长白山不同区域人参中挥发性、半挥发性成分的研究
2014-05-14赵锦花杨翠王娟李东浩
赵锦花, 杨翠, 王娟, 李东浩
(延边大学长白山生物资源与功能分子教育部重点实验室,吉林 延吉133002)
0 Introduction
Ginsengis one of the most precious traditional Chinese medicinal perennial herb belonging to the genusPanaxofAraliaceaefamily.Research has shown thatginsengbenefits human health against various diseases,such as increasing resistance to physical,chemical and biologi-cal stresses[1].It has been reported thatginsengcontain properties like anti-aging,anti-diabetic,anti-carcinogenic,analgesic,anti-pyretic,antistress,anti-fatigue,has tranquilizing activities and promote DNA,RNA and protein synthesis activities.Besides,as a traditional medicine,ginsengwas used in cancer patients[2-5].
Typicalginsengcontain,ginsengoils and sugars,organic acids,vitamins,amino acids and peptides.Among them,the main active non-volatile saponins.It is reported that plant volatiles play important role in biological signaling interaction.Ginsengalso contains a wide range of chemical compound classes,such as hydrocarbons,alcohols,aldehydes,ketones,acids,esters and so on.Moreover,the semi-volatile components ofginsengroot have reported containing a number of sequiterpenes[6],which prove that study on volatile and semi-volatile compounds inginsengare vital.Ginsengmatrix is very complex,and in analysis of volatile compounds,the isolation step is necessary before instrumental analysis.There are many sample preparation methods,such as Soxhlet extraction,microwave-assisted extraction,ultrasound-assisted extraction and supercritical extraction[7].Recently,gas purge microsyringe extraction (GP-MSE)was developed by Yang and co-workers, the method is environmentally friendly and can simultaneously analysis volatile and semi-volatile compounds in various sample matrix within a short time(less than 5min)[8-9].In this study,a rapid analysis method was established to investigate the volatile and semi-volatile compounds in Changbai Mountainginsengby gas purge microsyringe extraction(GP-MSE)coupled with gas chromatography mass spectrometry(GC-MS)technology.
1 Experimental
1.1 Chemical
Organic solvents(hexane)were HPLC grade obtained from Caledon(Georgetown,Ont.,Canada).
1.2 Experiment
Ginsengsample was collected in different area of Changbai Mountain,namely Changbai,Erdaobaihe and Fusong county.All of the threeginsengsamples were 4years old.Ginsengsamples were dried by VirTis-Freezer dryer(4KBTXL),grinded and kept in-4℃ until analysis.
Extraction were done using GP-MSE.5mgginsengsample were used with GP-MSE extrac-tion time of 4min;extraction temperature of 250℃;gas flow rate and condensing temperature were set to 2.0mL/min and-4℃,respectively.
1.3 GC-MS analysis
Volatile and semi-volatile chemicals were analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC/MS,GC-2010/QPMS-2010,Shimadzu)with DB-5MS capillary column (30m,0.25mm ID,0.25μm film thickness,J & W Scientific,USA).Helium (>99.999%pure)was used as carrier gas with a flow rate of 1.0 mL·min-1.The injector was set to 280℃ with splitless mode and the interface temperature was set to 280℃,the column temperature was maintained at 45℃ for 4min and then programmed from 45to 250℃at 4℃/min,250to 280℃at 6℃/min,then hold for 5min.Qualitative and quantitative data of volatile and semi-volatile chemicals was obtained using scan mode,the scan range wasm/z45-450.
2 Results and conclusion
2.1 Volatile and semi-volatile constituents in ginseng
Based on the GP-MSE sample preparation method coupled with GC-MS,each peak was qualitative compared with mass spectrum database NIST11 (National Institute of Standards and Technology).Quantitative was evaluated by relative area.The results showed 45compounds were determined fromginseng,accounting for 86%of the total peak area.Table 1listed major volatile and semi-volatile compounds determined fromginseng.The few most abundant compound were 2-Furanmethanol(13.91%),Hexadecanoic acid (12.42%),cis-Linoleic acid (9.24%),and so on.Inginseng,the volatile and semi-volatile chemical species cover furans(30%),acids(30%),aldehydes and ketones (12%),esters(6%),alcohols(3%),phenols(3%),and other heterocyclic compounds(2%).
2.2 Comparison of volatile and semi-volatile constituents in different Changbai area ginseng
Generally,ginsengs are cultivated under shade for 4to 6years to yield high-qualitygin-sengwith medicinal effects[10].With the different cultivate area,the chemical constituents inginsengcould be different,GP-MSE-GC-MS method were applied to compare volatile and semi-volatile compounds ofginsengtaken from Changbai,Erdaobaihe and Fusong county.
The typical gas chromatographic-mass spec-trum chromatograms obtained from three different areaginsengswere shown in Fig.1.Certain similarities and differences of compounds can be found from the chromatograms.Similarity of volatile compounds is higher than this obtained from semi-volatile compounds(shown in Fig.1).
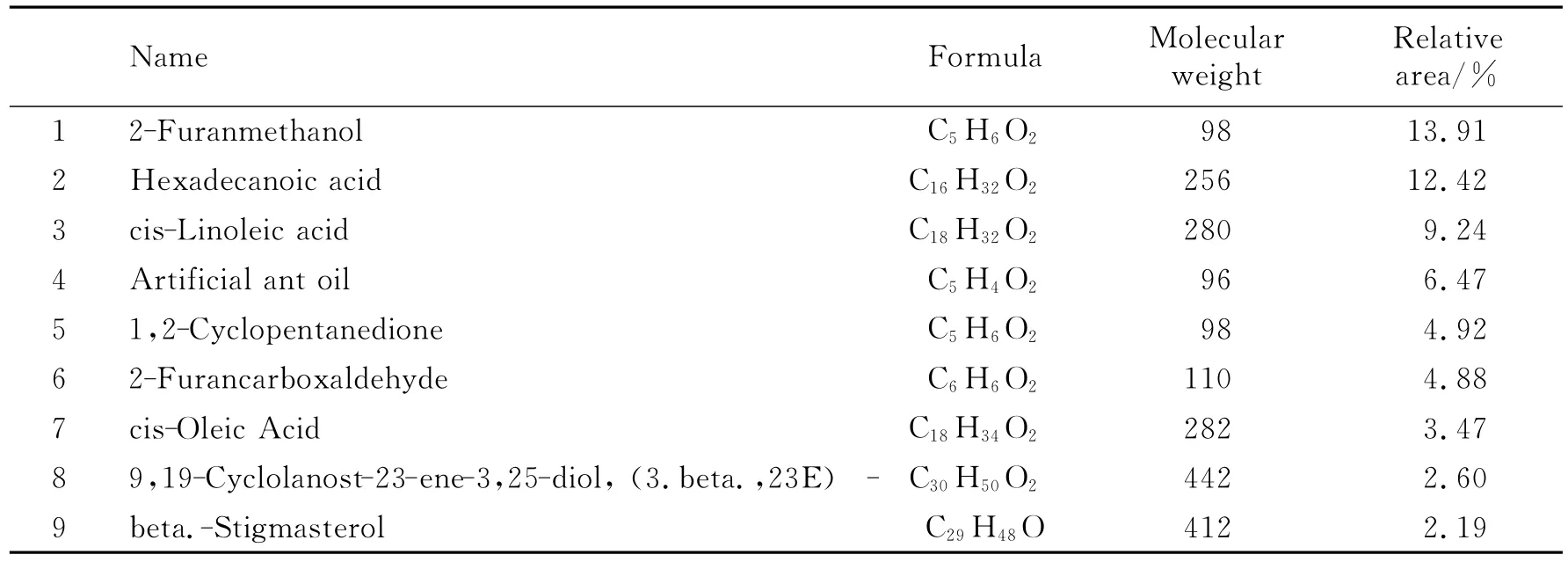
Table 1 Major volatile and semi-volatile compounds in ginseng

Fig.1 Different volatile and semi-volatile compounds in ginsengfrom different Changbai Mountain area
Fig.2showed that there are significant differences in 15selected compound of volatile and semi-volatile compound by comparing with amount(peak area).
As shown in Fig.1and Fig.2,most of compounds are frequently found in different area ofginseng,while their contents are significantly different.Typical chemicals are Furfural,2-Furanmethanol,3-Methyl-1,2-cyclopentanedione,3-Ethyl-2-hydroxy-2-cyclopenten-1-one,Creosol,Palmitic acid,Linoleic acid and so on.Although these compounds were all found inginseng,there are 2to 3times differences in amount.It has involvement with the differentginsenggrowth environment,such as soil moisture,microorganism and so on.So,different growth environments will induce different production and accumulation mechanism of the chemicals in plant.

Fig.2 Comparison of volatile and semi-volatile compounds in different Changbai Mount area (1.Furfural;2.2-Furanmethanol;3.Acetylfuran;4.3-Methyl-1,2-cyclopentanedione;5.Furyl hydroxymethyl ketone;6.3-Ethyl-2-hydroxy-2-cyclopenten-1-one;7.Creosol;8.gamma-Muurolene;9.n-Hexadecanoic acid methyl ester;10.Palmitic acid;11.n-Nonadecanol-1;12.Linoleic acid;13.Ethyl octadec-9,12-dienoate;14.Behenic alcohol;15.Stigmasterol.)
3 Conclusion
The gas purge microsyringe extraction coupled with GC/MS is a suitable analytical method for determination of volatile and semi-volatile chemicals in theginseng.Results of the comparison study are indicated that differences of different area ofginsengare mainly originated from different content of the volatile and semi-volatile chemicals.
[1]Lee H,Lee H,Yu H,et al.A comparison between high hydrostatic pressure extraction and heat extraction of ginsenosides from ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer)[J].J Sci Food Agric,2011,91:1466-1473.
[2]Angelova N,Kong H,Van der H R,et al.Recent methodology in the phytochemical analysis of ginseng[J].Phytochem Anal,2008,19:2-16.
[3]Woo H,Shin B,Cho I,et al.Antiobesity effect of carbon dioxide supercritical fluid extracts of Panax ginseng C.A.Meyer[J].J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem,2011,54:738-743.
[4]Chang Y,Seo E,Gyllenhaal C,et al.Panax ginseng:a role in cancer therapy?[J].Integr Cancer Ther,2003,2:13-33.
[5]Xie J,Zhou Y,Dey L,et al.Ginsengberry reduces blood glucose and body weight in db/db mice[J].Phytomedicine,2002,9:254-258.
[6]A M Abd El-Aty,Kim I,Kim M,et al.Determination of volatile organic compounds generated from fresh,white and red Panax ginseng(C.A.Meyer)using a direct sample injection technique[J].Biomed Chromatogr,2008,22:556-562.
[7]Sahena F,Zaidul I,Jinap S,et al.Application of supercritical CO2in lipid extraction:a review[J].J Food Eng,2009,95:240-253.
[8]Yang C,Wang J,Li D.Microextraction techniques for the determination of volatile and semivolatile organic compounds from plants:a review[J].Anal Chim Acta,2013,799:8-22.
[9]杨翠,任春燕,李东浩,等.气流式吹扫液相微萃取[J].延边大学学报:自然科学版,2011,37(2):111-114.
[10]Lee K,Kim G,Kim H Y,et al.Volatile compounds of C.A.Meyer cultured with different cultivation methods[J].J Food Sci,2012,77:C805-810.
