On Results the Growth of Meromorphic Solutions of Algebraic differential Equations
2013-08-10SUXIANFENGLIXIAOMENGANDHEZHONGWEI
SU XIAN-FENG,LI XIAO-MENGAND HE ZHONG-WEI
(1.Department of Mathematics,Huaibei Normal University,Huaibei,Anhui,235000) (2.Department of Public Education,Jiangxi Bluesky University,Nanchang,330029)
Communicated by Ji You-qing
On Results the Growth of Meromorphic Solutions of Algebraic differential Equations
SU XIAN-FENG1,LI XIAO-MENG1AND HE ZHONG-WEI2
(1.Department of Mathematics,Huaibei Normal University,Huaibei,Anhui,235000) (2.Department of Public Education,Jiangxi Bluesky University,Nanchang,330029)
Communicated by Ji You-qing
In this paper,we give an estimate result of Gol'dberg's theorem concerning the growth of meromorphic solutions of algebraic differential equations by using Zalcman Lemma.It is an extending result of the corresponding theorem by Yuanet al.(Yuan W J,Xiao B,Zhang J J.The general theorem of Gol'dberg concerning the growth of meromorphic solutions of algebraic differential equations.Comput.Math. Appl.,2009,58:1788–1791).Meanwhile,we also take some examples to show that our estimate is sharp.
meromorphic function,algebraic differential equation,normal family, spherical derivative
1 Introduction and Main Results
We assume that the reader is familiar with the elementary Nevanlinna theory of meromorphic functions(see[1–3]).Meromorphic functions are always non-constant,if not otherwise specif i ed.
In the past half century,many authors have studied the growth of meromorphic solutions of complex algebraic differential equations or the systems of complex algebraic differential equations in[4–7].Recently,the main method for investigating the related problems was basically adapted from[8–9],which is called the Zalcman Lemma.
In order to state these results,we introduce some notations:n∈N+={1,2,3,···}, rj∈N for j=1,2,···,n,and put r={r1,r2,···,rn}.Def i ne Ω(w)by

where
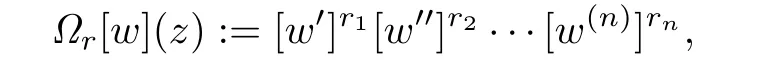
ar(z,w)is a rational function in both variables and I is a f i nite index set,and set Ω0[w]=1. We call
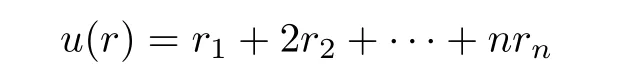
the weight of Ωr(w)and
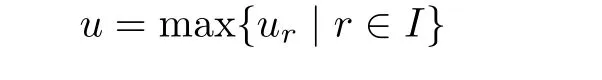
the weight of Ω(w).degz,∞ardenotes the degree at inf i nity in variable z concerning ar(z,w), and

Let F be a family of meromorphic functions defined on a complex domain D.F is said to be normal on D,if for every sequence{fn}∈F,there exists a subsequence{fnj}such that{fnj}locally uniformly converges by spherical distance to a function f(z)meromorphic in D.Conversely,F is not normal on D.
We define spherical derivative of the meromorphic function w(z)by

Bergweiler[5]considered the growth of the solutions of complex differential equation

where Ω[w]is a differential polynomial with the form(1.1),ar(z,w)is a rational function in z and w,and I is a f i nite index set.
As we all know,a research of the growth of meromorphic solution w(z)of the differential equation(1.2)in the complex plane C has become one of important topics.
Bergweiler proved the following result.
Theorem 1.1[5]Let w(z)be any meromorphic solution of the algebraic differential equation(1.2),n>u.Then the growth order σ(w)of w(z)is finite.
Yuan et al.[7]established a general estimate of growth order of w(z),and obtained the following result.
Theorem 1.2[7]Let w(z)be meromorphic in the complex plane,n∈N+,Ω[w]be a differential polynomial with the form(1.1),and n>u.If w(z)satisfies the differential equation(1.2),then the growth order σ(w)of w(z)satisfies

Question 1.1What is the result when the first-order derivative is replaced by kth-order in the left hand side of the equality(1.2)(k∈N+)?
In this paper,we give a general estimate of the order of w(z),which depend on the degrees of coefficients of differential polynomial for w(z),and it may be stated as follows.
Theorem 1.3Let w(z)be a non-polynomial meromorphic function in the complex plane, n,k∈N+,Ω[w]be a differential polynomial with the form(1.1),and nk>u.If w(z) satisfies the differential equation
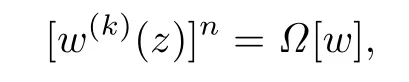
then the growth order σ(w)of w(z)satisfies
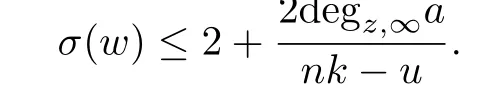
Remark 1.1Theorem 1.2 may be deduced from Theorem 1.3.
We notice that degz,∞a=0 when all ar(z,w)(r∈I)are rational functions in variable w with constant coefficients.Therefore,we can get the following result.
Corollary 1.1Let w(z)be a non-polynomial meromorphic function in the complex plane, n,k∈N+,Ω[w]be a differential polynomial with the form(1.1),and nk>u.If w(z) satisfies the differential equation
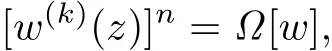
then σ(w)≤2.
2 Proof of Theorem 1.3
For the proof of our result,we need the following lemmas.
Lemma 2.1[7]Let f be a meromorphic function in the complex plane,and σ:=σ(f). Then for each,there exist pointssuch that
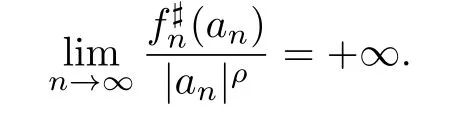
Lemma 2.2[9]Let F be a family of meromorphic functions on the unit disc,and α be a real number.Then F is not normal on the unit disc if and only if for each α with-1<α<1, there exists
(a)a number 0<r<1;
(b)points znwith|zn|<r;
(c)functions fn∈F;
(d)positive numbers ρn→0,
such that

converges locally uniformly to a nonconstant meromorphic function g(ζ),whose order is at most 2.In particular,we may choose wnand ρn,such that

In fact,Lemma 2.2 is an extending result of Zalcman[8]concerning normal families.
Lemma 2.3[3]Let w(z)be a meromorphic function in the complex plane.If w♯(z)is finite, then σ(w(z))≤2.
Proof of Theorem 1.3Assume that the conclusion of Theorem 1.3 does not hold.Then there would exist a meromorphic solution w(z)satisfying the differential equations

such that

m
that

Meanwhile,it implies that{wm(z):=w(am+z),m∈N+}is not normal at z=0.By Lemma 2.2,we have both sequences{bm}and{ρm}satisfying

Meanwhile,

converges locally uniformly to a nonconstant meromorphic function g(ζ),whose order is at most 2 by Lemma 2.3.Therefore,there exist bmand ρmsuch that

According to(2.1)–(2.4),we obtain

When bm+ρmζ replaces z in the differential equation
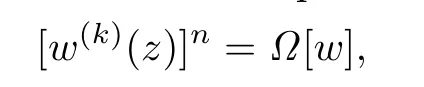
we have

where Ω[w]is a differential polynomial with the form(1.1).
At the same time,we have

Using(2.6)and(2.7),we gain
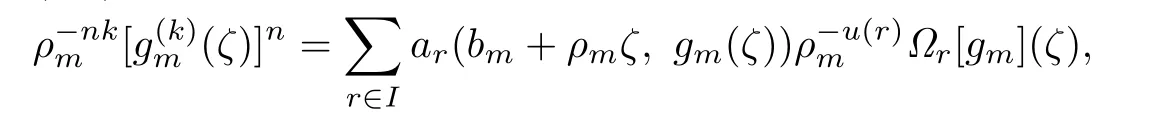
that is,
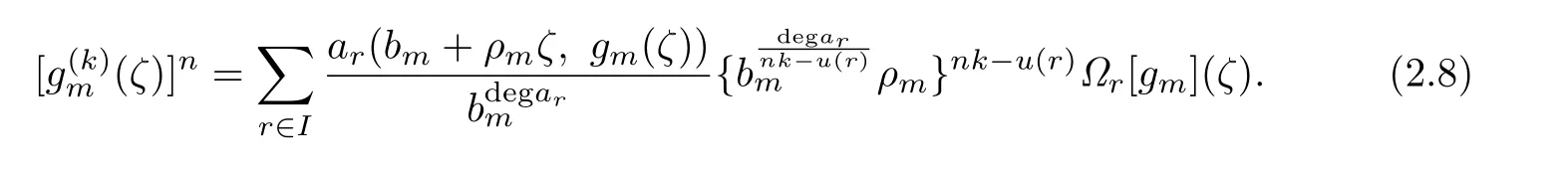
Because

we can get
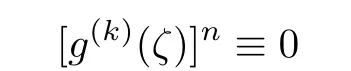
by(2.5)and(2.8),as m→∞.Thus we get that g(ζ)is a polynomial,which contradicts the condition of the theorem.The proof of Theorem 1.3 is completed.
3 Some Examples
We give some examples as follows.
Example 3.1For n≥2 the entire function w(z)=eznsatisfies the following algebraic differential equation:

where
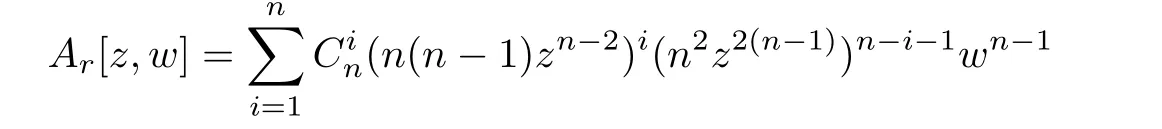
is a polynomial of its variables.We know that
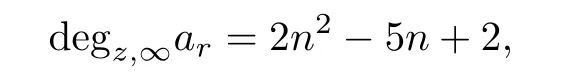
the growth of order σ(w)=n and u=1.The growth order σ(w)of any meromorphic solution w(z)of the equation(3.1)satisfies
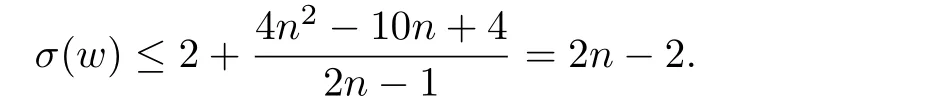
When n=2,we have
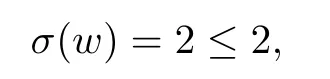
which also shows that our estimate is sharp.
Example 3.2[10]For n=2 the entire function w(z)=eezsatisfies the following algebraic differential equation:

We know that w(z)=eezis of infinite order.In this case,
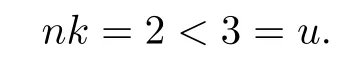
It shows that the condition of Theorem 1.3 nk>u is necessary.
4 Discussion
In this paper,we consider the following algebraic differential equation:

where Ai(z)(i=0,1,2,···,k-1)are polynomials with respect to z.We can gain a result as follows.
Theorem 4.1Let w(z)be a non-polynomial meromorphic function in the complex plane, n,k∈N+,Ω[w]be a differential polynomial with the form(1.1),and nk>u.If w(z) satisfies the differential equation(4.1),then the growth order σ(w)of w(z)satisfies
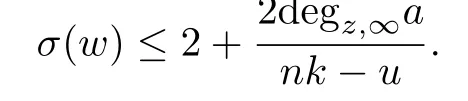
Proof.Similarly to the proceeding of the proof of Theorem 1.3,we have(2.2)–(2.5)and (2.7).Meanwhile,we obtain
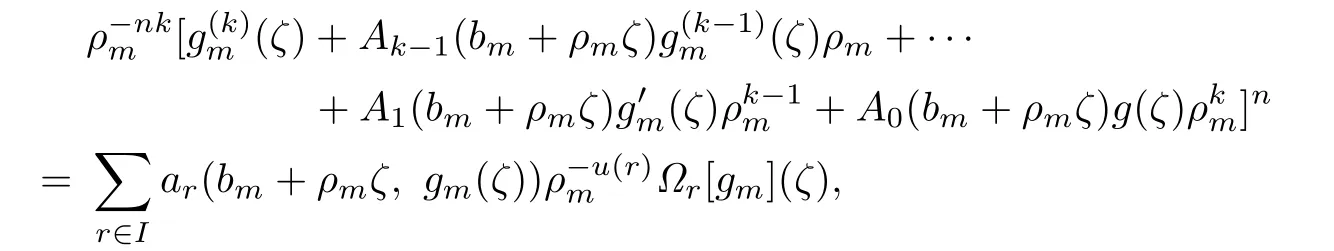
that is,

We can deduce
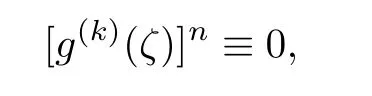
and get that g(ζ)is a polynomial,which is a contradiction.The proof of Theorem 4.1 is completed.
[1]Hayman W K.Meromorphic Functions.Oxford:Clarendon Press,1964.
[2]Laine I.Nevanlinna Theory and Complex differential Equations.Berlin:de Guyter,1993.
[3]Gu Y X,Pang X C,Fang M L.Normal Families Theory and Applications.Beijing:Science Press,2007.
[4]Gol'dberg A A.On single-valued solutions of first-order diferential equations(in Russian). Ukra¨ın.Mat.Zh.,1956,8:254–261.
[5]Bergweiler W.On a theorem of Gol'dberg concerning meromorphic solutions of algebraic differential equations.Complex Variables Theory Appl.,1998,37:93–96.
[6]Gao L Y.The order of the solution of a type of systems of complex algebraic differential equations.J.Math.(Wuhan),2005,25:157–159.
[7]Yuan W J,Xiao B,Zhang J J.The general theorem of Gol'dberg concerning the growth of meromorphic solutions of algebraic differential equations.Comput.Math.Appl.,2009,58: 1788–1791.
[8]Zalcman L.A heuristic principle in complex theory.Amer.Math.Monthly,1975,82:813–817.
[9]Pang X C.Normality conditions for differential polynomials(in Chinese).Chinese Sci.Bull., 1988,32:1690–1693.
[10]Zalcman L.Noraml families:New perspecttives.Bull.Amer.Math.Soc.(N.S.),1998,35: 215–230.
34A10,30D35
A
1674-5647(2013)04-0345-06
Received date:March 18,2011.
The NSF(10471065)of China,the Foundation(2011SQRL172)of the Education Department of Anhui Province for Outstanding Young Teachers in University,and the Foundation(2012xq26)of the Huaibei Normal University for Young Teachers.
E-mail address:suxianfeng2006@tom.com(Su X F).
杂志排行
Communications in Mathematical Research的其它文章
- Branched Coverings and Embedded Surfaces in Four-manifolds
- Invariants for Automorphisms of the Underlying Algebras Relative to Lie Algebras of Cartan Type
- COMMUNICATIONS IN MATHEMATICAL RESEARCH
- Annulus and Disk Complex Is Contractible and Quasi-convex
- An Extension of Chebyshev's Maximum Principle to Several Variables
- A Class of Regular Simple ω2-semigroups-II
