A Rat M odel of Autologous Oral M ucosal Epithelial Transplantation for Corneal Limbal Stem Cell Failure
2014-09-17WeihuaLiQiaoliLiWencongWangKaijingLiShiqiLingYuanzheYangLingyiLiang
Weihua Li, Qiaoli Li, Wencong Wang, Kaijing Li, Shiqi Ling, Yuanzhe Yang, Lingyi Liang,*
1 State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510060,China
2 Department of Ophthalmology, Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Guangzhou 510623,China
3 DepartmentofOphthalmology, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630,China

M aterials and methods
Animals and anesthesia

Equipment and reagents

Establishment of LSCD models


Autologous oralmucosa epithelial transplantation

Postoperative management

Results
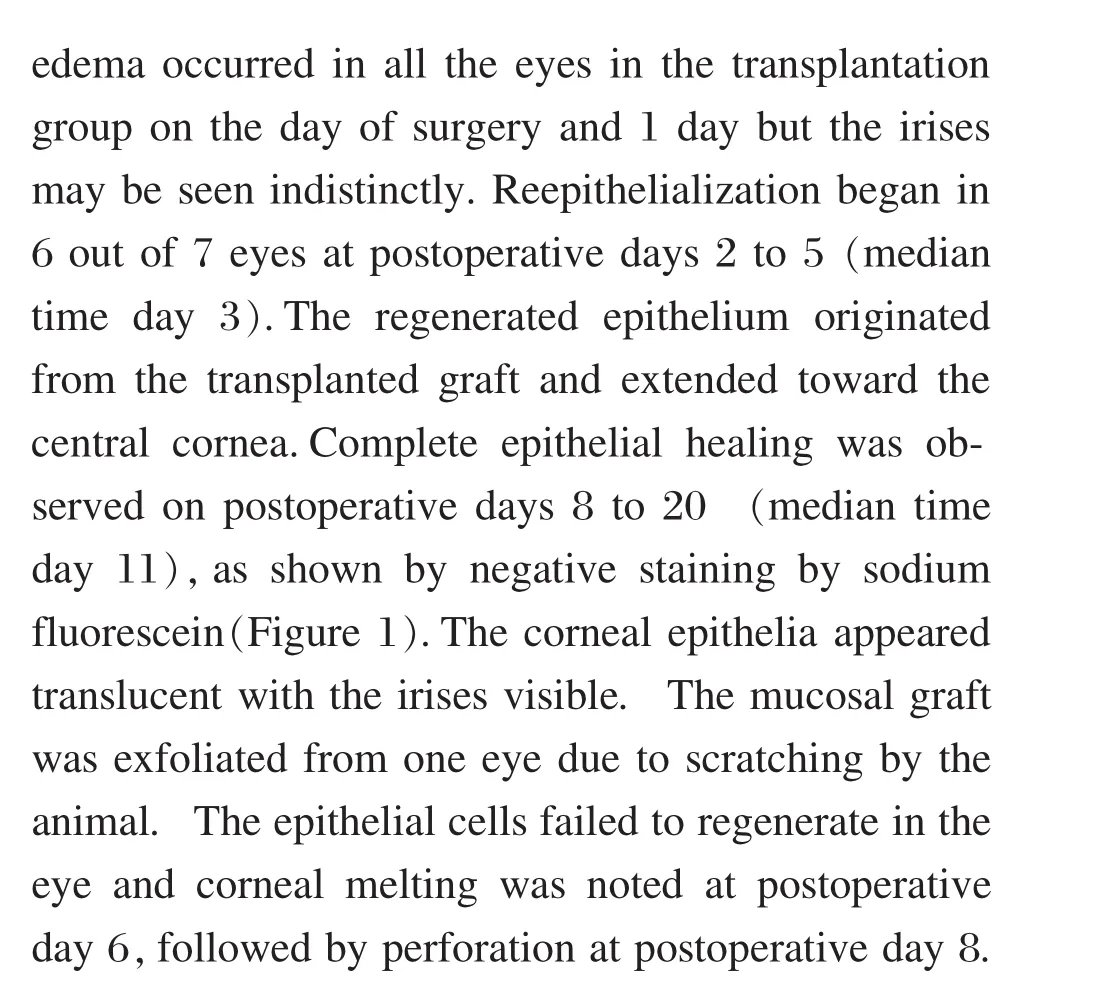
Establishment of the LSCD model

Corneal epithelial cell healing after autologous oralmucosal epithelial transplantation
Survival of the buccal mucosal graft


Figure 1 Postoperative slit-lamp exam ination of LSCD rat models transplanted autologous oral mucosa..Figure A reveals autologous oral mucosal epithelial transplantation after establishment of LSCD models..Figure B reveals the ocular surface of LSCD models.At postoperative 1 day,a large area of fluorescent staining can be seen in both groups A (C)and B.No significant staining can be observed surrounding the buccal mucosa graft in group A (E)..At 2 weeks postoperatively,.dot-shaped staining of corneal epithelial cells can be noted (G).In group B, a large area of staining can be seen at both postoperative 3 days(F) and 2 weeks(H),prompting severe corneal epithelial cell defects.(Black arrow:the site of autologous oral mucosa epithelial transplantation, × 25 magnification)
Ocular complications and oral mucosal wound healing

Discussion
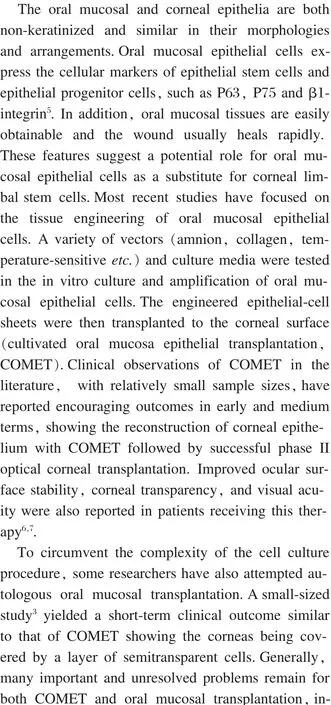
Foundation of treating LSCD w ith autologous oral mucosal transplantation

An LSCD animal model treated w ith autologous oral mucosal transplantation
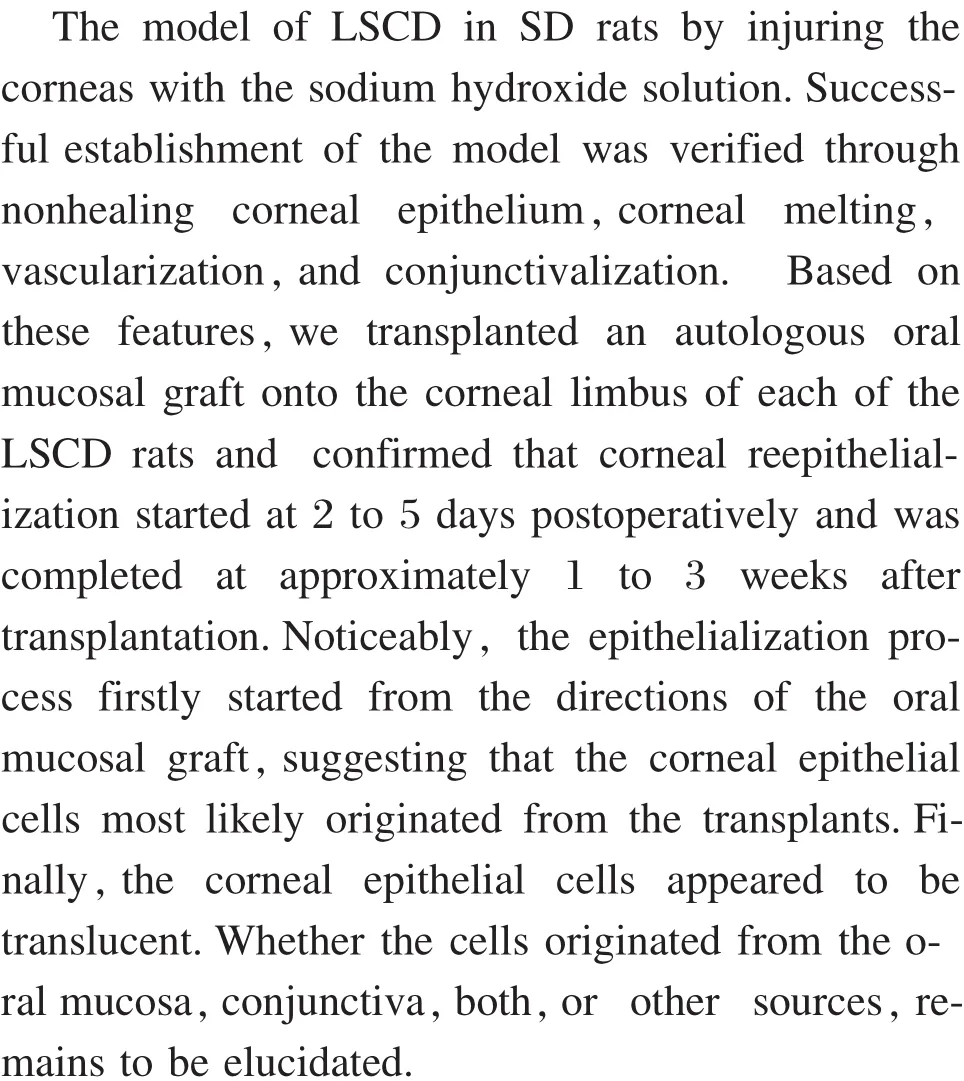
Key points in the model establishment


杂志排行
眼科学报的其它文章
- Instructions for authors
- Coordination Skills during Vitrectomy in Treatment of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- Ratio of Primary Episcleral Buckling Surgery versus Primary Vitrectom y for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
- IgG4-Related M ikulicz's Disease Associated w ith Thyroiditis:a Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Clinical Experience of External-route Retinal Detachment Surgery under a Surgical M icroscope
- Tendency for Evolution of High M yopia in 308 Chinese School Children from Xi'an City
