猪流行性腹泻病毒RT-PCR检测方法的建立
2015-01-04李海利徐引弟焦文强朱文豪王克领徐照学
李海利,徐引弟,焦文强,朱文豪,王克领,徐照学
(河南省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所,河南 郑州 450002)
猪流行性腹泻病毒RT-PCR检测方法的建立
李海利,徐引弟,焦文强,朱文豪,王克领,徐照学
(河南省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所,河南 郑州 450002)
为研究一种猪流行性腹泻早期快速分子生物学诊断方法,本研究根据GenBank中猪流行性腹泻(por⁃cine epidem ic diarrhea,PED)病毒基因组S基因序列,设计一对引物扩增特异的核苷酸序列(GenBank∶AB548624.1),预期扩增基因片段大小为200 bp。结果表明,设计的引物能扩增出目的基因,扩增的基因片段大小与预期的一致,且具有敏感性高、特异性和重复性好的特点。应用建立的条件和方法,采集临床疑似病例样本16份,9份均扩增出目的条带,具有较好的特异性。本研究为PED临床诊断提供一种快速、简便方法,可用于PED的净化诊断和流行病学调查。
猪流行性腹泻病毒;RT-PCR;分子诊断
猪流行性腹泻(porcine epidemic diar rhea, PED)是由猪流行性腹泻病毒引起的猪的一种高度接触性肠道传染病,以呕吐、腹泻和食欲下降为基本特征,各种年龄的猪均可易感。主要引起哺乳仔猪、架子猪和育肥猪群急性腹泻[1-5]。该病在许多国家和地区流行[6]。PED病毒可在猪群中持续存在,各种年龄的猪都易感,哺乳仔猪、架子猪和育肥猪的发病率可达100%,尤其以哺乳仔猪严重[7]。母猪的发病率在15%~90%。本病主要在冬季多发,夏季也可发生。PED的诊断方法主要有免疫电镜、免疫荧光、间接血凝试验、ELISA、RT-PCR、中和试验等[8-11]。随着分子生物学的不断发展,ELISA和RT-PCR的方法已成为检测PEDV的特异性诊断方法,在目前应用最为广泛。ELISA法的最大优点是可从粪便中直接检查PEDV抗原,也可用于PED抗体的检测。本研究对PEDV的RT-PCR扩增体系和反应条件进了优化,缩短了检测时间,使检测方法具有更加准确、特异、重复性好等优点,为PED临床诊断和分子流行病学调查提供一种有效的早期快速分子诊断方法。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与材料
1.1.1 病毒和细菌 猪流行性腹泻病毒(PEDV)、猪传染性胃肠炎病毒(TGEV)、轮状病毒(RTV)、沙门氏菌(S)、大肠杆菌(Coli)均由河南省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所分离并保存。
1.1.2 试剂 AMV逆转录酶,限制性内切酶,Taq DNA聚合酶,RNA酶抑制剂,100 bp DNA Marker,dNTP, MgCl2, RT-PCR Buf fer, DEPC-t reated ddH2O,RNase-f ree离心管,病毒和细菌RNA和DNA提取试剂盒、质粒DNA提取试剂盒与胶回收试剂盒均购自大连宝生物生物工程有限公司。
1.1.3 样品采集与处理 无菌采集患病动物的新鲜粪便,用生理盐水稀释5倍,漩涡搅拌均匀,8 000 r/ min离心10 min,取上清液置于-20℃保存备用或立即提取RNA。
1.2 引物的设计 根据数据库中PED病毒基因组S基因序列及相应参考文献[12-14],设计一对引物扩增特异的核苷酸序列,上游引物为:5′-TTTATTCTGTCACGCCAT-3′,下游引物∶ 3′-AGATTTACAAACACCTATGTTA-5′。预期扩增片段为200 bp,引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成,用超纯净水稀释为25 pmol/μL,备用。
1.3 RNA的提取 反转录合成cDNA及反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)采用柱式动物组织总RNA抽提纯化试剂盒(SK86952,上海生工),按照试剂盒说明书进行。反应体系为25μL,取提取的RNA 5μL,加入下游引物2μL,5×RT Buf fer 5μL,2.5 mmol/L dNTP 5μL,RNA酶抑制剂1μL,AMV反转录酶1μL,水1μL,充分混合均匀后短暂离心,在42℃作用1 h。
以上述cDNA为模板,按以下体系进行PCR扩增:反应总体积为25μL,无菌超纯水7μL,2×Buffer(Mg+)4.5μL,dNTPS4.0μL(2.5 mmol/μL),上游引物2μL(25 pmol/μL),下游引物2μL (25 pmol/μL),Taq enzyme 0.5μL(5 U/μL),cDNA 5μL。
PCR扩增程序为:95℃ 预变性3 min,94℃变性30 s,56℃退火1 min,72℃延伸1 min,32个循环,最后72℃ 延伸10 min。
1.4 RT-PCR产物的检测 取5μL扩增产物和5μL Loading Buf fer混匀,加到含EB的1.5%的琼脂糖凝胶中,同时加入对照和DNA Marker(100 bp),电压为120 V, 电泳1 h左右,然后在凝胶成像仪中观察。
1.5 RT-PCR产物序列分析 RT-PCR产物经胶回收纯化后,送宝生物生物工程有限公司测序,所得序列与数据库中的序列进行比对。
1.6 RT-PCR特异性试验 分别按照已建立的方法(1.3)提取感染猪传染性胃肠炎(TGEV)、轮状病毒(RTV)、沙门氏菌(S)、大肠杆菌(Coli)的基因组RNA或DNA,然后进行RT-PCR和PCR进行扩增。
1.7 RT-PCR敏感性试验 将提取的PDEV RNA定量,依次10倍稀释,取1μL样品加到9μL DEPC水中,再取1μL加到9μL DEPC水中,依次类推,使其为10μg、1μg、0.1μg、10 pg、1 pg、0.1 pg、0.01 pg、0.001 pg、0.000 1 pg、0.000 01 pg的RNA含量,反转录成cDNA后分别作为模板进行扩增,确定其敏感性。
1.8 RT-PCR重复性试验 用已建立的RT-PCR检测方法,对感染PED病料,TGEV、RTV、S、Col i、健康组织及3份检测为PED阳性的病料和3份阴性病料,重复检验3次,验证本方法的重复性和稳定性。1.9 临床应用 利用建立的RT-PCR检测方法检测临床送检的疑似病料16份,对RT-PCR阳性扩增产物进行序列测定。
2 结果与分析
2.1 扩增产物的检测 扩增产物经过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,PED病毒扩增产物在200 bp处可见特异性扩增条带,见图1,与预期大小相符。
2.2 RT-PCR产物序列分析 按常规方法,将PCR产物克隆于pMD18-T载体,重组质粒由宝生物生物工程有限公司测序。所得序列与NCBI数据库中数据比对与PED的同源性达99%以上。
2.3 RT-PCR特异性试验结果 利用设计的引物和方法对PED病毒扩增出了200 bp的目的基因片段,而对TGE、RT、S和Col i均未扩增出目的片段,见图2。
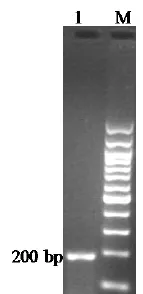
M:100 bp DNA Marker; 1:PED图1 目的基因的RT-PCR扩增Fig.1 Am plification of the target gene by RT-PCR
2.4 敏感性试验结果 敏感性试验结果显示,PCR检测灵敏度可达0.1 pg RNA,见图3。
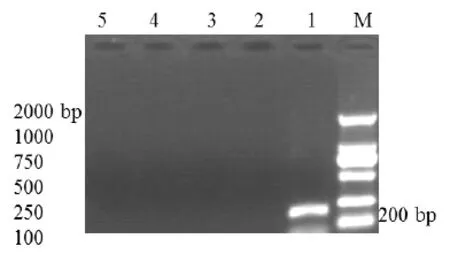
M:100 bp DNA Marker,1:PED;2:TGE;3:RT;4:Col i;5:H2O图2 RT-PCR特异性试验结果Fig.2 Am p lification o f the target gene by specific RT-PCR
2.5 重复性试验结果 3次重复检测的结果完全一致,说明该方法显示出了良好的稳定性。
2.6 临床应用 应用本研究建立的PEDV RT-PCR检测方法共检测了16份在不同地区采集的粪便病料。结果显示检出阳性样品9份,见图4,将阳性样品的RT-PCR扩增产物克隆后序列分析显示均为PEDV。
3 讨论
PED是猪消化道系统疾病的一种常发疾病,猪场一旦发生了本病,很难彻底根除和净化[12-17]。病猪和带毒猪是主要传染源,病毒多经发病猪的粪便排出[18]。传播途径是消化道。PED临床常单发或与猪传染性胃肠炎混合感染,有时与圆环病毒混合感染或与细菌病混合感染[19-22]。本研究所建立的方法具有灵敏度高、特异性好的特点,能快速早期的查出隐性感染带毒猪。
该病一旦发生,没有很好的治疗措施,猪用干扰素可以降低体重损失,与单克隆抗体配合使用可以降低仔猪的死亡率,治疗小猪要及时补充葡萄糖、甘氨酸和电解质溶液及口服补液盐。疫苗免疫接种是目前预防PED的主要手段。该病由于发病日龄小、发病急、死亡率高等特点,依靠自身的免疫往往来不及,因此大多是通过给母猪注射疫苗,依靠母乳中的特异性抗体给仔猪提供良好的保护[23]。母猪分娩前20~30 d肌肉或后海穴注射疫苗,仔猪通过采食初乳而获得被动免疫。预防本病要做好平时的饲养管理工作,发现有本病发生时及时采取隔离、消毒、减少人员流动、采用全进全出制等措施进行预防和控制。
RT-PCR的检测技术受到很多因素的影响,如引物的特异性及用量、RNA的用量、退火温度等均可以影响RT-PCR的扩增效率以及特异性,进而影响RT-PCR检测的灵敏度。其中最关键的是引物的敏感性和特异性,只有较强的敏感性和特异性的引物才能进行快速有效的检测。本研究针对RT-PCR反应的条件进行优化,以确保整个反应的准确高效扩增,降低非特异性反应。
本研究通过对引物浓度、MgCl2浓度、退火温度、循环条件等的优化,确立了最佳浓度和PCR反应程序,其最佳RT-PCR体系的最佳条件为:引物浓度:1.0~1.2μmol/L,MgCl2浓度:2 mmol/L,退火温度:56℃。最佳循环条件为:95℃ 3 min,94℃ 30 s,56℃ 30 s,72℃ 1 min,35个循环,最后72℃ 10 min。并对其特异性、敏感性、重复性和临床应用做了研究,特异性较好,敏感型可检测0.1 pg RNA,具有较好的敏感性,重复性做了三次,重复性较好,最后对临床样本进行了临床应用,共采集16份临床样品,检出9份阳性。
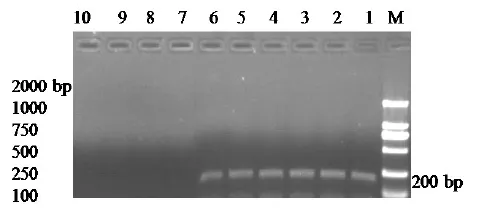
M:DL2000 bp DNA Marker;1:10μg RNA;2:1μg RNA;3:0.1μg RNA;4:10 pg RNA;5:1 pg RNA;6:0.1 pg RNA;7:0.01 pg RNA;8:0.001 pg RNA;9:0.0001 pg RNA;10:0.00001 pg RNA图3 RT-PCR敏感性试验结果Fig.3 Am plification of the target gene by sensitivity RT-PCR
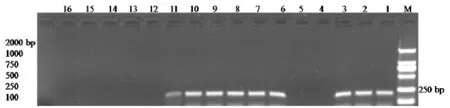
M:DL2 000 bp DNA Marker,1、2、3、6、7、8、9、10、11 positive sample;4、5、12、13、14、15、16 negative sample图4 临床样品的检测结果Fig.4 Results o f clinical sam ples
综上,本研究建立的PDE RT-PCR分子诊断方法,具有较好的特异性、敏感性和重复性,为PED临床快速检测提供了一种简便方法,同时为PED流行病学调查和分子诊断奠定了基础。
[1]Oh,J.S.,Song,D.S.,Yang,et al.Comparison of an enzyme-l inked immunosorbent assay with serum neutralization test for serodiagnosis of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection [J].J Vet Sci,2005,6(4)∶349-352.
[2]Lee,J.H.,Park,J.S.,Lee,S.W.,et al.Porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection∶Inhibition by polysaccharide f rom Ginkgo biloba exocarp and mode of its action[J].Virus Res, 2015,195∶148-152.
[3]Dee,S.,Neil l,C.,Clement,T.,et al.An evaluation of a l iquid antimicrobial (Sal CURB(R))for reducing the risk of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection of naive pigs during consumption of contaminated feed[J]. BMC Vet Res,2014,10(1)∶220.
[4]Dee,S.,Clement,T.,Schelkopf,A.,et al. An evaluation of contaminated complete feed as a vehicle for porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection of naive pigs fol lowing consumption via natural feeding behavior∶proof of concept[J].BMC Vet Res,2014,10(1)∶176.
[5]Lowe,J.,Gauger,P.,Harmon,K.,et al.Role of t ranspor tation in spread of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2014,20(5)∶872-874.
[6]Schoborg,R.V.,Borel,N.Porcine epidemic diar rhea virus(PEDV)co-infection induced chlamydial persistence/st ress does not require viral repl ication[J].Front Cel l Infect Microbiol,2014,4∶20.Front Cel l Infect Microbiol 4,20.
[7]Kotani,O.,Shirato,K.,Nagata,N.,et al. Neuropathogenesis of a mouse-adapted porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection in suckling mice[J].J Gen Virol,2013,94(Pt 4)∶831-836.
[8]Madson,D.M.,Magstadt,D.R.,Ar ruda,P.H., et al.Pathogenesis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus isolate (US/Iowa/18984/2013) in 3-week-old weaned pigs[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2014,174(1-2)∶60-68.
[9]Pujols,J.,Segales,J.Survivabil ity of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus(PEDV)in bovine plasma submit ted to spray drying processing and held at dif ferent time by temperature storage conditions[J].Vet Microbiol,2014, 174(3-4)∶427-432.
[10]Gerber,P.F.,Gong,Q.,Huang,Y.W.,et al. Detection of antibodies against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in serum and colostrum by indirect ELISA[J].Vet J,2014,202(1)∶33-36.
[11]Gerber,P.F.,Xiao,C.T.,Chen,Q.,et al. The spray-drying process is suf f icient to inactivate infectious porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in plasma [J]. Vet Microbiol, 2014,174(1-2)∶86-92.
[12]Song,D.S.,Kang,B.K.,Oh,J.S.,et al.Multiplex reverse t ranscription-PCR for rapid di f ferential detection of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus, t ransmissible gast roenteritis virus,and porcine group A rotavirus[J]. Vet Diagn Invest,18,278-281.
[13]Jung,K.,Chae,C.Ef fect of temperature on the detection of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus and t ransmissible gastroenteritis virus in fecal samples by reverse t ranscription-polymerase chain reaction[J].Vet Diagn Invest,16,237-239.
[14]Kim,S.Y.,Song,D.S.,Park,B.K.Di f ferential detection of t ransmissible gast roenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diar rhea virus by duplex RT-PCR[J].Vet Diagn Invest, 13,516-520.
[15]Wang,L.,Zhang,Y.,Byrum,B.Developmentand evaluation of a duplex real-time RT-PCR for detection and di f ferentiation of virulent and variant st rains of porcine epidemic diar rhea viruses f rom the United States[J]. J Virol Methods,2014,207∶154-157.
[16]Oka,T.,Sai f,L.J.,Marthaler,D.,et al. Cel l cul ture isolation and sequence analysis of genetical ly diverse US porcine epidemic diar rhea virus st rains including a novel strain with a large deletion in the spike gene[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2014, 173(3-4)∶258-269.
[17]Zhao,P.D.,Bai,J.,Jiang,P.,et al.Development of a mul tiplex TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR for discrimination of variant and classical porcine epidemic diar rhea virus[J].J Virol Methods,2014,206∶150-155.
[18]Park,J.E.,Shin,H.J.Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infects and replicates in porcine alveolar macrophages[J]. Virus Res, 2014, 191∶143-152.
[19]Temeeyasen, G., Srijangwad, A., Tripipat, T., et al. Genetic diversity of ORF3 and spike genes of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus in Thailand[J].Infect Genet Evol,2014, 21∶205-213.
[20]Choi,J.C.,Lee,K.K.,Pi,J.H.,et al.Comparative genome analysis and molecular epidemiology of the reemerging porcine epidemic diar rhea virus st rains isolated in Korea [J].Infect Genet Evol,2014,26∶348-351.
[21]Zhao,S.,Gao,J.,Zhu,L.,et al.Transmissible gast roenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diar rhoea virus infection induces dramatic changes in the tight junctions and microf i laments of polarized IPEC-J2 cel ls[J]. Virus Res,2014,192∶34-45.
[22]Wang,Y.,Li,J.R.,Sun,M.X.,et al.Triggering unfolded protein response by 2-Deoxy-D-glucose inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus propagation[J].Antiviral Res, 2014,106∶33-41.
[23]Olanratmanee,E.O.,Kunavongkrit,A.,Tummaruk,P.Impact of porcine epidemic diar rhea virus infection at dif ferent periods of pregnancy on subsequent reproductive per formance in gi l ts and sows[J].Anim Reprod Sci,2010, 122(1-2)∶42-51.
Establishmentand app lication of themethod ofmolecular diagnostic of porcine epidem ic diarrhea
Li Hai l i,Xu Yindi,Jiao Wenqiang,Zhu Wenhao,Wang Kel ing,Xu Zhaoxue
(Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Research Institute,Henan Academy of Agricul tural Sciences,Henan Zhengzhou 450002)
In order to study a method for the ear ly and rapid molecular diagnosis of porcine epidemic diarrhea,a pair of primers were designed according to the PED virus genome database sequences of S gene nucleotide sequence specif ic ampl i f ication,the expected expansion gene f ragment size was 200 bp.The resul ts show that the designed primers could ampl i fy the purpose gene, the ampl i f ication of gene f ragment size coincides with the expected,and high sensitivity,specificity and good repeatabil ity.Appl ied to the establ ished conditions and the method,total 9 bands were ampl if ied the purpose f rom16 col lected cl inical samples.This study provides a simple method for the cl inical diagnosis of PED,and used for the diagnosis and epidemiological survey of PED.
Porcine epidemic diar rhea virus;RT-PCR;Molecular diagnosis
S852.651
1672-9692(2015)08-0046-06
2015-06-05
李海利(1982-),男,博士,助理研究员,主要从事动物传染病临床分子诊断及防控研究工作。
河南省农业科学院博士科研启动基金;河南省农业科学院优秀青年科技基金(2013YQ22);河南省农业科学院自主创新科技基金。
