国际科技信息
2012-10-27
国际科技信息
NIH千人基因组计划数据集将免费对外开放
美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)3月29日宣布,他们的千人基因组计划的全部数据将免费对外开放。这些数据总量达到200TB,是世界上最大的人类基因变异数据集。亚马逊旗下的云计算公司——“亚马逊网络服务”将存储这个庞大的数据库。
千人基因组计划旨在为基因变异如何影响健康以及与疾病间关系的研究奠定基础。所有数据免费对外开放意味着更多科学家可以利用这些数据进行研究,以更快的速度得出基因型与癌症、糖尿病等疾病间关系的发现。
这项计划于2008年启动,立基于全世界26个国家和地区的2600多人的基因组。其中1700人的DNA排序结果将在不久后公布并进行云存储,余下900人的DNA将在2012年进行排序。
国立卫生研究院的千人基因组计划是一项规模更大的举措组成部分,用于管理科学研究产生的海量数据——数据管理本身就是一门科学。由于类似千人基因组计划这样的数据集规模庞大,很少有研究人员具备处理能力,因此也就无法使用。根据国立卫生研究院的计算,千人基因组计划的数据如果打印出来,可放满1600万个档案柜;如果使用标准DVD存储,需要3万多张DVD。
对于科学家和他们所在的研究机构来说,千人基因组计划数据进行云存储无疑是一个好消息,他们无需拥有更大带宽,数据存储和分析处理能力便可获取这些数据。亚马逊网络服务公司首席产品经理德帕克·辛格表示:“这意味着所有研究人员和实验室都可以获取完整的千人基因组计划数据,无论它们规模大小和预算多少。他们可以立即对这些数据进行分析,而无需在这方面投入资源。通常情况下,他们需要大量硬件、设施和人员才能获取这些数据。由于无需投入资源便可获得研究所需数据,科学家可以加快研究步伐。”
对于亚马逊网络服务公司来说,存储千人基因组计划的数据可能也是一个好消息。美国《纽约时报》报道称,处理如此海量数据需要极大的运算能力,亚马逊网络服务公司可以要求获得额外的资源,用于进一步处理或者分析这些数据。
白宫认为云存储千人基因组计划数据是他们的“大数据研究和发展倡议”所提出的解决方案的一个典范。美国科学和技术政策办公室29日宣布,将有2亿多美元投向6个联邦机构,用于推动大数据计算领域的研究——包括大数据分析——以及大数据在科学探索、环境和生物医学研究、教育以及国家安全领域的应用。

World's Largest Dataset on Human Genetic Variation Goes Public
The entire contents of the National Institutes of Health's 1000 Genomes Project—all 200-terabytes of it—will be made freely available to the public, the agency announced today. The project is touted as the world's largest set of data on human genetic variation. Amazon's cloud computing unit, Amazon Web Services, will store the database.
The project aims to provide a foundation for investigating how human genetic variation contributes to health and disease. Making the whole thing available for free means more scientists can use the data and, hopefully, conclusions about the relationship between genotype and such diseases as cancer and diabetes will be drawn at an accelerated rate.
The project was initiated in 2008 and is based on the genomes of more than 2600 people from 26 populations around the world. Results from sequencing the DNA of 1700 of those people will be released on cloud now. The remaining 900 samples will be sequenced this year.
The NIH's initiative is part of a larger movement to manage the deluge of "big data" in science, which has become a scientific discipline in itself. Such data sets have become so massive that few researchers have the computing power to use them. The NIH has calculated that the 1000 Genomes Project is the equivalent of 16 million file cabinets filled with text, or more than 30 000 standard DVDs.Making it available on cloud is a good deal for scientists and their institutions, who won't have to take on the costs of acquiring more bandwidth, data storage and analytical computing capacity just to access the data. "This means researchers and labs of all sizes and budgets have access to the complete 1,000 Genomes Project data and can immediately start analyzing and crunching the data without the investment it would normally require in hardware, facilities and personnel," says Deepak Singh, a principal product manager at Amazon Web Services. "Researchers can focus on advancing science, not obtaining the resources required for their research."
It may also end up being a good deal for Amazon Web Services (A.W.S.). Manipulating this much information requires a lot of computing power, and A.W.S. will be charging for additional resources that can be used to further process or analyze the data, reports the New York Times.
The White House, for its part, sees the 1000 Genomes Project on cloud as one example of the kind of solutions it is proposing through its Big Data Research and Development Initiative. The Office of Science and Technology Policy announced today that more than $200 million will be doled out to six federal agencies in an effort to make the most of the mountains of data being created for scientific discovery, environmental and biomedical research, education, and national security.
欧盟农业和科技界高层会聚布鲁塞尔 重新认识农业研发创新
两大相互关联又错综复杂的突出问题严重困扰着欧盟农业的可持续发展:一是人口持续增长、粮食食品安全、资源日益枯竭、能源对外依赖、生态环境退化和气候变化压力对农业的严峻挑战;二是农业研发创新的边际效应下降,造成公共和私人农业研发创新投入的逐年减少。两大突出问题相互制约,形成农业不可持续的恶性循环,解决问题刻不容缓。
2012年3月7日,欧盟农业和科技界高层聚会布鲁塞尔,探讨研究解决问题的路径,重现认识农业研发创新的重要意义,形成加强农业研发创新投入强度、加速农业研发创新突破的共识。
欧委会负责农业事务的委员乔罗仕(CIOLOS)认为,欧盟21世纪的农业必须依托研发创新,基于知识的研发创新是解决如此复杂问题的唯一途径。欧委会负责科研与创新事务的委员奎恩(QUINN)女士表示,科学技术支撑和创新解决方案是农业及食品加工业可持续发展的关键。欧盟轮值主席国丹麦农业部长吉奥斯古(GJERSKOV)女士指出,农业研发创新的重要意义是决定性的,农业可持续与应对各类社会挑战息息相关,必须增加农业研发创新公共财政投入,研发创新可以解决投入少产出多,在缓解生态环境压力的同时促进经济增长和扩大就业。欧盟议会农业委员会主席卡斯特洛(CASTRO)强调,需要进行一场绿色革命,充分利用研发创新成果提高农业生产率,解决资源匮乏,消除农业、能源和生物基产品相互争资源,限制农业对水、能源、农药和化肥的消耗,同时降低农产品浪费。法国农科院(INRA)院长贵瑶(GUILLOU)女士代表科技界发言,欧盟创新伙伴关系计划(EIPs)是解决农业研发创新和可持续的有效手段,三大主要问题需要农业研发创新的突破:1)食品需求增长与食品大量浪费的矛盾;2)粮食产量提高与可再生生物质产品的矛盾;3)粮食生产率与土壤、水、生物多样性、生态环境的矛盾。
E.U. conference examines innovation in agriculture
More than 300 stakeholders, researchers, academics and officials met in Brussels, Belgium on March 7 for a conference on "Enhancing innovation and the delivery of research in EU agriculture.”

This conference marked an important step in the discussions on the ways to enhance innovation and the translation of research results in the farming sector, as outlined in the Commission's CAP reform legislative proposals on Oct. 12, 2011, the E.U. said.
In his opening speech to the conference, E.U. Agriculture and Rural Development Commissioner Dacian Cioloș said, "Fostering research, knowledge transfer and innovation in the agricultural sector is vital for improving productivity, sustainability and competitiveness. Today I would like to issue a general call for action on the question of agricultural research and innovation, a subject which has for too long been left to the relative obscurity of scientific laboratories and academic publications. It is an area in which the European Commission has tabled very ambitious proposals. We are going to double the funding available and to put in place a complete toolbox. Apart from the budget, we need to ensure that all stakeholders are working together in an integrated way and that good ideas do not remain confined to scholarly publications but are, instead, made available to all players."
The objective of the conference was to discuss the main building blocks of EU support to research and innovation for the agricultural sector after 2013. After setting the stage of agricultural research and learning from recent experiences, the conference strived to highlight the critical aspects necessary for research to impact the agricultural sector. In particular, the role played by networks, advisory services, education and other actors in the translation of research results and in fostering innovative approaches were investigated.
The conference brought together:
· CAP stakeholders, European and national farmers' organisations;
· Representatives of Member States (Ministries, delegates of the Standing Committee on Agricultural Research (SCAR) and of the Programme Committee of DG RTD, representatives of national advisory bodies);
· Researchers and academics;
· Commission services and other EU institutions: EP, CoR, EESC.
日本用新型光源实现量子加密长距离传输
日本冲电气(OKI)公司成功开发了一种在理论上不可能泄密的量子加密方式,并可以在城市间实现长距离通信。该公司利用光的“量子纠缠”特性在验证试验中实现了140公里无中继信息传输。这一研究成果将在2015年投入使用。日本和欧洲都在进行关于量子加密通信的研究,但通信距离短一直是这一课题的难点。新的研究成果使这一技术的实用性得到大幅度提高。
量子加密通信是在被称为光子的光粒子上载荷密码的加密方式,冲电气公司为此开发了能够产生光子的新型激光光源。这种新型光源不但比现有的量子加密通信光源成本更低,而且能够兼容现有光通信系统中的光器件,有较好的实用性。冲电气公司以2015年为目标,计划首先在金融机关和医院等保密性要求较高的专用线路上应用。然后逐步向公众通信网普及。
冲电气公司在实验系统中,有效利用了两个一组的光子特有的“量子纠缠”特性。在进行加密通信时,将处于纠缠状态的两粒光子分别送到相距140公里的收、发两端,收发两端各取一粒光子作为仅限双方使用的通用密匙。发送端利用光子的物理特性,在“看到”光子的某一瞬间决定密匙的形式,接收端会使用这一密匙解密所收到的信息。在传输过程如果中遭到窃密,会残留“光痕迹”,系统能够立刻发现。
在现有的光通信系统中,由于激光光源强度较弱,无中继通信距离仅能达到100公里左右,新型光源技术使
得长距离通信成为可能,冲电气公司将与其他企业和大学协作,研发新型光通信系统。
【量子加密通信方式】
光具有“波”和“粒子”的两重性,从粒子的角度看被称为光子。上述研究的主要方向是利用光子载荷密匙,发送者和接收者通过共有密匙实现量子加密通信。根据物理学定律,光子在被第三者“看到”的瞬间,其物理状态会发生变化并留下“痕迹”,因此在该加密系统理论上是不可能失密的。
OKI Develops the World's Purest Quantum Entangled Light Source and Establishes Practical, Next-Generation Quantum Cryptography Technologies
OKI Develops the World's Purest Quantum Entangled Light Source and Establishes Practical, Next-Generation Quantum Cryptography Technologies
Drawing on proprietary technologies, OKI has developed a quantum entangled light source that offers the highest level of purity achieved to date. It has successfully generated the highpurity, entangled photon pairs for the first time anywhere in the world operating at room temperature and for conventional optical communication bands that are currently in use. Joint demonstrations performed with the research group conducted by Professor Shuichiro Inoue at Institute of Quantum Science, Nihon University confirm a signalto-noise ratio more than 100-fold better than optical fiber light sources. Transmission tests using this light source with standard optical fibers have successfully transmitted quantum entangled photon-pairs over a distance of 140 km, demonstrating the feasibility of next-generation quantum cryptography communication systems1 covering metropolitan area.
"Quantum cryptography technologies apply the principles of quantum mechanics for eavesdropping detection. They have attracted attention as an exceedingly high-security service for a smart community due to their potential to achieve indecipherable encoding. A number of major hurdles confront research and development teams working to achieve practical applications, including the need for ultra-lowtemperature cooling for light sources and the generation of light at wavelengths beyond the optical communications band, as well as difficulties achieving the photon purity needed," says Takeshi Kamijoh, General Manager of Research and Development Center at OKI. "In response, OKI has developed a quantum entangled light source based on cascaded nonlinear optical effects using a proprietary periodically poled lithium niobate (PPLN) ridge-waveguide device.2 Operating at room temperature and configurable at optical fiber communications wavelengths alone, the device represents a practical next-generation quantum cryptography technology."
The performance of this quantum entangled light source has been tested using a semiconductorbased single-photon detector developed by Institute of Quantum Science, Nihon University, which can detect photons with low noise and high efficiency at high repetition rates of 1 GHz. These tests show that the signal-to-noise ratio for the photon pairs generated is one to two orders of magnitude greater than for conventional light source and detector combinations and demonstrate the feasibility of quantum cryptography communications at low signal error rates, using the quantum entangled light source developed in this research program and the singlephoton detector.
Other tests performed to transmit generated quantum entangled photon pairs confirm that the quantum entanglement state can be sufficiently maintained even when transmitted over a distance of 140 km over standard optical fibers. This performance is sufficient for quantum cryptography communications over metropolitan area.
OKI will continue to refine this new quantum entangled light source while working to reduce size and cost to achieve a practical quantum cryptography communications system.

美发明空中风力涡轮机数百米高空“收风”发电

美国麻省理工学院下属的Altaeros风能公司最近成功研制出一款空中风力涡轮机(AWT),能利用高空中的风力发电。
AWT实际上是风车和飞艇的结合,它有一个充满氦气的外壳,能漂浮在空中收集风力发电,然后通过电缆传回地面。Altaeros公司日前在缅因州做了一项测试,AWT上升至107米的高度,收集到两倍于常规风电塔的电量后成功降落。
AWT控制风的能力是风电塔的5倍,还可以减少65%的能量消耗,安装也仅需几天时间。
另外,它几乎没有环境和噪音污染,很少需要维护。未来,AWT将取代柴油发电机应用于偏僻的工业区、军事阵地和村庄,为那里的设施和人员提供能源。
AWT的发明者本·格拉斯是Altaeros公司的首席执行官,他说,“数十年来,风力发电都需要用起重机和巨大的塔吊将涡轮放置在离地面几百英尺的塔顶上”,如今,“可充气材料能轻而易举将风力涡轮机带到任何有强劲风力的地方”。
Altaeros公司计划让AWT升至305米的高空,那里的风力更加强劲持久。
Altaeros Energies Achieves Breakthrough in High Altitude Wind Power
The company recently completed testing of a 35-foot scale prototype of the Altaeros Airborne Wind Turbine (AWT) at the Loring Commerce Center in Limestone, Maine. The prototype, fabricated in partnership with Doyle Sailmakers of Salem, Massachusetts, achieved several key milestones. The AWT climbed up 350 feet high, produced power at altitude, and landed in an automated cycle. In addition, the prototype lifted the top-selling Southwest Skystream turbine to produce over twice the power at high altitude than generated at conventional tower height. The turbine was successfully transported and deployed into the air from a towable docking trailer.
Altaeros is developing its first product to reduce energy costs by up to 65 percent by harnessing the stronger winds found over 1,000 feet high and reducing installation time from weeks to days. In addition, it is designed to have virtually no environmental or noise impact and to require minimal maintenance. The Altaeros AWT will displace expensive fuel used to power diesel generators at remote industrial, military, and village sites. In the long term, Altaeros plans to scale up the technology to reduce costs in the offshore wind market.
“For decades, wind turbines have required cranes and huge towers to lift a few hundred feet off the ground where winds can be slow and gusty,” explained Ben Glass, the inventor of the AWT and Altaeros Chief Executive Officer.“We are excited to demonstrate that modern inflatable materials can lift wind turbines into more powerful winds almost everywhere—with a platform that is cost competitive and easy to setup from a shipping container.”
The AWT uses a heliumfilled, inflatable shell to ascend to higher altitudes where winds are more consistent and over five times stronger than those reached by traditional tower-mounted turbines. Strong tethers hold the AWT steady and send electricity down to the ground.
The lifting technology is adapted from aerostats, industrial cousins of passenger blimps that for decades have lifted heavy communications and radar equipment into the air for long periods of time. Aerostats are rated to survive hurricane-level winds and have safety features that ensure a slow descent to the ground.
The emerging airborne or“high altitude” wind sector was recently featured on the cover of the March 2011 issue of Popular Mechanics. In December 2011, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) released draft guidelines allowing the new class of airborne wind systems to be sited under existing regulation.
Altaeros Energies is currently seeking partners to join its effort to launch the first commerciallyavailable high altitude wind turbine in the world.
About Altaeros:
Altaeros Energies was founded in 2010 to generate low cost renewable energy by harnessing the strong winds found at higher altitudes. Altaeros Energies won the 2011 ConocoPhillips Energy Prize, and has received funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the California Energy Commission, and the Maine Technology Institute.
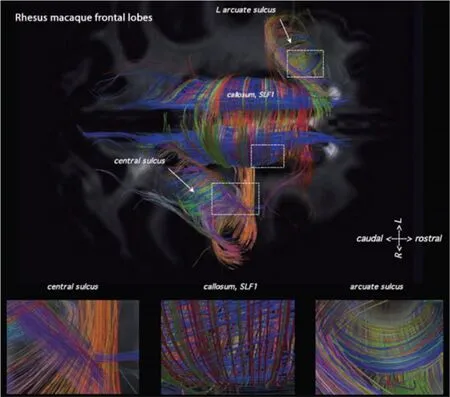
科学家首次发现人脑神经纤维排列方式
对于肉眼来说,人类大脑最显著的特点便是其波浪般的肿块和沟槽模式。
然而发表在3月30日出版的美国《科学》杂志上的一项最新研究指出,这些曲线当中实际上是由大约成直角的彼此交叉的神经纤维构成的网格。
研究人员利用一种新近开发出的方法——名为扩散光谱成像技术——推断了人类活体大脑中的神经纤维的位置。
这些扫描揭示了一种有序的神经纤维编织方式——这是一种比许多科学家之前所预想的要简单得多的结构。
研究人员对4种灵长类动物进行的扫描得出了一个类似的模型。
美国波士顿大学的脑神经学家Douglas L. Rosene和同事推断,这种像网格一样的结构或许在大脑的发育过程中是有利的,它的作用相当于高速公路的车道标记,从而帮助生长中的神经纤维找到通往目的地的道路。
这些发现为人们提供了一种分析大脑的新的框架,例如,科学家或许能够用这一坐标系统来精准地查明患病和健康大脑之间的差异。
大脑是由两种组织构成的,即由具有特定功能的神经细胞组成的灰质,以及由长长的相互连接的纤维组成的白质构成。
这些纤维的形状和轨迹——即它们在其行程中在何处及如何交叉和相遇——长期以来一直被认为是复杂且难以掌握的。而新的发现表明,这些纤维的形状是有组织的并具有几何形状,且惊人的简单。
Brain Wiring a No-Brainer?
The brain appears to be wired more like the checkerboard streets of New York City than the curvy lanes of Columbia, Md., suggests a new brain imaging study. The most detailed images, to date, reveal a pervasive 3D grid structure with no diagonals, say scientists funded by the National Institutes of Health.
“Far from being just a tangle of wires, the brain’s connections turn out to be more like ribbon cables — folding 2D sheets of parallel neuronal fibers that cross paths at right angles, like the warp and weft of a fabric,” explained Van Wedeen, M.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), A.A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging and the Harvard Medical School. “This grid structure is continuous and consistent at all scales and across humans and other primate species.”
Wedeen and colleagues report new evidence of the brain’s elegant simplicity March 30, 2012 in the journal Science. The study was funded, in part, by the NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), the Human Connectome Project of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, and other NIH components.
“Getting a high resolution wiring diagram of our brains is a landmark in human neuroanatomy,” said NIMH Director Thomas R. Insel, M.D. “This new technology may reveal individual differences in brain connections that could aid diagnosis and treatment of brain disorders.”
Knowledge gained from the study helped shape design specifications for the most powerful brain scanner of its kind, which was installed at MGH’s Martinos Center last fall. The new Connectom diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner can visualize the networks of crisscrossing fibers– by which different parts of the brain communicate with each other – in 10-fold higher detail than conventional scanners, said Wedeen.
“This one-of-a-kind instrument is bringing into sharper focus an astonishingly simple architecture that makes sense in light of how the brain grows,”he explained. “The wiring of the mature brain appears to mirror three primal pathways established in embryonic development.”
As the brain gets wired up in early development, its connections form along perpendicular pathways, running horizontally, vertically and transversely. This grid structure appears to guide connectivity like lane markers on a highway, which would limit options for growing nerve fibers to change direction during development. If they can turn in just four directions: left, right, up or down, this may enforce a more efficient, orderly way for the fibers to find their proper connections – and for the structure to adapt through evolution, suggest the researchers.
Obtaining detailed images of these pathways in human brain has long eluded researchers, in part, because the human cortex, or outer mantle, develops many folds, nooks and crannies that obscure the structure of its connections. Although studies using chemical tracers in neural tracts of animal brains yielded hints of a grid structure, such invasive techniques could not be used in humans.
Wedeen’s team is part of a Human Connectome Project Harvard/MGH-UCLA consortium that is optimizing MRI technology to more accurately to image the pathways. In diffusion imaging, the scanner detects movement of water inside the fibers to reveal their locations. A high resolution technique called diffusion spectrum imaging (DSI) makes it possible to see the different orientations of multiple fibers that cross at a single location – the key to seeing the grid structure.
In the current study, researchers performed DSI scans on postmortem brains of four types of monkeys – rhesus, owl, marmoset and galago – and in living humans. They saw the same 2D sheet structure containing parallel fibers crossing paths everywhere in all of the brains – even in local path neighborhoods. The grid structure of cortex pathways was continuous with those of lower brain structures, including memory and emotion centers. The more complex human and rhesus brains showed more differentiation between pathways than simpler species.
Among immediate implications, the findings suggest a simplifying framework for understanding the brain’s structure, pathways and connectivity.