Baxθ,a Novel Bax Variant,Lacks BH3 Domain and Promotes Cell Apoptosis
2014-09-22XUZhengxinWANGZhenzhenWANGRanXIELinjunXUEJinglunCHENJinzhong
XU Zheng-xin ,WANG Zhen-zhen,WANG Ran,XIE Lin-jun,XUE Jing-lun,CHEN Jin-zhong
(1.State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering,Institute of Genetics,School of Life Sciences,Fudan University,China,Shanghai 200433;2.Department of Pharmacology,Medical School,Yangzhou University,Yangzhou 225001,China)
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death which is executed and controlled by several groups of proteins[1-2].Proteins of the Bcl-2 family are major regulators of apoptosis and characterized by up to four Bcl-2 homology domains(BH1—BH4).The Bcl-2 family consists both antiapoptotic and proapoptotic proteins and can be divided into three subclasses.The first class is antiapoptotic and contains all four BH domains,including Bcl-2,Bcl-xl,Bcl-w and Mcl-1.The second class includes multidomain proapoptotic proteins such as Bax and Bak,containing BH1,BH2 and BH3 domains.Members of the last class are called BH3-only proteins,including Bim,Bad,Bid,Puma,Noxa and Bmf,which contain only BH3 domain and are also proapoptotic.The Bcl-2 family proteins can interact with themselves or other family members through BH domains to form homodimers or heterodimers,and the balance between antiapoptotic and proapoptotic proteins determines the fate of a cell[3-4].
In the process of apoptosis,Bax activation is an essential step,which is required for the subsequent release of cytochrome-c and the downstream caspase cascade[5].Thus Bax is regulated strictly in multiple levels including transcriptional,translational and post-translational control[6-9].Up to now,nine alternatively spliced isoforms of human Bax have been identified[10-14],and among them Baxα is the best characterized isoform.Baxα contains BH3,BH1,BH2 and a C-terminal transmembrane domain(TM).In healthy cells,Baxα exists as an inactive monomer in the cytosol or loosely attached to the outer mitochondrial membranes[15].After exposure to appropriate death stimuli,Baxα will undergo conformation changes,translocate and insert into the outer mitochondrial membranes as homodimers or heterodimers,resulting in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization[16-17].Baxβ shares all three BH domains with Baxα but has a longer and different C-terminus resulting from the unspliced mRNA of intron 5.Baxβ is constitutively active and can induce cytochrome c release from mitochondria more potently[18].Baxδ lacks the BH3 domain and is predicted to be unable to dimerize with Bcl-2 family members[10].Gene expression profiling identified that Baxδ is a novel tumor antigen in acute lymphoblastic leukemia[19-20].The other alternatively spliced isoforms are listed in Fig.1.Alternative splicing increases the diversity of the Bcl-2 family members but also raises the complication of apoptosis control[21].Although these Bax splice variants have been defined,their function in regulating apoptosis machinery is still unclear.

Fig.1 The other alternatively spliced isoforms
In this work,we report on the existence of a novel variant of human Bax,Baxθ (GenBank accession number:HQ889830).mRNA expression analysis revealed that Baxθ was expressed in a variety of human normal tissues.Baxθ could trigger strong apoptosis when it was overexpressed in HEK293 cells though it lacked BH3 domain.We also proved that the 27 amino acid in 43—69 region of Baxθ played an essential role in its proapoptotic activity.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Cell culture and transfections
HEK293 cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection(ATCC)and cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium(DMEM)supplemented with 10%fetal calf serum at 37℃in a 5%CO2humidified atmosphere.Plasmid DNAs were transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen)according to the manufacturer's protocol.
1.2 Plasmid construction
The cDNA of Baxβ and Baxθ was obtained by RT-PCR from total RNA of HEK293 cells using primers 5’-AAGAATTCTAATGGACGGGTCCGGGGAG-3’ and 5’-CAGCTCGAGGACACGTAAGG-AAAACGC-3’.The cDNA fragment of Baxθ was subcloned into the Eco RⅠand KpnⅠ sites of plasmid pEGFP-N1(Clontech)in order to express a Baxθ-GFP fusion protein.Myc-Baxβ was constructed by inserting the complete coding sequence(CDS)of Baxβ into pCMV-Myc(Clontech)between Eco RⅠ and XhoⅠ sites.The CDS of Baxθ (start from the second ATG)was amplified by primers 5 ’-AATGAATTCTAATGATTGCCGCCGTGGAC-3’and 5’-ACGGGTACCTCAGACACGTAAGGAAAACGC-3’,and then cloned into the pCMV-Myc between the EcoRⅠ and KpnⅠ sites to generate Myc-Baxθ.
For truncated mutants of Baxθ, BaxθC98 fragment was amplified with primers:5 ’-AAGAATTCCAGTGCTCAAGGCCCTGTGCACCAAG-3’and 5’-ACGGGTACCTCAGACACGTAAGGAAAAC-GC-3’, and then inserted into pCMV-Myc between the Eco RⅠand XhoⅠsites.Myc-BaxθΔC,Myc-BaxθN43 and Myc-Baxθ43-69 were created by PCR-based C-terminal deletion.Myc-BaxθΔ27 was obtained by using overlapping primers:5’-CAGCCCAACAGGCTGGCAAAGTAGAAAAGG-3’and 5’-CTTTGCCAGCCTGTTGGGCTGGATCCAAG-3’.The plasmids mentioned above were all verified by sequencing.
1.3 Western blotting
Cells were lysed with lysis buffer(20 mmol/L Tris pH 7.5,100 mmol/L NaCl,0.5% NP-40,0.5 mmol/L EDTA,0.5 mmol/L PMSF,0.5%protease inhibitor cocktail(Roche))and boiled in 2 ×loading buffer.Protein samples were then separated on 15%SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane,which was blocked in 5%skim milk in TBST and probed with the anti-GFP mouse monoclonal antibody(Santa Cruz)and HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG(Sigma).
1.4 Immunofluorescence
Cells were plated on coverslips in 6-well plates and transfected with the indicated plasmids.24 h later,cells were fixed in 4%paraformaldehyde for 5 min,permeabilized in 0.2%Triton X-100 for 10 min and followed by incubation with mouse anti-Myc antibodies(Santa Cruz,dilution 1∶100)overnight at 4℃.Cells were then incubated with an FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG(Jackson Immuno Research,dilution 1∶100)for 1 h at 37 ℃ in the dark.The nuclei were stained with DAPI(4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole).The coverslips were then mounted on slides,and analysis was performed using a confocal microscopy.
1.5 Propidium Iodide(PI)staining for apoptosis analysis
HEK293 cells were plated in 12-well plates and transfected with the indicated plasmids.After transfection for 24 h,cells were fixed and permeabilized with 70%ethanol at 4℃ for 12 h,washed with PBS and then stained with 50 μg/mL PI(Sigma)in PBS containing 50 μg/mL RNaseA(Promega)for 30 min.PI-fluorescence data were collected by a flow cytometer(BD Biosciences).
1.6 Expression pattern of Baxθ
Pre-made human multiple tissue cDNA panels were purchased from Clontech.The upstream primer for amplificat on of Baxθ was designed at the in-frame fusion site of exon1 and exon 4, as 5 ’-CAGCCCAGAGGCGGGGGATGATTG-3’;and the upstream primer of Baxβ was 5 ’-TCAGGATGCGTCCACCAAGAAGCTG-3’(exon3).Both of Baxθ and Baxβ shared the same downstream primer,5’-GTGGGGGTGAGGAGGCTTGAGGAG-3’(exon 6).PCR products were resolved on 2.0%agarose gel and specific bands were extracted from agarose gels,sequenced on an ABI3730 sequencer.
2 Results
2.1 Identification of a novel Bax variant missing BH3 domain
When amplifying the coding sequence of Baxβ (657 bp)from total RNA of HEK293 cells by RT-PCR,we obtained an unexpected DNA fragment which was smaller than Baxβ (458 bp).DNA sequence analysis and comparison with Bax genomic sequences indicated that its sequence is identical to Baxβ but lacks the region 35—233 bp of Baxβ CDS,including intact exon2 and exon3.This DNA fragment may be a novel variant of human Bax and we named it Baxθ.Using GeneDoc software,we predicted the novel Bax variant may contain two potential ATGs(Fig.2).If the translation started at the first ATG as other Bax isoforms,it would stop after translating a short peptide which contains 12 animo-acids.In contrast,the putative translated product would contain 140 animo-acids in case the second ATG was used,and the new isoform would share the same C-terminus but lacks 1—78 aa compared to Baxβ.In order to detect which one is adopted,the plasmid GFP-Baxθ was constructed by inserting the cDNA of Baxθ into pEGFP-N1 vector.HEK293 cells were transfected with GFPBaxθ,and 24 h later,cells were lysed and detected by western blotting using anti-GFP antibody.The result of Western blot showed a band of GFP fused protein was detected at the molecular mass of about 46 ku(Fig.3).Hence the molecular mass of the putative Baxθ protein might be 15—16 ku.These result indicated the genuine ORF of Baxθstarts at the second ATG and the translated product contains 140 animo-acids without BH3 domain for Baxθ lacking the death domain encoding exon3.

Fig.2 Two potential ATGs in the novel Bax variant
2.2 Subcellular localization of Baxθ
To investigate the subcellular distribution of Baxθ,Myc-Baxθ was transfected into HEK293 cells,and the intracellular localization of Myc-Baxθwas observed by fluorescence microscopy 24 h after transfection.Myc-Baxβ was also used as control.Immunostaining of transfected cells with anti-Myc antibody revealed that Myc-Baxθwas distributed mainly in cytoplasm like Myc-Baxβ.Missing BH3 domain does not affect the subcellular location of Baxθ(Fig.4).
2.3 The multiple tissue expression pattern of Baxθ
Pre-made human cDNA panel based PCR assay was to examine the distributions of Baxθ and Baxβ in a variety of human tissues.As shown in Fig.5,transcripts for Baxβ were detected in all tissues tested suggesting a constitutive expression pattern as reported.In contrast,High levels of Baxθ were observed in heart,brain,ovary,thymus,placenta 5’RACE cDNA and fetal brain cDNA library,while in muscle,pancreas,spleen,prostate and small intestine tissues,Baxθ was found at much lower levels.No Baxθ expression was detected in leukocyte.
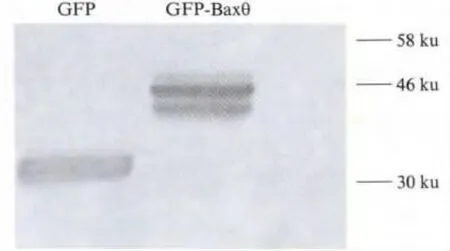
Fig.3 Western blot of GFP-Baxθ

Fig.4 Subcellular location of Baxθ
2.4 The proapoptotic activity analysis of novel isoform
The absence of exon2 and exon3 results in Baxθ lacking the BH3 domain, which is necessary for Bax to homodimerize and to induce apoptosis.Thus Baxθ may act as an inactive isoform.However,the cells transfected with Myc-Baxθ presented poor growth status under the microscope,with many dying cells floating in the culture medium just like the cells transfected with Myc-Baxβ.This suggests that this novel isoform of Bax might also induce apoptosis,see Fig.6.Flow cytometry assay using propidium iodide(PI)staining was carried out to detect apoptosis rate.Compared with the negative control of plasmid pCMV-Myc((4.13 ± 0.76)%),the percentage of sub-G1 phase was significantly raised when cells were transfected with Myc-Baxθ((29.56 ±1.56)%),although its proapoptotic activity is weaker than Myc-Baxβ ((33.86 ±4.06)%),see Fig.7.

Fig.5 Transcripts for Baxβ and Baxθ in all tissues

Fig.6 The cells transfected with Myc-Baxθ and Myc-Baxβ induce apoptosis
To detect the exact region of Baxθ to trigger cell death,a series of Baxθtruncation mutants were constructed and overexpressed in HEK293 cells(Fig.8).As it shown in Fig.8,the 43 amino acids in N-terminal of Baxθ is dispensable,for Myc-BaxθN43 just induced(6.50 ±1.33)% of cell to apoptosis.Myc-BaxθC98 and Myc-BaxθΔC both presented proapoptotic activity,the apoptosis rate was(25.19 ± 1.33)%and(25.63 ± 3.92)%,respectively.The minimal proapoptotic construct was Myc-Baxθ 43—69,of which apoptosis cell rate was(27.59 ±2.76)% .Moreover,deletion of amino acid 43—69 in Baxθ made the percentage of sub-G1 phase declined to(9.08 ±1.35)%(Myc-BaxθΔ27),indicating the region between 43 and 69 amino acid in Baxθ is crucial for its proapoptotic function.

Fig.7 The apoptosis rate of all truncation mutants of Baxθ

Fig.8 The domains of all Baxθ truncation mutants
3 Discussion
Alternative splicing is one of the major ways to regulate Bcl-2 family proteins,providing structure differences and functional diversification[21].Although multiple Bax isoforms has been reported,the mechanisms controlling this process and the exact roles of each Bax isoforms are still unknown.In our study,we discovered Baxθ,a novel Bax variant,the mRNA sequence of which is identical to Baxβ but lacks the intact exon 2 and exon 3.The translation of Baxθinitiates at the second ATG and the translated product contains 140 animo-acids without the BH3 domain.The absence of exon 2 and exon 3 and the usage of the second ATG has also been reported in Baxζ[22].When Baxθ was overexpressed in HEK293 cells it could trigger apoptosis though the proapoptotic potential was weaker than that of Baxβ.mRNA expression analysis revealed that Baxθ was highly expressed in some human tissues including heart,brain,ovary,thymus and placenta,suggesting a possible physiological role for Baxθ in controlling programmed cell death in these tissues.
Up to now,two models have been suggested to explain how Bcl-2 family proteins regulate apoptosis progress[23-25].One is the indirect activation model,the proapoptotic function of Bax or Bak is neutralized by antiapoptotic family members such as Bcl-2 and Mcl-1.BH3-only proteins could bind antiapoptotic proteins and release Bax or Bak.As in the second direct activaion model,BH3-only proteins are divided into activators(Bim,tBid and Puma)and sensitizers(Bad and Noxa).The activators could directly bind and activate Bax or Bak,while the sensitizer are responsible to bind antiapoptotic proteins.Both models depend on the interaction of Bcl-2 family members via BH3 domain.However,the in-frame fusion of exon 1 and exon 4 results in Baxθ lacking the BH3 death domain,thus Baxθ may introduce a different mechanism to induce apoptotic activities.To detect the possible proapoptotic domain of Baxθ,we firstly focused our attention on the unique C-terminus of Baxθ and Baxβ,which makes Baxβ be constitutively in an active conformation and plays an important role in regulating the proapoptotic activity of Baxβ isoform.The proapoptotic activity analysis of Baxθtruncation mutants revealed that deleting C-terminus of Baxθ only slightly impaired its proapoptotic ability,from(29.56 ±1.56)%to(25.63 ±3.92)%.The minimal proapoptotic construct was Myc-Baxθ43-69,which contained only 27 amnioacids 43VLKALCTKVPELIRTIMGWTLDF LRER69,and deleting the region made apoptosis cell rate decline to(9.08 ±1.35)%,suggesting it was a proapoptotic domain.Structure analysis showed these 27 amnio-acids are located on the centralα5 and α6 helices of Bax,and it was reported that theα5 and α6 helices of Bax mediated the insertion of the protein into mitochondrial membranes and were essential for the cytochrome C releasing activity of Bax.Neither the TM domain nor a functional BH3 domain is required for this step[26].This may explain why Baxθ could induce apoptosis independent of BH3 though the details remained unclear.Further studies will be carried out to determine whether other Bax isoform or Bcl-2 family proteins has participated in this progress.
[1]Chan SL,Yu V C.Proteins of the bcl-2 family in apoptosis signalling:from mechanistic insights to therapeutic opportunities[J].Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol,2004,31(3):119-128.
[2]Danial N N,Korsmeyer SJ.Cell death:critical control points[J].Cell,2004,116(2):205-219.
[3]Willis SN,Adams JM.Life in the balance:how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis[J].Current Opinion in Cell Biology,2005,17(6):617-625.
[4]Youle R J,Strasser A.The BCL-2 protein family:opposing activities that mediate cell death[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2008,9(1):47-59.
[5]Fletcher J I,Huang D C.Controlling the cell death mediators Bax and Bak:puzzles and conundrums[J].Cell Cycle,2008,7(1):39-44.
[6]Benard G,Neutzner A,Peng G H W,et al.IBRDC2,an IBR-type E3 ubiquitin ligase,is a regulatory factor for Bax and apoptosis activation[J].Embo Journal,2010,29(8):1458-1471.
[7]Mitchell K.O,Ricci M S,Miyashita T,et al.Bax is a transcriptional target and mediator of c-Myc-induced apoptosis[J].Cancer Res,2000,60(22):6318-6325.
[8]Miyashita T,Reed JC.Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene[J].Cell,1995,80(2):293-299.
[9]Wang Q H,Sun SY,Khuri F,et al.Mono-or double-site phosphorylation distinctly regulates the proapoptotic function of Bax[J].PLoSOne,2010,5(10):e13393.
[10]Apte SS,Mattei M G,Olsen B R.Mapping of the human BAX gene to chromosome 19q13.3-q13.4 and isolation of a novel alternatively spliced transcript,BAX delta[J].Genomics,1995,26(3):592-594.
[11]Cartron PF,Oliver L,Martin S,et al.The expression of a new variant of the pro-apoptotic molecule Bax,Bax psi,is correlated with an increased survival of glioblastoma multiforme patients[J].Human Molecular Genetics,2002,11(6):675-687.
[12]Schmitt E,Paquet C,Beauchemin M,et al.Characterization of Bax-sigma,a cell death-inducing isoform of Bax[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2000,270(3):868-879.
[13]Shi B,Triebe D,Kajiji S,et al.Identification and characterization of Bax epsilon,a novel Bax variant missing the BH2 and the transmembrane domains[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,1999,254(3):779-785.
[14]Zhou M,Demo SD,McClure T N,et al.A novel splice variant of the cell death-promoting protein BAX[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1998,273(19):11930-11936.
[15]Nechushtan A,Smith C.L,Hsu Y T,et al.Conformation of the Bax C-terminus regulates subcellular location and cell death[J].EMBO J,1999,18(9):2330-2341.
[16]Annis M G,Soucie EL,Dlugosz PJ,et al.Bax forms multispanning monomers that oligomerize to permeabilize membranes during apoptosis[J].EMBO J,2005,24(12):2096-2103.
[17]Wolter K G,Hsu Y T,Smith C L,et al.Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis[J].Journal of Cell Biology,1997,139(5):1281-1292.
[18]Fu N Y,Sukumaran SK,Kerk SY,et al.Bax beta:A Constitutively Active Human Bax Isoform that is under Tight Regulatory Control by the Proteasomal Degradation Mechanism[J].Molecular Cell,2009,33(1):15-29.
[19]Maia S,Ghia P,Haining W,et al.The BAX isoform BAX-DELTA is expressed by leukemia cells and is a novel tumor-associated antigen[J].Experimental Hematology,2003,31(7):140-141.
[20]Maia S,Haining W N,Ansen S,et al.Gene expression profiling identifies BAX-delta as a novel tumor antigen in acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J].Cancer Res,2005,65(21):10050-10058.
[21]Akgul C,Moulding D A,Edwards S W.Alternative splicing of Bcl-2-related genes:functional consequences and potential therapeutic applications[J].Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2004,61(17):2189-2199.
[22]Leber B,Lin J,Andrews D W.Still embedded together binding to membranes regulates Bcl-2 protein interactions[J].Oncogene,2010,29(38):5221-5230.
[23]Ewings K E,Wiggins C M,Cook SJ.Bim and the pro-survival bcl-2 proteins-Opposites attract,ERK repels[J].Cell Cycle,2007,6(18):2236-2240.
[24]Heimlich G,McKinnon A D,Bernardo K,et al.Bax-induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria depends on alpha-helices-5 and-6[J].Biochem J,2004,378:247-255.
[25]Shamas-Din A,Brahmbhatt H,Leber B,et al.BH3-only proteins:Orchestrators of apoptosis[J].Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Cell Research,2011,1813(4):508-520.
[26]Perez R P,Sanville H.BAXzeta a novel BAX variant,lacks BH3 domain and promotes cell death[C]∥Annual Meeting,Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research.USA:AACR,2000:153-154.
