孔洞型储层电阻率理论模拟及影响因素*
2014-06-01张兆辉高楚桥高永德
张兆辉,高楚桥,高永德
1.中国石油勘探开发研究院西北分院,甘肃兰州730020 2.长江大学地球物理与石油资源学院,湖北荆州434023 3.中海油南海西部研究院,广东湛江524057
孔洞型储层电阻率理论模拟及影响因素*
张兆辉1,高楚桥2,高永德3
1.中国石油勘探开发研究院西北分院,甘肃兰州730020 2.长江大学地球物理与石油资源学院,湖北荆州434023 3.中海油南海西部研究院,广东湛江524057
碳酸盐岩储层导电机理复杂,电阻率影响因素众多,储层划分及流体性质识别难度较大。通过构建合理的孔隙结构物理模型,理论模拟储层电阻率,并对各种影响因素(喉道粗细、地层水电阻率、岩石基质电阻率、孔洞延展方向及大小等)逐一进行分析,进一步探讨了各因素对电阻率的影响程度,较好地解释了电阻率异常层的成因。孔洞型储层电阻率随喉道直径增加快速下降,而随基质、地层水电阻率增加而增大;平行电流方向的孔洞延展对电阻率的影响高于垂直电流方向的孔洞延展,孔洞尺寸沿着电流方向增大,电阻率呈降低趋势。喉道直径对电阻率的影响高于孔洞尺寸;喉道直径对全含水岩石电阻率的影响大于全含油,而岩石基质电阻率、地层水电阻率、孔洞延展方向及大小则相反。
孔洞型储层;孔隙结构;物理模型;理论模拟;电阻率
张兆辉,高楚桥,高永德.孔洞型储层电阻率理论模拟及影响因素[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版,2014,36(2):79–84.
Zhang Zhaohui,Gao Chuqiao,Gao Yongde.Theoretical Simulation and Analysis Factors of Resistivity in Vuggy Reservoir[J].Journal of Southwest Petroleum University:Science&Technology Edition,2014,36(2):79–84.
引言
赵良孝等[1]将碳酸盐岩储层储集空间划分为孔隙、洞穴、喉道和裂缝等4大类,司马立强[2]在此基础上进行了完善细分。中国石油勘探生产与分公司专家从测井评价角度出发,根据孔隙类型及其组合关系将碳酸盐岩储层分为孔洞型、裂缝型、裂缝–孔洞型及洞穴型等4类[3-6]。不同储层类型的碳酸盐岩具备不同的储集、渗滤特征和导电机理[7],若对储层的导电机理认识不清,则对油水层的识别和饱和度的计算带来很大的困难,往往出现误判、错判等情况。物理实验和数值模拟是进行岩石物理基础研究的两种基本方法,当对一些介质的物理实验测量或者对某些物理量难以观测时,理论模拟研究能发挥其优越性。
国内外关于岩石微观结构的模型较多,包括毛管束模型、简化导电模型、电阻网络模型、分形理论等[7-14],不同模型适用于不同的岩石孔隙结构。本文在孔洞型储层孔隙结构及物理模型研究的基础上,建立物理模型对储层电阻率进行理论模拟,进一步探讨其影响因素,并解释电阻率异常层。
1 导电模型的建立
塔里木盆地塔中地区奥陶系孔洞型储层储集空间基本为洞径较小的溶蚀孔洞,另外包括粒内孔、粒间孔、晶间孔、小溶孔和一些微孔隙[15-17],几乎无裂缝,孔、洞为主要储集空间,喉道主要为渗滤通道,连通导电。在此孔隙结构特征认识的基础上,结合铸体薄片、扫描电镜等微观实验分析资料,建立储层电阻率理论模拟物理模型如图1所示[18],根据电阻并、串联导电原理,即岩石的电阻视为喉道和孔洞在电流方向上分别与岩石并联然后二者串联的结果。同时由实验分析可知,孔洞型储层孔喉配置关系极为复杂,加之碳酸盐岩储层本身的强非均质性,使得孔喉配位数对电阻率的影响较大,关于此方面的研究,毛志强等进行了尝试性研究[11],这里不再赘述。
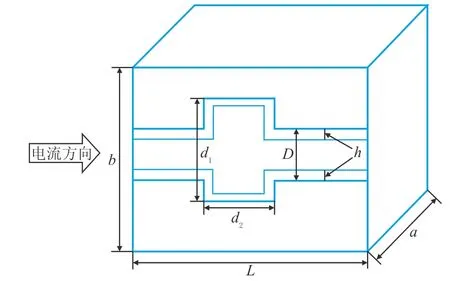
图1 孔洞型储层物理模型Fig.1 Physical model of vuggy reservoir
本文根据流体性质的不同分两种情况讨论。
(1)若孔洞与喉道中充满地层水,根据导电原理,岩石电阻为
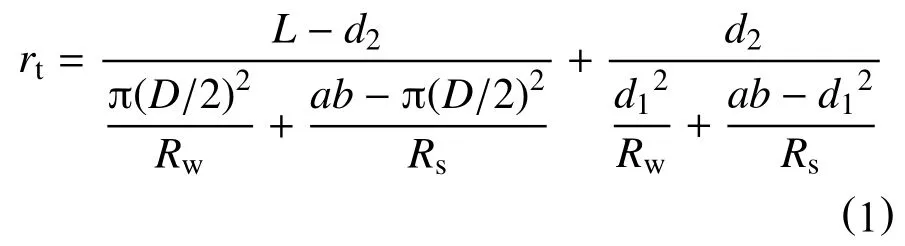
式中:rt—岩石电阻,Ω;Rw,Rs—地层水、岩石基质电阻率,Ω·m;a,b,L—岩石的宽、高、长,µm;D—喉道直径,µm;d1,d2—孔洞的高(宽)、长,µm。
同时,模型总电阻率为

将式(2)代入式(1),得到模型岩石总电阻率
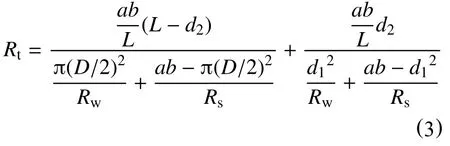
(2)孔隙和喉道充满油且水相润湿时,同理可得出模型岩石总电阻率为
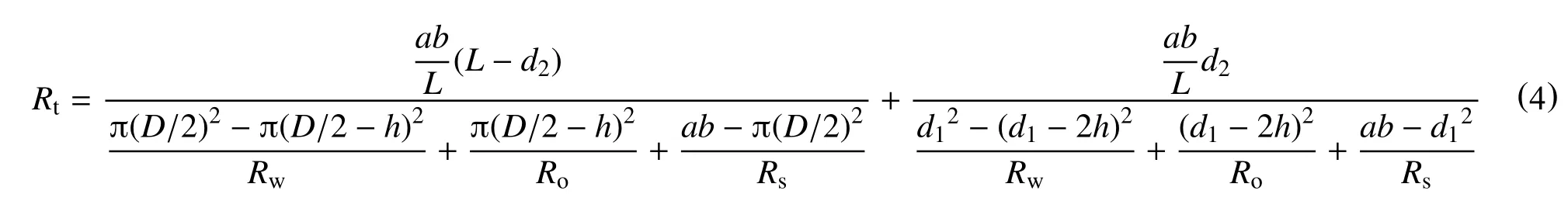
2 影响因素分析
为方便讨论,假设岩石模型外径a、b、L相等,且为单位长度1,无因次。
从式(3)、式(4)可以看出,储层电阻率的影响因素众多,各因素又相互作用,因此若模拟计算时同时考虑多种因素,则不能充分表达某一特定因素对电阻率的影响程度,因此,本次研究采用逐一分析的方法,图2~图6为理论模拟成果图。可见,喉道粗细、地层水电阻率高低、孔洞形状及基质电阻率对孔洞型储层电阻率的影响程度不尽相同,而且流体性质不同,各因素的影响程度也不同。
(1)岩石电阻率随着喉道尺寸的增加而减小,孔洞与喉道中全含水时喉道大小的变化对岩石电阻率的影响比全含油时影响更大(图2)。
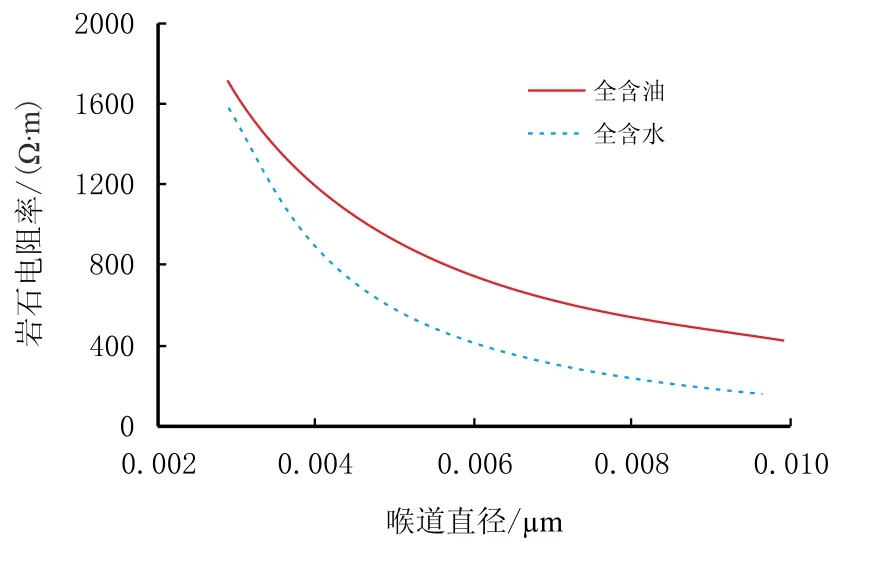
图2 喉道直径对岩石电阻率的影响Fig.1 Influence of throat diameter on rock resistivity
(2)岩石电阻率随着地层水电阻率的增大而增大,且孔洞与喉道中含油时比含水时对岩石电阻率影响更大(图3)。
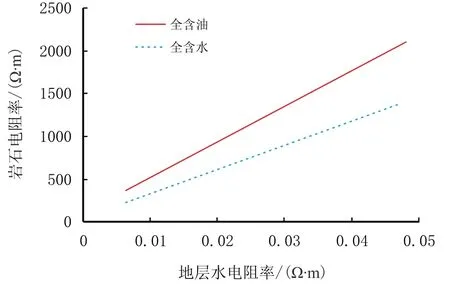
图3 地层水电阻率对岩石电阻率的影响Fig.3 Influence of formation water resistivity on rock resistivity
(3)孔洞与喉道含油时岩石电阻率随着岩石基质电阻率的增加而增加的趋势较明显,而含水时岩石电阻率随岩石基质电阻率的增大而增大的趋势不明显(图4)。
(4)孔洞尺寸在垂直电流方向(孔洞的宽、高延展方向)增加时对岩石电阻率的影响不大,基本上没有变化;而当孔洞尺寸在顺着电流方向(孔洞的长延展方向)增大时,岩石电阻率却呈现明显的降低趋势,且含油时孔洞尺寸对岩石电阻率的影响比含水时更明显(图5,图6)。
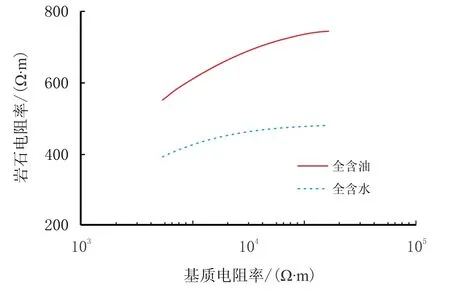
图4 岩石基质电阻率对岩石电阻率的影响Fig.4 Influence of matrix resistivity on rock resistivity
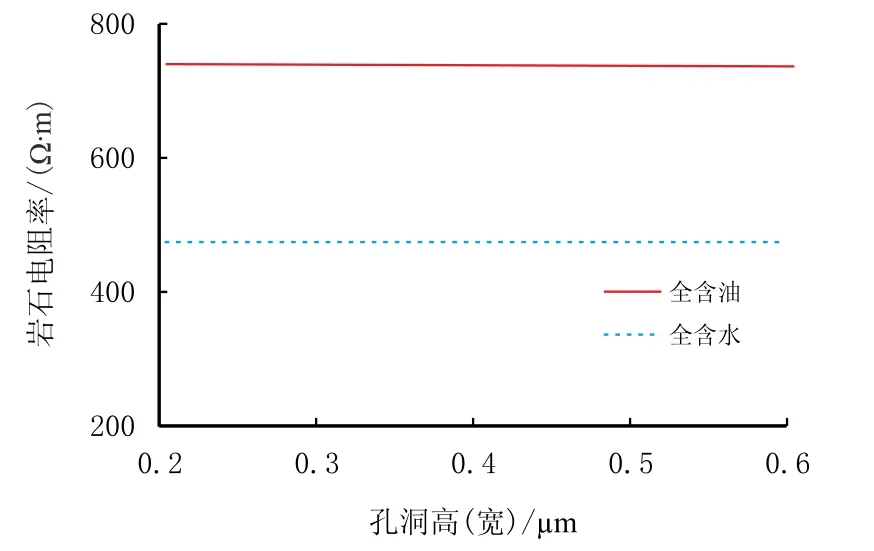
图5 孔洞垂直电流方向延展对岩石电阻率的影响Fig.5 Influence of vuggy extension along vertical current direction on rock resistivity
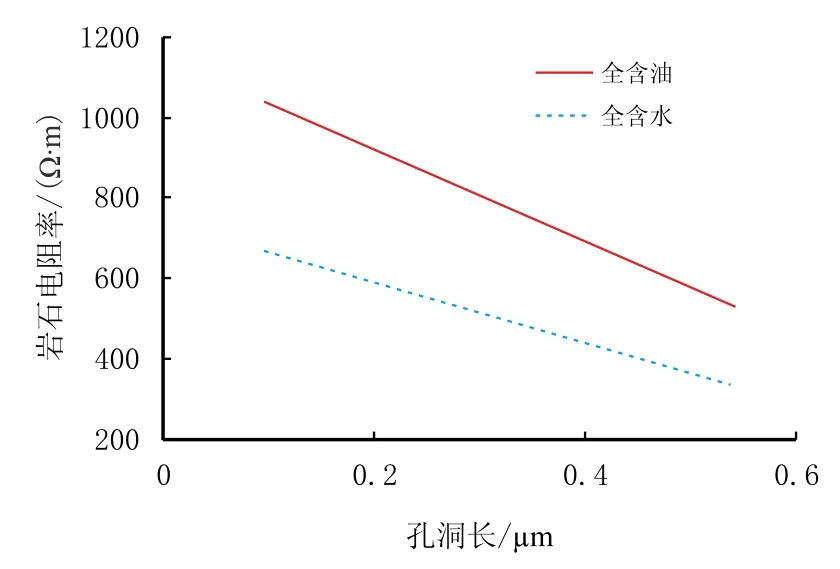
图6 孔洞顺着电流方向延展对岩石电阻率的影响Fig.6 Influence of vuggy extension along current along direction on rock resistivity
总体来看,喉道半径对岩石电阻率的影响比孔洞尺寸对电阻率的影响大;相同孔隙度情况下(孔洞体积相同),孔洞的延展方向也是影响岩石电阻率的一个重要因素。
3 异常电阻率成因分析
碳酸盐岩储层导电机理复杂,电阻率的影响因素众多,导致电阻率曲线经常出现一些异常情况,如异常高阻层、致密低阻层、高阻水层等,给储层划分及流体识别带来很大困难[19-27]。本文以高阻水层为例,在数值理论模拟的基础上进行成因分析。
图7为塔中地区塔中Z井实际资料,测井综合解释为孔洞型储层,4 695~4 710 m井段平均孔隙度为2.3%、电阻率约3 600 Ω·m,测井解释为油层,但试油测试日产油0.24 m3、日产水32.88 m3,呈现高阻产水现象。分析认为,单纯从测井响应特征及宏观参数难以解释这一异常现象,但采用前文理论模拟的方法从储层微观孔隙结构方面可以很好地解释。图8为依据实际资料模拟的全含水岩石电阻率与喉道大小关系图,可见,当喉道较细时,水层电阻率同样可能较高,甚至大于纯油层电阻率,而孔洞尺寸对岩石电阻率影响相对较小。
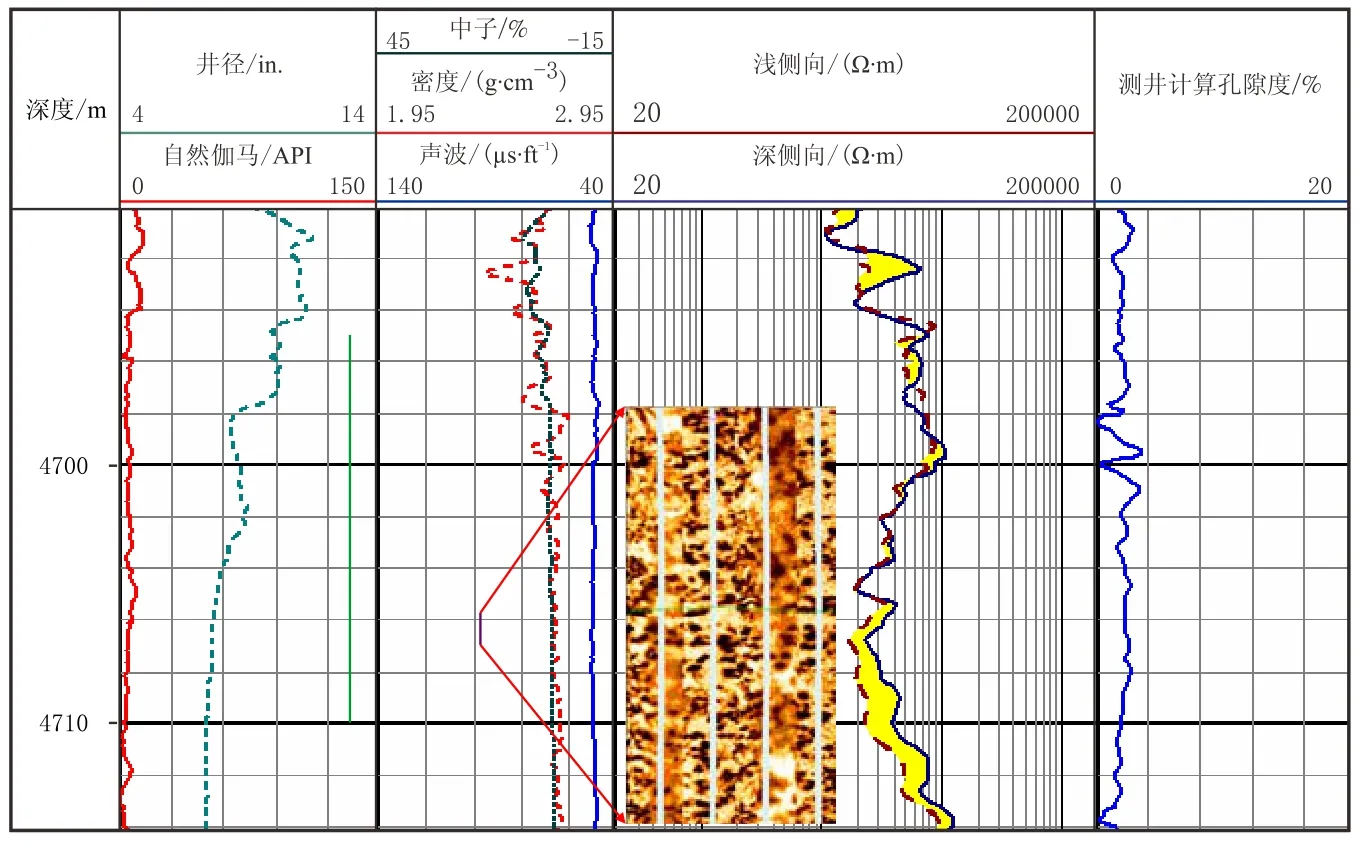
图7 Z井测井响应图Fig.7 Logging response of Well Z
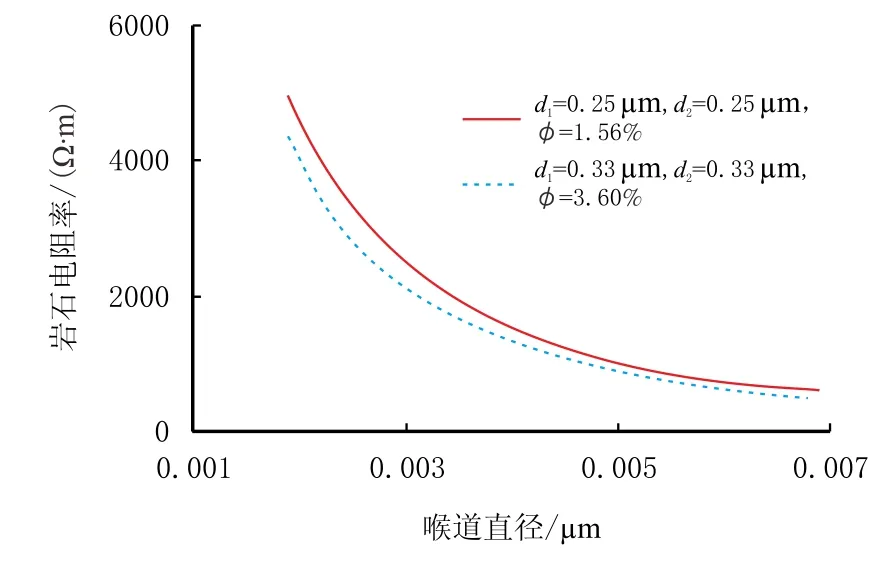
图8 全含水岩石电阻率与喉道直径的关系Fig.8 Relationship between completely water-saturated rocks resistivity and throat diameter
4 结论
(1)孔洞型储层岩石电阻率随喉道直径增加快速下降,随岩石基质电阻率、地层水电阻率增加而增大;顺着电流方向的孔洞延展对电阻率的影响大于垂直电流方向的孔洞延展,且随着孔洞尺寸顺着电流方向的增大,电阻率呈明显的降低趋势。
(2)喉道直径是影响电阻率高低的主要因素,其次是孔洞形状、尺寸、流体性质等;喉道直径对全含水岩石电阻率的影响大于全含油,而岩石基质电阻率、地层水电阻率、孔洞延展方向及大小则相反。
(3)高阻水层多出现在连通性不好的孔洞型储层,孔隙结构特征主要表现为孔喉半径小,导电不畅使得电阻率值较高,甚至超过油层电阻率。
[1]赵良孝,补勇.碳酸盐岩储层测井评价技术[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1994.
[2]司马立强.测井地质应用技术[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2002.
[3]中国石油勘探与生产分公司.碳酸盐岩油气藏测井评价技术及应用[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2009.
[4]崔文娟,李明,张丽娟,等.碳酸盐岩孔洞型储集层含油气分布——以塔里木盆地为例[J].新疆石油地质,2011,32(2):126–129. Cui Wenjuan,Li Ming,Zhang Lijuan,et al.Hydrocarbon distribution of Ordovician in carbonate vuggy reservoirs in Halahatang Area,Tarim Basin[J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2011,32(2):126–129.
[5]朱智鹏,黄勇,汪洋.四川盆地东部石炭系黄龙组岩溶角砾碳酸盐岩特征[J].天然气工业,2013,33(5):40–45. Zhu Zhipeng,Huang Yong,Wang Yang.Characteristics of karst brecciated carbonate of Carboniferous Huanglong FormationintheeasternSichuanBasin[J].NaturalGasIndustry,2013,33(5):40–45.
[6]袁秀婷,周红涛.用导电效率识别塔河油田碳酸盐岩储集层类型[J].新疆石油地质,2006,27(3):311–312. Yuan Xiuting,Zhou Hongtao.Identification of carbonate reservoir types in Tahe Oilfield with conductance[J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2006,27(3):311–312.
[7]雍世和,张超谟.测井数据处理与综合解释[M].东营:石油大学出版社,2002.
[8]陈宁宁,杨少春,黄建廷.胜坨油田沙河街组二段复杂断块油藏水淹层测井解释研究[J].地球科学与环境学报,2010,32(4):355–362. Chen Ningning,Yang Shaochun,Huang Jianting.Study on log interpretation for water flooded layer of the complexfaultblockoilreservoirinthesecondmemberofShahejie Formation of Shengtuo Oilfield[J].Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2010,32(4):355–362.
[9]原海涵.阿尔奇公式中的a、m与渗透率的关系——毛管理论在岩石电阻率研究中的应用[J].地球物理测井,1990,14(5):347–357. Yuan Haihan.Relationship between permeability and factors a,m in Archie equationCapillary theory in the study of rock resistivity[J].Geophysical Well Logging,1990,14(5):347–357.
[10]匡立春.利用测井资料评价储集层性质的探讨[J].测井技术,1992,16(2):117–119. Kuang Lichun.Evaluating reservoir nature with logging data[J].Well Logging Technology,1992,16(2):117–119.
[11]毛志强,高楚桥.孔隙结构与含油岩石电阻率性质理论模拟研究[J].石油勘探与开发,2000,27(2):87–90. Mao Zhiqiang,Gao Chuqiao.Theoretical simulation of the resistivity and pore structure of hydrocarbon bearing rocks[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2000,27(2):87–90.
[12]杨锦林,呙长艳,胡宗全.测井解释储集层孔隙结构与含油气性[J].天然气工业,1998,18(2):36–39. YangJinlin,WoChangyan,HuZongquan.Loginterpreted reservoir pore structure and hydrocarbon potential[J].Natural Gas Industry,1998,18(2):36–39.
[13]陈书荣,王达健,张雄飞,等.多孔介质孔隙结构的网络模型应用[J].计算机与应用化学,2001,18(6):531–534. Chen Shurong,Wang Dajian,Zhang Xiongfei,et al. Application of network models for pore structure medias[J].Computers and Applies Chemistry,2001,18(6):531–534.
[14]李留仁,袁士义,胡永乐.分形多孔介质渗透率与孔隙度理论关系模型[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版,2010,25(3):49–51. Li Liuren,Yuan Shiyi,Hu Yongle.A new model for describing the relationship between permeability and porosity for fractal porous media[J].Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition,2010,25(3):49–51.
[15]关雎,李军,郭秀丽.塔中地区碳酸盐岩储集层测井评价[J].石油勘探与开发,1998,25(4):84–86. Guan Ju,Li Jun,Guo Xiuli.Carbonate reservoir logging evaluation for Tazhong Field[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,1998,25(4):84–86.
[16]陶云光.轮古西地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层特征研究[J].天然气工业,2007,27(2):20–22. Tao Yunguang.Features of the Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in Lunguxi Area[J].Natural Gas Industry,2007,27(2):20–22.
[17]焦翠华,王清辉,徐怀民,等.准东地区北部二叠系致密油藏烃源岩测井评价[J].新疆石油地质,2013,34(5):524–527. Jiao Cuihua,Wang Qinghui,Xu Huaimin,et al.The Logging evaluation of source rocks in permian tight oil reservoirinnortherneastJunggarBasin[J].XinjiangPetroleum Geology,2013,34(5):524–527.
[18]高楚桥.复杂储层测井评价方法[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2003.
[19]齐宝权,张树东,王兆年,等.碳酸盐岩储层高电阻率影响因素探讨[J].西南石油大学学报,2007,29(1):26–29. QiBaoquan,ZhangShudong,WangZhaonian,etal.High resistivityaffectingfactorsofcarbonatereservoirinnortheast Sichuan Basin[J].Journal of Southwest PetroleumUniversity,2007,29(1):26–29.
[20]王月英,姚军,黄朝琴.缝洞型碳酸盐岩储集层离散介质模型的建模方法[J].新疆石油地质,2012,33(2):225–229. Wang Yueying,Yao Jun,Huang Zhaoqin.Discrete medium modeling method for fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoir[J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2012,33(2):225–229.
[21]张树东.复杂高电阻率碳酸盐岩储层深浅双侧向的解释探讨[J].测井技术,2005,29(1):33–36. Zhang Shudong.On deep&shallow laterolog data interpretation of complex carbonate reservoir with high resistivity[J].WellLoggingTechnology,2005,29(1):33–36.
[22]李军,肖承文,祁兴中.碳酸盐岩储集层测井解释方法在塔中地区的应用[J].勘探家,1998,3(1):27–30. Li Jun,Xiao Chengwen,Qi Xingzhong.Carbonate reservoir logging interpretation and it’s application in Tazhong area[J].Petroleum Explorationist,1998,3(1):27–30.
[23]李娴静,陈能贵,韩守华,等.准噶尔盆地南缘古近系—新近系储层测井解释模型及规模储层分布[J].中国石油勘探,2012,17(5):27–31. Li Xianjing,Chen Nenggui,Han Shouhua,et al.LogginginterpretationmodelanddistributionoftertiaryeffectivereservoirsinsouthernedgeofJunggarBasin[J].China Petroleum Exploration,2012,17(5):27–31.
[24]李国会,赵峰,杨鹏飞,等.塔北隆起英买2区块缝洞型碳酸盐岩等效孔隙度模型定量描述研究[J].中国石油勘探,2011,16(4):20–22. Li Guohui,Zhao Feng,Yang Pengfei,et al.Quantitative description of fracture-cavity type carbonate reservoir equivalent porosity model in YM 2 Well Area,Tabei Uplift[J].China Petroleum Exploration,2011,16(4):20–22.
[25]曾少军,何胜林,王利娟,等.基于流动单元的测井储层参数精细建模技术——以崖城13–1气田陵三段为例[J].天然气工业,2011,31(8):12–15. Zeng Shaojun,He Shenglin,Wang Lijuan,et al.Refined modeling of logging reservoir parameters based on flow units:A case study of the 3rd Member of the Lingshui Formation in the Yacheng 13-1 Gas Field[J].Natural Gas Industry,2011,31(8):12–15.
[26]傅海成,张承森,赵良孝,等.塔里木盆地轮南奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层类型测井识别方法[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版,2006,21(5):38–41. Fu Haicheng,Zhang Chengsen,Zhao Liangxiao,et al. Identification of the reservoir space types of the carbonate reservoir in Lunnan Area of Tarim Basin by means of logging data[J].Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition,2006,21(5):38–41.
[27]高俊华,郑淑芬,于晏,等.川渝油气田碎屑岩储层测井解释及流体识别[J].天然气工业,2011,31(7):32–36. Gao Junhua,Zheng Shufen,Yu Yan,et al.Logging interpretation of clastic reservoirs and fluid identification in Sichuan and Chongqing oil and gas fields[J].Natural Gas Industry,2011,31(7):32–36.
编辑:杜增利
编辑部网址:http://zk.swpuxb.com
Theoretical Simulation and Analysis Factors of Resistivity in Vuggy Reservoir
Zhang Zhaohui1,Gao Chuqiao2,Gao Yongde3
1.Northwest Branch,Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development,PetroChina,Lanzhou,Gansu 730020,China 2.School of Geophysics and Oil Resource,Yangtze University,Jingzhou,Hubei 434023,China 3.Research Institute of West of South Sea,CNOOC,Zhanjiang,Guangdong 524057,China
Because of the many factors influencing the resistivity of carbonate reservoir and the complex conductive mechanism,it is difficult to identify the reservoir and interpret the property of fluids.On the basis of pore-structure physical model,we simulated the resistivity of reservoir,and analyzed the factors which affect the resistivity of reservoir.The factors include the throat size,the resistivity of formation water,and the resistivity of matrix,and the vuggy size,and so on.At last,the influencing degree to resistivity of reservoir is discussed and the reason of abnormal resistivity in carbonate is interpreted in this paper.The resistivity of reservoir gradually reduces with the throat diameter increasing,and increases as the resistivity of matrix and formation water increases.Vuggy extension influence on resistivity along the direction of the current is higher than that along the vertical current direction.With the vuggy size along current direction increasing,the resistivity reduces.The effect of throat diameter on the resistivity of reservoir is bigger than vuggy size.The effect of throat diameter on the resistivity of completely water-saturated rocks is bigger than on completely oil-saturated rocks,but for the resistivity of the matrix and the formation water,the extended direction and size of the vuggy,the condition is opposite.
vuggy reservoir;pore structure;physical model;theoretical simulation;resistivity
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/doi/10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2012.08.30.14.html

张兆辉,1982年生,男,汉族,陕西渭南人,工程师,硕士,主要从事测井资料解释、沉积储层方面的研究。E-mail:zhangzhaohui_123@163.com

高楚桥,1966年生,男,汉族,湖北孝感人,教授,博士,主要从事测井新技术、新方法研究及相关教学工作。E-mail:gaocq@vip.163.com

高永德,1978生,男,汉族,山东临沂人,工程师,硕士,主要从事测井管理与技术研究。E-mail:ydgao1978@Hotmail.com
10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2012.08.30.14
1674-5086(2014)02-0079-06
TE132
A
2012–08–30< class="emphasis_bold">网络出版时间:
时间:2014–03–21
