腺瘤性结肠息肉(APC)蛋白截短突变对MDCK细胞中细胞-基质和细胞-细胞间黏附的影响
2013-05-07李文玲祝文思牛海波朱峰宋莉李卓玉
李文玲 祝文思 牛海波 朱峰 宋莉 李卓玉
(山西大学生物技术研究所-化学生物学与分子工程教育部重点实验室 太原 030006)
Introduction
Cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesive interactions play key roles in many different aspects of cell invasion and migration.These interactions are involved in the process of cell localization,effector recognition,and activation phenomena[1].
Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion receptors with well established roles in morphogenesis.Several studies have suggested that cadherin family members have important roles in the malignant progression of various human cancers.In addition to their established functions in modulating cell adhesion,aggregation,cell polarity,and morphogenesis,the classic aggregation molecules,E-cadherin,has also been implicated in the molecular pathogenesis of lung,breast,liver,and gastric cancers[2].In epithelial cells,E-cadherin is very important for compact association of the cells in epithelial sheets,and in this capability,E-cadherin might function as a suppressor of invasiveness and metastasis of epithelial tumors[3].CD29 (Integrin beta-1)is an integrin unit associated with very late antigen receptors.It is the beta subunit of an integrin family of molecules expressed on diverse cell types which function as the major receptors for extracellular matrix and as cell-cell adhesion molecules.
Adenomatous polyposis coli(APC),a tumor suppressor commonly mutated in cancer,is a cytoskeletal organizer for cell migration in the mammalian intestinal epithelium.Most human colorectal tumours carry mutations in the APC gene,which result in expression of truncated N-terminal APC fragments lacking sites required for the formation of theβ-catenin targeting complex,so that intracellular β-catenin is not regulated properly and the normal genetic programme is altered.In addition,APC participates in several other cellular processes,including cytoskeletal regulation,so that loss or truncation of APC also directly affects cell migration and chromosome segregation[4].Notably,APC truncation can be associated with these adherens junctions and evidence points to a role for APC in cellular adhesion.The association of truncated mutation of APC with the cytoskeleton and the plasma membrane at cell-cell junctions has led to suggestions of a role for APC in cell-cell adhesion[5],which could be relevant to its activity as a tumour suppressor.However,it is unknown whether there is a functional relationship between APC truncation and cell-cell contacts.
Here,we report that truncated APC affects cell-cell adhesion and cell-matrix adhesion,especially in MDCK-N2-APC,which contains N-terminal fragments 449-781residues of APC.Our experiments showed that cell adhesion is increased and cell-matrix adhesion was reduced respectively by the over-expression of N2-APC in the cells.These results implicate the roles of truncated N2-APC fragment with the residues of 449-781amino acids acting on cell-cell contacts and further effects on cancer cell invasion and migration.
Materials and Methods
Antibodies and cell culture Antibodies used in this study were:anti-E-cadherin (Bioworld),monoclonal anti-α-tubulin antibody(Sigma),anti-GFP(Cell Signaling),anti-CD29 (BD Biosciences).HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG(H+L)and goat antirabbit IgG (H+L)secondary antibodies were from Invitrogen.
MDCK-GFP and MDCK-N2-APC stable cells(respectively expressing wild type and truncated APC spanning residues 449-781)were routinely maintained in Dulbecco′s modified eagles medium(DMEM,HyClone) containing 250 μg/mL gentamycin(G418,Biosharp)at 37℃in a 5%CO2incubator.The media contained 10%fetal calf serum (Boster),1%penicillin/streptomycin(Solarbio).
Immunofluorescence staining Cells were grown on cover glasses in media at 37℃.Washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline(PBS),cells were fixed in 4%paraformaldehyde for 20 min,permeabilized with 0.3%Triton X-100/PBS for 3min,and pre-blocked in 3%BSA/PBS for 1 h.The slides were then incubated with a primary antibody(diluted 1∶1000in blocking solution)for 4hat 4℃,washed three times with PBS,and incubated with a secondary antibody with a TRITC-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody (diluted 1∶100)for 1h.After further washes,the slides were mounted with sealed tablet (Solarbio),and cells were examined with fluorescence optics on a confocal microscope.
Cell adhesion MDCK-GDP and MDCK-N2-APC cell adhesion was performed by apre-coated 96-well plate with fibronectin(10g/mL;Sigma)at 37℃for 1h.The cells were digested with 0.05%trypsin and resuspended at 5×105cells/mL in DMEM media.Cells(100μL)were added to each well and allowed to adhere for 0.5or 2.5h.At the end of the incubation period,cells were washed three times with PBS,and each well was added in 50μL 4%for 10min at room temperature.Then the wells were washed three times,stained with 0.5%crystal violet for 20min at room temperature.Then,50 μL of 1%sodium dodecyl sulfate was added to each well.The number of adherent cells was quantified by absorbance at 570nm(D570).Cell-matrix adhesion ratio was calculated by using the formula:experiment group D570/control group D570.Each experiment was repeated at least three times with identical results.
Cell aggregation assay Cells were washed with PBS twice and digested with 0.05%trypsin.Then were resuspended at 5×10per 100μL with DMEM media,and 100μL of the cell suspension was seeded in each well of 96-well plates.The plates were placed in a 37℃shaker and rotated at 80r/min for 1h.The wells were then gently stirred.The number of aggregates and single cells were counted with a hemacytometer.The rate of aggregation was calculated by the percentage of decrease in the number of single cells by using the formula [(N0- Ni)/N0]/100.Where N0is the number of single cells at time 0,and Niis the number of single cells detected in cultures at various time points after incubation.Each value is the average of at least three independent experiments.
RNA preparation and RT-PCR analysis To identify E-cadherin gene transcripts,quantitative real time PCR(qRT-PCR)was performed by using the Applied Biosystems.Total RNA isolation from cultured cells was performed by using Trizol on the basis of manufacturer′s instructions(TAKARA).1μg of DNA-free total RNAs was reverse transcribed using PrimeScript RT Master Mix according to the manufacturer′s instructions(TAKARA).For the qRTPCR assay,25μL reaction containing 4μL cDNA,1μL of each primer and 12.5μL SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM(TAKARA)were used to monitor double-strand DNA synthesis.Primers used were 5′-AG-GACCAGGTGACCACCCTAGA-3′ (forward),5′-ATGCCCAAGATGGCAGGAAC-3′(reverse)for E-cadherin and 5′-GCA-CCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3′(forward),5′-TGGTGAAGACGCCAGT-GGA-3′(reverse) for GAPDH.
Western blot Lysates were separated by 8%sodium dodecyl sulphatepolyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes.Anti-E-cadherin(1∶1000;Bioworld),anti-α-tubulin(1∶1000;Sigma),anti-CD29 (1∶1000;BD Biosciences)antibodies were primary antibodies.After three times washing,membranes were incubated with the appropriate horseradish peroxidase conjugated secondary antibody.Blots were developed with ECL plus Western blot detection system.
Statistical methods Statistical analysis was carried out using the SPSS software program.Data,derived from three or four independent experiments,are presented as the means±SD,and were analyzed with analysis of variance followed by the t test,with significance(P)set at 0.01.
Results
Expression of truncated N2-APC affected cellcell adhesion in MDCK cells To verify whether N2 fragment of APC is involved in the regulation of cell-cell adhesion (cell aggregation),we examined the cell aggregation ratio of MDCK-N2-APC and the control MDCK-GFP cells.MDCK-N2-APC is stable cells which express residues 449-781of APC.Fig 1Aindicated clearly that cell aggregation ratio was decreased in N2-APC expressed cells.The followed calculation showed that aggregation ratio with N2-APC was reduced by about 30%compared with GFP control cells (P=0.03,Fig 1B).These results suggested that N2-APC could affect cell-cell adhesion in MDCK cells.
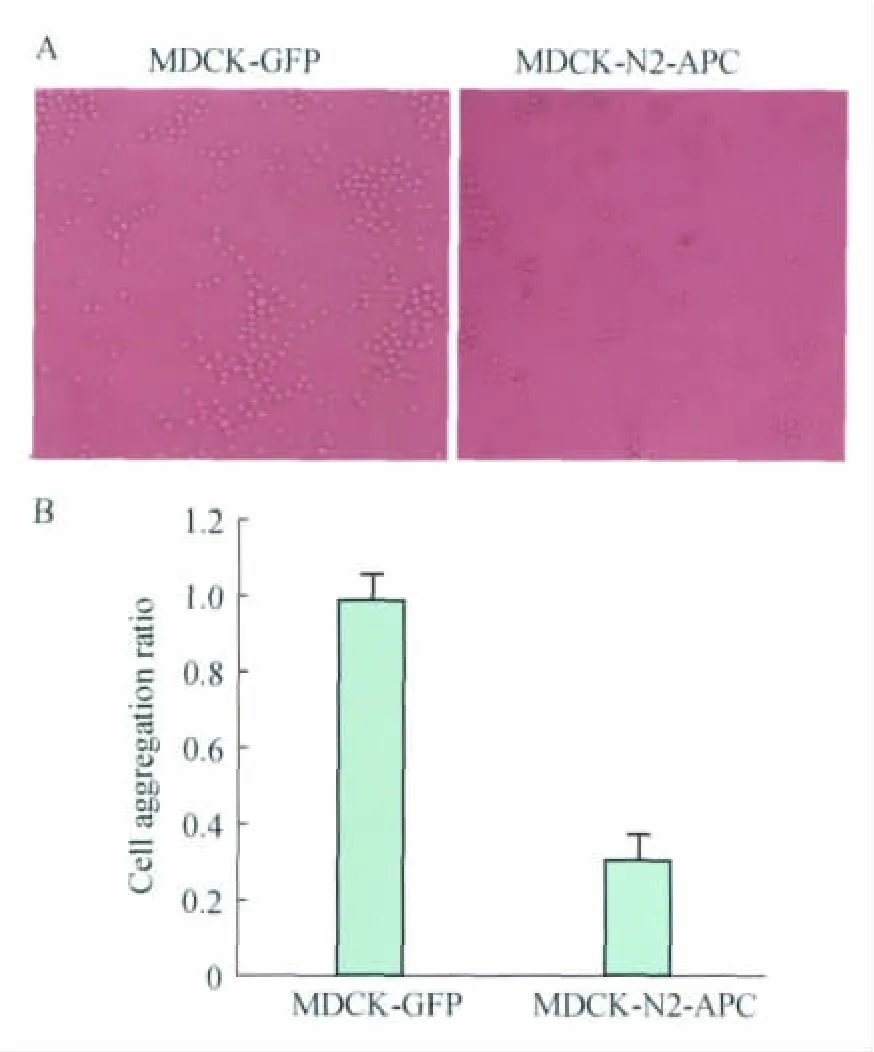
Fig 1 Cell-cell adhesion of MDCK stable cells was influenced by truncated APC
Expression of truncated N2-APC enervated E-cadherin expression level in MDCK E-cadherin is an essential molecule which has functions on cell aggregation process.In order to further elucidate the effect of N2fragment on cell aggregation,we examined mRNA level of E-cadherin in these two stable cell lines,MDCK-N2-APC and MDCK-GFP.As shown in Fig 2A,N2exhibited lower mRNA level of E-cadherin compared with control cells.The decreased extent was about 60% (P=0.04).Similar results were observed in our subsequent immunostaining experiments.In N2-APC expressed cells,E-cadherin staining was sharp weaker than GFP cells(Fig 2B).Moreover,we examined the protein expression level of E-cadherin by using Western analysis.Consistent with the above-mentioned results,N2-APC expressed cells had a lower level of E-cadherin (Fig 2C).Together,these results suggest that reduced aggregation of N2-APC expressed cell was possibly caused by diminishing E-cadherin expression level.
Truncated N2-APC promoted cell-matrix adhesion in MDCK cell line To determine the effects of N2-terminal APC on cell adhesion,we examined the cell adhesion ratio of MDCK-N2-APC to MDCK-GFP control.Compare with control cells of MDCK-GFP,we found that cells expressed N2-APC had relatively quick adhesion for various periods of time(Fig 3A).Then,we applied crystal violet to make further assay to the adhesion ratio.Consistent with the previous results,cell adhesion ratio was markedly increased in N2-APC stably expressed cells(P<0.01,Fig 3B).The rising extent was averagely 180%.Taking advantage of SPSS significance test,it demonstrated that these variations of cell adhesion ratio were pretty much behavior significant difference.At four different time points,cell-matrix adhesion ratios were 2.22±0.045,2.24±0.024,1.39±0.015and 1.36±0.012in N2expressed cells respectively.Taken together,these results indicated that there is an intimate relationship between cell-matrix adhesion and N2-APC.Over-expression of N2-APC fragment of APC might affect the ability of MDCK cells to the matrix.
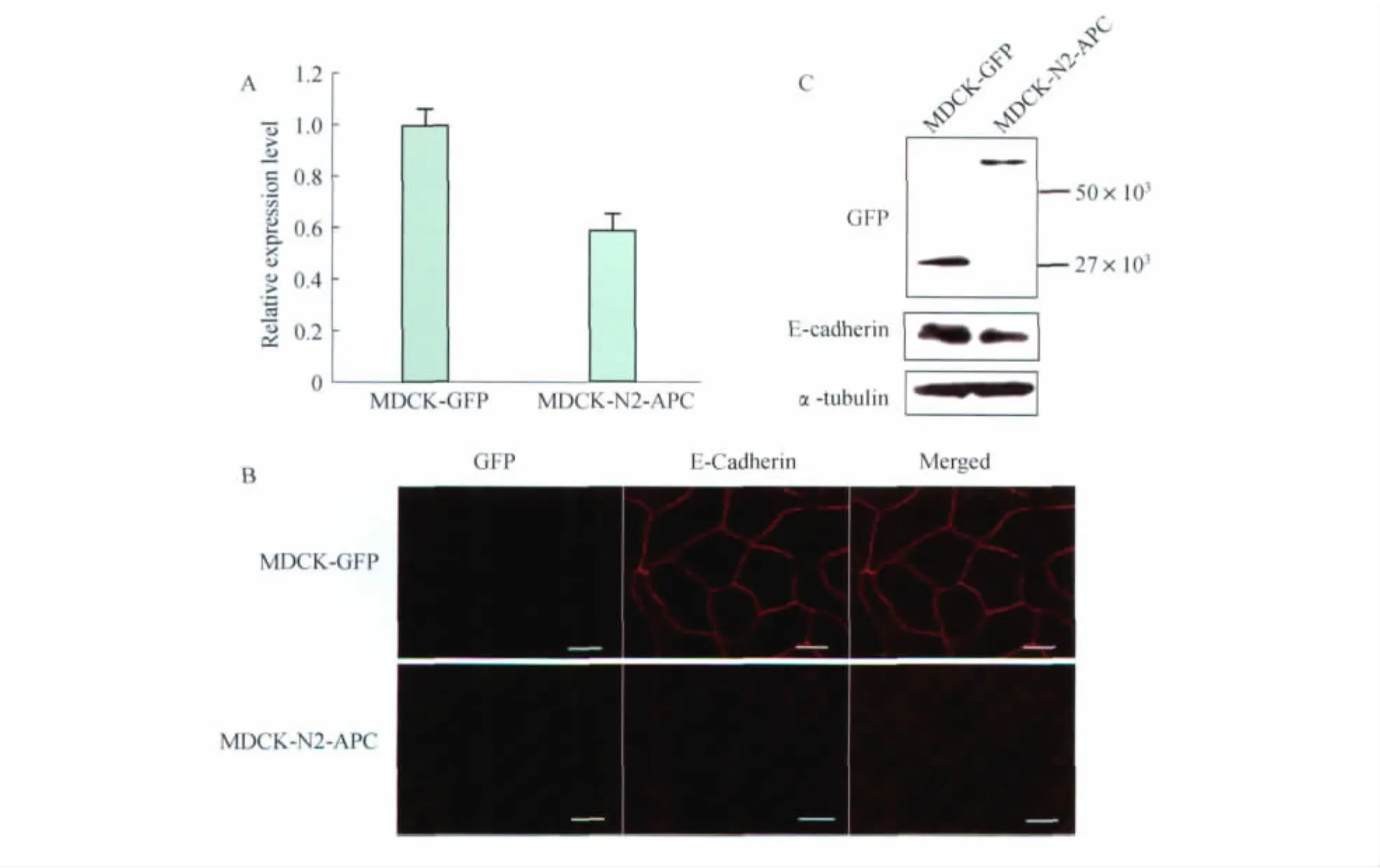
Fig 2 Cell-cell adhesion was reduced in MDCK-N2-APC cells

Fig 3 Truncated N2-APC increased cell-matrix adhesion in MDCK
Truncated N2-APC increased the expression of integrin beta-1in MDCK It has been known that CD29is a key molecule in the process of cell-matrix adhesion.To further study how truncated APC affect cell adhesion,we examined the protein expression level of CD29in these two stable cell lines.As shown in Fig 4,Western blot result illustrated that CD29expression level was notably increased in MDCK-N2-APC cells,which suggested that N2fragment could enhance cell adhesion by improving CD29expression level.
On analysing CD29protein in MDCK-GFP and MDCK-N2-APC cells,Western analysis for αtubulin from the same blot was shown as a loading control.
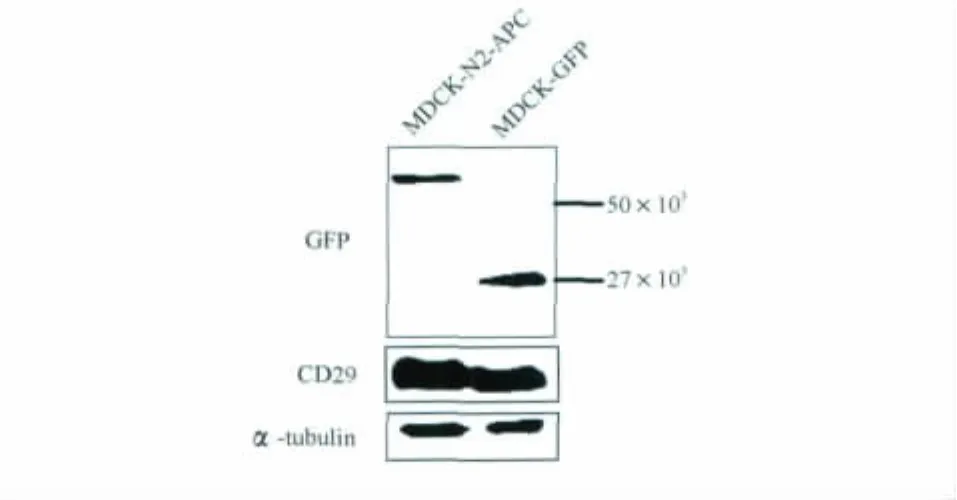
Fig 4 Integrin beta-1expression level was increased in MDCK-N2-APC
Discussion
APC is a cytoskeletal organizer for cell migration and a scaffold,and it affects GSK3β/CKI-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of the Wnt key molecularβ-catenin.A majority of colorectal cancers exhibit inactivating mutations in APC,and loss of APC function is an early event during tumorigenesis[6].Abrogation of cell-adhesive properties is a hallmark of invasive carcinomas.Full length APC has more recently shown to play a role in cell-cell adhesion.It has been detected at lateral plasma membrane in some cells,and loss of APC correlated with defective intercellular adhesion[7].Previous studies implicated APC in cell adhesion because expression of full-length APC in colon carcinoma cells restored cell-cell adhesion[8].It was reported in another study,however,that loss of both APC1and APC2did not impair cadherinbased cell-cell adhesion in Drosophila[9].Our results found that APC had a crucial role in cell adhesion.Truncated APC could result in significant variation of cell adhesion and aggregation in MDCK cells.The experiments implicated that N2-APC fragments has distinct effects on cell adhesion.
The specific mechanism of APC regulates cell adhesion and aggregation has not been completely clear.Harris[10]et al considered it unlikely that APC regulates cell-cell adhesion directly,as the interaction of APC with V/E-cadherin is minimal.However,Faux[8]et al also observed changes in the posttranscriptional modification of E-cadherin in APC truncated cells,which could be linked to its APC-induced redistribution to the plasma membrane.Kamal[11]and colleague testified that APC could dominate cell adhesion indirectly by regulating the validity of β-catenin for connecting into adherens junctions or by regulating vesicle transporting to and from the plasma membrane by tethering microtubules to cell-cell contacts.
In keeping with recent reported studies,we also found that truncated APC has powerful influences on cell adhesion and aggregation.N2fragment probably affected cell adhesion by regulating certain molecules which participate in cell-cell contacts process.In other words,intracellular distribution and expression level of these adhesion molecules were changed owing to loss of APC function.Consistent with previous results,the pathways of truncated APC that affects expression of these adhesion molecules may associate with alteration ofβ-catenin.Specifically,the basics of canonical Wnt signaling are well known:In the absence of Wnt signaling,cytoplasmic β-catenin is recruited to a complex containing axin,APC and GSK-3β,which is then able to phosphorylateβ-catenin,triggering its ubiquitin-dependent degradation.When the signaling pathway is aberrant activated,such as truncated mutation of APC,APC-β-catenin-GSK-3β complex disaggregated,which can result in accumulation ofβcatenin and its subsequent translocation into the nucleus .Because of the interaction betweenβcatenin and E-cadherin,redistribution ofβ-catenin can also lead to similar changes in E-cadherin,and can reduce its expression level in cell membrane.Integrin α3is a transmembrane integrin receptor subunit which forms heterodimers with integrinβ1(CD29)in MDCK cells[13].α3β1integrin is a laminin receptor that localizes to sites of cell-cell contacts through its interaction with the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex[14].Therefore,when APC mutated,β-catenin began to accumulate in cytoplasm.In the meantime it affected the expression level of CD29.
This study demonstrated that there is an intimate relationship between N2-APC and cell adhesion.In MDCK cells,N2may enhance cell adhesion via ascend of CD29,and reduce cell aggregation through lowering E-cadherin expression level.Evidence is beginning to emerge that APC proteins may be another example of a dual-function protein with dividable roles in Wnt signaling pathway and cell adhesion[5].However,up to now,it has not been shown that APC proteins participate directly in the two processes.There are multiple comprehensions to explain the mechanism how does APC control cell adhesion.Our data support the standpoint of Kamal[11],that truncated APC may influence cell adhesion by regulatingβ-catenin,which has interactions with certain adhesion molecules such as E-cadherin and CD29.This work concretely focuses on the N2fragment of APC,which affects cell adhesion and aggregation.Our experiments demon-strated that N-terminal of APC,especially N2fragment,has an important role in the process of cell adhesion.Our data provided novel evidence for studying the effects of APC truncation on cell adhesion in colon cancer cells.Further understanding on the mechanism of APC and cell adhesion will have a significant impact on promoting the fundamental study in the areas pertaining to APC and carcinomas,which in turn will hold great potential for clinical therapy of patients with tumors.
[1]Madri JA,Graesser D.Cell migration in the immune systemthe evolving inter-related roles of adhesion molecules and pretenses [J].Dev Immunol,2000,7(2-4):103-116.
[2]Huang ZY,Wu YL,Hedrick N,et al.Gutmann.T-cadherin-mediated cell growth regulation involves G2 phase arrest and requires p21CIP1/WAF1expression[J].Mol Cell Biol,2003,23(2):566-578.
[3]LI Z,Gallin WJ,Lauzon G,et al.L-CAM expression induces fibroblast-epidermoid transition in squamous carcinoma cells and down-regulates the endogenous N-cadherin[J].J Cell Sci,1998,111(Pt7):1005-1019.
[4]LI ZY,Kroboth K,Newton IP,et al.Novel selfassociation of the APC molecule affects APC clusters and cell migration [J].J Cell Sci,2008,121(Pt11):1916-1925.
[5]Bienz M,Hamada F.Adenomatous polyposis coli proteins and cell adhesion[J].Curr Opin Cell Biol,2004,16(5):528-535.
[6]Kinzler KW,Vogelstein B.Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer[J].Cell,1996,87(2):159-170.
[7]Rosin-Arbesfeld R,Ihrke G,Bienz M.Actin-dependent membrane association of the APC tumour suppressor in polarized mammalian epithelial cells[J].EMBO J,2001,20(21),5929-5939.
[8]Faux MC,Ross JL,Meeker C,et al.Restoration of fulllength adenomatous polyposis coli(APC)protein in a colon cancer cell line enhances cell adhesion [J].J Cell Sci,2004,117(3):427-439.
[9]McCartney BM,Price MH,Webb RL,et al.Testing hypotheses for the functions of APC family proteins using null and truncation alleles in Drosophila[J].Development,2006,133(12),2407-2418.
[10]Harris ES,Nelson WJ.Adenomatous polyposis coli regulates endothelial cell migration independent of roles in β-catenin signaling and cell-cell adhesion [J].Mol Biol Cell,2010,21(15):2611-2623.
[11]Kamal A,Goldstein LS.Connecting vesicle transport to the cytoskeleton[J].Curr Opin Cell Biol,2000,12(4):503-508.
[12]Gordon MD,Nusse R.Wnt signaling:multiple pathways,multiple receptors,and multiple transcription factors[J].J Biol Chem,2006,281(32):22429-22433.
[13]Schoenenberger CA,Zuk A,Zinkl GM,et al.Integrin expression and localization in normal MDCK cells and transformed MDCK cells lacking apical polarity [J].J Cell Sci,1994,104(2):527-541.
[14]Chattopadhyay N,Wang Z,Ashman LK,et al.alpha3beta1 integrin-CD151,a component of the cadherincatenin complex,regulates PTPmu expression and cell-cell adhesion[J].J Cell Biol,2003,163(6):1351-1362.
