weight and monosaccharide compositions of JMPS
FT-IR spectra of of JMPS

Fig.2 FT-IR spectra of JMPS-1(a),JMPS-2a(b),JMPS-2b(c)and JMPS-3(d)
As shown in Fig.2,the FT-IR spectra of four fractions were found to be similar.The strong and broad absorption peak between 3600 and 3200 cm-1(JMPS-1∶3429.32 cm-1,JMPS-2a∶3455.16 cm-1,JMPS-2b∶3436.77 cm-1,JMPS-3∶3454.48 cm-1),represented the stretching vibrations of the hydroxyl groups.The small band at around 2926 cm-1(JMPS-1∶2928.60 cm-1,JMPS-2a∶2926.59 cm-1,JMPS-2b∶2931.04 cm-1,JMPS-3∶2929.30 cm-1)was attributed to the C-H stretching,and absorption peak at around 1340 cm-1(JMPS-1∶1384.42 cm-1,JMPS-2a∶1384.61 cm-1,JMPS-2b∶1384.51 cm-1,JMPS-3∶1401.35 cm-1)for C-H bending vibrations.The bound at 1636.43 cm-1(JMPS-1),1606.60 cm-1(JMPS-2a),1640.53 cm-1(JMPS-2b)and 1623.69 cm-1(JMPS-3)were due to the bound water.Each particular polysaccharide had a specific band in the 1200~1000 cm-1region.This region was dominated by ring vibrations overlapped with stretching vibrations of(C-OH)side groups and the(C-O-C)glycosidic band vibration.Furthermore,characteristic peaks at 1746 cm-1(JMPS-1∶1746.31 cm-1,JMPS-2a∶1744.57 cm-1,JMPS-2b∶1749.60 cm-1,JMPS-3∶1744.31 cm-1)for esterified carboxylic groups(-COOR).These characteristic absorptions indicated that the JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3 were polysaccharides[18].
Inhibition activities of JMPS on SMMC-7721 cells
Fig.3 showed the inhibition rate of the purified JMPS(JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3)on the SMMC-7721 cells at different concentration for 48 h.Under the experimental conditions,four samples exhibited a marked inhibition on the survival of SMMC-7721 cells in a concentration-dependent manner.From Fig.3,the inhibition activities of the polysaccharides JMPS-1 and JMPS-3 increased significantly with the increasing of sample concentration ranging from 25 to 200 μg/mL,the inhibition rate was 15.3%-53.6% for JMPS-1 and 8.8%-20.6% for JMPS-3,respectively.However,the inhibition activities of JMPS-2a and JMPS-2b were significant weaker than that of JMPS-1 and JMPS-3,even at the high dose(200 μg/mL),the inhibition activities were only 11.3% and 10.7%.From the figure,inhibition activities in the order was JMPS-1>JMPS-3>JMPS-2a>JMPS-2b.JMPS-1 had strong inhibition activities against SMMC-7721 cells.
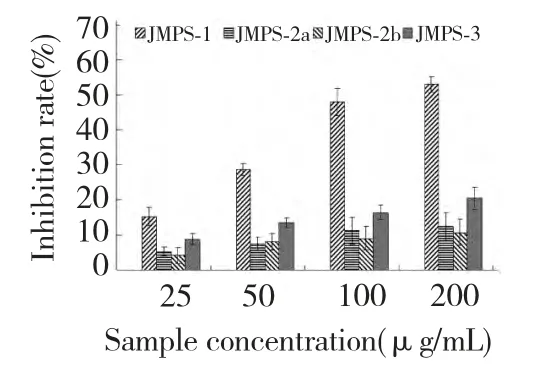
Fig.3 Inhibition rate of four JMPS on the SMMC-7721 cells at different concentrations for 48h.Results were presented as means±standard deviations(n=3)
DNA content and cell cycle analyzed by flow cytometry
The SMMC-7721 cells were treated with the JMPS-1 on the SMMC-7721 cells at different concentrations for 48 h.The cell cycle phase distribution of SMMC-7721 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry with PI staining and the percentages of cells in G0/G1,S and G2/M phases were calculated using MultiCycle AV DNA Analysis DEMO software.

Fig.4 Flow cytometry plots of JMPS-1.The data were expressed as mean±SD of three experiments.
Flow cytometry analysis showed range in the percentages of cells under different cell cycle stages after JMPS-1 treatment(Fig.4).For JMPS-1,the percentage of G0/G1 stage cells decreased while that of S and G2/M stage cells increased.Compared with control group cells(9.081%),the G2 group(indicated as %)significantly increased after SMMC-7721 cells were exposed to JMPS-1(50 μg/mL∶12.909%,100 μg/mL∶13.836%,200 μg/mL∶17.071%);Compared with control group cells(14.063%),the S group(indicated as%)significantly increased after SMMC-7721 cells were exposed to JMPS-1(50 μg/mL∶14.564%,100 μg/mL∶16.261%,200 μg/mL∶20.346%).These results suggest that JMPS-1 could induce cell cycle arrest at G2/M and S phase in SMMC-7721 in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion
In the present study,the crude JMPS were obtained by hot water extraction,ethanol precipitation and deproteination with Sevag method,and then fractionated by DEAE-52 column chromatography to afford four purified fractions of JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3.The HPGPC-ELSD analysis showed that the average molecular weight of JMPS-1,JMPS-2a,JMPS-2b and JMPS-3 were 227.9 kDa,28.6 kDa,23.1 kDa,and 12.7 kDa,respectively.The monosaccharide compositions of polysaccharides were analyzed by GC-FID method.The structural characteristics of the JMPS fractions were determined by IR spectrophotometer.The evaluation of anticancer activity suggested that JMPS-1 had strong inhibition activities for SMMC-7721 cells.Flow cytometry analysis showed that JMPS-1 can induce cell cycle arrest at G2/M and S phase in SMMC-7721 in a dose-dependent manner.The results suggested that JMPS-1 has demonstrated anticancer activities and may be explored as a natural anticancer substance.
1 Kim SH,Lee KS,Son JK,et al.Cytotoxic compounds from the roots of Juglans mandshurica.J Nat Prod,1998,61:643-645.
2 Li ZB,Wang JY,Jiang B,et al.Benzobijuglone,a novel cytotoxic compound from Juglans mandshurica,induced apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer cells.Phytomedicine,2007,14:846-852.
3 Liu Lj,Li W,Tatsunori S,et al.Juglanone,a novel a-tetralonyl derivative with potent antioxidant activity from Juglans mandshurica.J Nat Med,2010,64:496-499.
4 Min BS,Lee SY,Kim JH,et al.Anti-complement activity of constituents from the stem-bark of Juglans mandshurica.Biol Pharm Bull,2003,26:1042-1044.
5 Omar S,Lemonnier B,Jones N,et al.Antimicrobial activity of extracts of eastern north American hardwood trees and relation to traditional medicine.Thnopharmacol,2000,73:161-170.
6 Lee KS,Li G,Kim SH,et al.Cytotoxic diarylhetanoids from the roots of Juglans mandshutica.J Nat Prod,2002,65:1707-1708.
7 Li G,Xu ML,Choi HC,et al.Four new diarylheptanoids fromthe roots of Juglans mandshutica.Chem Pharm Bull,2003,51:262-264.
8 Yang XP,Guo DY,Zhang JM,et al.Characterization and antitumor activity of pollen polysaccharide.Int Immunopharmacol,2007,7:427-434.
9 Zhu W,Chiu LC,Ooi VE,et al.Antiviral property and mechanisms of a sulphated polysaccharide from the brown alga Sargassum patens against Herpes simplex virus type 1.Phytomedicine,2006,13:695-701.
10 Luo AX,He XJ,Zhou SD,et al.Purification,composition analysis and antioxidant activity of the polysaccharides from Dendrobium nobile Lindl.Carbohydr Polym,2010,79:1014-1019.
11 Navarini L,Gilli R,Gombac V,et al.Polysaccharides from hot water extracts of roasted Coffea arabica beans:Isolation and characterization.Carbohydr Polym,1999,40:71-81.
12 Xu Rj,Ye H,Sun Yi,et al.Preparation,preliminary characterization,antioxidant,hepatoprotective and antitumor activities of polysaccharides from the flower of tea plant(Camellia sinensis).Food Chem Toxicol,2012,50:2473-2480.
13 Xu DJ,Xia Q,Wang JJ,et al.Molecular weight and monosaccharide composition of Astragalus polysaccharides.Molecules,2008;13:2408-2415.
14 Qiao D,Hu B,Gan D,et al.Extraction optimized by using response surface methodology,purification and preliminary characterization of polysaccharides from Hyriopsis cumingii.Carbohydr Polym,2009,76:422-429.
15 Barker SA,Bourne EJ,Stacey M,et al.Infrared spectra of carbohydrates.Part I.Some derivatives of D-glucopyranose.J Chem Soc,1954,171-176.
16 Mosmann T.Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survivals:application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays.J Immunol Methods,1983,65:55-63.
17 Yang GM,Yan R,Wang ZX,et al.Antitumor effects of two extracts from Oxytropis falcata on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Chin J Nat Med,2013,11:519-524.
18 Peng XB,Li Q,Ou LN,et al.GC-MS,FT-IR analysis of black fungus polysaccharides and its inhibition against skin aging in mice.Int J Biol Macromol,2010,47:304-307.
