A high precision analytic potential function applied to diatomic molecules and ions
2014-05-12YuChangfengandYanXiangan
Yu Changfengand Yan Xiang'an
College of Science,Xi'an Polytechnic University,Xi'an 710048,P.R.China
A high precision analytic potential function applied to diatomic molecules and ions
Yu Changfeng†and Yan Xiang'an
College of Science,Xi'an Polytechnic University,Xi'an 710048,P.R.China
A new analytic potential energy function applied to both neutral diatomic molecules and charged diatomic molecular ions is obtained.The potential energy function is examined by 18 examples for eight different basic kinds of diatomic molecules or ions——homonuclear ground-state for neutral diatomic molecule O2-X3,homonuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecule K2-B1Πu,homonuclear ground-state for charged diatomic molecular ion-X2Πg,homonuclear excited-state for charged diatomic molecular ion-B2,heteronuclear ground-state for neutral diatomic molecule PS-X2Π1/2,heteronuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecule BaO-A1Σ,heteronuclear ground-state for charged diatomic molecular ion37ClF--X2Σ+,heteronuclear excited-state for charged diatomic molecular ion(CS)+-A2Π,etc..It is found that,the theoretical values for the vibrational energy level of molecules calculated with the potential energy function are in high-precision consistence with RKR(Rydberg-Klein-Rees)data or experimental data.
molecular physics;potential energy function;diatomic molecules and ions;Rydberg-Klein-Rees(RKR)method;force constant;spectroscopic parameter
Analytical potential energy functions are of great significance in the study of material science,molecular spectrum,reaction dynamics of atoms and molecules,vibrational and rotational energy-level structures of molecules,interactions between laser and matter,photoionization etc.[1-6].So far,several kinds of representative analytical potential energy functions have been proposed,such as Morse potential[7],Rydberg potential[8],Murrell-Sorbie(M-S)potential[9]and Huxley-Murrell-Sorbie(HMS)potential[10],etc..The potentials above are valid in describing the behaviors of some individual or classificatory molecules and ions,but none are suitable for all situations.One of the best and most extensively used analytical potential energy functions is M-S potential which is applied to most of the ground-state diatomic molecules.But M-S potential is shown to be unsatisfactory in describing the excited-state diatomic molecules.In this paper,by using a cosine function as a basic potential function and,through derivations,a high precision analytical potential function is obtained,which can describe many kinds of diatomic molecules--the neutral diatomic molecules and the charged diatomic molecular ion etc..
This potential energy function is examined with 18 examples of diatomic molecules and compared with RKR data and M-S potential.It is shown that the computational precision on the vibrational energy level of molecules calculated with this potential function is superior to that of M-S potential.
1 Derivation of the high-precision analytic potential function
Suppose that basic potential function of diatomic molecular satisfies Eq.(1)[11]
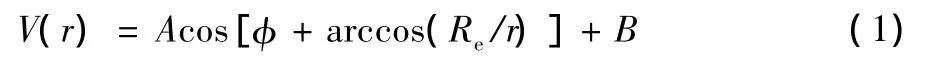
where,r is inter-nuclear distance,A and B are undetermined constants,φ is the equivalent phase difference between two interacting atoms,Reis equilibrium inter-nuclear distance.From Eq.(1)and through theoretical derivations,a universal analytic potential function describing diatomic molecules is obtained
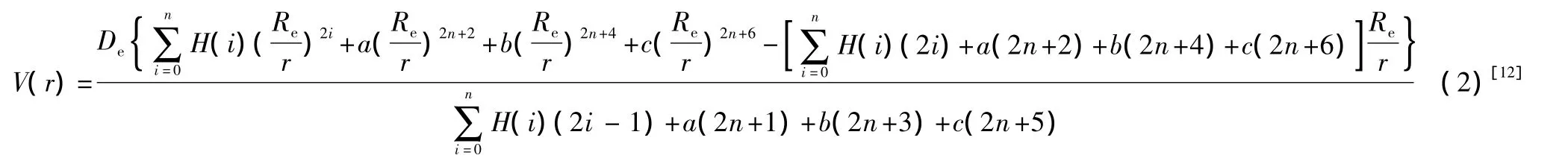
where Deis the dissociation energy of diatomic molecules;H(i)=(2i)!/[4i(i!)2(2i-1)];a,b and c are undetermined parameters which can be determined with the experimental spectroscopic parameters(ωe,ωeχe,αe,Be).For example,when n=1,3,from Eq.(2),we have
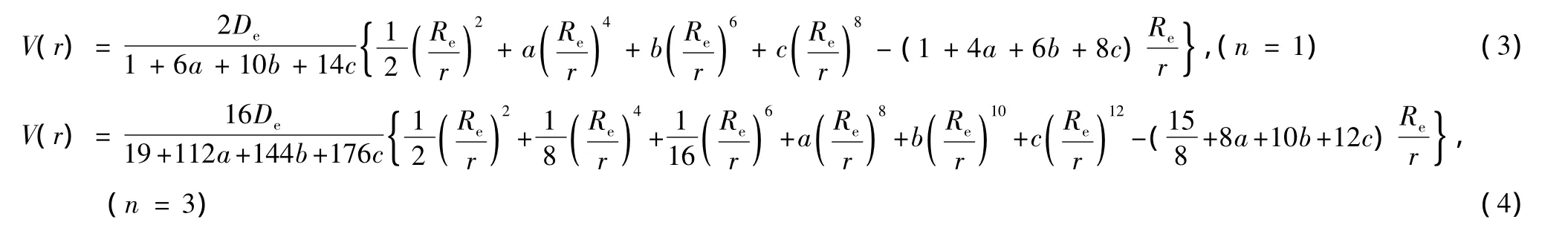
Examinations show that Eq.(3)or Eq.(4)can accurately describe the interaction of diatomic molecules on a larger range of equilibrium internuclear distance in calculating the vibrational energy level of molecules but there is a definite deviation between the potential values of the long-range attractive branch of potential curve and RKR data or experimental data.So in order to further ameliorate the qualities of the long-range attractive branch,it is necessary to improve the potential energy function.In this paper,through derivations,an analytical potential function which can describe the whole range of the potential curve is obtained.The potential function is as follows


We use the exactly same function for the potentialsV1(a,b,c,r)and V2(a0,b0,c0,r),which can be selected from one of Eq.(3)and Eq.(4).From Eq.(5)to Eq.(8),when n=1,3 the following potential functions can be given


the parameters in Eq.(9)and Eq.(10)can be calculated by the following relations

the undetermined parameters a,b,c can be determined with the experimental spectroscopic parameters(ωe,ωeχe,αe,Be)of diatomic molecules.But a0,b0,c0can be obtained by solving the following equations
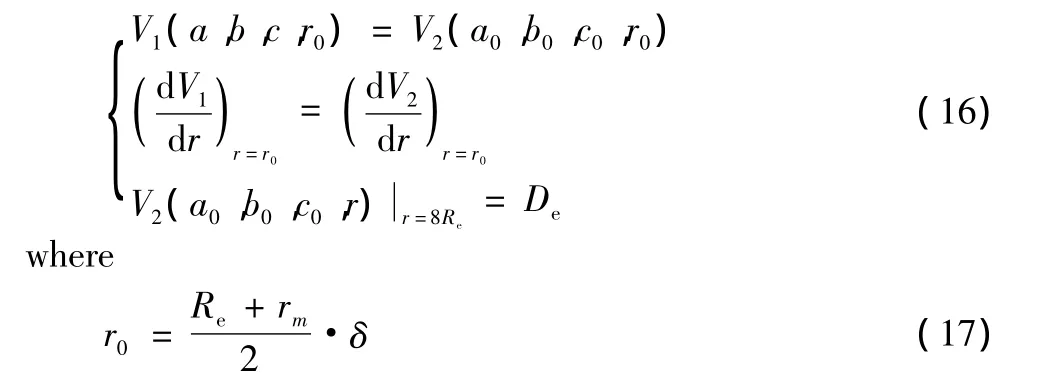
Here,rmis the value of inter-nuclear distance when V1(a,b,c,r)+De=De.δ is a parameter for adjusting precision.
2 Using experimental spectroscopic parameters to determine a,b,c
The undetermined parameters a,b and c can be determined with the experimental spectroscopic parameters(ωe,ωeχe,αe,Be)of diatomic molecules or ions.The principle of this method is,according to the relation between undetermined parameters and force constants,to obtain a,b,c by solving linear equations.The relation between force constants and spectroscopic parameters are as follows
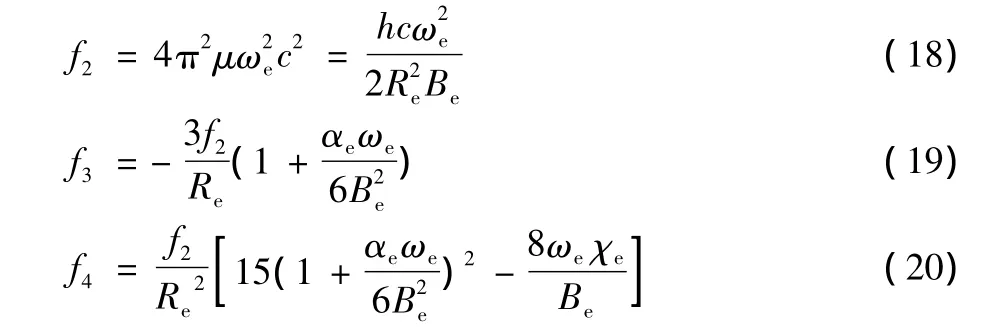
where the force constants at the equilibrium inter-nuclear distance can be given as follows

From Eq.(3)and Eq.(4),when n=1,3,the following linear equations can be obtained

The Eq.(22)and Eq.(23)above are all linear equations,which have unique real number solutions for the undetermined parameters a,b and c.In order to compare the potential functions Eq.(9)and Eq.(10)with M-S potential,we also provide it in the following form

The relations between undetermined parameters a1,a2,a3and force constants are as follows

3 RKR inverse-method
Although Rydberg-Klein-Rees(RKR)inverse-method is a pure theoretical method,the values of the vibrational energy level of molecules calculated with this method are extremely and exactly consistent with the experimental data.Hence,the RKR data are usually considered as the experimental data.Under the condition of no experimental data,one of the best method is to use the RKR data to examine a certain potential energy function.The method for calculating RKR data is given as follows[13]

Where rmaxand rminare the maximum and minimum classical turning points of the inter-nuclear distance for a molecule vibrating with energy U,U is the value of potential energy.From Eq.(26),f(unit:cm)and g(unit:cm-1)can be determined when the spectroscopic parameters ωe,ωeχe,αe,Beare given,and then the maximum and minimum classical turning pointsrmaxand rmincan be calculated by using Eq.(26),and the potential curve of U(r)can be plotted out.
4 Examinations for the analytical potential energy function
Substituting the potential parameters in Table 4 and Table 5 into Eq.(9)or Eq.(10),a specific analytic potential energy function of diatomic molecules can be obtained.For examining potential energy functions of Eq.(9)and Eq.(10),18 kinds of neutral diatomic molecules and charged diatomic molecular ions have ever been investigated,and the values of the vibrational energy level of molecules calculated by the potential function are compared with RKR data,M-S potential or experimental data.The experimental data on spectroscopic parameters and the potential parameters of part diatomic molecules calculated from Eq.(16)to Eq.(25)are listed in Table 1 to Table 4.The potential parameters r0,a0,b0,c0are calculated with Eq.(16).Table 5 is calculated with Eq.(11)to Eq.(15).The vibrational energy levels and classical turning points of heteronuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecules AsCl-1Δ and heternuclear ground-state for charged diatomic molecular ion(CS)+-X2Σ+calculated by Eq.(9),Eq.(10),Eq.(24)and Eq.(26)are listed in Table 6 and Table 7.(Note:the relation between zero-point dissociation energy Deand ground-state dissociation energy D0given by Ref.[14] is De=D0+ ωe/2- ωeχe/4).For the limitation of the length,the computational values of the vibrational energy level of other diatomic molecules are omitted.
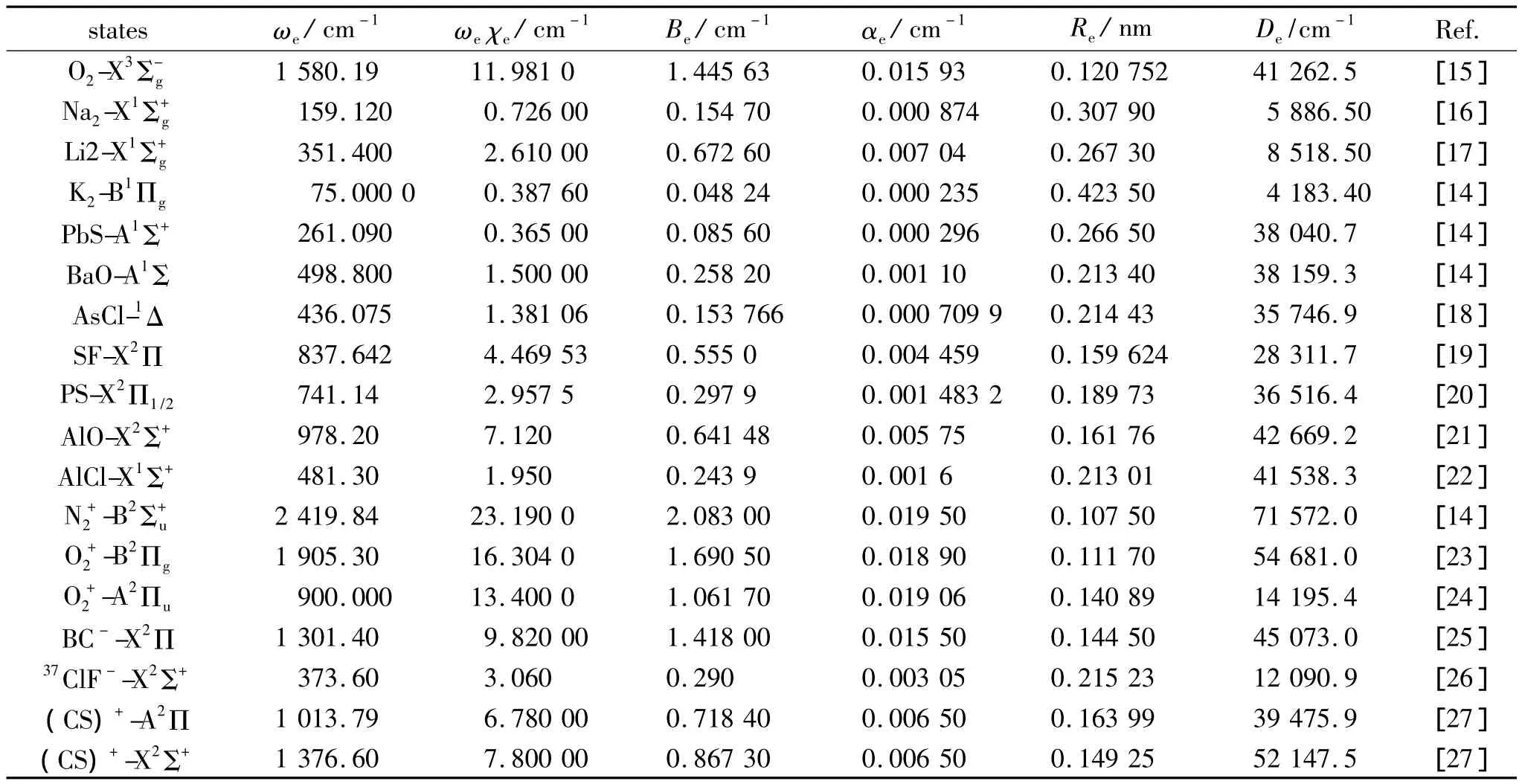
Table 1 Experimental spectroscopic parameters of diatomic molecules表1 双原子分子光谱实验参数

Table 2 Parameters of part diatomic molecules表2 部分双原子分子势能参数

Table 3 Parameters a0,b0,c0of part the electronic states表3 部分电子态的a0,b0,c0参数
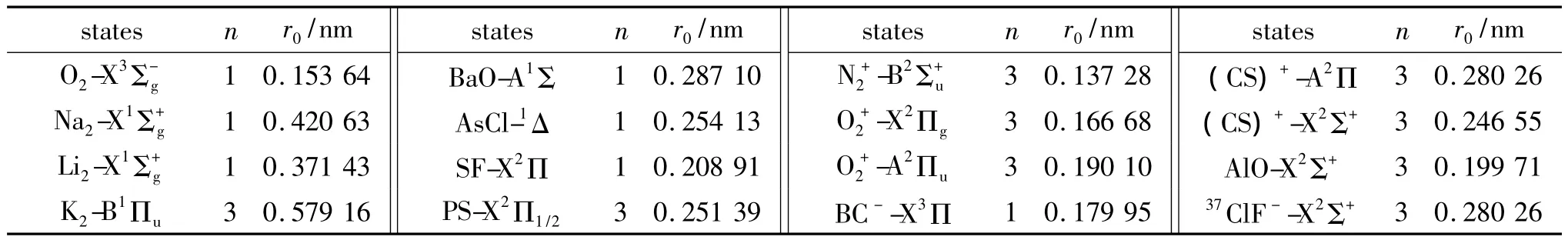
Table 4 n and r0parameters of diatomic molecules表4 双原子分子的n和r0参数
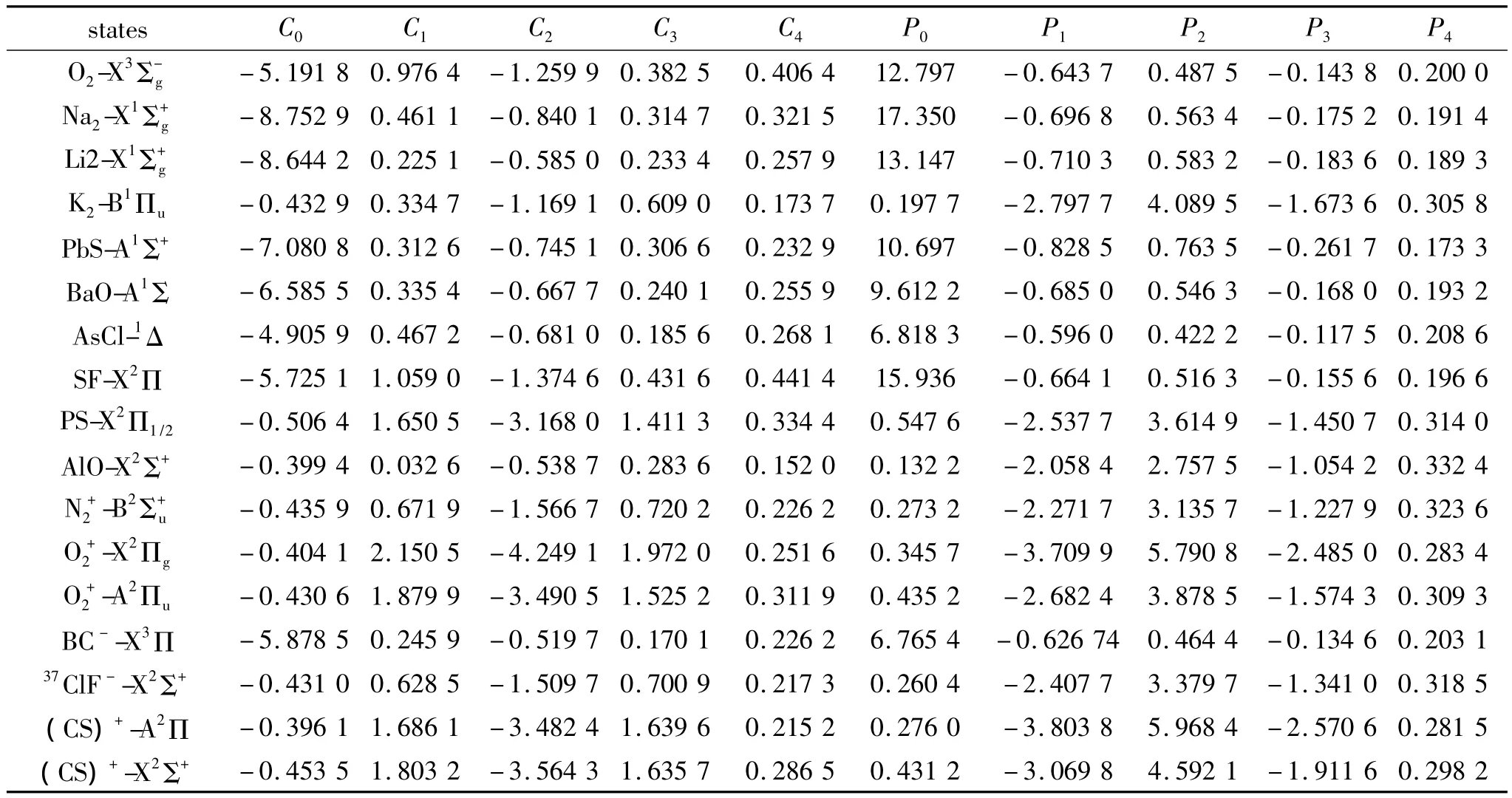
Table 5 Parameters of diatomic molecules表5 双原子分子势能参数
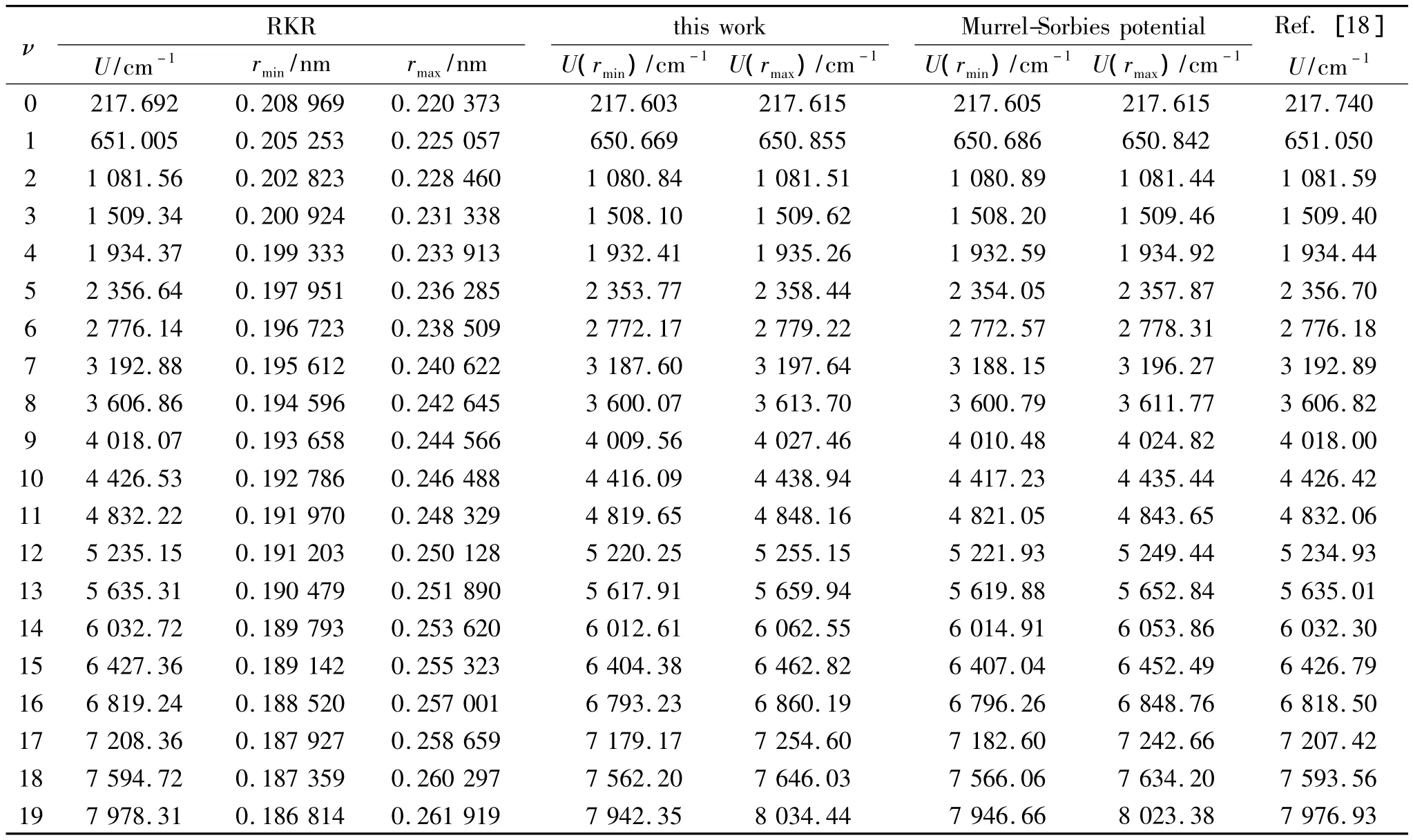
Table 6 The vibrational energy levels of heteronuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecular ion AsCl-1Δ表6 异核激发态中性双原子分子AsCl-1Δ的振动能级
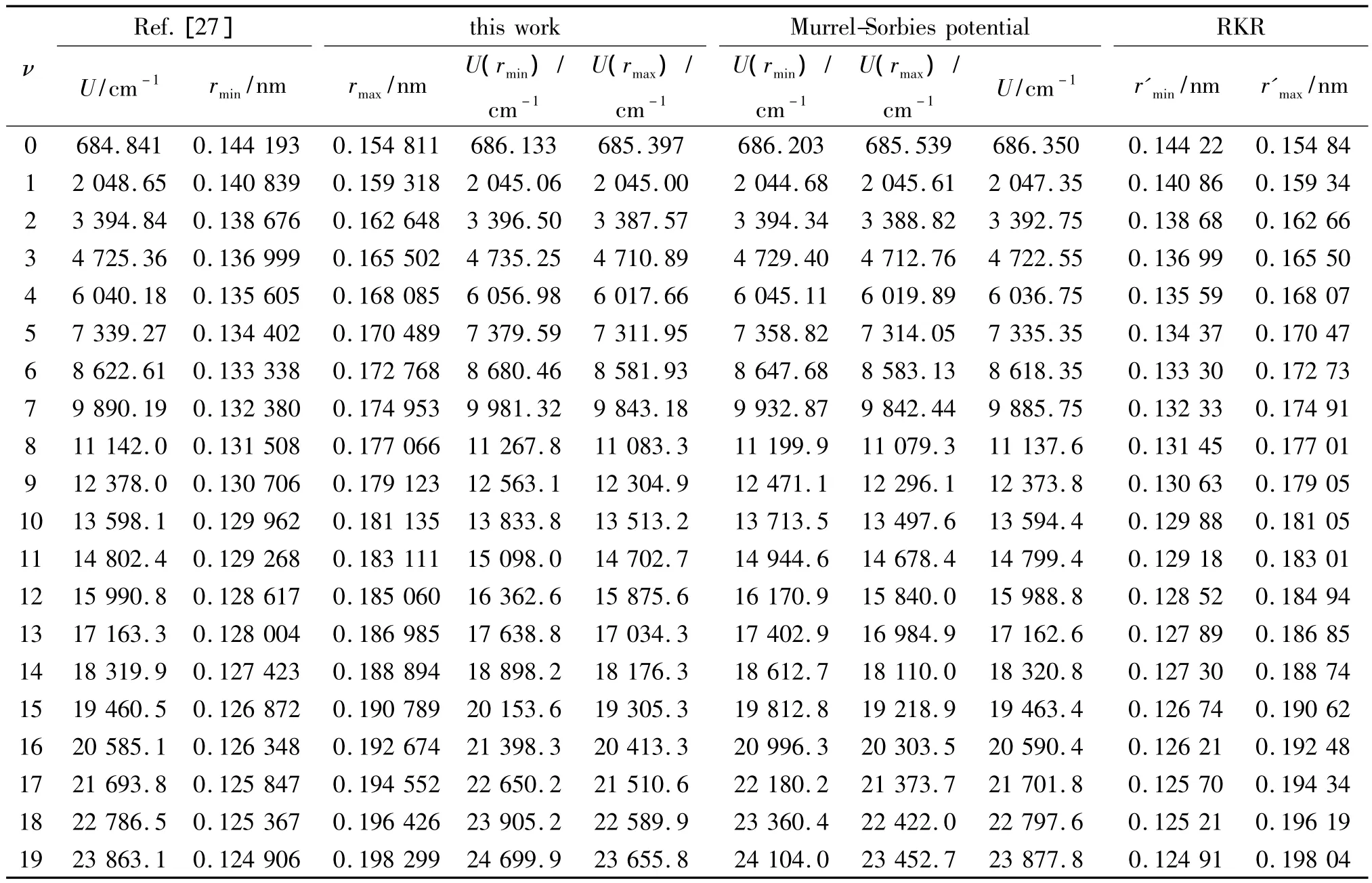
Table 7 The vibrational energy levels of heteronuclear ground-state for charged diatomic molecular ion(CS)+-X2Σ+表7 异核基态带电双原子分子离子(CS)+-X2Σ+的振动能级
In order to examine the calculation precision of Eq.(9)and Eq.(10),the root-mean-square-errors(RMSE)and relative root-mean-errors between the potential values of 18 kinds of electronic states and RKR data or experimental data are listed in Table 8.For comparison,the calculation precision of MS are also listed in Table 8.The RMSE and relative root-meansquare-errors(RRMSE)are given in the following formulas

The potential curves of four diatomic molecules are plotted with Origin 6.0 by using potential Eq.(9)and Eq.(10),RKR data and M-S potential are shown in Table 1.

Table 8 The root-mean-square-errors and relative root-mean-errors between the values of potentials and RKR表8 势能函数值与RKR数据比较的均方根误差和相对均方根误差
As shown from Table 6 to Table 8,the potential function given in this paper can describe the behaviors of the whole range of the potential curve.And as for the computational precision,this potential function is superior to M-S potential.
Conclusions
A new analytic potential energy function which is used to describe diatomic molecules and ions is presented with a basic potential function V(r)=Acos[φ +arccos(Re/r)]+B,and good results are obtained.This potential function has two merits:① The good universality and high computational precision.This potential is suitable for describing eight kinds of fundamental diatomic molecules——homonuclear ground-state for neutral diatomic molecules,homonuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecules,homonuclear ground-state for charged diatomic molecules,homonuclear excited-state for charged diatomic molecules,heteronuclear ground-state for neutral diatomic molecules,heteronuclear excited-state for neutral diatomic molecules,heternuclear ground-state for charged diatomic mo-lecular ions,heteronuclear excited-state for charged diatomic molecular ions.② As concerning the computational precision,this potential function is superior to M-S potential which is extensively used in atomic and molecular physics at present.

Fig.1 Energy curves of diatomic molecules(☆=exp.;○=RKR;—=this work;┄=M-S)图1 双原子分子势能曲线
[1]Yiannopoulou A ,Jeung G H,Park S J,et al.Undulation of the potential energy curves for highly excited electronic states in diatomic molecules related to the atomic orbital undulations[J].Physical Review A,1999,59(2):1178-1186.
[2]Liu Guoyue,Sun Weiguo,Feng Hao.Studies on the analytical potential energy function of diatomic molecular ion XY+using variational method[J].Science in China Series G:Physics,Mechanics& Astonomy,2004,47(2):154-164
[3]Maniero M,Acioli P H.Full configuration interaction pseudopotential determination of the ground-state potential energy curves of Li2and LiH[J].International Journal of Quantum Chemistry,2005,103(5):711-717.
[4]Xie Ruihua,Gong Jiangbin.Simple three-parameter model potential for diatomic systems:from weakly and strong to metastable molecular ions[J].Physical Review Letters,2005,95(26):263202-1-263202-4.
Therefore,the translators shall be equipped with the knowledge of Chinese history and culture.In addition,the translation shall adapt to Chinese audience needs.Following discussion is made from these three aspects,i.e.adaptability to history fact,culture and audience’s need.
[5]Yu Changfeng,Yan Kun,Liu Daizhi.A universal analytic potential-energy function based on a phase factor[J].Acta Metallurgica Sinca 2006,19(6):455-468.
[6]Esteves C S,de Oliveira H C B,Ribeiro L,et al.Modeling diatomic potential energy curves through the generalized exponential function [J]. Chemical Physics Letters,2006,427(1):10-13.
[7]Morse P M.Diatomic molecules according to the wave mechanics.Ⅱ.vibrational levels[J].Physical Review Letters,1929,34:57-64.
[8]Rydberg R.Graphische darstellung einiger bandenspektroskopischer ergebnisse[J].Zeitschrift für Physik,1932,73(5/6):376-385.
[9]Murrel J N,Sorbie K S.New analytic from for the potential energy curves of stable diatomic state[J].Journal of the Chemical society,Faraday Transactions,II,1974,70:1552-1557.
[10]Huxley P,Murrel J N.Ground-state diatomic potential[J].Journal of the Chemical society,Faraday Transactions,II,1983,79:323-328.
[11]Yu Changfeng.Principles of phase[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press,2007:26-233.(in Chinese)
于长丰.相位力学原理[M].北京:国防工业出版社,2007:26-233.
[12]Yu Changfeng.Research on the universal analytic potential function applied to diatomic molecules[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2012,32(8):2056-2060.(in Chinese)
于长丰.普适性双原子分子解析势能函数的研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析.2012,32(8):2056-2060.
[13]Rees A L G .The calculation of potential-energy curves from band-spectroscopic data[J].Proceedings of the Physical Society,1947,59(6):998-1008.
[14]Herzberg G.Molecular spectra and molecular structure(I.Spectra of diatomic molecules)[M].Beijing:Science Press,1983:69,394-474.(in Chinese)
Herzberg G.分子光谱与分子结构 (双原子分子光谱)[M].北京:科学出版社,1983:69,394-474.
[15]Huber K P,Herzberg G,Molecular Spectra and molecular structure,IV.constant of diatomic molecules table[M].Princeton:Van Nostrand,1979:64.
[16]Yu Benhai,Dai Qirun,Shi Deheng,et al.Investigations on spectroscopic parameters,vibrational levels,classical turning points and internal rotation and centrifugal distortion constant for the X1Σ+gstates of sodium dimer[J].Chinese Physics,2007,16(10):2962-2967.
[17]Shi Deheng,Sun Jinfeng,Zhu Zunlue,at al.Investigation on vibrational levels,inertial rotation and centrifugal distotion constants of7Li2(X1Σ+g)[J].Acta Physica Sinica.2008,57(1):165-171.(in Chinese)
施德恒,孙金锋,朱遵略,等.7Li2(X1Σ+g)分子的振动能级、转动惯量及离心畸变常数 [J].物理学报,2008,57(1):165-171.
[18]Zhu Zunlue,Lang Jianhua,Qiao Hao.Study on spectroscopic properties and molecular constants of the ground and excited states of AsCl free-radical[J].Acta Physica Sinica.2013,62(11):113103-1-113103-7.(in Chinese)
朱遵略,郎建华,乔 浩.AsCl自由基的基态及激发态的势能函数与光谱常数的研究 [J].物理学报,2013,62(11):113103-1-113103-7.
[19] Zhu Zunlue,Lang Jianhua,Qiao Hao.Spectroscopic properties and molecular constants of the ground and excited states of SF molecule[J].Acta Physica Sinica.2013,62(16):163103-1-163103-6.(in Chinese)
朱遵略,郎建华,乔 浩.SF分子基态及低激发态势能函数与光谱常数的研究 [J].物理学报,2013,62(16):163103-1-163103-6.
[20]Liu Hui,Xing Wei,Shi Deheng,et al.Potential energy curve and spectroscopic properties of PS(X2II)radical[J].Acta Physica Sinica,2013,62(20):202104-03104-6.(in Chinese)
刘 慧,邢 伟,施德恒,等.PS自由基 (X2II)态的势能曲线和光谱性质 [J].物理学报,2013,62(20):203104-1-203104-6.
[21]Kou Suha,Liu Yan,Lang Jianghua,et al.Theoretical study on the potential energy curve for the ground states of AlO molecule[J].Journal of Henan Normal University Natural Science Edition.2013,41(3):68-70.(in Chinese)
寇素华,刘 艳,郎建华,等.AlO分子自由基态势能曲线的理论研究[J].河南师范大学学报自然科学版,2013,41(3):68-70.
[22]Liu Hui,Su Yuelin,Shi Deheng.Study on spectros-copic properties of AlCl(X1Σ+)molecule [J].Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics.2013,30(5):715-722.(in Chinese)
刘 慧,苏跃林,施德恒.AlCl分子X1Σ+电子态的光谱性质 [J].原子与分子物理学报,2013,30(5):715-722.
[23]Kaur S,Mahajan C G.Wei Hua's four-parameter potential comments and computation of molecular constants αeand ωeχe[J].Pramana-Journal of Physics,1999,52(4):409-420.
[24]Chen Hongli,Sun Weiguo,Liu Guoyue,at al.Studies on the potential energy curves of homonuclear diatomic molecular ions using energy consistent method[J].Journal of Atomic Molecular Physics,2006,23(1):27-32.(in Chinese)
陈红丽,孙卫国,刘国跃,等.同核双原子分子离子的势能研究 [J].原子与分子物理学报,2006,23(1):27-32.
[25]Tzeli D,Mavridis A.Continuing our study on the electronic structure of the carbides BC and AlC[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry A,2001,105:1175-1184.
[26]Li Song,Chen Shanjun,Zhu Desheng,et al.Structureand potential energy function of ClF-molecular ion[J].Acta Physico Chimica Sinica,2013,29(4):737-744.(in Chinese)
李 松,陈善俊,朱德生,等.ClF-分子离子的结构与势能函数[J].物理化学学报,2013,29(4):737-744.
[27]Liu Hui,Xing Wei,Shi Deheng,et al.Study on spectroscopic parameters and molecular constants of CS+(X2Σ+)and CS+(A2Π)by MRCI [J].Acta Physica Sinica.2011,60(4):043102-1-043102-1-10.(in Chinese)
刘 慧,邢 伟,施德恒,等.用MRCI方法研究CS+同位素离子X2Σ+和A2Π态的光谱常数与分子常数[J].物理学报,2011,60(4):043102-1-043102-1-10.
双原子分子和离子的高精度解析势能函数
于长丰,严祥安
西安工程大学理学院,西安 710048
研究得到一种既适于中性双原子分子又适于带电双原子分子离子的新的解析势能函数.用8种基本类型的双原子分子——同核中性基态双原子分子O2-X3、同核中性激发态双原子分子K2-B1Πu、同核带电基态双原子分子离子-X2Πg、同核带电激发态双原子分子离子-B2、异核中性基态双原子分子PS-X2Π1/2、异核中性激发态双原子分子BaO-A1Σ、异核带电基态双原子分子离子37ClF--X2Σ+和异核带电激发态双原子分子离子(CS)+-A2Π,通过18个算例对势能函数进行验证,并与RKR(Rydberg-Klein-Rees)实验数据进行比较,计算结果与RKR数据吻合.
分子物理学;势能函数;双原子分子和离子;RKR法;力常数;光谱参数
国家自然科学基金资助项目 (61405151)
于长丰 (1962-),男 (汉族),河北省武邑县人,西安工程大学教授.E-mail:yuh55@126.com
/References:
O 561.1;O 561.3
A
10.3724/SP.J.1249.2014.06561
2014-02-17;
2014-07-27
Foundation:National Natural Science Foundation of China(61405151)
†
Professor Yu Changfeng.E-mail:yuh55@126.com
:Yu Changfeng,Yan Xiang'an.A high precision analytic potential function applied to diatomic molecules and ions [J].Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering,2014,31(6):561-569.(in Chinese)
引 文:于长丰,严祥安.双原子分子和离子的高精度解析势能函数[J].深圳大学学报理工版,2014,31(6):561-569.
【中文责编:晨 兮;英文责编:木 南】
