鹿、羊和人腰椎生物学参数的比较及其意义
2012-12-07刘国民韩宏志于海涛孙红辉
刘国民,孔 宁,韩宏志,于海涛,张 琪,孙红辉
(1.吉林大学第二医院骨科,吉林 长春130041;2.吉林大学药学院医用生物材料教研室,吉林 长春130021;3.吉林大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学教研室,吉林 长春130021;4.吉林大学学报编辑部,吉林 长春130021;5.长春中医药大学附属医院骨科,吉林 长春130021)
鹿、羊和人腰椎生物学参数的比较及其意义
刘国民1,孔 宁2,韩宏志3,4,于海涛5,张 琪1,孙红辉1
(1.吉林大学第二医院骨科,吉林 长春130041;2.吉林大学药学院医用生物材料教研室,吉林 长春130021;3.吉林大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学教研室,吉林 长春130021;4.吉林大学学报编辑部,吉林 长春130021;5.长春中医药大学附属医院骨科,吉林 长春130021)
目的:比较鹿、羊和人腰椎的生物学参数,探讨梅花鹿作为脊椎内固定动物模型的可行性,为相关医学研究和体内动物实验提供实验动物腰椎的形态学参数、骨密度和生物力学数据。方法:选取新鲜鹿、羊腰椎各10套,新鲜东北男性尸体腰椎10套,对3组腰椎椎体和椎弓根进行形态学观测,对椎体松质骨密度、极限应力和弹性模量进行测量及比较。结果:鹿、羊和人椎弓根高 (右侧)比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中鹿最大,羊次之,人最小。鹿、羊和人椎弓根宽 (右侧)比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中人最大,鹿其次,羊最小。鹿、羊和人椎间盘前高比较差异有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中人最大,鹿其次,羊最小。鹿、羊和人腰椎表观密度、弹性模量及极限应力各组间比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.05),其中羊最大,鹿次之,人最小。结论:梅花鹿腰椎在解剖形态学和生物力学方面较羊更接近人类,更适合用于建立脊椎内固定动物模型。
腰椎;动物模型;人;鹿;羊;形态学参数
脊椎外科内固定器等手术器械的研发,推动了脊柱外科的进步和手术方法的改进,而各种内固定器和手术方法在应用于临床之前,必须有赖于动物实验证明其可行性,因此动物模型的建立和使用已成为脊柱外科的重要研究手段。动物模型应与人类的脊柱具有良好的相似性和可比性,而用于脊柱的体内、外内固定实验的动物模型比较少。目前已被建立并广泛应用于脊柱研究的动物模型包括小牛、羊等[1-2]。但近年来由于牛海绵体病和甲型 H1N1流感的流行,使牛、羊动物模型始终存在感染人类的潜在危险,从而制约和限制了其在医学领域中的应用。鹿未见有人畜共患性疾病的报道,且鹿与人类在形体和体质量方面具有良好的相似性,但该方面的研究报道较少。本实验观测鹿、羊和人腰椎生物学参数,并进行对比分析,旨在为鹿、羊作为人类脊柱动物模型提供解剖学数据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取年龄在1.5~2.0年的成年雌性梅花鹿10只,体质量80~100kg,由长春双阳鹿场提供;年龄1.5~2.0年的成年雄性绵羊10只,体质量70~90kg,由长春皓月绵羊养殖中心提供。鹿和羊均静脉注射戊巴比妥那过量致死。选择捐献的新鲜男性尸体10具,年龄23~35岁,体质量64~91kg。常规操作分离腰椎,用生理盐水纱布包裹后置于-20℃冰箱冷藏保存。实验前将标本于室温下自然解冻,剔除标本周围的软组织,保留其韧带和椎间盘,人的腰椎是5节,因此选取羊、鹿的腰椎L1~L5节段。采集及处理过程严格遵守2002年 《实验动物哺乳类实验动物的遗传质量控制》[3]的相关规定。所选椎骨均经CT扫描排除腰椎存在肉眼可见的病理性改变,并确定椎体骨骺已闭合 (图1,见插页二)。
1.2 鹿、羊和人椎弓根线性测量 测量鹿、羊椎弓根高、椎弓根宽和椎间盘前高。脊椎是对称性的,所以本实验仅观测标本右侧椎弓根高和宽(图2)。人的腰椎形态学数据来自于中国成人男性腰椎[4]。

图2 鹿、羊和人腰椎椎弓根的三维重建Fig.2 Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lumbar pedicles of deer,sheep and humanA:Deer;B:Sheep;C:Human.
1.3 极限载荷和弹性模量学实验 选取鹿、羊和人腰椎各10具,去除椎体周围的组织和结构。腰椎各椎体平均分成左右两部分,保留上下终板,铣磨成长×宽为12mm×12mm的规则试件,用骨水泥填补使各组试件的上下面水平。在试件前面中上1/3处贴上电阻应变片 [德国都利公司,标距1mm×1mm (胶基泊式),阻值120Ω,灵敏度(K)2.12],保证各试件的纵向电阻应变片位于同一水平面上,将应变片导线连于电阻应变仪上 (上海华东电子仪器厂,YJ-26型静态电阻应变仪),采用万能材料实验机 (日本岛津AG-107A自动控制电子万能试验机)以0、50和100牛顿级别生理载荷分级加载,在电阻应变仪上直接读取各试件相应载荷下的应变位移,算出弹性模量,然后去除应变片,进行极限载荷试验。
1.4 鹿、羊和人腰椎表观密度的测量 随机选取鹿、羊腰椎各10具,去除椎体周围的组织和结构。人腰椎椎体选用生物力学实验余下的椎体部分。实验样本冰冻状态下数控铣床铣磨,动物与人椎体均制成长×宽×高为7mm×7mm×20mm规则试件,试件体积为Va。清水反复冲洗6h后,于20 000U·mL-1的肝素溶液中浸泡12h,其中每6h换1次溶液,再用生理盐水刷洗6h,完全去除髓腔内的血液及组织碎屑。用无水分析酒精对试件脱脂48h,24h更换酒精1次。脱脂试件在空气中干燥24h后用电子分析天平 (精度0.000 1g)称其质量 (W),表观密度=W/Va。
1.5 统计学分析 采用SPSS 10.0统计软件包进行统计学分析。鹿、羊和人椎弓根及椎间盘的形态学参数、骨密度和生物力学数据以±s表示。多组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析,组间比较采用q检验。
2 结 果
2.1 鹿、羊和人椎体线性测量结果 鹿、羊与人椎弓根高比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中鹿最大,羊其次,人最小。鹿、羊与人椎弓根宽 (右侧)比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中人最大,鹿其次,羊最小。鹿、羊与人椎间盘前高比较差异有统计学意义 (P<0.01),其中人最大,鹿其次,羊最小。见表1~3。
表1 鹿、羊和人椎弓根高度比较Tab.1 Comparison of pedicle heights between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)

表1 鹿、羊和人椎弓根高度比较Tab.1 Comparison of pedicle heights between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)
*P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.01compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Right pedicle height L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6±2.80 35.04±2.68 30.71±3.07 Sheep 23.55±2.78* 24.75±2.11* 25.42±2.51* 25.51±2.72 25.58±2.77* 22.15±2.74 Human 16.06±0.66*△ 16.63±0.70*△ 15.82±0.85*△ 15.20±0.99*△ 14.90±0.97*△Deer 32.18±2.06 34.24±2.39 34.80±2.00 34.86-
表2 鹿、羊和人椎弓根宽度比较Tab.2 Comparison of pedicle widths between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)
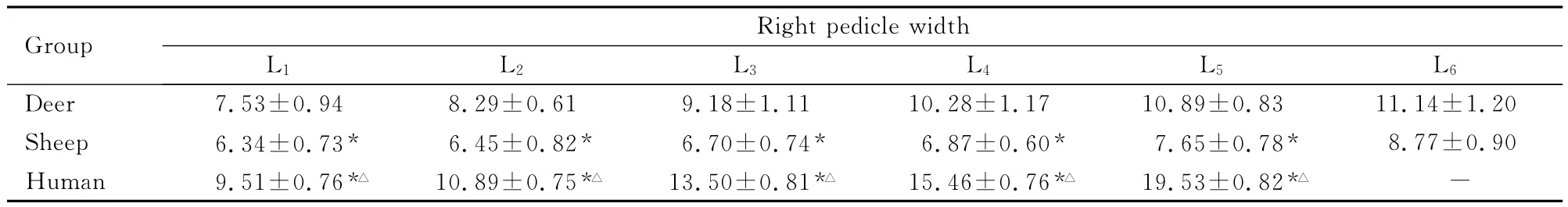
表2 鹿、羊和人椎弓根宽度比较Tab.2 Comparison of pedicle widths between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)
*P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.01compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Right pedicle width L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 17 10.89±0.83 11.14±1.20 Sheep 6.34±0.73* 6.45±0.82* 6.70±0.74* 6.87±0.60* 7.65±0.78* 8.77±0.90 Human 9.51±0.76*△ 10.89±0.75*△ 13.50±0.81*△ 15.46±0.76*△ 19.53±0.82*△Deer 7.53±0.94 8.29±0.61 9.18±1.11 10.28±1.-
表3 鹿、羊和人椎间盘前部高度比较Tab.3 Comparison of anterior disc heights between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)
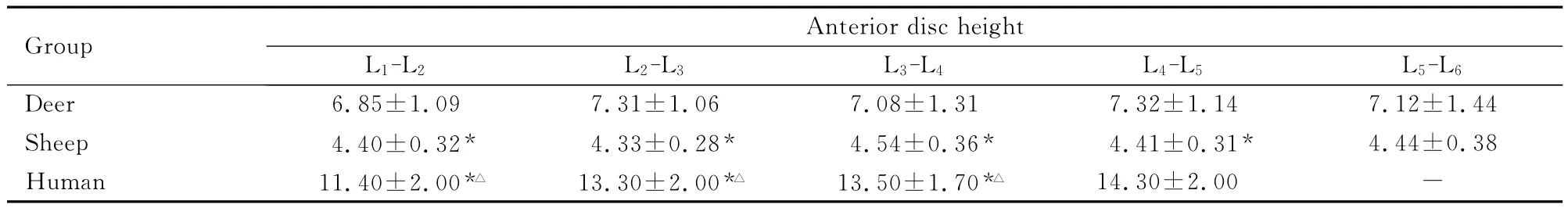
表3 鹿、羊和人椎间盘前部高度比较Tab.3 Comparison of anterior disc heights between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,l/mm)
*P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.01compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Anterior disc height L1-L2 L2-L3 L3-L4 L4-L5 L5-L 6 4 7.12±1.44 Sheep 4.40±0.32* 4.33±0.28* 4.54±0.36* 4.41±0.31* 4.44±0.38 Human 11.40±2.00*△ 13.30±2.00*△ 13.50±1.70*△Deer 6.85±1.09 7.31±1.06 7.08±1.31 7.32±1.1 14.30±2.00 -
2.2 鹿、羊和人腰椎表观密度、弹性模量及极限应力 鹿、羊和人腰椎表观密度、弹性模量及极限应力各组间比较差异均有统计学意义 (P<0.05或P<0.01),其中羊最大,鹿次之,人最小。见表4~6。
表4 鹿、羊和人的表观密度比较Tab.4 Comparison of apparent densities between deer,sheep and human [n=10,±s,ρB/(g·cm-3)]
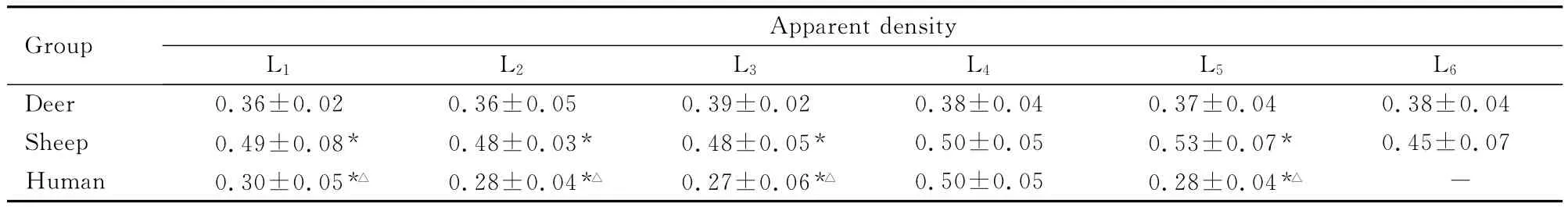
表4 鹿、羊和人的表观密度比较Tab.4 Comparison of apparent densities between deer,sheep and human [n=10,±s,ρB/(g·cm-3)]
*P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.01compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Apparent densit y L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 4 0.37±0.04 0.38±0.04 Sheep 0.49±0.08* 0.48±0.03* 0.48±0.05* 0.50±0.05 0.53±0.07* 0.45±0.07 Human 0.30±0.05*△ 0.28±0.04*△ 0.27±0.06*△ 0.50±0.05 0.28±0.04*△Deer 0.36±0.02 0.36±0.05 0.39±0.02 0.38±0.0-
表5 鹿、羊和人弹性模量比较Tab.5 Comparison of elastic modulus between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,P/MPa)
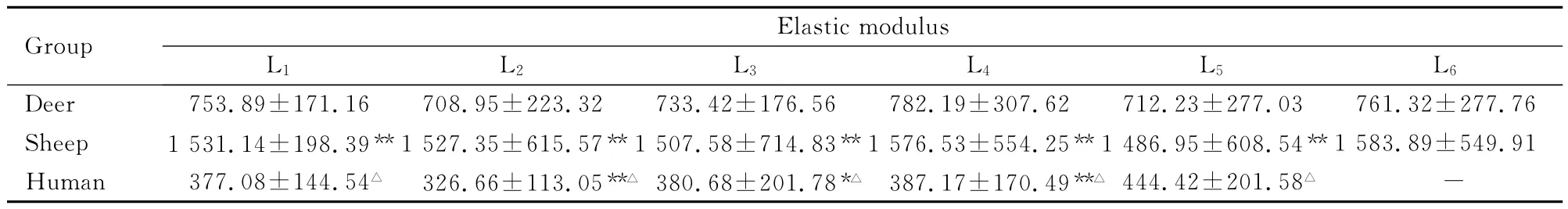
表5 鹿、羊和人弹性模量比较Tab.5 Comparison of elastic modulus between deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,P/MPa)
*P<0.05,**P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.05compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Elastic modulus L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 7.76 Sheep 1 531.14±198.39**1 527.35±615.57**1 507.58±714.83**1 576.53±554.25**1 486.95±608.54**1 583.89±549.91 Human 377.08±144.54△ 326.66±113.05**△ 380.68±201.78*△ 387.17±170.49**△ 444.42±201.58△Deer 753.89±171.16 708.95±223.32 733.42±176.56 782.19±307.62 712.23±277.03 761.32±27-
表6 鹿、羊和人极限强度比较Tab.6 Comparision of ultimate stress of deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,P/MPa)

表6 鹿、羊和人极限强度比较Tab.6 Comparision of ultimate stress of deer,sheep and human (n=10,±s,P/MPa)
*P<0.05,**P<0.01compared with deer;△P<0.01compared with sheep;“-”:No data.
Group Ultimate stress L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6±2.64 16.05±2.03 16.87±3.16 Sheep 22.36±4.39** 21.47±3.76** 22.28±6.01* 23.91±5.17** 21.52±12.16* 22.05±5.25 Human 4.44±0.82**△ 4.31±0.74**△ 4.61±0.78**△ 4.52±0.60**△ 4.80±0.52**△Deer 17.03±3.06 15.70±4.24 18.47±3.31 16.37-
3 讨 论
人腰椎椎弓根宽由L1至L5逐渐增宽,这种变换趋势与腰椎横径的变化趋势相似,可以增加椎弓根的稳定性,加固了脊柱前柱和后柱的机械连接。椎弓根高由L1至L5呈明显的下降趋势。鹿、羊腰椎椎弓根宽由L1至L6逐渐增大,与人腰椎具有相似的变化趋势,鹿椎弓根的宽度较羊更接近于人。鹿、羊腰椎椎弓根高由L1至L5存在逐渐增大趋势,与人椎弓根高的变化趋势相反,鹿椎弓根的高度较羊与人存在较大的差异。脊柱椎弓根螺钉内固定手术中,椎弓根的宽度对螺钉在椎骨内生物力学稳定性起决定性作用。各种椎弓根螺钉动物模型的建立,椎弓根的宽是重要考虑的因素。因此鹿适合于椎弓根螺钉内固定的实验动物,虽然鹿椎弓根的高与人有较大的差异,但椎弓根高在螺钉的固定过程中不起主要的作用。
人的椎间盘前高从头侧到尾侧逐渐增大,鹿、羊的椎间盘前高没有明显的变化趋势,鹿更接近于人。这与Kunar等[5]的测量结果较为一致。近些年国内外许多科研机构相继研发出不同类型的人工间盘和椎间融合器,而这些内植物应用于临床前必须有动物实验证明其可行性。鹿椎间盘较羊更接近于人,因此更适合该类内植物动物模型的建立。
椎骨松质骨的各项生物力学指标对脊椎内固定物的稳定性有很大影响[6-8]。螺钉植入后,很大程度影响了其轴向拔出力。松质骨主要是由矿物质(羟磷灰石结晶和磷酸钙)和Ⅰ型胶原构成,松质骨中骨的含量通常以某种矿物质当量表示。与骨含量类似的另外一个描述指标是孔隙率,松质骨的孔隙率对其力学特性的影响类似于其他的多孔工程材料。表观密度是描述以上2项指标的一个综合指标,是松质骨的一项重要的与力学性能关系密切的指标。许多研究[9-10]显示:表观密度与弹性模量、极限强度之间呈非线性正相关关系。
人、鹿和羊组内比较,弹性模量和极限载荷从头侧向尾侧各椎体间未见明显差异。人、鹿和羊腰椎组间比较,鹿的表观密度与人的相近,而羊的表观密度近似人的2倍。鹿的弹性模量近似人的2倍,羊是人的4倍。鹿的极限载荷近似人的4倍,羊近似人的5倍,说明鹿较羊其生物力学性质和密度参数更接近于人。因此,以鹿作为脊椎内植物动物模型,对内植物在椎骨内的力学分析研究具有十分重要的意义。
我国盛产梅花鹿和绵羊,梅花鹿已被广泛圈养,而且价格较绵羊低,抗病能力强。本研究通过对人、鹿和羊腰椎的解剖形态学参数、骨密度和生物力学参数的对比发现:鹿腰椎的各项参数较羊更接近人类,更适合于建立脊椎内固定动物模型。
[1]Thomas A,Kepler CK,Meyers K,et al.The effect of sacral decortication on lumbosacral fixation in a calf spine model[J].Spine,2011,36 (6):E388-E392.
[2]Wang Z,Lu B, Chen L,et al. Evaluation of an osteostimulative putty in the sheep spine [J].J Mater Sci Mater Med,2011,22 (1):185-191.
[3]中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB14923-2001实验动物 哺乳类实验动物的遗传质量控制 [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2002.
[4]Li ZJ,Xu F.Measurement on vertebral body morphology of adults in North China [J].J Clin Rehabilitat Tissue Engin Res,2008,12 (28):5530-5535.
[5]Kumar N,Kukreti S,Ishaque M.Anatomy of deer spine and its comparison to the human spine [J].Anatom Record,2000,260 (2):189-203.
[6]Seller K, Wahl D. Pullout strength of anterior spinal instrumentation:aproduct comparison of seven screws in calf vertebral bodies[J].Eur Spine J,2007,16 (7):1047-1054.
[7]Hasegawa T,Inufusa A, Yoshiyuki Imai Y,et al.Hydroxyapatite-coating of pedicle screws improves resistance against pull-out force in the osteoporotic canine lumbar spine model:apilot study [J].Spine J,2005,5 (3):239-243.
[8]JanuüI,KoĉišJ,Návrat T,et al.A comparative analysis of socon CS and socon pedicle screws in view of their use for treatment of osteoporotic fractures of the thoracolumbal spinea biomechanical study [J].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech,2011,78 (4):334-338.
[9]Draca N,Tikvica A, Eljuga D,et al.Biomechanical properties of bones from rats treated with sevelamer [J].Coll Antropol,2011,35 (2):557-563.
[10]Charlebois M,Pretterklieber M,Zysset PK.The role of fabric in the large strain compressive behavior of human trabecular bone[J].J Biomech Eng,2010,132 (12):1201-1206.
Comparisons of biological parameters among deer,sheep and human lumbar and their significances
LIU Guo-min1,KONG Ning2,HAN Hong-zhi3,4,YU Hai-tao5,ZHANG Qi1,SUN Hong-hui1
(1.Department of Orthopedics,Second Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130041,China;2.Department of Medical Biomaterials,School of Pharmacy,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China;3.Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics,School of Public Health,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China;4.Editorial Board of Journal of Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China;5.Department of Orthopedics,Affiliated Hospical,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130021,China)
ObjectiveTo study the feasibility of vertebral internal fixation using deer as animal models by comparing the biological parameters of deer,sheep and human lumbar and to provide the morphological parameters,the bone density,and the biomechanical data of laboratory animals for related medical research.Methods10sets of fresh sika deer lumbar,10sets of fresh sheep lumbar,and 10sets of fresh lumbar of male cadavers were selected as the materials.The morphological observation of the lumbar vertebral bodies and pedicles of three groups were taken,and the cancellous bone density,ultimate stress and elastic modulus were measured and compared.ResultsThere were significant differences of heights of right vertebral pedicles between three groups (P<0.01);the deer had the largest one,the sheep followed,and the human had the smallest one.There were remarkable differences of the widths of right vertebral pedicles and anterior disc heights between three groups (P<0.05);the human had the largest one,the deer followed,and the sheep had the smallest one.There were significant differeces of apparent density,elastic modulus and ultimate stress between three groups(P<0.05);the sheep had the largest one,the deer followed,and the human had the smallest one.ConclusionDeer lumbar is more similar as that of human according to anatomic form and biomechanics compared with the sheep lumbar.Therefore,deer is a more suitable to set up animal model for vertebral internal fixation research.
lumbar;animal model;human;deer;sheep;biological parameter
R322.3
A
1671-587Ⅹ(2012)06-1096-05
2012-04-29
吉林省科技厅国际合作项目资助课题 (20100417)
刘国民 (1979-),男,吉林省长春市人,主治医师,医学博士,主要从事骨微形态学方面的研究。
孙红辉 (Tel:0431-88796174,E-mail:liuyedao123@163.com)
