Caveolin-1及其与肿瘤多药耐药的研究进展
2012-09-06邢颖,韩英
邢 颖,韩 英
Caveolin-1及其与肿瘤多药耐药的研究进展
邢 颖,韩 英
Caveolin-1(Cav-1)是细胞膜上caveolae的重要组成蛋白,在大多数正常细胞中高表达,通过其绞手架区可与多种信号分子相连接,参与分子运输、细胞黏附和信号转导在内的许多细胞活动。近来研究发现Cav-1与肿瘤细胞的增殖、分化、侵袭、转移、凋亡以及多药耐药(multidrug resistance,MDR)关系密切,且其表达水平存在明显差异,取决于肿瘤的类型、分期和分级。本文就Cav-1蛋白的结构和功能,及其与MDR的关系做一综述,为改善肿瘤治疗中MDR问题提供新思路。
肿瘤;多药耐药相关蛋白质类;Caveolin-1
Caveolae又称“小窝”,是胞膜上脂筏表面穴样凹陷的微区域,1953 年由 Palade[1]发现,1955 年Yamada[2]给予命名。Caveolae 直径 50 ~100 nm,以caveolin-1(Cav-1)为骨架分子,富含胆固醇和鞘糖脂。Caveolae存在于多种类型细胞中,在内皮细胞、脂肪细胞、血管平滑肌细胞、纤维母细胞和肺上皮细胞中尤其丰富,参与各种信号分子和信号通路的整合[3]。Cav-1是caveolae的主要结构蛋白和重要组成部分,与caveolae共同参与多种细胞过程,如细胞内脂质稳态、囊泡运输(转胞吞作用、内吞作用和胞饮作用)、细胞迁移、细胞周期、细胞极性、细胞转化和信号转导等[4]。本文就Cav-1蛋白的结构和功能及其与肿瘤多药耐药(multidrug resistance,MDR)的关系做一综述,为改善肿瘤治疗中MDR问题提供新思路。
1 概述
1.1 Cav-1的结构特征 人Cav-1基因定位于7q31.1,其蛋白分子量为 22 kd,长度为 178 AA,Cav-1的N端和C端均朝向胞浆内,中间具疏水性的第102~134氨基酸残基形成发夹结构(hairpin structure),插入到膜内,从而将该蛋白链分为2个胞浆区[5],结构示意图见图 1。
在N端部分,有两个对结构和功能起主要作用的功能域(domain):一个是邻近穿膜区的第61~101氨基酸残基,称为Caveolin寡聚化功能域(caveolin oligomerization domain,COD),它是 caveolin单体之间相互作用形成寡聚体的部位;另一个是包括在COD之内的第82~101氨基酸残基,称为Cav-1绞手架区(caveolin scaffolding domain,CSD),可识别ωxωxxxω 或 ωxxxxωxxω(ω 代表芳香族氨基酸)的cav结合序列,是Cav-1与胞内其他信号分子相互作用的区域[6-8]。最近,发现了Cav-1分子上负责离开内质网的功能域,即第66~70氨基酸,称为signature domain,这个区域是Cav-1分子中最保守的区域,去除这个区域导致Cav-1滞留在内质网中[9]。
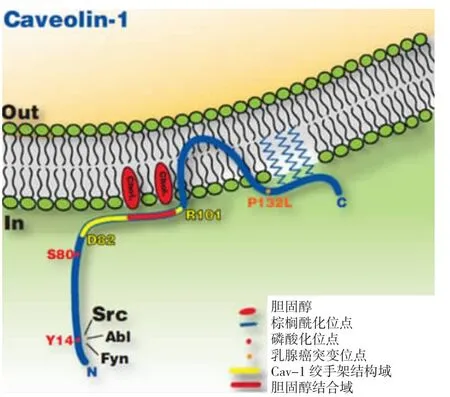
图1 Cav-1结构示意图
1.2 Cav-1的功能 Cav-1是caveolae不可缺少的组成部分,Cav-1缺陷的小鼠无明显的caveolae形成[10-11]。同时,Cav-1也是caveolae发挥细胞内吞作用的关键蛋白,白蛋白、霍乱毒素和破伤风毒素均通过此途径进入细胞内[12]。
Cav-1可结合胆固醇和长链不饱和脂肪酸,从而参与caveolae介导的细胞内胆固醇运输[13]。在肝细胞损伤后脂质代谢和增殖反应的协调中,Cav-1同样起着至关重要的作用。敲除已行部分肝切除的小鼠Cav-1基因,其肝脏的再生能力明显下降;此外,缺失Cav-1基因的小鼠肝细胞,其利用脂肪酸作为主要能量来源的能力也受损,同时伴有脂滴形成减少[14]。
Cav-1通过其CSD结构域将大量的蛋白聚集于caveolae上,如受体酪氨酸激酶(receptor tyrosine kinase,RTK)、丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶、磷脂酶、G蛋白偶联受体(G protein-coupled receptors,GPCR)和接头蛋白等,从而调节这些蛋白的活性,调控细胞的信号转导[15](图2)。在大多数情况下,Cav-1是细胞信号的负性调节者。Cav-1招募 β-catenin聚集于caveolae膜区域,从而阻断β-catenin介导的转录,抑制Wnt信号通路[16]。Cav-1与内皮型一氧化氮合酶相互作用后抑制后者的活性,以调节内皮细胞增生和血管形成。过表达重组的Cav-1能阻断neu(cerbB2,表皮生长因子家族中一种重要的受体)介导的信号转导[17]。转染Cav-1后能抑制信号从表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、Raf-1、MEK-1和Erk2向核内传递,反义抑制 NIH3T3细胞的 Cav-1能活化Erk1/2。此外,体外实验已证实Cav-1第32~95氨基酸残基衍生的肽段能抑制MEK-1和Erk2的激酶活性[18-19]。在某些信号通路中,Cav-1也能起着正性调节作用。PI3K/AKT通路是介导细胞存活的重要信号通路,PI3K定位于内皮细胞、成纤维细胞和髓样细胞的caveolae上并可与Cav-1相互作用[20];过表达HEK293和HeLa细胞的Cav-1可提高磷酸化AKT的基础水平[21];同样转染 Cav-1的 MCF-7乳腺癌细胞可组成性地表达磷酸化AKT[22]。

图2 Cav-1调节细胞内信号传导
2 Cav-1与肿瘤MDR
2.1 MDR MDR是指细胞对结构和功能不同的多种化疗药物产生交叉耐药性,这是肿瘤细胞免受化疗药物攻击的最重要的防御机制,也是导致化疗失败的主要原因之一[23-24]。肿瘤MDR的机制非常复杂,主要包括:①细胞中药物转运蛋白如P-gp、MRP1、LRP、GST等表达增加,药物外排功能增强;②胞膜结构特性(黏弹性、渗透性)改变致细胞药物代谢改变;③细胞凋亡和(或)生长停滞的通路调节异常[25]。
2.2 Cav-1参与MDR Cav-1在大多数的肿瘤组织、细胞中表达下调甚至缺如,如胃癌、乳腺癌、肺癌、宫颈癌、结肠癌、甲状腺滤泡状癌等。然而,在一些诱导MDR的肿瘤细胞系中Cav-1的水平显著上调,如秋水仙碱诱导的人结肠癌细胞HT-29/MDR和小鼠黑色素瘤细胞 B16-MDR[26];多柔比星诱导的人乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7/AdrR[27];长春新碱诱导耐药的人卵巢癌细胞SKVLB1和紫杉醇、阿霉素或依托泊苷诱导耐药的人肺癌细胞A549[28-30]。同时,通过对73例吉西他滨治疗的非小细胞肺癌的临床病例研究,发现Cav-1阳性患者化疗不良反应发生率明显较低,且有较差的无进展生存率和总生存率[31]。以上的研究均提示,Cav-1参与了MDR的获得和维持。
然而,也有少数研究发现,在乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7他莫昔芬耐药过程中Cav-1的表达可下降甚至丢失[32];Cav-1过表达可降低胞膜胆固醇水平,增加胞膜流动性,从而间接抑制P-gp的转运活性,导致细胞耐药性降低[33];有报道,30例口腔鳞状细胞癌的活检标本染色显示Cav-1阳性与化疗应答率呈正相关,而7例染色阴性者中6例无化疗不良反应[34]。
2.3 Cav-1调节MDR的机制 目前,Cav-1增强肿瘤MDR的机制尚未完全明确,可能原因有:①与MDR有关的胞膜脂质成分改变(胆固醇、GlcCer)。依赖Cav-1的细胞内胆固醇外向转运可将大量细胞毒性药物(大多数为脂溶性)逆浓度梯度带至胞膜caveolae,最终由定位于caveolae的药物外排泵将药物转移至细胞外,从而降低肿瘤细胞内的药物浓度,导致化疗失败[35];在多种MDR肿瘤细胞系(包括MCF-7/AdrR、KB-V、NIH:OVCAR-3)中均发现 GlcCer有明显提高[36],且 Lucci等[37]对6 例黑色素瘤和1例乳腺癌样本进行研究,发现GlcCer的水平和患者化疗反应呈反比关系;此外,GlcCer大量聚集于caveolae,且与 Cav-1有紧密联系,推测 GlcCer对MDR的调节可能与Cav-1有一定关联。②Cav-1与MDR蛋白的相互作用。P-gp是最具代表性的耐药蛋白,位于胞膜的脂筏和 caveolae内。Demeule等[38]对中国仓鼠卵巢癌细胞的研究表明,无论是在耐药的CH(R)C5细胞,还是在药敏的AuxB1细胞,均有相当一部分的P-gp和Cav-1共同定位在caveolae。用环孢素A或秋水仙碱处理CH(R)C5细胞,可以使定位在caveolae的P-gp和 Cav-1的量增加。实验还发现P-gp和Cav-1有共沉淀现象,提示两者之间存在着直接的相互作用。Pang等[39]研究了正常人与白血病患者骨髓细胞中Cav-1和MDR-1基因(P-gp的编码基因)的表达,发现二者表达呈正相关。提示两者相互作用,共同引起多药耐药的发生;Li等[40]对人乳腺癌耐药细胞系进行研究也得到类似结果,紫杉醇可诱导P-gp和PrPC复合物在caveolae微区域的聚集,且该过程与Cav-1的再分布同步;此外,Cav-1 还可与 MGr1-Ag[41]、BCRP/ABCG2[42]等MDR相关蛋白相互作用,参与化疗药物的抵抗。③Cav-1与过氧化物酶体增殖因子活化受体(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor,PPAR)-γ相互作用,提高肿瘤细胞抵抗细胞毒性药物的能力,从而导致MDR发生[43]。④Cav-1可能作为促存活、抗凋亡的蛋白参与MDR。Tirado等[44]研究发现ESFT细胞中Cav-1水平越高,对化疗药物的抵抗就越强,且Cav-1能活化ESFT细胞PKCα磷酸化,从而增强其抵抗阿霉素和顺铂所致细胞凋亡的能力,而敲除细胞Cav-1基因,细胞磷酸化PKCα水平下降,同时伴有凋亡敏感性增强,再次表达Cav-1可逆转上述变化,推测Cav-1通过调节PKCα磷酸化而增强细胞对药物诱导的凋亡抵抗,产生MDR;Zhang等[45]观察到在前列腺癌细胞系LNCap和22RV1中Id-1和Cav-1相互作用,参与上皮间质转变、细胞侵袭性增加以及对紫杉醇诱导的细胞凋亡抵抗。
3 结语
综上所述,Cav-1在肿瘤发生发展中的作用机制十分复杂[46],在肿瘤发生早期阶段,Cav-1水平下调以减弱其生长抑制作用,使细胞获得非贴壁依赖性生长的性质,促进肿瘤细胞恶性转化;在晚期阶段,肿瘤细胞获得转移性或耐药性时,Cav-1表达再次升高,以发挥其促进肿瘤细胞存活的作用。然而目前,肿瘤进展时Cav-1从肿瘤抑制到肿瘤促进的转变机制尚不清楚,推测不同时期结合Cav-1的蛋白、Cav-1自身磷酸化状态以及异构体的差异表达可能均参与其中[8]。阐明Cav-1与肿瘤及MDR之间的双重性作用机制,寻找肿瘤耐药逆转新的突破点,提高化疗药物敏感性,是未来Cav-1在肿瘤研究中亟需解决的问题。
[1]Palade G E.Fine structure of blood capillaries[J].Journal of Applied Physiology,1953,24:14-24.
[2]Yamada E.The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse[J].J Biophys Biochem Cyto,1955,1(2):445-458.
[3]Cohen A W,Hnasko R,Schubert W,et al.Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease[J].Physiol Rev,2004,84(4):1341-1379.
[4]Thompson T C,Tahir S A,Li L.The role of caveolin-1 in prostate cancer:clinical implications[J].Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis,2010,13(1):6-11.
[5]Goetz J G,Lajoie P,Wiseman S M,et al.Caveolin-1 in tumor progression:the good,the bad and the ugly[J].Cancer Metastasis Rev,2008,27(4):715-735.
[6]Bastiani M,Parton R G.Caveolae at a glance[J].J CellSci,2010,123(Pt 22):3831-3836.
[7]Schlegel A,Lisanti M P.A molecular dissection of caveolin-1 membrane attachment and oligomerization.Two separate regions of the caveolin-1 C-terminal domain mediate membrane binding and oligomer/oligomer interactions in vivo[J].J Biol Chem,2000,275(28):21605-21617.
[8]Shatz M,Liscovitch M.Caveolin-1:a tumor-promoting role in human cancer[J].Int J Radiat Biol,2008,84(3):177-189.
[9]Machleidt T,Li W P,Liu P,et al.Multiple domains in caveolin-1 control its intracellular traffic[J].J Cell Biol,2000,148(1):17-28.
[10]Drab M,Verkade P,Elger M,et al.Loss of caveolae,vascular dysfunction,and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice[J].Science,2001,293(5539):2449-2452.
[11]Razani B,Engelman J A,Wang X B,et al.Caveolin-1 null mice are viable but show evidence of hyperproliferative and vascular abnormalities[J].J Biol Chem,2001,276(41):38121-38138.
[12]Nabi I R,Le P U.Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis[J].J Cell Biol,2003,161(4):673-677.
[13]Fielding C J,Fielding P E.Caveolae and intracellular trafficking of cholesterol[J].Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2001,49(3):251-264.
[14]Fernandez M A,Albor C,Ingelmo Torres M,et al.Caveolin-1 is essential for liver regeneration[J].Science,2006,313(5793):1628-1632.
[15]Staubach S,Hanisch F G.Lipid rafts:signaling and sorting platforms of cells and their roles in cancer[J].Expert Rev Proteomics,2011,8(2):263-277.
[16]Galbiati F,Volonte D,Brown A M,et al.Caveolin-1 expression inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin/Lef-1 signaling by recruiting beta-catenin to caveolae membrane domains[J].J Biol Chem,2000,275(30):23368-23377.
[17]Engelman J A,Lee R J,Karnezis A,et al.Reciprocal regulation of neu tyrosine kinase activity and caveolin-1 protein expression in vitro and in vivo.Implications for human breast cancer[J].J Biol Chem,1998,273(32):20448-20455.
[18]Engelman J A,Chu C,Lin A,et al.Caveolin-mediated regulation of signaling along the p42/44 MAP kinase cascade in vivo.A role for the caveolin-scaffolding domain[J].FEBS Lett,1998,428(3):205-211.
[19]Galbiati F,Volonte D,Engelman J A,et al.Targeted downregulation of caveolin-1 is sufficient to drive cell transformation and hyperactivate the p42/44 MAP kinase cascade[J].EMBO J,1998,17(22):6633-6648.
[20]Zundel W,Swiersz L M,Giaccia A.Caveolin-1 mediated regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity by ceramide[J].Mol Cell Biol,2000,20(5):1507-1514.
[21]Shack S,Wang X T,Kokkonen G C,et al.Caveolin-induced activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway increases arsenite cytotoxicity[J].Mol Cell Biol,2003,23(7):2407-2414.
[22]Ravid D,Maor S,Werner H,et al.Caveolin-1 inhibits cell detachment-induced p53 activation and anoikis by upregulation of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors and signaling[J].Oncogene,2005,24(8):1338-1347.
[23]王钧,王婧,周毅.环氧合酶-2与肿瘤多药耐药[J].肿瘤学杂志,2011,17(3):216-220.
[24]倪彦彬,章国良.异源物代谢核受体PXR与肿瘤多药耐药相关性的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2011,42(1):67-71.
[25]Szakacs G,Paterson J K,Ludwig J A,et al.Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2006,5(3):219-234.
[26]Lavie Y,Liscovitch M.Changes in lipid and protein constituents of rafts and caveolae in multidrug resistant cancer cells and their functional consequences[J].Glycoconj J,2000,17(3-4):253-259.
[27]Lavie Y,Fiucci G,Liscovitch M.Up-regulation of caveolae and caveolar constituents in multidrug-resistant cancer cells[J].J Biol Chem,1998,273(49):32380-32383.
[28]Yang C P,Galbiati F,Volonte D,et al.Upregulation of caveolin-1 and caveolae organelles in Taxol-resistant A549 cells[J].FEBS Lett,1998,439(3):368-372.
[29]Belanger M M,Gaudreau M,Roussel E,et al.Role of caveolin-1 in etoposide resistance development in A549 lung cancer cells[J].Cancer Biol Ther,2004,3(10):954-959.
[30]Belanger M M,Roussel E,Couet J.Up-regulation of caveolin expression by cytotoxic agents in drug-sensitive cancer cells[J].Anticancer Drugs,2003,14(4):281-287.
[31]Ho C C,Kuo S H,Huang P H,et al.Caveolin-1 expression is significantly associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy[J].Lung Cancer,2008,59(1):105-110.
[32]Thomas N B,Hutcheson I R,Campbell L.Growth of hormone-dependent MCF-7 breast cancer cells is promoted by constitutive caveolin-1 whose expression is lost in an EGF-R-mediated manner during development of tamoxifen resistance[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2010,119(3):575-591.
[33]Cai C,Chen J.Overexpression of caveolin-1 induces alter-ation of multidrug resistance in Hs578T breast adenocarcinoma cells[J].Int J Cancer,2004,111(4):522-529.
[34]Nakatani K,Wada T,Nakamura M,et al.Expression of caveolin-1 and its correlation with cisplatin sensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2005,131(7):445-452.
[35]Liscovitch M,Lavie Y.Multidrug resistance:a role for cholesterol efflux pathways?[J].Trends Biochem Sci,2000,25(11):530-534.
[36]Lavie Y,Cao H,Bursten S L,et al.Accumulation of glucosylceramides in multidrug-resistant cancer cells[J].J Biol Chem,1996,271(32):19530-19536.
[37]Lucci A,Cho W I,Han T Y,et al.Glucosylceramide:a marker for multiple-drug resistant cancers[J].Anticancer Res,1998,18(1B):475-480.
[38]Demeule M,Jodoin J,Gingras D,et al.P-glycoprotein is localized in caveolae in resistant cells and in brain capillaries[J].FEBS Lett,2000,466(2-3):219-224.
[39]Pang A,Au W Y,Kwong Y L.Caveolin-1 gene is coordinately regulated with the multidrug resistance 1 gene in normal and leukemic bone marrow[J].Leuk Res,2004,28(9):973-977.
[40]Li Q Q,Cao X X,Xu J D,et al.The role of P-glycoprotein/cellular prion protein interaction in multidrug-resistant breast cancer cells treated with paclitaxel[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2009,66(3):504-515.
[41]Linge A,Meleady P,Henry M.Bleomycin treatment of A549 human lung cancer cells results in association of MGr1-Ag and caveolin-1 in lipid rafts[J].Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2011,43(1):98-105.
[42]Herzog M,Storch C H,Gut P.Knockdown of caveolin-1 decreases activity of breast cancer resistance protein(BCRP/ABCG2)and increases chemotherapeutic sensitivity[J].Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2011,383(1):1-11.
[43]Lin S Y,Yeh K T,Chen W T,et al.Promoter CpG methylation of caveolin-1 in sporadic colorectal cancer[J].Anticancer Res,2004,24(3A):1645-1650.
[44]Tirado O M,MacCarthy C M,Fatima N.Caveolin-1 promotes resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in E-wing's sarcoma cells by modulating PKCalpha phosphorylation[J].Int J Cancer,2010,126(2):426-436.
[45]Zhang X,Ling M T,Wang Q,et al.Identification of a novel inhibitor of differentiation-1(ID-1)binding partner,caveolin-1,and its role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and resistance to apoptosis in prostate cancer cells[J].J Biol Chem,2007,282(46):33284-33294.
[46]Shatz M,Liscovitch M.Caveolin-1 and cancer multidrug resistance:coordinate regulation of pro-survival proteins?[J].Leuk Res,2004,28(9):907-908.
Caveolin-1 and Its Role in Cancer Multidrug Resistance
XING Ying1,HAN Ying2(1.Medical University of PLA,Beijing 100853,China;2.General Hospital of Beijing Military Area Command,Beijing 100700,China)
Caveolin-1(Cav-1),an integral membrane protein in caveolae and extremely abundant in many normal cell types,exhibits an unusual ability to interact and modulate many cellular processes such as molecular transport,cell adhesion and signal transduction via its caveolin scaffolding domain(CSD).Cav-1 has been recently reported to closely correlate with multiple cancer-associated processes including cellular generation,differentiation,infestation,transformation,apoptosis and multidrug resistance(MDR),and there are obvious differences in expressive levels which depend on the types,staging and grading of the tumor.This paper surveys the structure and function of Cav-1,especially its relationship with cancer MDR so as to provide a new thread for improving MDR in treatment.
Neoplasms;Multidrug resistance-associated proteins;Caveolin-1
R73
A
2095-140X(2012)08-0010-05
10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2012.08.003
2012-06-12 修回时间:2012-06-28)
2009年国家自然科学基金资助项目(30940032)
100853北京,解放军医学院2010级博士(邢颖);100700北京,北京军区总医院(韩英)
韩英,E-mail:yh721303@sina.com
