两种龟消化道黏膜上皮的扫描电镜观察
2014-10-16李贵生唐福星
李贵生, 唐福星
(暨南大学1.生命科学技术学院生物工程学系;2.实验技术中心,广东广州510632)
Turtles are a group of ancient reptiles with unique structures in shape.Since ancient times,the turtles are regarded as longevity auspicious animal and much loved by Chinese people,and they have very high medicinal and scientific research values.The culture of turtles has broad and profound prospect.Chinemys reevesii is the most widely spread species with largest quantity in China.The turtle has strong adaptability,broad recipe,and is a most common breeding species.As a fine variety of breeding mossback turtle with the range of distribution region next to Chinemys reevesii,Mauremys mutica has a high breeding rate and is very welcome by the people of breeding turtles in recent years.But in the artificial breeding,with the increase of pollution of the environment and increase of the breeding density of the turtles,all kinds of turtle disease appeared in succession,such as gastroenteritis is a kind of common turtle disease.Prevention and treatment of turtle disease is very importance and very impendency.Study on the ultrastructure of alimentary tract not only can enrich the comparative morphology of the turtles,but also can provide reference for the breeding and disease control of the turtles.The ultrastructure of alimentary tract of the turtle is very rare,the study on alimentary tract of the turtle by scanning electron microscopic(SEM)has not been reported.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Experimental materials
Chinemys reevesii and Mauremys mutica are sampled from the reptile animal breeding farm of department of biotechnology of Jinan university,the Chinemys reevesii is male and body weight is 350 g.Mauremys mutica is female and body weight is 400 g.
1.2 Experiment methods
The turtles are live dissected,and the stomach and intestine are taken out.The gastral cavity and intestinal cavity are cleaned with 0.85%NaCl thoroughly,and cut into 6 mm × 8 mm pieces immediately,then they are flattened and fixed on the cardboard,and immersed in 2.5%glutaraldehyde.After 3 h,following change the liquid and keeping on fixing 24 h,then the samples are rinsed with 0.1 mol/L phosphoric acid buffer solution,dehydrated by gradient with alcohol,then the alcohol is replaced by isoamyl acetate,the samples are dried with liquefied CO2by Hcp-2 type critical point drying apparatus and gilded by JFC-1100 ion sputtering instrument,observed an photograph under PHILIPS XL-30 ESEM.
2 Results
2.1 The gastrointestinal tract mucosa structure of Mauremys mutica
(1)Gastric mucosal epithelia Under SEM,the surface of gastric mucosal epithelia is uneven,divided into sub-areas of different sizes.In which,the part of concavity is the channel,the part of ridge is the promontory(figure 1A).The mucosal epithelia of having fingerlike projections are observed in cardiac region of stomach(figure 1B).The cells of mucosal epithelia of the body of stomach are big,irregular,most pentagon or hexagon in shape.The cell outline is clear,concave in the edge.The combine is compact between cells.The gastric pits are observed in mucous which are the opening of gastric glands(figure 1C).The columnar mucous epithelial cells are seen in some spots.The secretory holes are found in some mucous epithelial cells.The microvillus is not seen,and the goblet cell is not observed either.The protuberant tiny ridges ap-pear in the pyloric section of stomach.

Fig.1 Scanning electron microscope observation of stomach mucosa epithelia of Mauremys mutica
(2)Intestinal tract mucosal epithelia The intestinal tract of Mauremys mutica may divide into the small intestine and the large intestine.The small intestine may divide into the duodenum,the jejunum and the ileum.
①The observation of mucosal epithelia of the small intestine by SEM The transverse plicas are appeared in the duodenum,the plicas divide into main plica and petit plica.The main plica is wide and high,the petit plica is short and narrow(figure 2A).There are irregular cells in the surface of the duodenum.The structure of channel and promontory as well as the opening of intestinal gland can be observed in the duodenum(figure 2B).There are many circular goblet cells on the surface of the duodenum(figure 2C).The longitudinal plicas are observed in ileum.The channel of the plica is deep and also can divided into main plica and petit plica.(figure 2D).The absorption cells is irregular,the size of cells is similar,and the opening of intestinal gland can be seen in the ileum.
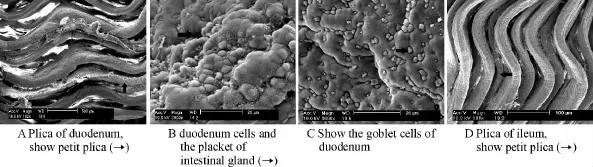
Fig.2 Scanning electron microscope observation of small intestine of Mauremys mutica
②The observation of mucosal epithelia of the large intestine by SEM The mucous plicas are shallow in the large intestine(figure 3A)in which there are goblet cells distribution(chart 3B).

Fig.3 Scanning electron microscope observation of large intestine of Mauremys mutica
2.2 The gastrointestinal tract mucosa structure of Chinemys reevesii
(1)Gastric mucosal epithelia The surface structures of gastric mucosal epithelia of Chinemys reevesii are similar to Mauremys mutica and present the uneven channel and promontory structure.There are two kind of different mucous epithelial cells,one is central concave,squamous and the arrangement is close(figure 4A).The other is anomalous and the center is protuberant(figure 4B).The gastric gland opens in the gastric pits.There are many secretory cells in gastric bottom,and the mamillary prominencys are observed in this cells(figure 4C).There are secretory hole in the center of some mamillary prominencys(figure 4D).The microvillus is not seen,and the goblet cell is not discovered either.

Fig.4 Scanning electron microscope observation of stomach mucosa epithelia of Chinemys reevesii
(2)Intestinal tract mucosal epithelia
①The observation of mucosal epithelia of the small intestine by SEM.The zone of intestine of Chinemys reevesii is similar to Mauremys mutica.The plica is not obvious in the duodenum which is close to the pyloric section of stomach,but the plica is obvious which is close to the jejunum.The plica also can divided into main plica and petit plica.In jejunum,the plica is developed and there are many goblet cells.
②The observation of mucosal epithelia of the large intestine by SEM.The are different size cells in the surface of mucosal epithelia in the large intestine and the cells arrange more dense than the cells in Mauremys mutica.The cluster arrangement of the mucus secreting cells are observed(Figure 5).

Fig.5 Show mucus secreting cells
3 Discussion
SEM is suitable very much for studying the digestive system of animals because it can present intuitively the surface texture of tissue and organ.SEM applied more in the study of digestive system of fish[1-2],it also applied in the studies of digestive system of amphibians and reptiles[3-5].The stomach is the place of animal holding food and the preliminary digesting food.The different species of animal,because the difference of evolution degree,food type and the living condition,is different in the stomach structure.For example,some fishes lack the typical stomach[6].The majority of fish have the structure of stomach,but the feeding habits of fishes are different,the stomach structures of fishes are also different,such as the stomach of Centropristis striata is V shape[7],and the stomach of Hucho taimen is also V shape[8].The stomachs of Siniperca chuatsi and Microperus salmoides are Y shape,and the stomachs of Silurus asotus and Pseudobagrus fulvidraco are U shape.The stomach of Monopterus albus is I shape[9].The stomach of Cromileptes altivelis is divided into cardia,caecus and pylorus[10],but the stomach of Acipenser baerii is divided into cardia,corpus and pylorus[11].
In Siganus canaliculatus,the arrangement of the gastric mucosal folds is longitudinal,the mamillary prominency is often seen between cranny,there are many thich concavity on the mucosa epithelia and the microvillus is not seen[12].There are punctual microvilli in the stomach mucosa epithelia of Channa argus and there are typical microvilli on the stomach of Pseudobagrus fulvidraco,Mystus macropterus and Batrachuperus pinchonii[4].In Otistarda limaells, the stomach is divided into fore stomach and muscular stomach,there are microvilli in the fore stomach and corneum in the muscular stomach[13].
The goblet cells had been found in the stomach of Channa argus[2].The major function of the goblet cell is secreting mucin.The goblet cells are also seen in the stomach of Batrachuperus pinchonii[4].In Bufo gargariizans which is amphibian,the stomach is obviously divided into cardia,corpus and pylorus and the goblet cell is not seen in the mucosa epithelia of stomach[14].The structure of the snake stomach has significant characteristics,the channel and promontory is deep and the protuberating is particularly clear,explained its stomach has a considerable degree of extension and contractility,this characteristics is adapted to the physiological behaviour of the snake[5].
The stomach of Trionyx sinensis is U shape,its cavity surface has 7 ~ 9 longitudinal plica.The plica is composed by the prominency of mucosa and strata submucosum.The gastric gland is single tubular or branch tubular and is only composed by wall cells and mucous cells.The wall cells have the function of secreting hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen[15].No goblet is seen in the stomach mucosa epithelia of Trionyx sinensis.
The stomach of Chinemys reevesii is slightly U shape and can be divided into cardia,corpus and pylorus according to the morphological structure,similar to the structure of stomach of Alligator sinensis[16],Sacalia quadriocellata[17],Chinemys nigricans[18]and Mauremys mutica[19],but is obviously difference from the stomach structure of Trionyx sinensis.This research indicated that,the structures of stomach mucosa of two turtles are similar to the snakes,has the developed channel and promontory.In addition,the goblet cell has not discovered in the gastric mucosa epithelial cells of these two kinds of turtles,and the microvillus is not seen.In the amphibian and reptile animals that had been studied,no goblet cell in stomach had been reported.In birds and mammalian,the goblet cell is also not seen in stomach.Whether beginning from the amphibian animals,the goblet cell is not appeared in the stomach,it is required for further researching to confirmation this theory.
The small intestine is the main place that animal digesting and absorbing foods.In fish,the mucosal folds of intestinal tract has a certain degree of development and there are obviously structure of microvillus in the mucosal surface of intestine[20].In Batrachuperus pinchonii,there are moss like microvilli which are coarctation and multi-branches in the free surface of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells.In addition,there are many goblet cells[21].There are also developed microvilli in the intestinal epithelial cells of Andrias davidianus[22].The microvilli increase the contacting area with foods,prolongate the resident time that food is kept in the digestive tract,raise the effective area of digestion and absorption,and are in favor of the food fully digested and the nutritive material fully absorbed.The structures of the small intestines of Chinemys reevesii and Mauremys mutica are similar,have the developed plica and the multitudinous goblet cells.The characteristic of the large intestine mucous membrane epithelial cells is that the microvilli are scarce,the cell arrangement is neat,the size of the column cell is homogeneous,and there are the goblet cells.These structures are adapt to the function of only absorbing water and forming feces as well as discharging feces in large intestine.
[1]LIN Shimei,LUO Li,YE Yuanshi.Observation on digestive tract mucosa of Pseudobagrus fulvidraco and Mystus macropterus by scanning electron[J].Sichuan Journal of Zoology,2003,22(2):63-65.
[2]LI Yuhe,GUO Shuhua.SEM study on the mucosa of digestive tract of ophicephalus argus cantor[J].Acta Anatomica Sinica,1992,23(1):98-101.
[3]SUN Heng,WANG Yanping,SUN Xiaoliang,et al.Light and scanning electron microscopic observation on small intestine of Bufo faddei[J].Journal of Tonghua Teachers College,2007,28(4):106 -108.
[4]AN Shucheng,LI Zhongjie,ZHANG Yuhui.Study on mucosa of digestive tract of Batrachuperus pinchonii by SEM[J].Chinese Journal of Zoology,2000,35(3):13-15.
[5]YANG Youjin,LI Zhongjie,HE Jianru.Study on the mucosa epithilia in gastrointestinal tract of Enhydris chinensis with scanning electron microscope[J].Bulletin of Science and Technology,2004,20(1):42-44.
[6]WANG Zongbao,WU Duansheng,SONG Ying,et al.Study on microscopic structure and ultrastructure of main organs and tissues of carassius auratus red variety[J].Chinese Journal of Laboratory Animal Science,2002,12(2):82-86.
[7]LI Haiyan,ZHU Junquan,CHEN Fei,et al.The morphology of the digestive tract of Centropristis striata[J].Journal of Biology,2 011,29(4):35-38,50.
[8]ZHANG Yongquan,JIA Zhonghe,LIU Yi,et al.Study on morphology and histology of digestive system of Hucho taimen[J].Freshwater Fisheries,2011,41(2):32 -37.
[9]PAN Qiansheng,GUO Guangquan,FANG Zhiping,et al.The comparative anatomy studies on digestive system of 6 fish species of stomch-containing teleost in fresh water[J].Journal Huazhong(Central China)Agricultural University,1996,15(5):463-469.
[10]OU Youjun,GOU Xiaowei,LI Jiaer.The histology and histo-chemistry studies of the digestive system of Cromileptes altivelis[J].Marine Fisheries,2011,33(3):51-58.
[11]CHEN Ningning,ZHANG Longzhen,ZHUANG Ping,et al.The preliminary study on morphology and histology of digestive tract of Acipenser baerii[J].Marine Fisheries,2011,33(1):22-29.
[12]ZHANG Longzhen,YANG Jinhai,LIU Jianyi,et al.Scanning electron microscope observation on the mucosal epithelium of the digestive tract in Siganus canaliculatus[J].Chinese Journal of Zoology,2010,45(2):121 -125.
[13]LIU Yutang,TIAN Xiuhua,YU Xuewei,et al.The studies on the ultrastructure of proventriculu and gizzard in bustard[J].Acta Anatomica Sinica,2003,34(1):103-105,84.
[14]YUE Xingjian,ZHANG Yaoguang,WANG Zhijian.The histology and histo-chemistry studies of the digestive tract of the toad in China,Bufo gargariizans[J].Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science),2002,27(3):383-389.
[15]SU Zehong,CHEN Xiaowu,CHEN Qiusheng.Ultrastructure of mucous membrane and glandular epithelium of stomach in soft-shelled turtle,Trionyx sinensis[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2004,27(3):139-141.
[16]WU Xiaobin,ZHANG Shengzhou,CHEN Bihui,et al.Histochemical and ultrastructural studies on the stomach of Alligator sinesis[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2001,25(3):289-293.
[17]HONG Meiling,FU Lirong,SHI Haitao,et al.Anatomy of digestive and respiratory systems in the four eye-spotted turtle[J].Chinese Journal of Zoology,2004,39(1):68-71.
[18]XU Jinlong,LI Guisheng.Study on histology of digestive system of Chinemys kwangtungensis[J].Ecological Science,2009,28(2):189-192.
[19]ZHU Ye,LI Guisheng.Histological observation of the digestive system of Mauremys mutica[J].Ecological Science,2010,29(5):451-455.
[20]LIN Jinxing,ZHANG Linli,YAO Yilin,et al.Study on microscopic structure and ultrastructure of the digestive tract of Danio rerio[J].Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2013,64(3):64-70.
[21]AN Shucheng,LI Zhongjie,ZHANG Yuhui.Study on mucosa of digestive tract of Batrachuperus pinchonii by SEM[J].Chinese Journal of Zoology,2000,35(3):13-15.
[22]WANG Shanghong,YU Yangfan,WANG Fang,et al.Observations on microstructure and ultrastructure of small intestine and pancreas in Andrias davidianus[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(35):94-98.
