基于Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子的广义Bézier曲线
2013-03-16韩力文
韩力文, 楚 瑛, 李 丁, 刘 凤
(1. 河北师范大学数学与信息科学学院,河北 石家庄 050024;2. 河北省计算数学与应用重点实验室,河北 石家庄 050024)
基于Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子的广义Bézier曲线
韩力文1,2, 楚 瑛1, 李 丁1, 刘 凤1
(1. 河北师范大学数学与信息科学学院,河北 石家庄 050024;2. 河北省计算数学与应用重点实验室,河北 石家庄 050024)
提出了一种全新的广义Bézier曲线。首先,从Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子出发,得到了一组有理函数,该函数带有一个形状参数,是经典Bernstein基函数的自然推广。然后,构造了相应的广义Bézier曲线,本文称之为Lupas q-Bézier曲线,并研究了其基本性质。Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有与经典Bézier曲线相类似的升阶公式和de Casteljau算法。
计算机辅助几何设计;Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子;Lupas q-Bézier曲线;升阶公式;de Casteljau算法
经典的Bernstein算子具有很好的逼近性、收敛性和保形性,是逼近论中最重要的算子之一,被广泛应用于分析、几何和计算机等领域。近年来,随着q-微积分的发展,一类基于q-整数的广义Bernstein算子得到迅速发展。1987年,Lupas首次提出包含q-整数的广义Bernstein算子,即Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子[1]。1996年Phillips提出的q-Bernstein算子[2]是目前研究比较广泛的广义Bernstein算子。
1972年,Bézier[3]采用经典的Bernstein基函数构造了Bézier曲线,为自由型曲线曲面的发展奠定了坚实的基础。随着广义Bernstein算子的产生,经典 Bézier曲线也得到进一步推广。2003年,Oruc和Phillips利用q-Bernstein算子的基函数构造了q-Bézier曲线[4]。Disibuyuk等人分别于2007年和2008年定义了有理q-Bézier曲线[5]及张量积型的q-Bézier曲面[6]。近几年,国内学者也研究并构造了含形状参数的广义 Bézier曲线曲面[7-8]。Simeonov等人更深入地为两类广义Bézier曲线建立了相应的开花形式和细分过程[9-10]。
相比而言,Lupas q-模拟 Bernstein算子在CAGD中的研究较少。对该算子的研究工作主要集中于逼近论方面。1987年,Lupas研究了Lupas q-模拟Bernstein 算子的逼近性和保形性[1]。2006年,Ostrovska讨论了该算子的一致收敛性[11]。Phillips于2010年指出Lupas q-模拟Bernstein 算子还没有任何应用性研究[12]。
首先,介绍Lupas q-模拟Bernstein 算子的表示形式,并从中提取出Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数,进而构造了Lupas q-Bézier曲线。Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有仿射不变性、凸包性、变差缩减性、保凸性等。特别是,Lupas q-Bézier曲线的变差缩减性、升阶性和Lupas q-de Casteljau算法为Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子在CAGD中的应用奠定了基础。
1 Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子
为了介绍Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子,首先引入以下记号和定义:
定义1.1[13]对于给定的实数 0q> ,及任意i N∈ ,定义q-整数[i]如下:
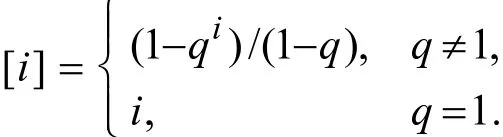
事实上,对于给定实数 0q> 且 1q≠ ,q -整数是关于q的有理函数,而当 1q= 时,q -整数为通常意义下的非负整数。
定义1.2[13]对于给定的实数 0q> ,及任意i ∈ N,定义q -阶乘[i] !如下:
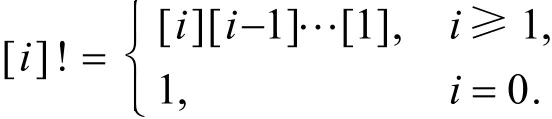
定义1.3[13]对于给定的实数 q> 0,及任意整数 n ≥ i≥ 0,定义q -二项式系数如下:。
特别地,q -二项式系数满足帕斯卡型递推关系式
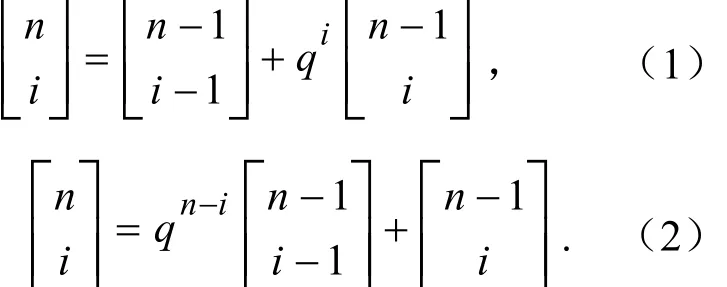
定义1.4[1](Lupas q -模拟Bernstein算子)令 f( x) ∈ C[0,1],线性算子定义为:
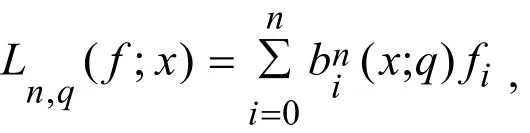
2 Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数及其递推公式
从Lupas q-模拟Bernstein算子中,我们提取出n次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数

本文称之为q-逆对称性。而且,当 q= 1时,Lupas q-模拟 Bernstein有理函数退化为经典 Bernstein基函数。 bn(t; q ), t ∈ [0,1], i = 0,1,… ,n 是线性i无关的。
如图 1所,当 q=1.5时五次 Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数的图像。
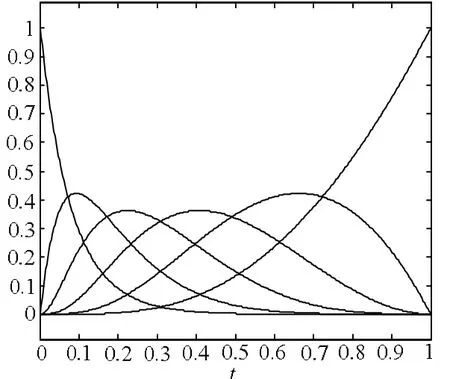
图1 五次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数(q=1.5)
Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数具有与经典Bernstein基函数类似的递推公式。
定理 2.1 n次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数可由两个n+1次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数递推得到,即

证明:

定理 2.2 n次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数可由两个n-1次Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数递推得到,即
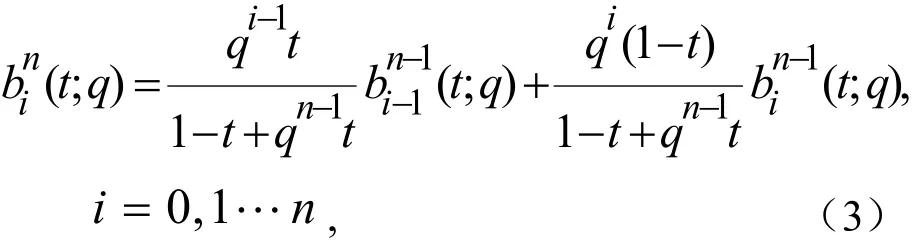
和

利用式(1),得
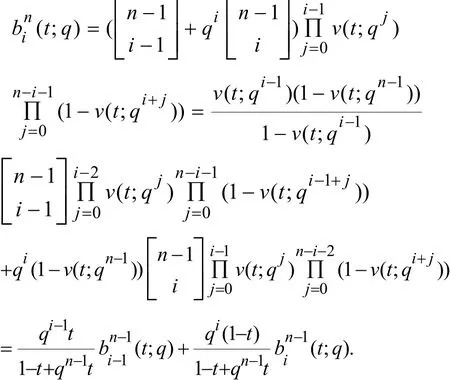
利用式(2),得

3 Lupas q-Bézier曲线及其性质
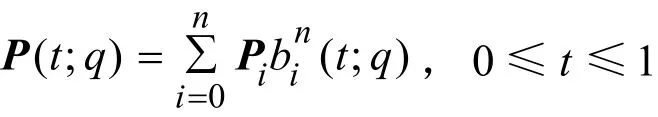
定义3.1(Lupas q-Bézier曲线) 给定 n+1个向量 Pi∈ R2(i =0,1,… ,n)及实数 q> 0,称n次参数曲线段为一条n次Lupas q-Bézier曲线。 Pi称为控制顶点。依次用直线段连接相邻两个 Pi,i =0,1,2,…,n ,所得的n边折线多边形称为Lupas q-Bézier曲线的控制多边形。
Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有一个形状参数,在控制多边形不变的情况下,通过调整参数q可以调控曲线的形状。如图2所示,分别取q=1, 0.3, 5, 9时三次Lupas q-Bézier曲线的图像,当q=1时,Lupas q-Bézier曲线即为经典的Bézier曲线。
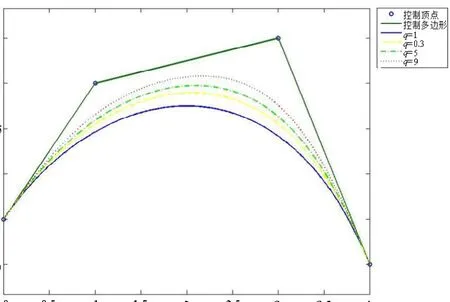
图2 取q=1, 0.3, 5, 9的三次Lupas q-Bézier曲线
定理 3.1 Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有如下基本性质:
1) 曲线是几何不变和仿射不变的。
2) 曲线位于控制多边形的凸包内。
3) 曲线插值于控制多边形首尾两端点,即P (0;q) =P0, P (1;q ) =Pn。
这表明Lupas q-Bézier曲线以控制多边形的首尾两边为其起点和终点的切方向。
4)(q-逆对称性)如果将一条以q0为参数的Lupas q-Bézier曲线的控制顶点逆序排列,得到的新的Lupas q-Bézier曲线和以1/q0为参数,原顺序控制顶点为顶点的曲线是同一条曲线。
5)(退化性)当 q= 1时,Lupas q-Bézier曲线退化为经典Bézier曲线。
证明:下面只对q-逆对称性进行证明,其他4条性质可根据相应的Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数的性质推导得到。
定理 3.2(变差缩减性) Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有变差缩减性,即Lupas q-Bézier曲线与所在平面内的任一直线的交点个数不会超过它的控制顶点与该直线的交点个数。
记Lupas q-Bézier曲线为C,任取其所在平面内的一直线L,记C与L的交点数为 I( C, L)。以L为横轴建立直角坐标系,由Lupas q-Bézier曲线的几何不变性,记控制顶点的新坐标为(xi, yi)(i = 0,1,… ,n),其中 0≤ x0≤x1≤…≤xn=1记控制多边形为P,则P与L的交点数为 I( P, L)。下面只需证明 I( C, L ) ≤ I( P, L)。
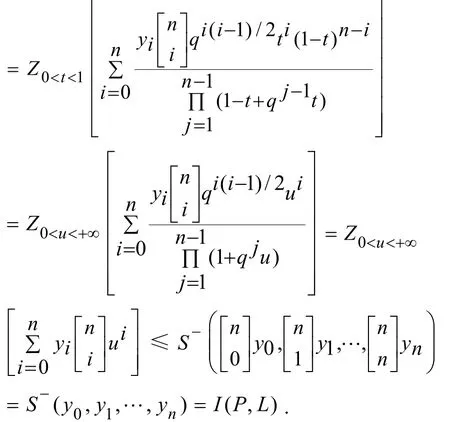
推论 Lupas q-Bézier曲线具有保凸性,即当控制多边形是凸的,则所定义的 Lupas q-Bézier曲线也是凸的。保凸性可看作是变差缩减性的特殊情况。
根据Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数的递推性质,可以推导出Lupas q-Bézier曲线的升阶公式与de Casteljau算法,它们均是经典Bézier曲线的升阶公式和de Casteljau算法的推广形式。
定理3.3(升阶公式) 一条n次Lupas q-Bé zier曲线可以形式上看作一条 n+ 1次的 Lupas q-Bézier曲线,即
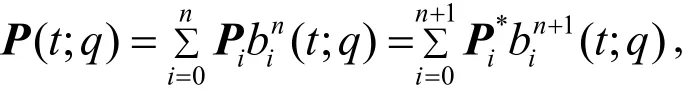
其中
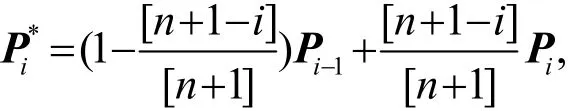
其中
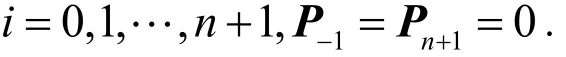
说明:当q=1时,Lupas q-Bézier曲线的升阶公式退化为经典Bézier曲线的升阶公式。若记原n阶曲线的控制顶点组成的向量为
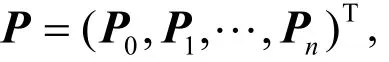
升阶后的 n+ 1次曲线的控制顶点组成的向量为
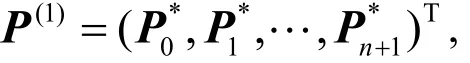
则可以把升阶过程表示为:P(1)=TP.

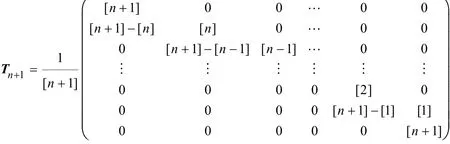
称为升阶算子,它是一个(n + 2)× (n + 1)阶矩阵。对r ∈ N不断升阶为n + r次 Lupas q-Bézier曲线,可得控制顶点为
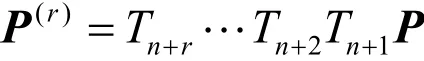
当r→∞时,控制多边形 P(r)收敛到Lupas q-Bézier曲线。
定理 3.4 (de Casteljau算法) 一条 n次Lupas q-Bézier曲线可表示为分别由前后n个控制顶点决定的两条 1n- 次Lupas q-Bézier曲线的线性组合,进而得到Lupas q-Bézier曲线上某一点递归求值的de Casteljau算法:

或
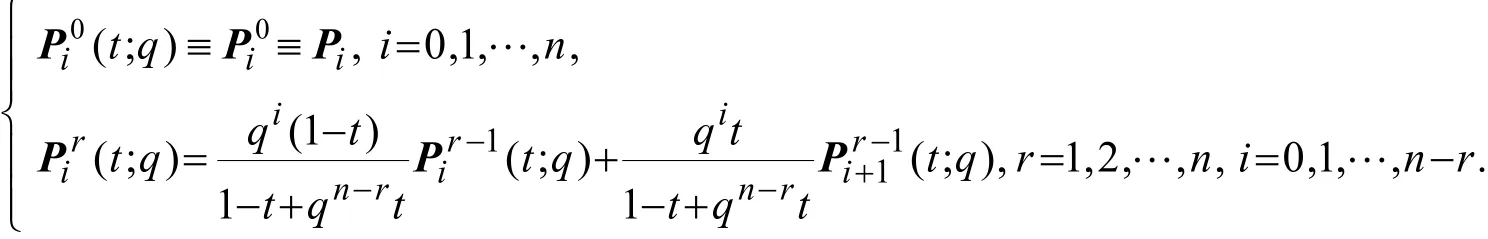
说明:当q=1时,Lupas q-Bézier曲线的Lupas q-de Casteljau算法退化为经典Bézier曲线的de Casteljau算法。若记
则de Casteljau算法可表示为:

其中 Mr(t; q)是一个(n - r + 1)× (n - r+ 2)阶矩阵,且
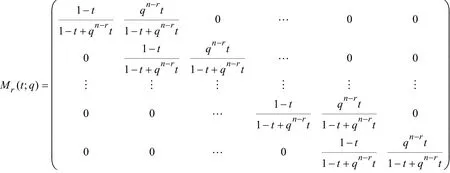
或
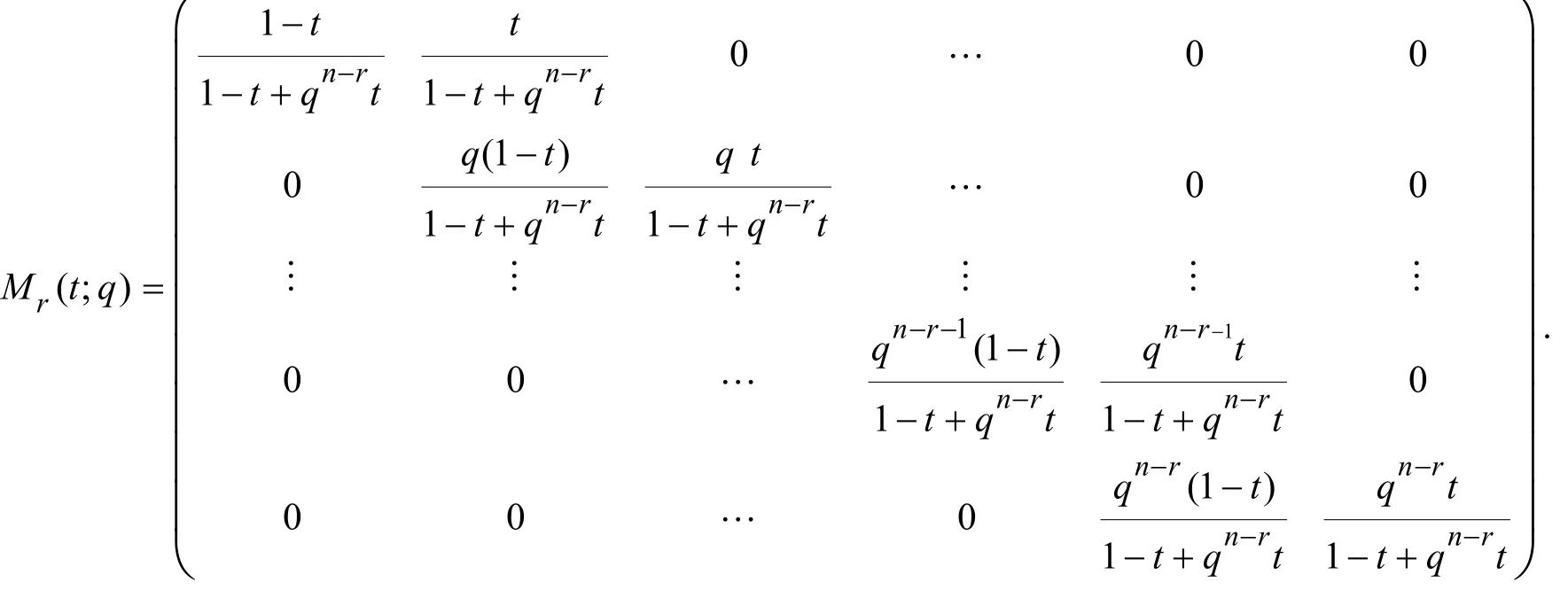
4 结 论
本文利用Lupas q-模拟Bernstein有理函数族构造了一种全新的广义Bézier曲线,即Lupas q-B ézier曲线。研究了Lupas q-Bézier曲线的仿射不变性、凸包性、插值端点性、q-逆对称性、变差缩减性及保凸性。推导出Lupas q-Bézier曲线的升阶公式和de Casteljau算法。
在该文研究的基础上,将进一步探索 Lupas q-Bézier曲线与有理Bézier曲线、q-Bézier曲线的关系,并对Lupas q-Bézier曲线的开花形式与细分过程的构造进行更为深入的研究。
[1] Lupas A. A q-analogue of the Bernstein operator [R]. University of Cluj-Napoca, Seminar on Numerical and Statistical Calculus, Preprint, 1987, (9): 85-92.
[2] Phillips G M. On generalized Bernstein polynomials [J]. Numerical Analysis: A. R. Mitchell 75thBirthday Volume, 1996: 263-269.
[3] Bézier P E. Numerical control-mathematics and applications [M]. London: John Wiley & Sons, 1972.
[4] Oruc H, Phillips G M. q-Bernstein polynomials and Bézier curves [J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2003, 151: 1-12.
[5] Disibuyuk C, Oruc H. A generalization of rational Bernstein-Bézier curves [J]. BIT Numerical Mathematics, 2007, 47: 313-323.
[6] Disibuyuk C, Oruc H. Tensor product q-Bernstein polynomials [J]. BIT Numerical Mathematics, 2008, 48: 689-700.
[7] Han Xi’an, Ma Yichen, Huang Xili. A novel generation of Bézier curve and surface [J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2008, 271: 180-193.
[8] Chen Jie, Wang Guojin, A new type of the generalized Bézier curves [J]. Applied Mathematics-A Journal of Chinese Universities, 2011, 26(1): 47-56.
[9] Simeonov P, Zafiris V, Goldman R. h-Blossoming: a new approach to algorithms and identities for h-Bernstein bases and h-Bézier curves [J]. Journal of Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2011, 28: 549-565.
[10] Simeonov P, Zafiris V, Goldman R. q-Blossoming: a new approach to algorithms and identities for q-Bernstein bases and q-Bézier curves [J]. Journal of Approximation Theory, 2012, 164: 77-104.
[11] Ostrovska S. On the Lupas q-analogue of the Bernstein operator [J]. Journal of Mathematics, 2006, 36(5): 1615-1629.
[12] Phillips G M. A survey of results on the q-Bernstein polynomials [J]. MA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 2010, 30: 277-288.
[13] Andrews G E, Askey R, Roy R. Special functions [M].London: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
Generalized Bézier Curves Based on Lupas q-analogue of Bernstein Operator
Han Liwen1,2, Chu Ying1, Li Ding1, Liu Feng1
( 1. College of Mathematics and Information Science, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang Hebei 050024, China; 2. Hebei Province Key Laboratory of Computational Mathematics and Application, Shijiazhuang Hebei 050024, China )
This paper presents a novel generalization of Bézier curves. Firstly, a class of rational functions with one shape parameter is presented. It comes from the Lupas q-analogue of Bernstein operator and is a natural extension to classical Bernstein basis. Then, the corresponding generalized Bézier curves, the so-called Lupas q-Bézier curves, are also constructed and their properties are studied. The new generalized Bézier curves share the degree evaluation and de Casteljau algorithm of the classical Bézier curves.
computer aided geometric design; Lupas q-analogue of Bernstein operator; Lupas q-Bézier curves; degree elevation; de Casteljau algorithm
O 241.5
A
2095-302X (2013)04-0063-06
2012-09-02;定稿日期:2012-11-06
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61170107);河北省教育厅自然科学研究项目(Q2012041)
韩力文(1974-),女,河北石家庄人,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为计算机辅助几何设计,数字几何处理。E-mail:hanliwen@sina.com
