四川红格层状侵入体中角闪石和金云母的矿物学特征及其成因意义*
2014-05-30栾燕宋谢炎陈列锰郑文勤田小林冉启渝
栾燕 宋谢炎 陈列锰 郑文勤 田小林 冉启渝
1.中国科学院地球化学研究所,矿床地球化学国家重点实验室,贵阳 550002
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3.四川省地质矿产勘查开发局106地质队,成都 611130
1 引言
层状侵入体是镁铁-超镁铁质岩浆在岩浆房中演化的产物,记录了岩浆在岩浆房中演化的过程以及物理化学条件(Wager and Brown,1968;Naldrett,1989;宋谢炎等,1997;Barling et al.,2000;钟宏等,2007;夏昭德等,2011)。反演层状岩体形成时的物理化学条件(温度、压力、氧逸度等)已成为揭示幔源岩浆演化和岩浆矿床成因的重要手段(钟宏等,2007),其中氧逸度变化是控制基性岩浆演化形成岩浆钒钛磁铁矿矿床的关键因素之一(Toplis and Carroll,1995,1996;Botcharnikov et al.,2008)。前人对峨眉山大火成岩省内带层状岩体中钒钛磁铁矿形成时的温压和氧逸度条件等进行了一定的探讨,如Pang et al.(2008a,b,2009)认为铁钛氧化物是在接近液相线时与橄榄石等硅酸盐矿物同时结晶形成的,并根据磁铁矿和钛铁矿电子探针成分估计了攀枝花岩体氧化物结晶的温度和氧逸度(1000℃,FMQ>+1.5),但由于磁铁矿和钛铁矿都发生了固溶体分离,因此根据电子探针成分估算的温度和氧逸度可能存在较大误差。张晓琪等(2011)利用攀枝花岩体没有发生固溶体分离的斜长石估算了攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿矿层形成时的温度区间(1079~1121℃),但未对矿层形成时的氧逸度范围进行限定。Bai et al.(2012)根据磁铁矿以及母岩浆中的V含量估算了红格岩体磁铁矿结晶时的氧逸度范围(FMQ+1~FMQ+2),但母岩浆中V含量的不确定性使得估算的氧逸度存在一定误差。所以,利用上述方法探讨钒钛磁铁矿矿层形成时的物理化学条件受到了一定限制。
红格岩体不同于峨眉山大火成岩省内带其它赋存大型钒钛磁铁矿矿床的层状岩体(如攀枝花岩体,Song et al.,2013;白马岩体,Zhang et al.,2012)的一个显著特征是,岩体各岩相带中角闪石和金云母普遍分布,尤其是下部岩相带角闪(磁铁)辉石岩和角闪(磁铁)橄辉岩中角闪石含量高达5%~15%;并且角闪石和金云母均未发现固溶体分离形成的出溶条纹,其电子探针成分可以代表它们结晶时的原始成分。前人研究表明,角闪石和金云母的成分受温度、压力、氧逸度和熔体总成分的影响,可以反映岩浆分离结晶过程中物化条件的改变(Kesler et al.,1975;Hammarstrom and Zen,1986;陈光远等,1988;周作侠,1991;Feeley and Sharp,1996;Selby and Nesbitt,2000;Ridolfi et al.,2008,2010),这样就为我们估算红格岩体形成时的物理化学条件提供了一个很好的机会,所以本文试图利用角闪石和金云母的成分对红格岩体的温压以及氧逸度条件进行约束。
2 地质背景
峨眉山大火成岩省位于扬子板块西部至青藏高原东缘的广大地区,并一直延伸至越南北部,出露面积超过5×105km2(图1)。它主要由峨眉山玄武岩、镁铁-超镁铁质层状侵入体以及同源的酸性、碱性侵入岩组成,一般认为是二叠纪峨眉山地幔柱作用的产物(Chung and Jahn,1995;Song et al.,2001;Xu et al.,2001;宋谢炎等,2001;Zhou et al.,2002;Zhang et al.,2006,2008,2009,2014)。攀西地区位于峨眉山大火成岩省的内带,沿南北向磨盘山-元谋断裂和攀枝花断裂带出露一系列含V-Ti磁铁矿矿床的基性-超基性层状岩体,从北向南依次为太和岩体(262±3Ma,Zhou et al.,2008)、白马岩体(262±3Ma,Guo et al.,2004)、新街岩体(259±3Ma,Zhou et al.,2002)、红格岩体(259±1.3Ma,Zhong and Zhu,2006)和攀枝花岩体(263±3Ma,Zhou et al.,2005;259.8±0.8Ma,Hou et al.,2012;261.4±4.6Ma,Hou et al.,2013)(图1)。根据岩石组合的不同,这些含矿岩体可以分为两类:(1)镁铁-超镁铁质侵入体,如红格、新街岩体;(2)镁铁质侵入体,如攀枝花、太和、白马岩体。红格岩体是攀西地区最大的赋存V-Ti磁铁矿矿床的层状岩体(攀西地质大队,1984①攀西地质大队.1984.攀枝花-西昌地区钒钛磁铁矿共生矿成矿规律与预测研究报告.166-180)。
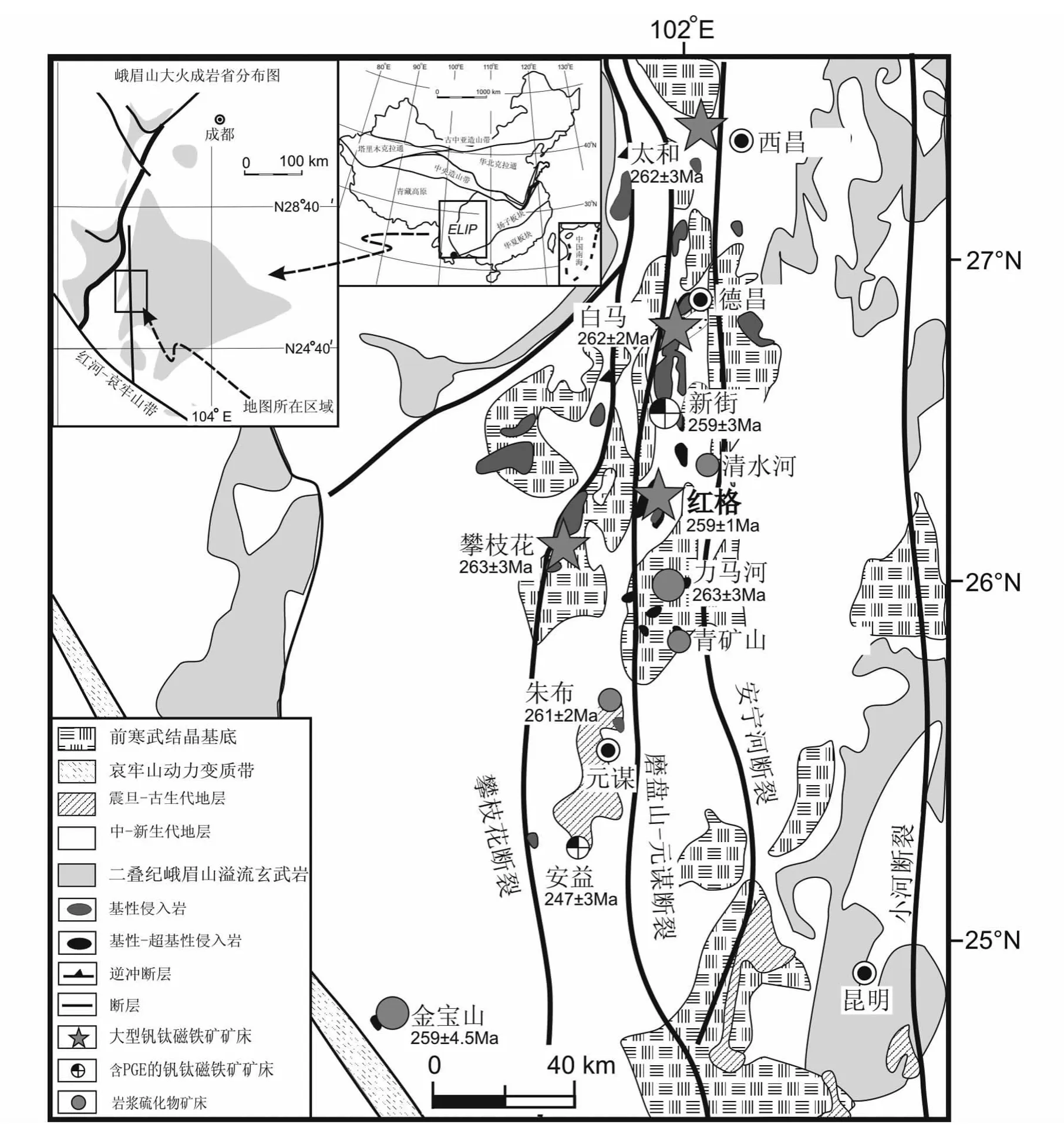
图1 攀西地区镁铁-超镁铁质层状侵入体分布图(据Song et al.,2009)各侵入体年龄分别引自 Zhou et al.(2002,2005,2008),Guo et al.(2004),Zhong and Zhu(2006),Tao et al.(2009)和 Yu et al.(2014)Fig.1 Distribution of the layered mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the central zone of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province(after Song et al.,2009)Ages of these intrusions are from Zhou et al.(2002,2005,2008),Guo et al.(2004),Zhong and Zhu(2006),Tao et al.(2009)and Yu et al.(2014)
3 红格岩体地质特征
近水平的红格岩体呈南北走向,长约16km,宽约5~10km,厚约1.2km(图2a,b)。地表主要出露上部岩相带的辉长岩和中部岩相带的辉石岩(图2a)。该岩体北部侵位于中元古代片岩和变质砂岩中,南部侵位于新元古代的白云质灰岩中;在岩体东北角,上部岩相带的辉长岩与峨眉山玄武岩直接接触。由于后期二叠纪花岗岩和正长岩的侵入(255.2±3.6Ma,Xu et al.,2008),红格岩体与围岩的接触关系被破坏,部分岩体呈捕掳体被包裹在花岗岩中(图2a,b)。
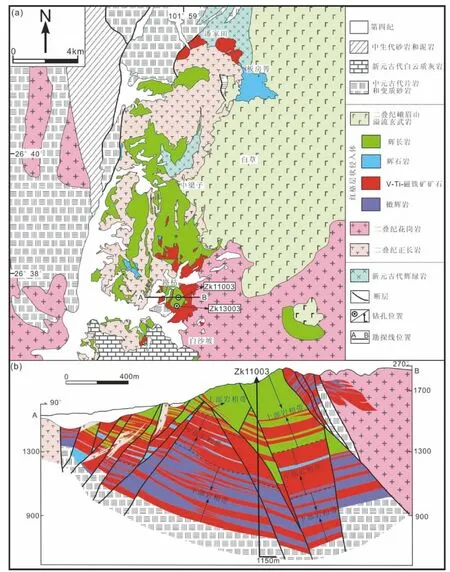
图2 红格层状岩体地质简图(a)和勘探线剖面图(b)(据四川106地质队,2010① 四川106地质队.2010.四川省攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿整装勘查项目报告修改)Fig.2 Simplified geological map(a)and cross section of the exploration line(b)of the Hongge layered intrusion
根据矿物组合及含量变化,特征矿物相(磷灰石、橄榄石)的出现和消失以及岩石结构构造特征等,红格岩体从下往上可分下部岩相带、中部岩相带和上部岩相带3个岩相带(Luan et al.,2014)。下部岩相带以含量高达5% ~15%的角闪石为特征;中部岩相带以块状矿石的出现为特征;上部岩相带以大量自形磷灰石的出现为特征(Luan et al.,2014)。

表1 红格岩体岩性及造岩矿物结构特征Table 1 Lithological features and mineral as semblages of the Hongge intrusion
下部岩相带可以分为4个旋回(从下往上依次为I、II、III、IV),每个旋回从下往上伴随着橄榄石的减少,由下部的角闪(磁铁)橄辉岩过渡为上部的角闪(磁铁)辉石岩(表1)。中部岩相带可以分为4个旋回(从下往上依次为V、VI、VII、VIII),伴随着Fe-Ti氧化物的减少,每个旋回由下部的块状矿石,向上过渡为磁铁橄辉岩、磁铁辉石岩或者(磁铁)辉长岩(表1)。上部岩相带可以分为2个旋回(IX、X),旋回IX主要为磷灰石磁铁辉长岩,旋回X主要为磷灰石辉长岩,间夹少量磷灰石磁铁辉长岩层(表1)。
4 角闪石和金云母的产出特征
角闪石主要赋存在岩体下部岩相带的角闪(磁铁)辉石岩以及角闪(磁铁)橄辉岩岩中。角闪辉石岩中含有70% ~75%单斜辉石,8% ~20%Fe-Ti氧化物,7% ~10%角闪石,<5%橄榄石以及少量的斜长石和磷灰石。角闪橄辉岩中含有10%~35%橄榄石以及40% ~75%单斜辉石,而角闪磁铁辉石岩和角闪磁铁橄辉岩中磁铁矿含量超过20%。在中部和上部岩相带中,角闪石含量一般小于3%,局部含量可达5%~15%(表1)。红格岩体角闪石主要有以下三种形态(表1、图3):(1)嵌晶状角闪石(粒度可达5cm),其中包裹橄榄石、单斜辉石以及Fe-Ti氧化物等矿物(图3a),主要分布在下部岩相带;(2)填隙状角闪石,呈它形充填在单斜辉石、橄榄石及Fe-Ti氧化物颗粒之间(图3b,e),主要分布在下部岩相带,在中部岩相带和上部岩相带的局部出现;(3)反应边角闪石,构成单斜辉石的反应边(图3c),在三个岩相带中均会出现。
金云母在红格岩体中分布不均,主要出现在下部岩相带,一般含量低于4%,局部含量达到5% ~8%(表1)。金云母解理发育,呈他形填隙状并包裹自形的Fe-Ti氧化物颗粒(图3d)或者呈自形-半自形状(图3f)。
5 分析方法及结果

图3 红格岩体角闪石和金云母单偏光下结构特征(a)-角闪磁铁橄辉岩中嵌晶状角闪石包裹橄榄石和自形Fe-Ti氧化物;(b)-角闪辉石岩中的填隙状角闪石;(c)-磁铁橄辉岩中的角闪石反应边结构;(d)-角闪辉石岩中金云母充填在单斜辉石颗粒之间,并包裹自形Fe-Ti氧化物;(e)-磁铁辉石岩中的填隙状角闪石;(f)-磁铁辉石岩中的自形-半自形金云母.Ox-Fe-Ti氧化物;Ol-橄榄石;Cpx-单斜辉石;Hb-角闪石;Phl-金云母Fig.3 Textures of hornblende and phlogopite from the Hongge intrusion under plane-polarized light(a)-poikilitic hornblende enclosing olivine and euhedral Fe-Ti oxides in hornblende magnetite olivine clinopyroxenite;(b)-interstitial hornblende in hornblende clinopyroxenite;(c)-hornblende reaction rims in the magnetite olivine clinopyroxenite;(d)-phlogopite enclosing euhedral Fe-Ti oxides and filling between clinopyroxene grains in hornblende clinopyroxenite;(e)-interstitial hornblende in magnetite clinopyroxenite;(f)-euhedralhypidiomorphic phlogopite in magnetite clinopyroxenite.Ox-Fe-Ti oxide;Ol-olivine;Cpx-clinopyroxene;Hb-hornblende;Phl-phlogopite
角闪石和金云母电子探针成分分析在中国科学院地球化学研究所电子探针实验室完成。分析仪器为:日本岛津公司生产的 EMPA-1600电子探针。分析条件为:加速电压25kV,电流10nA,分析束斑直径为10μm。分析时所用标样为:美国生产的标样SPI#2753-AB,分析精度为0.01。主要氧化物百分含量的分析误差<2%,分析结果见表2、表3。

图4 红格岩体角闪石分类与命名(据Leake et al.,1997)Fig.4 Classification of the hornblende in the Hongge intrusion(after Leake et al.,1997)
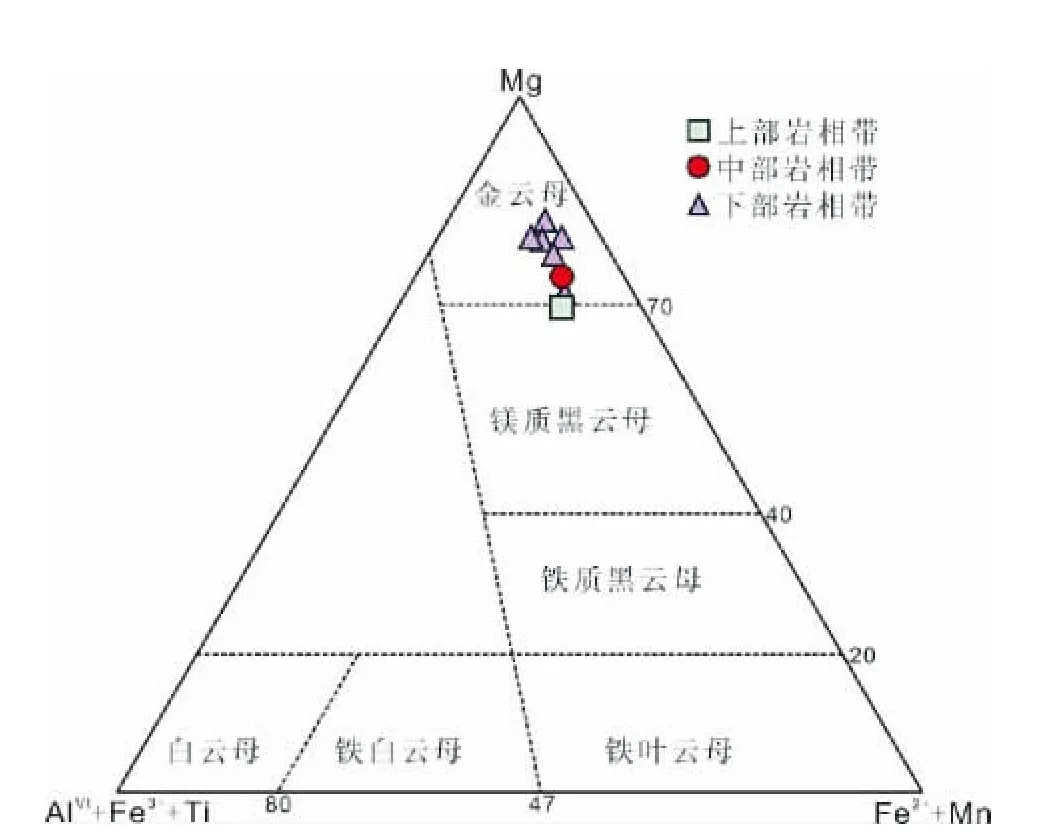
图5 红格岩体云母Mg-(AlVI+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn)分类图解(据Foster,1960)Fig.5 Mg-(AlVI+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn)diagram of the mica in the Hongge intrusion(after Foster,1960)
根据角闪石化学分子式(表2),角闪石阳离子特征为:CaB=1.72~1.9,(Na+K)A=0.66~0.92。按国际矿物学协会角闪石专业委员会提出的命名原则,红格岩体角闪石属于钙角闪石(CaB≥1.5,(Na+K)A≥0.5)。按钙角闪石的进一步分类命名原则,红格岩体角闪石Si=5.91~6.34,Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)=0.65~0.78,投影到Si-Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)图解上定名为韭闪石、镁绿钙闪石和钛闪石(图4)(Leake et al.,1997)。红格岩体角闪石化学成分显示以下特征:富镁(13.0% ~15.0%)、富CaO(11.0% ~12.5%)和贫钾、富钠(K2O=0.5% ~1.5%,Na2O=2.0% ~3.0%)。其TiO2含量主要分布在3.5%~5.0%之间,Al2O3含量主要在10.5% ~12.0%之间(表2)。
在云母的Mg-(AlVI+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn)分类图解中(图5)(Foster,1960),红格岩体的云母成分投点均在金云母区域。红格岩体金云母具有高镁、低铝、低铁的特征(MgO=18.7% ~22.9%,Al2O3=13.1% ~15.2%,FeOT=6.30%~11.4%)。其K2O含量为8.65% ~9.82%,Na2O含量为0.02%~0.96%,CaO含量小于 0.14%,K/Na比值大于16.7,显示高钾、低钠、贫钙的特征。
6 讨论

H b px 100-C b 4.2.22.8.15.3.10.5.7.23.19.03.3.22 H 692 4241101001311212996$b px 98 H 3.1.0.0.2.4 M t-C 717 423.62 120.00 8.00 0.07 15122.20 1.16 2.03 986.21 b96H O c p 735439.6.2.2.3.7 4.63 120.99 9.20 0.11 14122.53 0.97 2.01 985.91 t-b H95-Mb px C 749441.5.22.2 11.00.5.6.10.8.4.47 4.06 0.00 100.20 1311 H 212986 c p H b94 t-O 5 760 41.3.78.0.48 12.7.20.3.7.09 1.50 3.29 80.03 1412.10 20 M 2986 b H93 c pt-O 3 773 42.7.62.0.00 11.7.3.7.09.7 0.44 10.16 0 3.01 1311.34 21 M 2986#H b c p-O b 916 792 41.4.17.7.77 11.4.30.9.3.1 0.48 4.09 90.03 1411.11 21 H 2996 H b90 pxb -C 810540.9.67.2.07 11.5.6 10.14.2 13.6 12 0.27 3 021.09 1.98 976.18带岩相H H b c p.6.8.7.0.2部b-O 8283413.23 101.52 8.90 0.11 14122.48 0.83 2.01 986.21下89H H b86 O c p 860342.1.4.4.0.2 4.44 110.00 100.09 14122.21 1.16 2.04 100 6.18 b t-"84 H -M c p 5.1.88.5.32.0.11.9.0.12.19.02.1.22 H b O 891 4231101001312212996 b t-82 H c p 4.1.77.0.01.4.11.7.6.10.49.01.3.11 H b-M O 916 4141111001311212996)b px w t%H b-C 9372.5.05.3.64.0.13.6.8.35.10.01.5.33 i nt r us i o n(80H 4241011001310212986 H b c p-O b 795 954.7 40.54.3 11.69.0.80.1.7.3.48 4.05 00.00 14.09 11 H 9212986)t%o ng g e b tw H -M c p 3.3.8.4.5.7.1(H !78b H O 969 414.65 110.32 100.12 13112.47 0.89 2.02 996.13成t he组b t-物f r o m H -M c p 5.8.91.4.68.9.12.5.0.31.13.02.8.05化77H b O 988 4041101001312212996氧要b t-主H b-M O c p 9984.1.72.4.51.30.21.0.5.45.86.02.0.09的ho r nbl e nde 76H 414111901411202996石o f闪角I VSi体o x i de s型 ) 位岩a j o r 带回号 类m(数O3O3 nO g O O O O 占格M 相旋品 石 度点Si O2i O2 T l2e O a O F a2 e2o t a l F 子M岩 样M C K2 N H2T红岩 深A 离2阳2表a bl e T.781.270.470.010.020.271.000.972.010.841.150.490.220.010.700.710.330.911 1057.05 0 1.79 0.30 0.40 0.01 0.00 0.99 0.01 3.30 0.00 1.92 0.08 0.55 0.22 0.00 0.77 0.71 0.34 2.56 1021 0.58 2.09 0.06 0.52 0.01 0.11 1.15 0.00 3.15 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.71 0.19 0.09 0.73 0.69 0.36 2.39 1056 0.14.801.180.470.010.000 1.31 0.01.02 30.00 1.88.12 00.60 0.20.00 00.70 0.72.32 02.03 1082 0.07.901.190.420.010 0.17 1.02.00 03.20 0.03.95 10.03 0.68.05 00.14 0.76.71 00.34 2.35 959.41 0.661.270.410.010.000.331.040 2.94 0.00.83 10.17 0.53.22 00.00 0.69.73 00.30 1.84 1091.13 0.891.140.460.010 0.09 1.15.00 03.14 0.03.89 10.09 0.62.21 00.07 0.73.71 00.33 2.29 1080.31 0 1.82 0.17 0.42 0.02 0.01 1.32 0.00 3.06 0.00 1.97 0.03 0.63 0.21 0.01 0.70 0.72 0.32 2.04 1027 0.25 1.79 0.10 0.36 0.01 0.17 1.11 0.00 3.24 0.03 1.92 0.04 0.68 0.16 0.13 0.75 0.73 0.30 2.36 1040 0.69 1.82 0.15 0.49 0.01 0.00 1.28 0.01 3.06 0.00 1.92 0.08 0.55 0.22 0.00 0.70 0.72 0.32 2.13 1021 0.11.781.230.430.010.040.241.000.063.010.901.090.520.220.030.710.720.320.052 1020.27 0.891.040.530.010.110.301.000.003.030.861.110.500.280.080.700.710.320.082 1071.11 0.671.140.450.020.180.241.000.972.050.721.220.460.210.130.710.740.290.931 1114.28 0.911 0.08.51 00.01 0.08 1.23.00 03.09.02 01.88 0.10 0.62 0.20 0.06 0.72.71 00.33 2.25 1084.15 0.10 1.88 0.19 0.52 0.02 0.04 1.28 0.00 2.96 0.01 1.86 0.13 0.58 0.17 0.03 0.70 0.70 0.34 1.97 1062-0.95.07 1.05 0.55 0.02 0.08 0.35 1.00 0.97 2.02 0.91 1.07 0.59 0.21 0.05 0.69 0.70 0.33 0.03 210480-.911.080.530.030.170.161.000.043.050.821.130.580.160.130.730.710.330.202 1066.12 0 l l i n ++a g g a a a IA l)I VA 32V IA T M F e F e C M M C N N K+)V +值2e +比F +)2e )O]+2l F ℃N 4]数+e F A +N[6[系3e ++i +逸度T(%T位C位B位A位 子F g T 3e 氧离M +F 和阳+/(3/(/(度F e M g Si/Si A l/Si M g 温

b b 51 H -M t-G 5.3.6.8.4.5.5 p 15414.87 100.47 100.18 13112.55 0.85 2.00 986.18 1.82 0.06 A b H b 52p-G 4.9.7.1.5.2.2.6 A 30 40411.35 110.20 01311.58 2.77 0.00 298.12 6.88 1.08 0 b&b 54 H t-G 4.8.7.1.4.2 p-M 70414.41 111.76 8.80 0.14 14112.43 0.60 2.04 996.15 1.85 0.18 A b H b-G p 3 114.8.7.7.3.1.9 A 141 39.48 511.00 011.15 01212.18 2.42 1.99 198.99 5.01 2.06 0带相b岩b部H t-G 342.51.7.87.9.22.3.1.89.62.02.1.24.76.12上57-M 179 4100100131120299610 A p b H b 58-G 4.1.6.8.8.1.9 A p 211 423102.02 9.90 0.21 13112.95 0.42 2.02 986.24 1.76 0.13 b b H64 t-G 4.8.1.7.2 p-M 221413.64 120.65 8.80 0.10 14112.92 0.50 2.02 986.09 1.91 0.32%A b b 65 H t-G 4.4.9.5.6.2.0 p-M 239 403.88 122.79 7.60 0.09 141121.08 2.03 995.97 2.03 0.20 A b b H67 t-G-M 3.9.2.9.8.7 p 270 41.28 312.50 1.80 7.10 01411.42 2.75 0.04 298.17 6.83 1.29 0 Ab H b t-G .9 343.8 71.2 439.9.94.2.9 11 M 40.00 100.09 13122.24 1.63 2.00 985.97 2.03 0.04$H b33 bt-G .5384 4.8 38.4.64.6.6 11.1.9.00 5 M 011.11 01212.44 2.25 1.97 197.91 5.05 2.00 0带H b204 G b 4134.5.75.7.14.60.07.0.1.11.41.01.3.03.97.08相40311270151221298610岩部px中b#H 22t-C-M 4.4.25.5.00.20.08.6.2.43.44.02.1.13.87.13 b 543 41411090141221299610 H b px"H 72t-C 4.4.9.5.9.8.9 M 596 40.82 311.81 011.11 01211.81 2.82 0.00 298.06 6.94 1.17 0 H b107 c p!2.4.7.7.00.00.06.6.0.55.28.03.2.11.90.14 M t-O 633 41411090141221299610 I VSi I VA l l 2 IA V a bl e 位带 号型)m O 占T 相回品类(数O3 i O2O3O e O nO O g O a O旋a2o t a l石子度点岩 样Si O2 T l2 A F e2F M M C N K2H2T 离]4[2深岩阳表T位续o nt i nue d C辉.55.02.05.36.00.96.01.84.14.60.16.04.69.72.30.03 1086.10铁00010201000000020-磁-b p-G;A.53.09岩长0.03 0.15 0.31 1.00 0.90 2.04 0.80 1.16 0.59 0.15 0.10 0.69 0.71 0.32 0.91 110940-b-辉G;岩石0.49 0.02 0.20 1.09 0.00 3.04 0.06 1.79 0.15 0.54 0.11 0.15 0.74 0.71 0.33 2.12 1034 0.20辉铁磁.62.55闪0.02 0.00 0.48 1.05 0.77 2.00 0.90 1.10 0.54 0.27 0.00 0.65 0.69 0.35 0.80 11052-0 px-角t-C 出.50.08-M b 得0.03 0.10 0.35 1.00 0.91 2.03 0.77 1.21 0.63 0.12 0.07 0.69 0.72 0.30 0.88 111420-H; 算岩石1计为.40.03.23.23.00.99.06.77.17.68.08.16.71.73.30.92 1125.30辉 数00010201000000010铁px-磁系其据.41.01.07.09.00.10.02.87.11.73.10.06.74.70.37.12 1099.22t-C 根M 量00010301000000020;岩石O含.43.01.31.93.00.11.07.84.09.54.20.25.77.69.37.21 1038.48辉 ;H2闪 )00000301000000020 px-角1998-C ,a l..36b;H e t 0.01 0.17 0.95 0.00 0.22 3.05 0.87 1.09 0.60 0.14 0.15 0.77 0.71 0.34 0.32 21029.64 0岩e l l石o w P(.56.01.00.27.00.11.00.96.04.61.31.00.71.69.35.36 1086.06px-辉 算00010301000000020;C 计岩 件辉X软.65.55橄.01.00.47.01.85.00.97.03.69.24.00.66.69.35.93 1081A 00010201000000010铁-磁据闪3+根e.42c p-角F和0.01 0.24 0.95 0.00 0.30 3.03 0.93 1.04 0.57 0.27 0.20 0.78 0.71 0.34 0.63 21040.73 0t-O-M 数b 子离.47;H岩 .阳0.01 0.00 0.14 1.02 0.23 3.00 0.91 1.09 0.61 0.27 0.00 0.74 0.71 0.33 0.54 21097.36 0辉岩橄 长铁 辉.43.08铁磁0.01 0.09 0.44 1.00 0.85 2.03 0.90 1.08 0.74 0.16 0.06 0.67 0.70 0.35 0.69 11113c p-磁-0t-O 石;M 灰岩-磷.52b.01.00.11.03.20.00.87.13.60.24.00.74.71.33.58 1111.21辉00010301000000020橄t-G闪p-M;A i l)-角T n ++岩M 3e 2a g g a a a IA c p F F e C M M C N N K+)V +-O 长值2e +b 辉比F +)2e )O ;H 铁]+2l F ℃N 岩6数+e A +N -磁[系3e F++i b辉逸A位B位 ’度T(g子C位+/(F T +3e 氧-橄t-G离M +F 和c p ;M阳3e /(/(度 :O 岩F g M Si/Si l/Si A M g 温 注长
角闪石的成分除受其寄主岩浆总成分的影响外,很大程度上与岩浆的结晶条件(温度、压力、氧逸度、水逸度、碱度等强度参数)有关。前人研究表明,随着压力的升高,钙质角闪石的Si含量降低,全铝AlT、AlVI和Na2O含量则升高;AlIV与Ti呈正相关关系,与温度、压力及氧逸度有关,角闪石中AlIV和Ti含量随温度的升高而增加,而AlVI含量随温度的变化不明显 (Hammarstrom and Zen,1986;Blundy and Holland,1990;Ague,1997;Ridolfi et al.,2008,2010)。红格岩体角闪石和金云母的镜下观察未发现固溶体分离形成的出溶条纹,其电子探针成分可以代表它们结晶时的原始成分,因此,角闪石和金云母成分可以用来估算红格岩体形成时的物理化学条件。
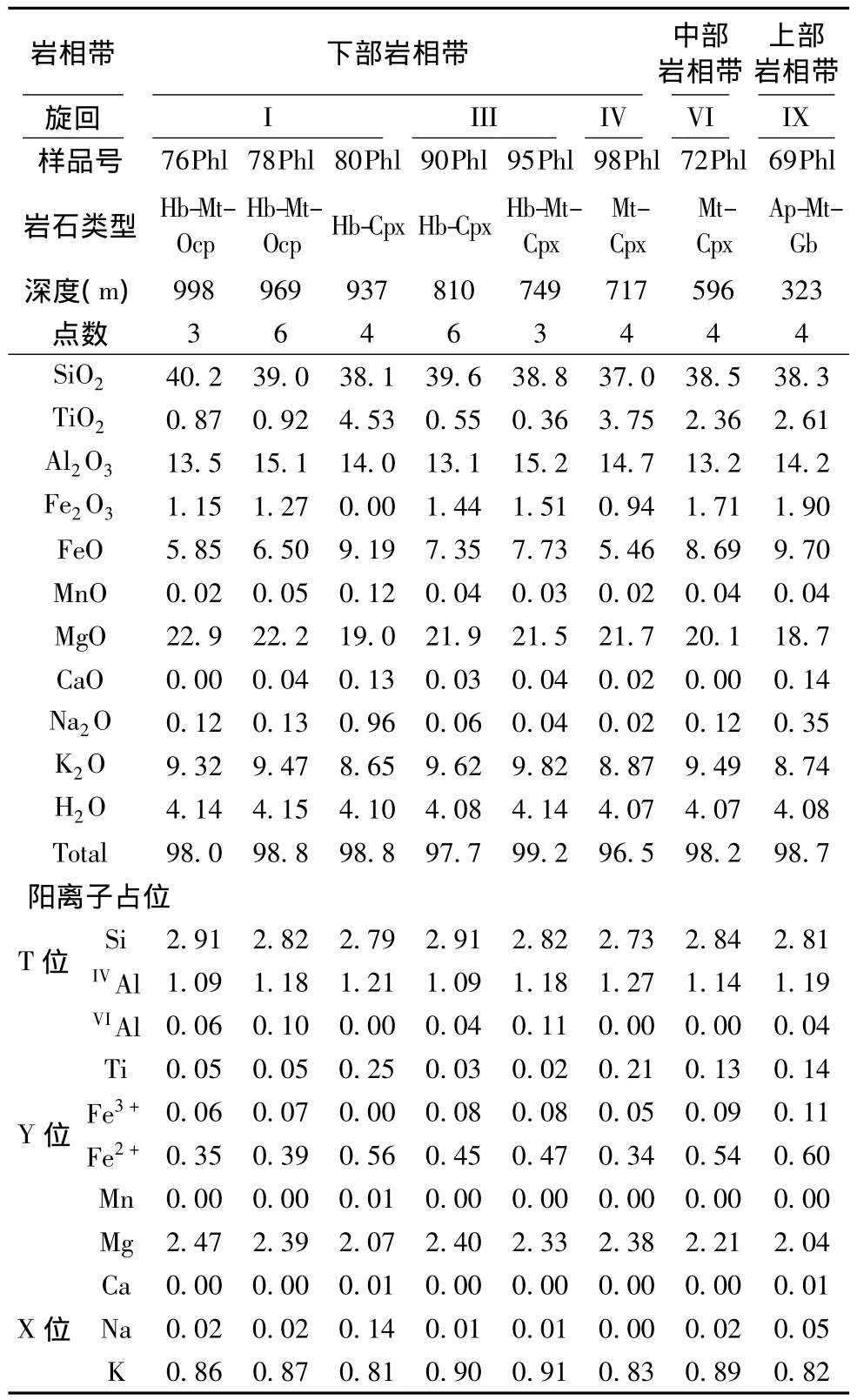
表3 红格岩体金云母的主要氧化物组成(wt%)Table 3 Major oxides of phlogopite from the Hongge intrusion(wt%)
6.1 角闪石和金云母的成因
角闪石的嵌晶状结构及其在光学显微镜下显示的均一干涉色均表明红格岩体的角闪石是岩浆成因的,而非后期热液蚀变的产物(Luan et al.,2014)。红格岩体角闪石Al2O3含量为10.5% ~12.0%,Si/(Si+Ti+Al)=0.69~0.74,结合钙质角闪石的Al2O3-TiO2分类图解(图6a)可知,红格岩体角闪石具有幔源岩浆角闪石的特征(Al2O3>10%,Si/(Si+Ti+Al)≤0.765)(姜常义和安三元,1984);其Al/Si比值为0.30~0.37,Mg/(Fe3++Fe2++VIAl)比值为1.69~2.63,具有中-基性岩浆角闪石的特征(Al/Si=0.10~0.67,Mg/(Fe3++Fe2++VIAl)=1.50~2.0),在 Al/Si-Mg/(Fe3++Fe2++VIAl)图解上,投影在中-基性岩浆角闪石区域(图6b)(据薛君治等,1987)。将红格岩体金云母的化学分析结果在MgO-FeOT/(MgO+FeOT)图上投点,主要落在幔源岩浆相关区域(图6c)(周作侠,1986,1988),暗示红格岩体金云母的形成也与幔源岩浆作用有关。上述特征都说明红格岩体角闪石和金云母都是与幔源岩浆作用有关的原生矿物。
6.2 角闪石结晶温度和压力估算
邓晋福(1983)提出了通过Ca/(Ca+Na+K)数值计算角闪石结晶温度的公式:
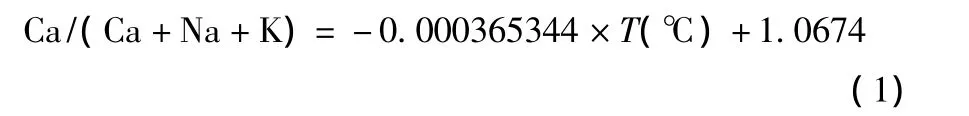
根据公式(1)计算得出,红格岩体角闪石的结晶温度为1000~1100℃,与Luan et al.(2014)通过MELTs模拟计算得出的角闪石结晶温度(~1080℃)相吻合。如图3a所示,Fe-Ti氧化物呈自形被角闪石包裹,说明Fe-Ti氧化物结晶早于角闪石,其结晶温度也高于角闪石。Luan et al.(2014)通过MELTs模拟得出磁铁矿开始结晶的温度为1165℃,所以红格岩体钒钛磁铁矿矿层的形成温度大致为1100~1165℃,略高于攀枝花层状岩体中钒钛磁铁矿矿层的形成温度(1079~1121℃,张晓琪等,2011),这可能是因为红格岩体母岩浆富含水分,从而促进了磁铁矿的早期结晶(Luan et al.,2014)。
Ernst and Liu(1998)给出了从玄武质岩浆中结晶的角闪石中Al2O3和TiO2含量随温度、压力同时变化的曲线格子,可用于半定量估算角闪石结晶时的温度和压力。红格岩体角闪石Al2O3含量主要分布在10.5% ~12.0%,TiO2含量在3.5% ~5.0%左右(表2),通过内插法得出角闪石结晶时温度在960~1040℃之间,而压力小于2.6kbar(图7)。这种半定量方法估算的角闪石结晶温度明显低于根据公式(1)定量计算的角闪石结晶温度(1000~1100℃),所以其估算的压力也偏大,通过角闪石结晶温度(1000~1100℃)校正后得出其结晶压力小于2.2kbar,暗示红格岩体的侵位深度小于7.3km。
6.3 氧逸度估算及其相对变化
角闪石和金云母中都含有变价元素Fe,其Fe3+/Fe2+比值对氧逸度(fO2)的变化非常敏感。如图8a,b所示,下部岩相带和中部岩相带每个旋回内,从下往上红格岩体角闪石Fe3+/(Fe3+/Fe2+)比值逐渐降低,与全岩Fe3+/Fe2+和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值的变化一致(图8c,d),暗示下部岩相带和中部岩相带每一次新补充的岩浆在结晶分异过程中氧逸度是逐渐降低的。Ridolfi et al.(2008)得出了根据角闪石分子式计算其结晶时氧逸度的公式,并且他们对公式进行了校正(Ridolfi et al.,2010):

根据公式(2)计算出红格岩体角闪石结晶时氧逸度变化范围在NNO-0.55到NNO+0.73之间(表2、图8b)。

图6 红格岩体角闪石和金云母成因判别图解(a)-角闪石Al2O3-TiO2图解(据姜常义和安三元,1984);(b)-角闪石Mg/(Fe3++Fe2++VIAl)-Al/Si图解(据薛君治等,1986);(c)-金云母MgO-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)图解(据周作侠,1986)Fig.6 Binary plots of the hornblende and phlogopite from the Hongge intrusion(a)-Al2O3-TiO2diagram of hornblende(after Jiang et al.,1984);(b)-Mg/(Fe3++Fe2++VIAl)-Al/Si diagram of hornblende(after Xue et al.,1986);(c)-MgO-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)diagram of phlogopite(after Zhou,1986)
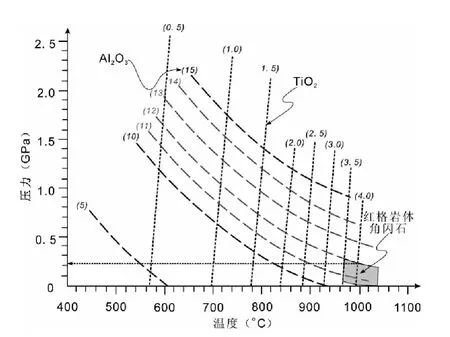
图7 角闪石 Al-Ti温压曲线格子(据 Ernst and Liu,1998)Fig.7 Temperature and pressure grid ofAl-Tiin hornblende(after Ernst and Liu,1998)
如图9所示,红格岩体三个岩相带金云母在Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解中投点均位于NNO(镍-氧化镍)缓冲剂附近并与其平行(Wones and Eugster,1965),说明红格岩体金云母结晶时的氧逸度为NNO(~FMQ+0.7),与公式(2)计算得出的角闪石氧逸度相吻合。而根据角闪石成分计算得出其形成温度为1000~1100℃(见上文),即其对应的氧逸度绝对值(lgfO2)在-10.8到-8之间(图10)。红格岩体角闪石和金云母都属于晶间矿物,其结晶温度低于磁铁矿的结晶温度(~1165℃,Luan et al.,2014),而且其结晶时的氧逸度也是低于磁铁矿的。所以,推测红格岩体磁铁矿结晶时的氧逸度高于NNO+0.73(FMQ+1.43),在1165℃时的绝对氧逸度也大于-7.3(图10)。
V作为一种变价元素对氧逸度的变化也非常灵敏,其在磁铁矿与硅酸盐熔体之间的分配系数主要受到氧逸度的影响(Horn et al.,1994;Canil,1999,2002;Toplis and Corgne,2002;Mallmann and O’Neill,2009)。V在磁铁矿中主要以V3+的形式存在,而岩浆中V的价态随着氧逸度的升高可能从V3+变成V5+,所以磁铁矿中V的含量会随着氧逸度的升高而降低。V在磁铁矿中的分配系数(DV磁铁矿/玄武质岩浆=26,Rollinson,1993)远远高于其在钛铁矿中的分配系数(DV钛铁矿/玄武质岩浆=8.8 ~9.2,Dygert et al.,2013),所以磁铁矿发生钛铁矿的固溶体分离时,其V含量基本不受影响,因此磁铁矿中的V可以用来估算氧逸度的相对变化。如图8e所示,下部岩相带和中部岩相带每个旋回自下而上,磁铁矿中V2O3含量是逐渐升高的,因为伴随着磁铁矿的结晶,岩浆中的Fe3+/Fe2+比值和氧逸度随之降低。这与下部岩相带和中部岩相带全岩Fe3+/Fe2+和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值,以及角闪石Fe3+/Fe2+比值反映的氧逸度变化相吻合。而在上部岩相带IX旋回中,从下往上全岩Fe3+/Fe2+和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值随着磁铁矿V2O3含量的降低而逐渐升高,与下部岩相带和中部岩相带的变化规律相反(图8c,d,e),暗示IX旋回在分离结晶过程中氧逸度是升高的,这可能与上部岩相带母岩浆中的P2O5有关。红格岩体上部岩相带母岩浆与下部岩相带和中部岩相带的残余岩浆混合后富集P2O5(Luan et al.,2014)。Toplis et al.(1994a,b)的实验研究表明玄武质熔体中的P2O5会还原熔体中的Fe3+,从而抑制磁铁矿的结晶。但随着磷灰石的大量结晶,熔体中的P2O5含量逐渐降低,导致Fe3+/Fe2+比值升高和氧逸度逐渐升高,磁铁矿结晶受到的抑制作用也随之逐渐减小。所以全岩Fe3+/Fe2+和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值从下往上逐渐升高,而磁铁矿中的V2O3含量逐渐降低。但上部岩相带IX旋回中角闪石的Fe3+/Fe2+比值与下部岩相带和中部岩相带角闪石变化一致,并未呈现出相反的变化趋势。这是因为磷灰石大量结晶消耗了熔体中的P2O5,残余岩浆中的P2O5含量降低,导致其对残余岩浆中Fe3+/Fe2+比值的影响减小。所以,从残余岩浆中结晶出来的角闪石的Fe3+/Fe2+比值不受P2O5影响,显示出与下部岩相带和中部岩相带角闪石相同的变化趋势。

图8 红格岩体角闪石Fe3+/(Fe3++Fe2+)比值(a)和氧逸度(b),全岩Fe3+/Fe2+(c)和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值(d),以及磁铁矿V2O3含量(e)随深度变化柱状图全岩和磁铁矿数据来自Luan et al.(2014)Fig.8 Stratigraphic variations of the Hongge hornblende Fe3+/(Fe3+/Fe2+)ratios(a)and oxygen fugacity(b),the whole-rock Fe3+/Fe2+and Mt/(Mt+Ilm)ratios(c and d,respectively),the magnetite V2O3contents(e)The whole-rock and magnetite data are from Luan et al.(2014)
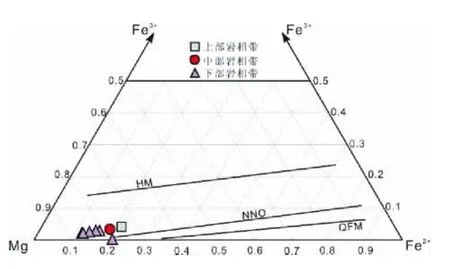
图9 红格岩体金云母 Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg三元图解(据Wones and Eugster,1965)Fig.9 Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg ternary diagram of phlogopite in the Hongge intrusion(after Wones and Eugster,1965)

图10 红格岩体角闪石lgfO2-T曲线图实线代表氧缓冲剂(据Eugster and Wones,1962),虚线代表红格岩体角闪石结晶时的氧逸度Fig.10 Plots of lgfO2vs.T diagram of the hornblende from the Hongge intrusionSolid represents oxygen buffer(after Eugster and Wones,1962)and dash represents the oxygen fugacity when the hornblende of the Hongge intrusion crystallized
7 结论
(1)红格岩体角闪石的结晶温度为1000~1100℃,推测钒钛磁铁矿矿层的形成温度大致为1100~1165℃。
(2)红格岩体角闪石的结晶压力小于2.2kbar,暗示红格岩体的侵位深度小于7.3km。
(3)红格岩体角闪石和金云母结晶时的氧逸度为NNO-0.55~NNO+0.73,估算磁铁矿结晶时的氧逸度高于NNO+0.73。
(4)下部岩相带和中部岩相带每个旋回自下而上,角闪石Fe3+/(Fe3+/Fe2+)比值以及全岩Fe3+/Fe2+和Mt/(Mt+Ilm)比值有规律地逐渐降低,暗示每一次新补充的岩浆随着磁铁矿的结晶分异,氧逸度总是逐渐降低的。而上部岩相带IX旋回氧逸度的升高是受上部岩相带母岩浆中P2O5的制约。
致谢 野外考察得到了四川106地质队的大力帮助;在中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学国家重点实验室完成电子探针分析过程中,得到周国富研究员、刘世荣副研究员给予的诸多指导和帮助;在此一并深表谢意!
Ague JJ.1997.Thermodynamic calculation of emplacement pressures for batholithic rocks,California:Implications for the aluminum-inhornblende barometer.Geology,25(6):563 -566
Bai ZJ,Zhong H,Naldrett AJ,Zhu WG and Xu GW.2012.Whole-rock and mineral composition constraints on the genesis of the giant Hongge Fe-Ti-V oxide deposit in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province,Southwest China.Econ.Geol.,107(3):507 -524
Barling J,Weis D and Demaiffe D.2000.A Sr-,Nd-and Pb-isotopic investigation ofthe transition between twomegacyclic ofthe Bjerkreim-Sokndal layered intrusion,South Norway.Chem.Geol.,165(1-2):47-65
Blundy JD and Holland TJB.1990.Calcic amphibole equilibria and a new amphibole-plagioclase geothermometer. Contrib. Mineral.Petrol.,104(2):208 -224
Botcharnikov RE,Almeev RR,Koepke J and Holtz F.2008.Phase relations and liquid linesofdescentin hydrous ferrobasalt-Implications for the Skaergaard intrusion and Columbia River flood basalts.J.Petrol.,49(9):1687 - 1727
Canil D.1999.Vanadium partitioning between orthopyroxene,spinel and silicate melt and the redox states of mantle source regions for primary magmas.Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta,63(3-4):557-572
Canil D.2002.Vanadium in peridotites,mantle redox and tectonic environments:Archean to present.Earth Planet.Sci.Lett.,195(1-2):75-90
Chen GY,Sun DS and Yin HA.1988.Genetic Mineralogy and Prospecting Mineralogy.Chongqing:Chongqing Publishing House,555-647(in Chinese)
ChungSL and Jahn BM.1995. Plume-lithosphereinteraction in generation of the Emeishan flood basalts at the Permian-Triassic boundary.Geology,23(10):889-892
Deng JF.1983.Melt-mineral Equilibrium Thermodynamics.Beijing:Geological Publishing House(in Chinese)
Dygert N,Liang Y and Hess P.2013.The importance of melt TiO2in affecting major and trace element partitioning between Fe-Ti oxides and lunar picritic glass melts.Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta,106:134-151
Ernst WG and Liu J.1998.Experimental phase equilibrium study of Al and Ti contents of calcic amphibole in MORB-A semiquantitative thermobarometer.Am.Miner.,83(9 -10):952-969
Eugster HP and Wones DR.1962.Stability relations of the ferruginous biotite,annite.J.Petrol.,3(1):82 -125
Feeley TC and Sharp ZD.1996. Chemical and hydrogen isotope evidencefor in situ dehydrogenation ofbiotitein silicic magma chambers.Geology,24(11):1021 -1024
Foster MD.1960.Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas.U.S.Geol.Surey.Prof.Paper,345:11 -49
Guo F,Fan WM,Wang YJ and Li CW.2004.When did the emeishan mantle plume activity start?Geochronological and geochemical evidence from ultramafic-mafic dikes in southwestern China.Int.Geol.Rev.,46(3):226 -234
Hammarstrom JM and Zen EAN.1986.Aluminum in hornblende:An empirical igneous geobarometer.Am.Miner.,71(11 -12):1297-1313
Horn I,Foley SF,Jackson SE and Jenner GA.1994.Experimentally determined partitioning of high field strength-and selected transition elements between spinel and basaltic melt.Chem.Geol.,117(1 -4):193-218
Hou T,Zhang ZC and Pirajno F.2012.A new metallogenic model of the Panzhihua giant V-Ti iron oxide deposit in the Emeishan large province:Based on high-Mg olivine-bearing wehrlites and new field evidence.Int.Geol.Rev.,54(15):1721 -1745
Hou T,Zhang ZC,Encarnacion J,Santosh M and Sun YL.2013.The role recycled oceanic crust in magmatism and metallogenesis:Os-Sr-Nd isotpes,U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of picritic dykes in the Panzhihua giant Fe-Ti oxide deposit,central Emeishan large igneous province.Contrib.Mineral.Petrol.,165(4):805 -822
Jiang CY and An SY.1984.On chemical characteristics of calcic amphiboles from igneous rocks and their petrogenedid sigificance.J.Mineral.Petrol.,(3):1 - 9(in Chinese with English abstract)
Kesler SE, Issgonis MJ,Brownlow AH,Damon PE, Moore WJ,Northcote KE and Preto VA.1975.Geochemistry of biotites from mineralized and barren intrusivesysterms.Econ.Geol.,70(3):559-567
Leake BE,Woolley AR,Arps CES,Birch WD,Gilbert MC,Grice JD,Hawthorne FC,Kato A,Kisch HJ,Krivovichev VG,Linthout K,Laird J,Mandaring JA,Maresch WV,Nichel EH,Rock NMS,Schumacher JC, Simth DC, Stephenson NCN, UngarettiL,Whittaker EJW and Youzhi G.1997.Nomenclature of amphiboles:Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association,Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names.The Canadian Mineralogist,82(9 -10):1019-1037
Luan Y,Song XY,Chen LM,Zheng WQ,Zhang XQ,Yu SY,She YW,Tian XL and Ran QY. 2014. Key factorscontrolling the accumulation of the Fe-Ti oxides in the Hongge layered intrusion in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province,SW China.Ore Geol.Rev.,57:518-538
Mallmann G and O’Neill HSC.2009.The Crystal/Melt partitioning of V during mantle melting as a function of oxygen fugacity compared with some other elements(Al,P,Ca,Sc,Ti,Cr,Fe,Ga,Y,Zr and Nb).J.Petrol.,50(9):1765 -1794
Naldrett AJ.1989. Magmatic Sulfide Deposits. New York:Oxford University Press
Pang KN,Li CS,Zhou,MF and Ripley EM.2008a.Abundant Fe-Ti oxide inclusions in olivine from the Panzhihua and Hongge layered intrusions,SW China:Evidence for early saturation of Fe-Ti oxides in ferrobasaltic magma.Contrib.Mineral.Petrol.,156(3):307 -321
Pang KN,Zhou MF,Lindsley D,Zhao D and Malpas J.2008b.Origin of Fe-Ti oxide ores in mafic intrusions:Evidence from the Panzhihua intrusion,SW China.J.Petrol.,49(2):295 -313
Pang KN,Li CS,Zhou MF and Ripley EM.2009.Mineral compositional constraints on petrogenesis and oxide ore genesis of the Late Permian Panzhihua layered gabbroic intrusion,SW China.Lithos,110(1 -4):199-214
Powell R,Holland T and Worley B.1998.Calculating phase diagrams involving solid solutions via non-linear equations,with examples using THERMOCALC.J.Metamorphic Geol.,16(4):577 -588
Ridolfi F,Puerini M,Renzulli A,Menna M and Toulkeridis T.2008.The magmatic feeding system of El Reventador volcano(Sub-Andean zone, Ecuador) constrained by texture, mineralogy and thermobarometry ofthe 2002 erupted products. J. Volcanol.Geotherm.Res.,176(1):94-106
Ridolfi F,Renzulli A and Puerini M.2010.Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas:An overview,new thermobarometric formulations and application to subductionrelated volcanoes.Contrib.Mineral.Petrol.,160(1):45 -66
Rollinson HR. 1993. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation,Presentation,Interpretation. New York:Longman Scientific &Technical,1 -108
Selby D and Nesbitt BE.2000.Chemical composition of biotite from the Casino porphyry Cu-Au-Mo mineralization, Yukon, Canada:Evaluation of magmatic and hydrothermal fluid chemistry.Chem.Geol.,171(1 -2):77 -93
Song XY,Wang YL,Zhang ZJ,Ma RZ.1997.Critical factors of the formation of the rhythmic layering of layered intrusion.Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,24(4):61-64(in Chinese with English abstract)
Song XY,Zhou MF,Hou ZQ,Cao ZM,Wang YL and Li YG.2001.Geochemical constraints on the mantle source of the upper Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts,southwestern China.Int.Geol.Rev.,43(3):213-225
Song XY,Hou ZQ,Cao ZM,Lu JR,Wang YL,Zhang CJ and Li YG.2001.Geochemical characteristic and period of Emei Igneous Province.Acta Geologica Sinica,75(4):498 -506(in Chinese with English abstract)
Song XY,Keays RR,Xiao L,Qi HW and Ihlenfeld C.2009.Platinumgroup element geochemistry of the continental flood basalts in the central Emeisihan Large Igneous Province,SW China.Chem.Geol.,262(3-4):246-261
Song XY,Qi HW,Hu RZ,Chen LM,Yu SY and Zhang JF.2013.Formation of thick stratiform Fe-Ti oxide layers in layered intrusion and frequent replenishment of fractionated mafic magma:Evidence from the Panzhihua intrusion,SW China.Geochem.Geophys.Geosyst.,14(3):712 -732
Tao Y,Ma YS,Miao LC and Zhu FL.2009.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the Jinbaoshan ultramafic intrusion,Yunnan Province,SW China.Chin.Sci.Bull.,54(1):168 -172
Toplis MJ,Carroll MR and Libourel G.1994a.The effect of phosphorus on the iron redox ratio,viscosity,and density of an evolved ferrobasalt.Contrib.Mineral.Petrol.,117(3):293 - 304
Toplis MJ,Libourel G and Carroll MR.1994b.The role of phosphorus in crystallisation processes of basalt:An experimental study.Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta,58(2):797-810
Toplis MJ and Carroll MR.1995.An Experimental study of the influence of oxygen fugacity on Fe-Ti oxide stability,phase relations,and mineral-melt equilibria in ferro-basaltic systems.J.Petrol.,36(5):1137-1170.
Toplis MJ and Carroll MR.1996.Differentiation of ferro-basaltic magmas under conditions open and closed to oxygen:Implications for the Skaergaard intrusion and other natural systems.J.Petrol.,37(4):837-858
Toplis MJ and Corgne A.2002.An experimental study of element partitioning between magnetite,clinopyroxene and iron-bearing silicate liquids with particular emphasis on vanadium.Contrib.Mineral.Petrol.,144(1):22 - 37
Wager LR and Brown GM.1968.Layered Igneous Intrusions.Edinburgh and London:Oliver and Boyd,1-588
Wones DR and Eugster HP.1965.Stability of biotite:Experiment,theory,and application.Am.Miner.,50(9):1228 -1272
Xia ZD,Jiang CY,Xia MZ,Ling JL and Lu RH.2011.Characteristics and magmatism of mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions.Northwestern Geology,44(1):85-94(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu YG,Chung SL,Jahn BM and Wu GY.2001.Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China.Lithos,58(3 -4):145-168
Xu YG,Luo ZY,Huang XL,He B,Xiao L,Xie LW and Shi YR.2008.Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on crustal melting associated with the Emeishan mantle plume.Geochim.Cosmochim.Acta,72(13):3084-3104
Xue JZ,Bai XR and Chen W.1986.Genetic Mineralogy.Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,114 -121(in Chinese)
Yu SY,Song XY,Chen LM and Li XB.2014.Postdated melting of subcontinental lithospheric mantle by the Emeishan mantle plume:Evidence from the Anyi intrusion,Yunnan,SW China.Ore Geol.Rev.,57:560 -573
Zhang XQ,Zhang JF,Yuan P,Song XY,Guan JX and Deng YF.2011.Implications of compositions of plagioclase and olivine on the formation ofthe Panzhihua V-Timagnetite deposit,Sichuan Province.Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(12):3675 - 3688(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang XQ,Song XY,Chen LM,Xie W,Yu SY,Zheng WQ,Deng YF,Zhang JF and Gui SG.2012.Fractional crystallization and the formation of thick Fe-Ti-V oxide layers in the Baima layered intrusion,SW China.Ore Geol.Rev.,49:96 -108
Zhang ZC,Mahoney JJ,Mao JW and Wang FS.2006.Geochemistry of picritic and associated basalt flows of the western Emeishan flood basalt province,China.J.Petrol.,47(10):1997 -2019
Zhang ZC,Zhi XC,Chen L,Saunders AD and Reichow MK.2008.Re-Os isotopic compositions of picrites from the Emeishan flood basalt province,China.Earth Planet.Sci.Lett.,276(1 -2):30 -39
Zhang ZC,Mao JW,Saunders AD,Ai Y,Li Y and Zhao L.2009.Petrogenetic modeling of three mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions in the Emeishan large igneous province,SW China,based on isotopic and bulk chemical constraints.Lithos,113(3-4):369-392
Zhang ZC,Hou T,Santosh M,Li HM,Li JW,Zhang ZH,Song XY and Wang M.2014.Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China:An overview.Ore Geology Reviews,57:247-263
Zhong H and Zhu WG.2006.Geochronology of layered mafic intrusions from the Pan-Xi area in the Emeishan large igneous province,SW China.Miner.Deposita,41(6):599 -606
Zhong H, Hu RZ, ZhuWG andLiu BG.2007. Genesis and mineralization of layered intrusion.Earth Science Frontiers,14(2):159-172(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou MF,Malpas J,Song XY,Robinson PT,Sun M,Kennedy AK,Lesher CM and Keays RR.2002.A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province(SW China)and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction.Earth Planet.Sci.Lett.,196(3 -4):113-122
Zhou MF,Robinson PT,Lesher CM,Keays RR,Zhang CJ and Malpas J.2005.Geochemistry, petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Panzhihua gabbroic layered intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits,Sichuan Province,SW China.J.Petrol.,46(11):2253-2280
Zhou MF,Arndt NT,Malpas J,Wang CY and Kennedy AK.2008.Two magma series and associated ore deposit types in the Permian Emeishan large igneous province,SW China.Lithos,103(3 -4):352-368
Zhou ZX.1986.The origin of intrusive mass in Fengshandong,Hubei Province.Acta Petrotogica Sinica,2(1):59-70(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou ZX.1988.Chemical characteristics of mafic mica in intrusive rocks and its geological meaning.Acta Petrotogica Sinica,4(3):63-73(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou ZX.1991.Application of Mg-Fe mica chemical composition,rare elements,REE,Cu,Cl,F to distinguishing petrogenetic types.In:Wu LR and Li BL(eds.).Two Great Mesozoic Types of Porphyry Ore Deposits in the East of China.Beijing:Science Press,76 -82(in Chinese)
附中文参考文献
陈光远,孙岱生,殷辉安.1988.成因矿物学与找矿矿物学.重庆:重庆出版社,555-647
邓晋福.1983.熔浆-矿物平衡热力学.北京:地质出版社
姜常义,安三元.1984.论火成岩中钙质角闪石的化学组成特征及其岩石学意义.矿物岩石,(3):1-9
宋谢炎,王玉兰,张正阶,马润则.1997.层状侵入体韵律层理成因的关键因素.成都理工学院院报,24(4):61-64
宋谢炎,侯増谦,曹志敏,卢记仁,汪云亮,张成江,李佑国.2001.峨眉大火成岩省的岩石地球化学特征及时限.地质学报,75(4):498-506
夏昭德,姜常义,夏明哲,凌锦兰,卢荣辉.2011.镁铁质-超镁铁质层状岩体基本特征及岩浆作用.西北地质,44(1):85-94
薛君治,白学让,陈武.1986.成因矿物学.武汉:中国地质大学出版社,114-121
张晓琪,张加飞,宋谢炎,邓宇峰,官建祥,郑文勤.2011.斜长石和橄榄石成分对四川攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿床成因的指示意义.岩石学报,27(12):3675-3688
钟宏,胡瑞忠,朱维光,刘秉光.2007.层状岩体的成因及成矿作用.地学前缘,14(2):159-172
周作侠.1986.湖北丰山洞岩体成因探讨.岩石学报,2(1):59-70
周作侠.1988.侵入岩的镁铁云母化学成分特征及其地质意义.岩石学报,4(3):63-73
周作侠.1991.Mg-Fe云母的化学成分、微量元素、REE、Cu、Cl、F 等在识别岩石成因类型上的应用.见:吴利仁,李秉伦编.中国东部中生代两类斑岩型矿床.北京:科学出版社,76-82