磷酸肌酸对缺血大鼠心室中层心肌细胞瞬间外向钾电流的影响
2012-11-13时向民李天德王玉堂单兆亮杨庭树
时向民, 李天德, 王玉堂, 单兆亮, 杨庭树
(解放军总医院 1南楼心内科,2普通心内科,北京100853)
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1 Materials
The following solutions were prepared:(1)Tyrode solution(mmol/L):CaCl21.8,NaCl 116,KCl 5.4,NaHCO315,NaH2PO41.4,MgSO41,glucose 15,taurine 30,pH was adjusted to 7.4 with HCl.(2)Ca2+-free Tyrode solution(mmol/L):NaCl 116.0,KCl 5.4,NaHCO315,NaH2PO41.4,MgSO41,glucose 315,taurine 30,gassed with 95%O2plus 5%CO2,pH was adjusted to 7.4 with HCl.(3)KB medium(mmol/L):KOH 90,L - glutamic acid 70,taurine 20,KCl 30,KH2PO410,HEPES 10,glucose 10,EGTA 0.5,pH was adjusted to 7.3 with KOH.(4)Internal pipette solution for Itocurrent recording(mmol/L):KCl 140,MgCl20.53,EGTA 10,HEPES 10,pH was adjusted to 7.3 with KOH.(5)External pipette solution for Itocurrent recording(mmol/L):NaCl 116,KCl 5.4,NaHCO315,NaH2PO41.4,MgSO41,glucose 15,taurine 30,BaCl21,CoCl22,pH was adjusted to 7.4 with HCl.(6)Simulated ischemic solution(mmol/L):NaCl 123,KCl 10,NaH2PO40.9,MgSO40.5,CaCl22.7,pH was adjusted to 6.8 with NaOH.All the chemicals including protease E,EGTA,BSA,HEPES and taurine were obtained from Sigma.Exogenous phosphocreatine(PCr)was provided from Aassermann.Thirty Wistar rats weighing(150±45)g were provided by Medical Experimental Animal Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital.
2 Ventricular M cell isolation
Single left ventricular M cells were isolated enzymatically from the rats using previously described methods[3].Briefly,the heart was rapidly excised and perfused via the coronary artery with Ca2+-free Tyrode solution for 5 min,followed by Ca2+- free Tyrode solution containing protease E,BSA(0.5 g/L)and CaCl2(150 mmol/L)for 5 min until the heart became soft.All solutions were gassed with 95%O2plus 5%CO2,warmed to 37℃and the perfusion pressure was maintained at 70 cmH2O.The medium layer of left ventricle was separated and cut into small pieces.The isolated ventricular M cells were stored in KB medium after filtration.The obtaining rate of calcium-tolerant ventricular M cells was 70%~80%.Only rod-shaped noncontracting cells with clear cross striations were used for the whole-cell patch-clamp studies(Figure 1).
Figure 1.Isolation of left ventricular M cells.A:an isolated left ventricular M cell wityh clear cross striations;B:an left ventricular M cell giga-sealed by a micropipette.
3 Whole-cell patch-clamp recording
Based on the conventional Hamil method,M cells were placed in a chamber on the stage of an inverted microscope(Nikon).After 5 min of deposition,M cells adhered to the bottom of the chamber.Itocurrent was recorded by whole-cell patch-clamp technique(patch-clamp amplifier,Axonpatch 700A,Axon Instruments).The amplifier was connected with a personal computer.The experimental protocol and data acquisition were performed with pCLAMP 8.2 software(Axon Instruments).Micropipettes were pulled by a continuous two-step puller(P-97,Sutter Instrument),which had tip resistance of 2~4 MΩ with average diameter of 2~3μm when filled with internal pipette solution.Liquid junction potentials were corrected after the pipette immersed in the solution.After a tight pipette-membrane seal was obtained(seal resistance>1 GΩ),fast capacitance was compensated,then the membrane was ruptured with gentle suction to obtain the whole-cell voltage-clamp configuration,and slow capacitance and series resistance were compensated.
4 Method of recording Ito current
Isolated M cells were divided into the following 6 groups:Tyrode solution,simple simulated ischemic solution,and simulated ischemic solution containing PCr at concentrations of 5,10,20 and 30 mmol/L.The chamber was continuously superfused with test solution at a speed of 2 mL/min at 37℃after suction of M cells.Tyrode solution was gassed with 95%O2+5%CO2,while the solutions in other groups were gassed with 95%N2+5%CO2.Ten minutes later,peak Itocurrent was recorded in every group and expressed as current density.Itocurrent amplitudes were calculated as difference between peak inward and steady-state currents.To get rid of the effect of capacitance on the peak Itocurrent amplitude,Itocurrent density was compared between different groups.The Itocurrent was evoked by 250 ms step depolarization between-30 mV and+70 mV with a 10 mV increment from a holding potential of-40 mV,and stimulation frequency was set to be 0.5 Hz.Current- voltage relationship(I- V)curves were generated by applying a series of depolarizing pulse from a holding potential of-40 mV to different membrane potential(-30~+70 mV)with a 10 mV increment.During the process of experiment,oxygen tension(PO2)and oxygen saturation(SO2)of the perfusion solutions were measured by blood gas analyzer(Nova Biomedical),which indicated PO2> 60 mmHg and SO2> 90%in Tyrode solution,as well as PO2<60 mmHg and SO2<90%in simulated ischemic solution.The osmolality of the perfusion solutions was also monitored(JC216-8P)and varied between 290~320 mOsm.
5 Statistical analysis
All results were expressed as mean±standard deviation(¯x±s).Mean comparison among groups was performed by ANONA and LSD -t test using SPSS12.0 software.P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
1 Characteristics of Ito current and steady-state current-voltage relationship
High amplitude outward current was recorded in Tyrode solution group,which presented quick activation and inactivation process,as well as voltage-dependent character(Figure 2).Itowas activated at-30 mV and reached its peak at 70 mV(Figure 3 and Table 1).Compared with Tyrode solution group,peak Itocurrent in M cells superfused with simulated ischemic solution greatly decreased by(76.1 ± 6.3)%(P < 0.05).However,the peak Itocurrent of Tyrode solution group significantly reduced after washout by simple simulated ischemic solution(Figure 2).

Figure 2.Ito current curves in different groups.A - F:Ito currents of ventricular M cells superfused with Tyrode solution,simple simulated ischemic solution,simulated ischemic solution containing PCr at concentrations of 5,10,20 and 30 mmol/L,respectively;G:Ito current after washout of simulated ischemic solution with 30 mmol/L PCr;H:depolarizing pulses applied in A-G;I:scales of the coordinated axes in A-G.
2 Effect of PCr at different concentrations on Ito under the condition of ischemia
In relation to PCr concentration elevation in simulated ischemic solution,peak Itocurrent and current density gradually improved.Meanwhile,the numbers of dead M cells markedly reduced.Compared with the cells superfused with Tyrode solution,simulated ischemic solution containing PCr at concentrations of 5,10,20 and 30 mmol/L reduced peak Itocurrent density by(57.1 ±9.6)%(P <0.05),(40.3 ±10.3)%(P <0.05),(34.3 ±9.6)%(P <0.05)and(32.1 ±10.6)%(P <0.05),respectively.There was statistical difference among ischemic solution without PCr and containing PCr at concentrations of 5 and 10 mmol/L(P<0.05),and no statistical difference among groups of 10,20 and 30 mmol/L PCr was observed(P >0.05).Within the concentration ranging from 0~10 mmol/L,PCr displayed a prominent dose-dependent effect on Itoimprovement.However,if the concentration was more than 10 mmol/L,Itocurrent increased slowly and the dose-dependent manner did not exist(Figure 2 and Table 1).
The I-V curve position of M cells superfused with Tyrode solution was higher than that with ischemic solution or combined with different concentrations of PCr.However,the peak - value potential,the activation potential and the I-V curve shape remained unchanged(Figure 3).
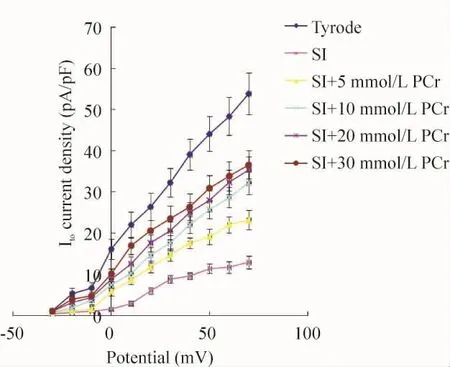
Figure 3.The effects of different superfusion solutions on current- voltage relationship of Ito.SI:simulated ischemic solution.¯x±s.n=8.

Table 1.Peak Ito current and current density in M cells superfused with different solutions(¯x±s.n=8)
DISCUSSION
Itois the key outward potassium current in early stage of action potential with character of rapid voltage-dependent activation and inactivation,which is more prominent in M cells than myocytes in endo-and epicardium.It has been proved that inhibition of Itoin ischemia would significantly prolong the effective refractory period(ERP)of M cells and consequently amplify transmural repolarization dispersion,which could be the underlying mechanism of arrhythmia.
It was reported that IKATPaugmented largely and was responsible for the increased outward potassium in ischemia[4].With the purpose of eliminating influence of IKATP,IKATPblocker glibenclamide was added to all perfusion solution.Simultaneously,the holding potential maintained at-40 mv as well as the addition of CoCl2in external solution effectively inhibited INaand ICachannels.On the other hand,the recorded current was significantly blocked by 4-aminopyridine in experimental study,which demonstrated the current was Ito.
The results of our study demonstrated that peak Itocurrent density was reduced by 80%under simulated ischemic condition.Many researches revealed that inhibition of Itoattributed to intercellular acidosis and oxidative stress[5].It has been reported that the intercellular ATP level rapidly decreased with accumulation of ADP in ischemia.As a normal physical response with the purpose of maintaining ATPlevel,ATPsynthesis was initiated by means of Lomman reaction employing substrate of ADP and PCr(ADP+PCr→ATP+Cr),which was closely correlated with decomposition of ATP.Finally,the net intercellular metabolic result was expressed as PCr→Cr+Pi,and the level of PCr was dramatically decreased[6].In our experiment,supplement of different concentrations of exogenous PCr exerted its remarkable effect on increasing Itopeak current and peak current density.PCr is known as the fundamental substrate for ATP synthesis,therefore supplement of exogenous PCr could be an effective and feasible way to improve intercellular ATP under the condition of ischemia.Conway et al[7]demonstrated that PCr,which labeled with14C and97P,could readily penetrate membrane of myocytes in ischemia.Meanwhile,Perepech et al[8]suggested that PCr or PCr combined with thrombolysis significantly reduced the occurrence of fatal arrhythmia within 6 h in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
Our study showed that the concentration of exogenous PCr did not lineally correlate with the increase in Itocurrent.PCr at different concentrations significantly improved peak current and peak current density.When the concentration was over 10 mmol/L,PCr displayed minor improvement on Itocurrent,and there was no statistical difference among simulated ischemic solution containing PCr of 10,20 and 30 mmol/L.This observation suggested that exogenous PCr promoted ATPsyn-thesis via another pathway rather than simple substrate of ATP.If PCr merely serves as substrate of ATP,the dosage in our experiment could not meet the abundant ATP need in the body.Another key mechanism responsible for this sign is that PCr could protect the pool of Σ(ATP+ADP+AMP)via inhibiting 5'- nucleotidase and maintaining the substrate of ATP[9].This function may reach a plateau when the concentration exceeded 10 mmol/L[10],which could explain the dose - effect curve between PCr and Itocurrent.Our result reconfirmed that 10 mmol/L of PCr was the optimal concentration for the treatment of ischemic heart disease in many clinical practice[11].
Our experiment demonstrates that supplement of exogenous PCr reverses the inhibition of Itocurrent in M cells under simulated ischemic condition,indicating the underlying electrophysiological mechanism for preventing arrhythmia by means of increasing velocity and amplitude of repolarization in phase 1,shortening action potential duration(APD)and ERP in the M cells,reducing transmural repolarization dispersion and subsequently inhibiting reentry formation.
[1] Antzelevitch C.Modulation of transmural repolarization[J].Ann N Y Acad Sci,2005,1047:314 -323.
[2] Calloe K,Soltysinska E,Jespersen T,et al.Differential effects of the transient outward K+current activator NS5806 in the canine left ventricle[J].JMol Cell Cardiol,2010,48(1):191 -200.
[3] Hamil OP.Twenty odd years of stretch - sensitive channels[J].Pflugers Arch,2006,453(3):333 -351.
[4] Day YJ,Gao Z,Tan PC,et al.ATP sensitive potassium channel and myocardial preconditioning[J].Acta Anaesthesiol Sin,1999,37(3):121 -131.
[5] Fukuda K,Davies SS,Nakajima T,et al.Oxidative mediated lipid peroxidation recapitulates proarrhythmic effects on cardiac sodium channels[J]Circ Res,2005,97(12):1262-1269.
[6] Grzyb K,Skorkowski EF.Creatine kinase isoenzymes:characterization and functions in cell[J].Postepy Biochem,2008,54(3):274-283.
[7] Conway MA,Allis J,Ouwerkerk R,et al.Detection of phosphocreatine to ATP ratio in failing hypertrophied human myocardium by31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J].Lancet,1991,338(8773):973 -976.
[8] Perepech NB, Nedoshivin AO,Nesterova IV, et al.Neoton and thrombolytic therapy of myocardial infarction[J].Ter Arkh,2001,73(9):50-55.
[9] Saks VA,Dzhaliashvili IV,Konorev EA,et al.Molecular and cellular aspects of the cardioprotective mechanism of phosphocreatine[J].Biokhimiia,1992,57(12):1763 -1784.
[10] Menin L,Panchichkina M,Keriel C,et al.Macrocompartmentation of total creatine in cardiomyocytes revisited[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2001,220(1 -2):149 -159.
[11] Brosnan JT,Brosnan ME.Creatine:endogenous metabolite,dietary,and therapeutic supplement[J].Annu Rev Nutr,2007,27:241 -261.
