山楂酸减少L02细胞脂质累积作用的研究
2012-11-23穆冬姸
柳 军,王 雪,尚 靖,穆冬姸
中国药科大学新药筛选中心,南京210009
山楂酸减少L02细胞脂质累积作用的研究
柳 军*,王 雪,尚 靖,穆冬姸
中国药科大学新药筛选中心,南京210009
非酒精性脂肪性肝在发达国家和发展中国家中是一种常见的肝脏疾病。引起非酒精性脂肪性肝病的最常见原因有肥胖、糖尿病和高胆固醇。尽管非酒精性脂肪性肝病的发病率日益升高,事实上至今尚未发现可以用于治疗的药物。山楂酸是一种五环三萜化合物,已报道具有多种药理特性,包括抗炎、抗氧化以及免疫调节作用。我们的前期研究表明,山楂酸能够抑制高脂饲料诱导大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病的生成。本研究中,我们将探讨山楂酸体外对肝细胞(LO2)脂质累积的抑制作用。结果表明,山楂酸可抑制游离脂肪酸(FFA)诱导的LO2细胞脂质累积,进一步研究表明,山楂酸可抑制LO2细胞的SCAP mRNA水平和蛋白水平的表达。
山楂酸;肝细胞脂肪变性;LO2细胞;固醇调节元件结合蛋白裂解激活蛋白
Introduction
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)is fatty inflammation of the liver when this is not due to excessive alcohol use.It is reported that NAFLD relates to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome,and may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin resistant states,such as weight loss,metformin and thiazolidinediones[1]. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)is the most extreme form of NAFLD,which is regarded as a major cause of cryptogenic cirrhosis of the liver[2].
MA(Fig.1)occurs naturally in a wide variety of plant species such as Leguminosae,Boraginaceae and Asteraceae.We have previous reported that MA is capable of lowering serum glucose and preventing high fat diet induced fatty liver in rats[3].However,the molecular/ cellular mechanisms of MA on lipid metabolism remain unknown.
Sterol regulatory element binding protein cleavage activating protein(SCAP)is regarded as an important regulator in synthesis and absorbance of lipid[4],and playing a critical role in regulating the balance of lipid metabolism.
In this study,steatosis models of hepatocytes were established by adding free fatty acids(FFA,oleate/palmitate,2∶1)to the growing L02 cell.The lipid droplets in the hepatocytes were observed with oil red staining and the contents of triglyceride in hepatocytes were measured with analyzed kit.The mRNA and protein levels of SCAP were measured as well.The over expression of SCAP in model cell groups could lead to disturbance of lipid metabolism and probably participate the process of steatosis of hepatocytes.Treatment with MA showed that MA can decrease effectively lipids accumulation in FFA-induced L02 cells.Furthermore,MA can regulate the lipid metabolism through regulating the mRNA and protein expression of SCAP in L02 cells.
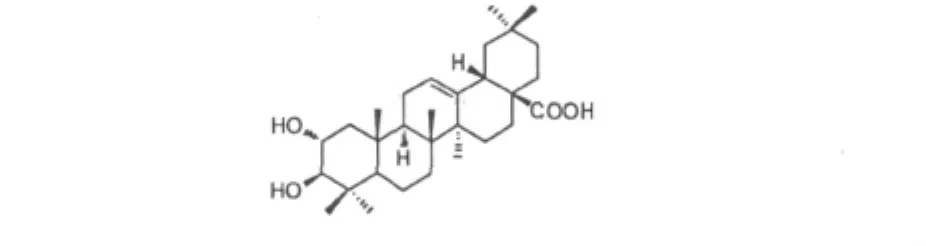
Fig.1 The structure of MA
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
Human normal liver L02 cells(Cell Bank,Type Culture Collection of Chinese Academy of Sciences)were cultured in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% heat inactivated FBS,100 U/mL penicillin,100(g/mL streptomycin,and 2 mM glutamine.Cells were incubated at 37℃ in a humidified atmosphere(5%CO2).FFA(oleate/palmitate,2∶1)were mixed with FFA-free BSA and added into medium to a final concentration of 1 mM.
Chemicals and reagents
Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640(RPMI-1640),fetal bovine serum(FBS),horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody were purchased from GIBCO-BRL.Rabbit monoclonal antibody against actin was from Sigma.Nitrocellulose membranes (Hybond),and an enhanced chemiluminescence detection system were all obtained from Amersham Pharmacia.DNA Taq polymerase was obtained from Fermentas(Shanghai,China),M-MLV reversetranscriptase was obtained from Promega(Madison,WI).TRIzol reagent was obtained from Gibco(Gaithersburg,MD,USA).All other reagents unless indicated were from Sigma Chemical Co. MA was obtained by semi-synthesis starting from readily available oleanolic acid as previously described.[5,6]MA was stored at room temperature until use.
Oil red O staining
Oil red O staining was used specifically for lipid droplet accumulation.L02 cells were stained by the Oil Red O method.[7]Cells were treated with 1 mM of FFA together with MA(1 μM and 10 μM)for 24 h.After treatments,cells were washed three times with iced PBS and fixed with 10%formalin for 60 min.After fixation,cells were washed and stained with Oil Red O solution (stock solution,3 mg/mL in isopropanol;working solution,60%Oil Red O stock solution and 40%distilled water)for 60 min at room temperature.After staining,cells were washed with water to remove unbound dye.Quantitative analysis of Oil Red O content levels,isopropanol was added to each sample,and shaken at room temperature for 5 min.The samples were read spectrophotometrically at 510 nm by Tecan reader (Megallan Company,Swiss).
SCAP gene analysis with RT-PCR
L02 cells were treated with 1mM FFA together with various concentrations of MA for 24 h.Total RNA of each group was extracted from L02 cells with homogenization in TRIzol reagent(Gibco,Maryland,USA)according to the manufacturer's instructions.Reverse transcription and cDNA-PCR process were done according to general RT-PCR method.PCR amplification was carried out in the thermal cycler using a protocol of initial denaturing step at 95℃ for 10 min;followed 35 cycles of 95℃for 1 min,60℃ for 40 s and 72℃ for 40 s;and final cycle of 72℃ for 10 min.The PCR products were run on 2%agarose gel in 1×TBE buffer and measured as height value by using Quantity One main program (BIO-RAD,USA).Sequences of the deoxyribonucleotide for PCR are as table 1.
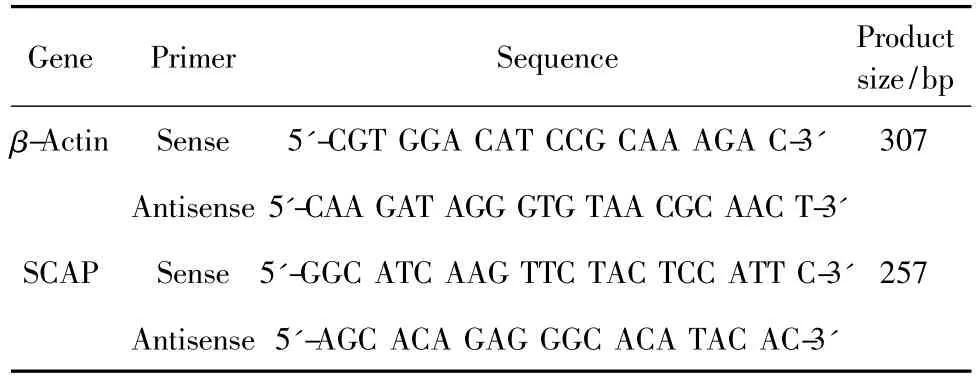
Table 1 Oligonucleotide sequences of primers
Western blot analysis
Total cell lysates were prepared and processed as described previously[8].The expression levels of SCAP were detected with specific antibodies.(-actin was used as loading control.The densities of immunoblot bands were analyzed using Quantity One main program (BIO-RAD,USA).
Statistical analysis
All values are expressed as means±standard error of the mean(SEM).Student's t-test was used to determine the significance of differences in multiple comparisons.Values of P<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results

Fig.2 Effects of MA on intracellular lipid accumulation in L02 cells
MA inhibit L02 cellular lipid accumulation
Previous studies have suggested that MA have hypolipidemia effects in high fat diet induced fatty liver rats[3].To evaluate the hypolipidemia effects in L02 cells,1 mM FFA(oleate/palmitate,2∶1)was used in the present study.We examined whether MA was able to prevent FFA-induced lipid accumulation in L02 cells using oil red O staining.As shown in Fig.2,the intracellular lipid content could be reduced significantly by treatment with MA.
Gene Expression of SCAP
A single transcript(257 bp)was observed in all groups.RT-PCR analysis of SCAP showed a significant increased in FFA-overloaded cells,while the expression of SCAP mRNA in MA-treated cells was decreased when compared with model cells.(Fig.3)

Fig.3 Effect of MA on the mRNA levels of SCAP in L02 cells
MA inhibit the protein levels of SCAP in L02 cells Compared with the initial level,L02 cells already had increased levelsof SCAP after 24h at highFFA conditions.However,these levels reduced undercoincubation with MA.(Fig.4)
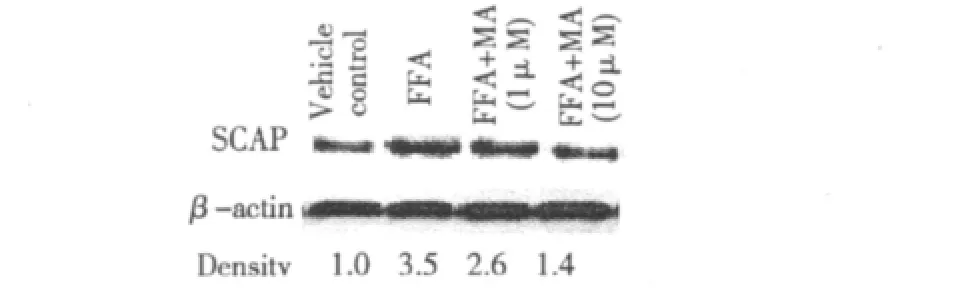
Fig.4 Effect of MA on SCAP expression in L02 cells
Discussions
The causes ofNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)remain unknown.However,it is related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome[10].Recent studies have shown that NAFLD develops in a relatively short period of irreversible liver damage;some patients can progress to cirrhosis of the liver[11].
SCAP is regarded as an important regulator in synthesis and absorbance of lipid[4].Sterol regulatory element binding proteins(SREBPs)are a family of membranebound transcription factors that control the synthesis of cholesterol and fatty acids in animal cells[12].SCAP activates SREBP,and initiates the release of NH2-terminal fragments from cell membranes;the liberated fragments enter the nucleus and stimulate transcription of genes involved in synthesis and uptake of cholesterol and fatty acids[13].This regulatory mechanism underlies the adaptation to cholesterol synthesis inhibitors(statins)and high calorie diets(insulin).
FFA plays an important role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.As a part of our studies that we have reported that MA,as a natural product to be an agent for lowing blood glucose and improvement insulin resistance and has therapeutic effect on fatty liver as we reported previously[8,9].Whether MA has any beneficial effects on FFA-induced hepatic toxicity remains to be characterized.In this study,we found that the mRNA expression levels and protein expression levels of SCAP increased after adding FFA on cultured liver cells for 24 h.The model group cells increased steatosis,and total lipid,triglyceride and cholesterol content increased significantly.Oil red O staining of liver cells shows that fatty degeneration also increased.After treating with MA,the lipid accumulation will decrease(Fig.1).The present study provided the first evidence for the protective effect of MA on FFA-induced lipotoxicity in L02 cells.MA not only reduced FFA-induced lipid accumulation,but also significantly inhibited SCAP expression(Fig.3 and 4).In summary,MA inhibits the lipid accumulation in L02 cells and maybe as a natural and effect agent in treating NAFLD.
1 Farrell GC,Larter CZ.Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:from steatosis to cirrhosis.Hepatology,2006,43(Suppl 1):S99-S112.
2 Hai S,Kubo S,Shuto T,et al.Hepatocellular carcinoma arising from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:report of two cases.Surg Today,2006,36:390-394.
3 Liu J,Sun HB,Wang XF,et al.Effects of oleanolic acid and maslinic acid on hyperlipidemia.Drug Develop Res,2007,68: 261-266.
4 Salek L,Lutucuta S,Ballantyne CM,et al.Effect s of SREBF-1a and SCAP polymorphisms on plasma levels of lipids,severity,progression and regression of coronary atherosclerosis and response to therapy with fluvastatin.J Mol Med,2002,80:737-744.
5 Wen XA,Sun HB,Liu J,et al.Pentacyclic triterpenes.Part 1:The first examples of naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenes as a new class of inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylases.Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2005,15:4944-4948.
6 Wen XA,Zhang P,Liu J,et al.Pentacyclic triterpenes.part 2:Synthesis and biological activity of maslinic acid derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2006,16:722-726.
7 Hwang JT,Park IJ,Shin JI,et al.Genistein,EGCG,and capsaicin inhibit adipocyte differentiation process via activating AMP-activated protein kinase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2005,338:94-699.
8 Gao Y,Feng HC,Walder K,et al.Regulation of the selenoprotein SelS by glucose deprivation and endoplasmic reticulum stress—SEPS1 is a novel glucose-regulated protein.FEBS Lett,2004,563:185-190.
9 Bligh EG,Dyer WJ.A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification.Can J Biochem Physiol,1959,37:911-917.
10 Adams LA,Angulo P.Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Postgrad Med J,2006,82:315-322.
11 Cassiman D,Jaeken J.NASH may be trash.Gut,2008,57: 141-144.
12 Brown MS,Goldstein JL.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1999,96: 11041-11048.
13 Marc IS.Pharmacological regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor expression:current status and future development.Pharmacol Ther,2006,111:424-433
November 25,2011;Accepted February 28,2012
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(No.JKP2011004)
Effect of Maslinic Acid on Attenuating Lipid Accumulation in L02 Cell
LIU Jun*,WANG Xue,SHANG Jing,MU Dong-yan
National Drug Screening Center,China Pharmaceutical University,Nanjing 210009,China
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)is the most common liver disorder both in western industrialized countries and in developing countries.The most common causes of NAFLD are obesity,diabetes,and high cholesterol levels.Despite the increasing prevalence of NAFLD,the therapeutic agents are remained to be discovered.Maslinic acid (MA)has a variety of pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,and immune-modulating activities.In our previous study,we have reported that MA has protected NAFLD effect in the high-cholesterol induced hyperlipidemia rats.In the present study,we examined the effects of MA on attenuating lipid accumulation in human normal liver L02 cells.The study showed that MA can prevent free fatty acid(FFA)induced lipid accumulation in L02 cells.Furthermore,MA can suppress the mRNA expression and protein levels of SCAP induced by FFA in L02 cells.
maslinic acid;steatosis hepatocyte;L02 cell;SCAP
1001-6880(2012)10-1355-04
*Corresponding author Tel:86-25-83271043;E-mail:junliu@cpu.edu.cn
R966
A
