Unifor a Predator-Prey Model with Beddington-DeAngelis Functional Response*
2014-09-05XUChangjinYAOLingyun
XU Changjin,YAO Lingyun
(1.Guizhou Key Laboratory of Economics System Simulation,Guizhou University of Finance and Economics,Guiyang 550004,China;2.Library,Guizhou University of Finance and Economics,Guiyang 550004,China)
UniforaPredator-PreyModelwithBeddington-DeAngelisFunctionalResponse*
XU Changjin1,YAO Lingyun2
(1.Guizhou Key Laboratory of Economics System Simulation,Guizhou University of Finance and Economics,Guiyang 550004,China;2.Library,Guizhou University of Finance and Economics,Guiyang 550004,China)
An asymptotically periodic predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response is investigated.Some sufficient conditions for the uniformly strong persistence of the system are obtained.
predator-prey model;uniform persistence;asymptotically periodic;Beddington-DeAngelis functional responseCLCnumberO175.13DocumentcodeA
10.3969/j.issn.1007-2985.2014.01.003
1 Introduction
The qualitative properties such as boundedness,stability,permanence and existence of periodic solutions have attracted a lot of attention and many good results have already been reported.For example,GYLLENBERG M et al[1]studied limit cycles of a competitor-competitor-mutualist Lotka-Volterra model.SONG X Y et al[2]made a discussion on the linear stability of trivial periodic solution and semi-trivial periodic solutions and the permanence of the periodic predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower Holling-type II schemes and impulsive effect.AGGELIS G et al[3]considered the coexistence of both prey and predator populations of a prey-predator model.AGIZA H N et al[4]investigated the chaotic phenomena of a discrete prey-predator model with Holling type II.SEN M et al[5]analyzed the bifurcation behavior of a ratio-dependent prey-predator model with the Allee effect.ZHANG Z Q et al[6]gave a theoretical study on the existence of multiple positive periodic solutions for a delayed predator-prey system with stage structure for the predator.ZHANG Z Q et al[7]focused on the existence of at least four positive periodic solutions for a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with multiple exploited (or harvesting) terms.KO W et al[8]discussed the coexistence states of a nonlinear Lotka-Volterra type predator-prey model with cross-diffusion.FAZLY M et al[9]dealt with periodic solutions of a predator-prey system with monotone functional responses.One can see ref.[10-19] etc.for more related studies.However,the research work on asymptotically periodic predator-prey model is very few at present.

In2011,HAQUEM[20]investigatedthestability(localandglobal)andbifurcation(saddle-node,transcritical,Hopf-Andronov,Bogdanov-Takens)ofthefollowingBeddington-DeAngelispredator-preymodel
(1)
wherex(t)andy(t)denotethedensitiesofpreyandpredator,respectively,attimet;r,k,m,a,b,c,e,d,harepositiveconstantsthatstandforpreyintrinsicgrowthrate,carryingcapacityoftheenvironment,consumptionrate,preysaturationconstant,predatorinterference,anothersaturationconstant,conversionrate,predatordeathrate,predatorinterspeciescompetition,respectively.Indetails,onecanseeref. [20].
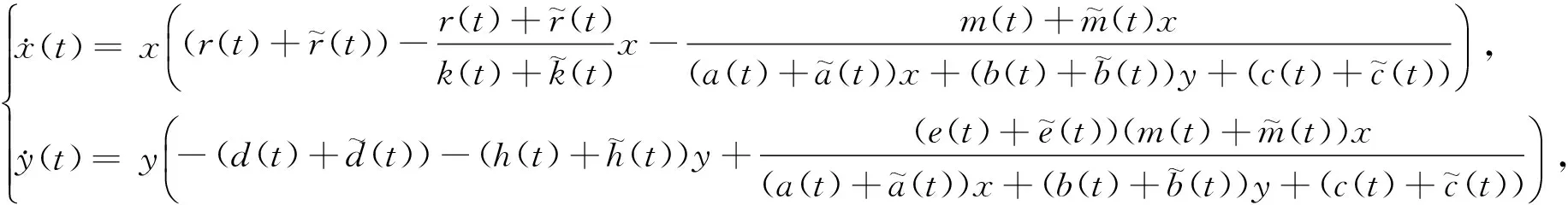
(2)
withinitialconditionsx(0)=φ1(0)≥0,y(0)=φ2(0)≥0.
Theprincipleobjectofthisarticleistoexploretheuniformlystrongpersistenceofsystem(2).Thereareveryfewpaperswhichdealwiththistopic,seeref. [10,21].
Inordertoobtainourresults,weassumethatsystem(2)alwayssatisfies:

2 Uniformly Strong Persistence

fl-ε≤f(t)≤fu+εfort≥T.
(3)

Lemma1 Both the positive and nonnegative cones ofR2are invariant with respect to system (2).
It follows from lemma 1 that any solution of system (2) with a nonnegative initial condition remains nonnegative.

In what follows,we will establish our result.
Theorem2 LetA1,A2andB1be defined by (5),(7) and (9),respectively.Assume that conditions (H) andblrl>mu,elmlB1>du(auA1+buA2+cuhold,then system (2) is uniformly strong persistence.
ProofIt follows from (3) that for anyε>0,there existsT1>0 such that
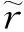
(4)
Substitute (4) into the first equation of system (2),then we have
By lemma 2,we get
(5)
Then for anyε>0,there existsT2>T1>0 such that
x(t)≤A1+εt≥T2.
(6)
Similarly,from (3) and the second equation of system (2),we obtain that for anyε>0,there existsT3>T2>0 such that
In view of lemma 2,we derive
(7)
Then for anyε>0,there existsT4>T3>0 such that
y(t)≤A2+εt≥T4.
(8)
According to (6),(8) and the first equation of system (2),we obtain that for anyε>0,there existsT5>T4>0 such that
Using lemma 2 again,we have
(9)
Thus for anyε>0,there existsT6>T5>0 such thatx(t)≥B1-ε.
According (6),(8) and the second equation of system (2),we obtain that for anyε>0,there existsT7>T6>0 such that
Using lemma 2 again,we have
Thus the proof of theorem 1 is complete.
[1] GYLLENBERG M,YAN P,WANG Y.Limit Cycles for Competitor-Competitor-Mutualist Lotka-Volterra Systems[J].Physica D,2006,221(2):135-145.
[2] SONG Xinyu,LI Yongfei.Dynamic Behaviors of the Periodic Predator-Prey Model with Modified Leslie-Gower Holling-Type II Schemes and Impulsive Effect[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2008,9(1):64-79.
[3] AGGELIS G,VAYENAS D V,TSAGOU V,et al.Prey-Predator Dynamics with Predator Switching Regulated by a Catabolic Repression Control Mode[J].Ecological Modelling,2005,183(4):451-462.
[4] AGIZA H N,ELABBASY E M,EL-METWALLY H,ELSADANY A A.Chaotic Dynamics of a Discrete Prey-Predator Model with Holling Type II[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2009,10(1):116-129.
[5] SEN M,BANERJEE M,MOROZOV A.Bifurcation Analysis of a Ratio-Dependent Prey-Predator Model with the Allee Effect[J].Ecological Complexity,2012,doi.org/10.1016/j.ecocom.2012.01.002
[6] ZHANG Zhengqiu,LUO Jianbo.Multiple Periodic Solutions of a Delayed Predator-Prey System with Stage Structure for the Predator[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2010,11(5):4 109-4 120.
[7] ZHANG Zhengqiu,HOU Zhenting.Existence of Four Positive Periodic Solutions for a Ratio-Dependent Predator-Prey System with Multiple Exploited (or Harvesting) Terms[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2010,11(3):1 560-1 571.
[8] KO W,RYU K.Coexistence States of a Nonlinear Lotka-Volterra Type Predator-Prey Model with Cross-Diffusion[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Theory,Methods & Applications,2009,71(12):1 109-1 115.
[9] FAZLY M,HESAARAKI M.Periodic Solutions for a Discrete Time Predator-Prey System with Monotone Functional Responses[J].Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences-Series I,2007,345(4):199-202.
[10] CHEN Fengde.On a Nonlinear Nonautonomous Predator-Prey Model with Diffusion and Distributed Delay[J].J. Comput. Appl. Math.,2005,180(1):33-49.
[11] LIU Zijian,ZHONG Shouming,LIU Xiaoyuan.Permanence and Periodic Solutions for an Impulsive Reaction-Diffusion Food-Chain System with Holling Type III Functional Response[J].J. Franklin Inst.,2011,348(2):277-299.
[12] NINDJIN A F,AZIZ-ALAOUI M A,CADIVEL M.Analysis of a Predator-Prey Model with Modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-Type II Schemes with Time Delay[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2006,7(5):1 104-1 118.
[13] SCHEFFER M.Fish and Nutrients Interplay Determines Algal Biomass:A Minimal Model[J].Oikos,1991,62:271-282.
[14] LI Yongkun,ZHAO Kaihong,YE Yuan.Multiple Positive Periodic Solutions of Species Delay Competition Systems with Harvesting Terms[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Real World Appl.,2011,12(2):1 013-1 022.
[15] XU Rui,CHEN Lansun,HAO Feilong.Periodic Solution of a Discrete Time Lotka-Volterra Type Food-Chain Model with Delays[J].Appl. Math. Comput.,2005,171(1):91-103.
[16] KAR T K,MISRA S,MUKHOPADHYAY B.A Bioeconomic Model of a Ratio-Dependent Predator-Prey System and Optimal Harvesting[J].J. Appl. Math. Comput.,2006,22(1/2):387-401.
[17] BHATTACHARYYA R,MUKHOPADHYAY B.On an Eco-Epidemiological Model with Prey Harvesting and Predator Switching:Local and Global Perspectives[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applications,2010,11(5):3 824-3 833.
[18] CHAKRABORTY K,CHAKRABORTY M,KAR T K.Bifurcation and Control of a Bioeconomic Model of a Prey-Predator System with a Time Delay[J].Nonlinear Anal.:Hybrid Sys.,2011,5(4):613-625.
[19] ZHANG Weipeng,ZHU Deming,BI Ping.Multiple Periodic Positive Solutions of a Delayed Discrete Predator-Prey System with Type IV Functional Responses[J].Appl. Math. Lett.,2007,20(10):1 031-1 038.
[20] HAQUE M.A Detailed Study of the Beddington-Deangelis Predator-Prey Model[J].Math. Bios.,2011,234(1):1-16.
[21] YANG,Yu,CHEN Wencheng.Uniformly Strong Persistence of a Nonlinear Asymptotically Periodic Multispecies Competition Predator-Prey System with General Functional Response[J].Appl. Math. Comput.,2006,183(1):423-426.
(责任编辑 向阳洁)
具有Beddington-DeAngelis功能反应的捕食模型
徐昌进1,姚凌云2
(1.贵州财经大学贵州省经济系统仿真重点实验室,贵州 贵阳 550004;2.贵州财经大学图书馆,贵州 贵阳 550004)
研究了一类具有Beddington-DeAngelis 功能反应的渐近周期捕食模型,得到了该系统一致强持久的充分条件.
O175.13
A
1007-2985(2014)01-0008-04
date:2013-05-04
National Natural Science Foundation of China (11261010,11201138);Soft Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province (2011LKC2030);Natural Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (J[2012]2100);Governor Foundation of Guizhou Province ([2012]53)
Biography: XU Changjin (1970-),male,was born in Huaihua City,Hunan Provinve,professor,Ph.D.;research areas are theory and its applications of delay differential equations.
键词:捕食模型;一致持久;渐近周期;Beddington-DeAngelis 功能反应
