BNCT医院中子照射器辐射场特性参数初步测量
2012-08-18李春娟宋明哲姚顺和刁立军姚艳玲张紫竹高集金张瀷凡
陈 军,李春娟,宋明哲,李 玮,姚顺和,刁立军,姚艳玲,张紫竹,高集金,张瀷凡
(1.中国原子能科学研究院,北京 102413;2.北京凯佰特科技有限公司,北京 102413)
1 前言
自G.L.Locher提出中子俘获治疗(neutron capture therapy,NCT)的概念后[1],其潜在的治疗功效备受人们关注。硼中子俘获治疗(boron neutron capture therapy,BNCT)是基于10B(n,α)7Li反应的二元疗法,即将亲肿瘤细胞的含硼药物注射入病人血液中,含硼药物在肿瘤细胞中聚集,利用热中子或超热中子轰击病灶区,与同位素10B反应产生具有较高能量的α粒子和反冲7Li核,从而有选择性地杀死肿瘤细胞。目前,我国首个用于临床治疗的BNCT医院中子照射器Ⅰ型(in-hospital neutron irradiator mark 1,IHNI-1)已建造完毕,但需开展照射器辐射场特性参数测量,以验证照射器的设计效果并确定辐射源项,为进一步开展临床生物剂量学试验研究奠定基础。
2 照射器结构与设计指标
IHNI-Ⅰ主体为30 kW的微型反应堆,对称方向设置热中子和超热中子两个照射孔道,标准孔径为φ12 cm,并由热中子孔道切向引出一条实验孔道,孔径为φ3 cm,用于血硼浓度分析,如图1所示。
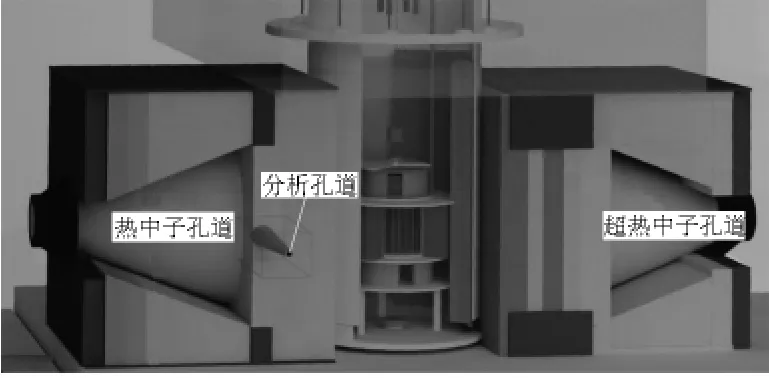
图1 医院中子照射器Ⅰ型结构示意图Fig.1 Structure diagram of IHNI-1
该照射器中子通量密度设计指标:
1)热中子孔道口中心处热中子通量密度:≥1 ×109cm-2·s-1;
2)超热中子孔道口中心处超热中子通量密度:≥2.5 ×108cm-2·s-1;
3)实验孔道口中心处热中子通量密度:≥1×106cm-2·s-1。
3 实验方案设计
国际上针对BNCT照射器辐射场特性参数测量未形成通用的标准测量方法,而是根据各自照射器的特点,研发适当的测量装置,主要包括阈活化箔探测器[2]、多球谱仪[3,4]、气泡探测器[5]、中子飞行时间测 量 系 统[6,7]、共 振 吸 收 过 滤 装 置[8]、电 离室[9,10]、带有中子转换体的半导体或闪烁体探测器[11,12]、中子和 γ 成像装置[13]、热释光剂量计(thermoluminescent dosimetry,TLD)[14]、组织等效正比计数器(tissue equivalent proportional counters,TEPC)[15,16]、电子自旋共振谱仪[17]、硫酸亚铁剂量计[18]等。本着充分利用现有资源,自主研发的原则,根据IHNI-1的特点,开展相关测量技术研究。
3.1 中子能谱测量
采用多球谱仪测量热中子孔道和超热中子孔道中子能谱。除已建常规多球谱仪(包括裸3He正比计数器及将其置于2.5~12 in聚乙烯球中共10个探测单元)外(1 in=25.4 mm),为提高谱仪在超热能区的分辨率,利用MCNP-4C程序优化设计了4个包硼壳(1 mm铝包裹天然B4C粉末)探测单元,分别为4 mm、10 mm、30 mm厚硼壳包裹3 in球和40 mm厚硼壳包裹4 in球,如图2所示。计算了各探测单元的响应函数,如图3所示,并经过252Cf中子源校准和验证。

图2 多球谱仪的探测单元Fig.2 Detection units of the multi-sphere spectrometer

图3 多球谱仪响应函数Fig.3 Response functions of the multi-sphere spectrometer
由于孔道口处中子束不能覆盖所有探测单元,且多球谱仪探测效率高,无法选择适当的反应堆功率消除死时间过大的影响,为此设计的实验方案如下:
1)在孔道口处增加一个φ3 cm的小准直器进行限束,小准直器结构如图4所示。探测单元距准直器口110 cm处进行测量,在反应堆运行于最小稳定功率时(此时堆芯通量密度为1×109cm-2·s-1,反应堆最大功率时堆芯通量密度为1×1012cm-2·s-1),各探测单元计数率死时间影响均小于10%,同时,测量位置的中子束可覆盖所有探测单元。
2)由于IHNI-1照射器孔道为锥形准直,中子束呈发散状分布,因而需利用蒙特卡洛方法将各探测单元的计数率从不均匀束修正到均匀束。
设计的小准直器应满足以下条件:a.准直器具有良好的限束效果;b.准直器对中子能谱没有较大改变。为此,利用MCNP-4C程序对其进行了模拟分析(源项为设计计算的中子能谱),结果如图5和图6所示。对于热中子束和超热中子束,从准直器屏蔽层透射的中子分别占总中子数的0.08%和0.15%,且对中子能谱未产生较大影响。
3.2 中子通量密度测量及其空间分布
利用197Au箔和235U裂变电离室测量中子通量密度及其空间分布。为实现不同能区中子通量密度的测量,利用裸197Au箔和包镉(1 mm厚)197Au箔测量热中子(0.5 eV以下)和超热中子(0.5 eV~10 keV)通量密度,计算公式如式(1)和式(2)。利用30 mm厚硼壳(1 mm镉包裹天然B4C粉末)包裹235U裂变电离室测量快中子(10 keV以上)通量密度,计算公式如式(3)。
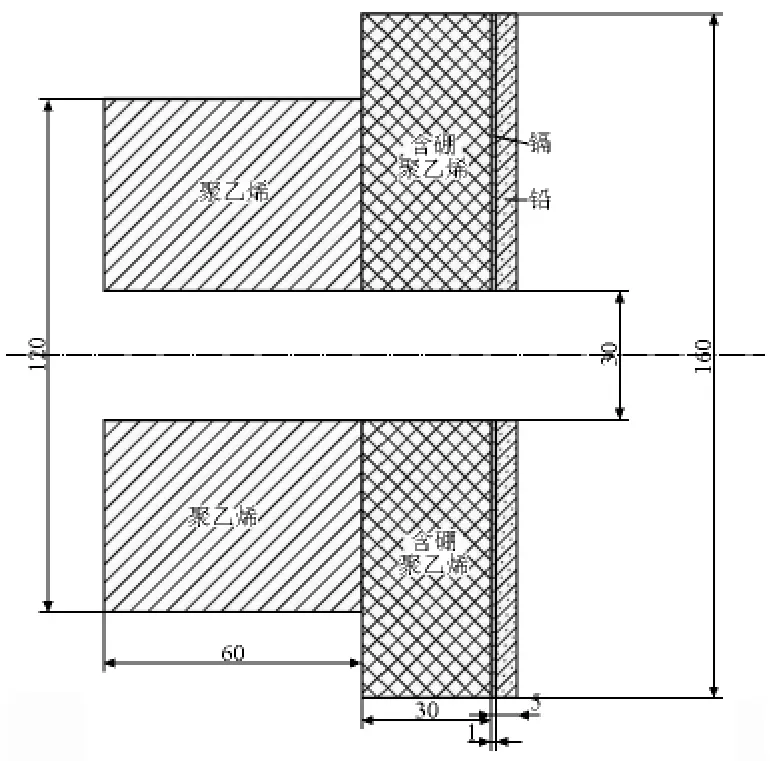
图4 φ3 cm孔径小准直器结构示意图(单位:mm)Fig.4 Structure diagram of the small collimator with a φ 3 cm aperture(unit:mm)
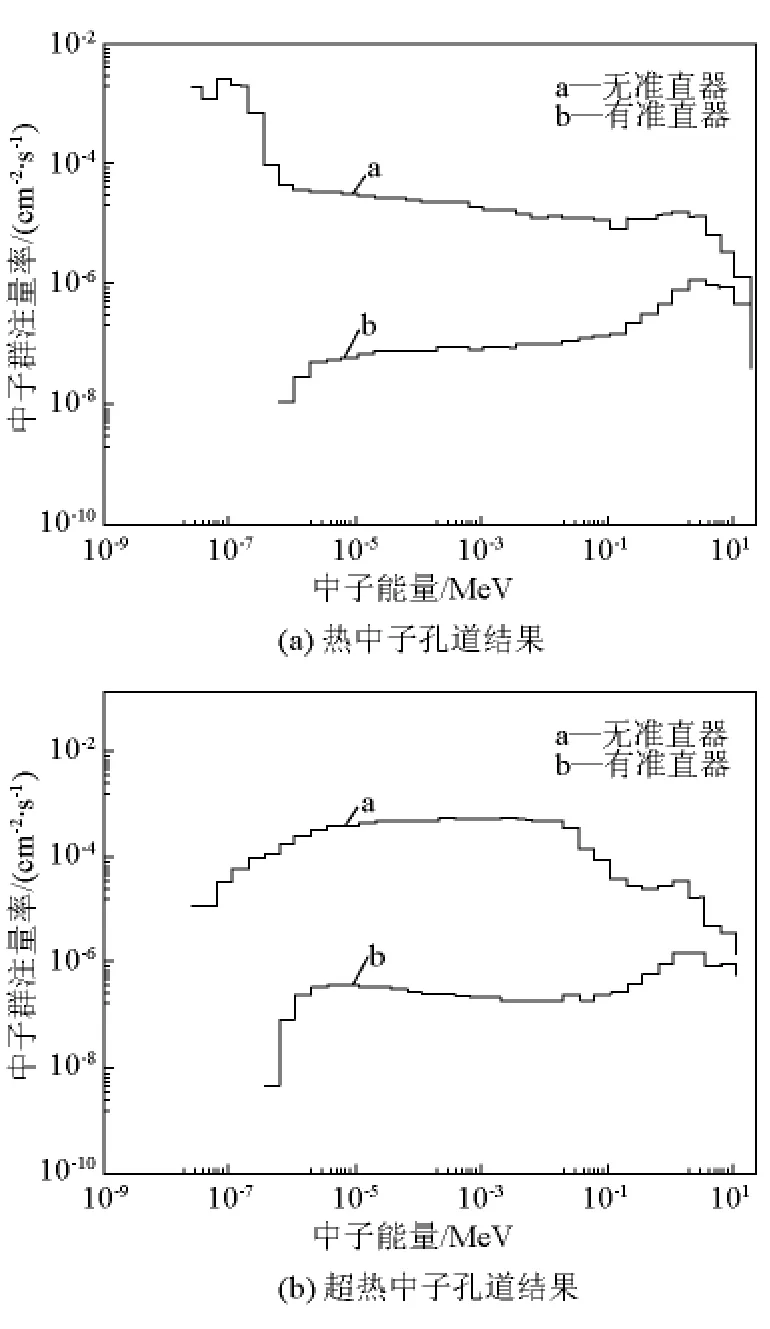
图5 小准直器的限束效果模拟计算Fig.5 Simulation of the limitation of neutron beams with the small collimator

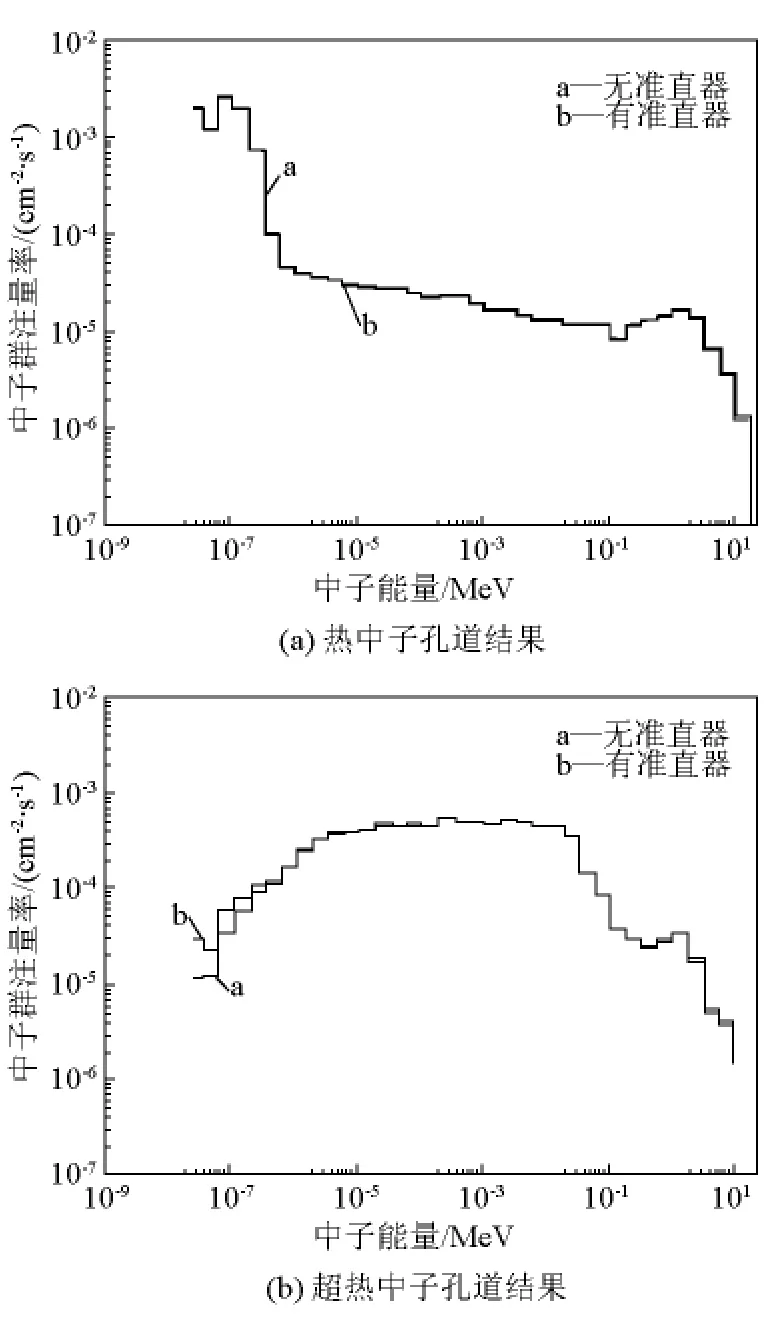
图6 小准直器对中子能谱的影响模拟计算Fig.6 Simulation of the influence of neutron spectra with the small collimator
式(1)中,k为修正因子;A为归一化辐照条件并按比活度扣除包镉金箔活度后,裸金箔测量时刻的活度;λ为198Au的衰变常数;NAu为裸金箔内197Au的原子核数目;为197Au(n,γ)反应在热能区的谱平均截面;tr和tc分别为裸金箔的辐照时间和冷却时间。
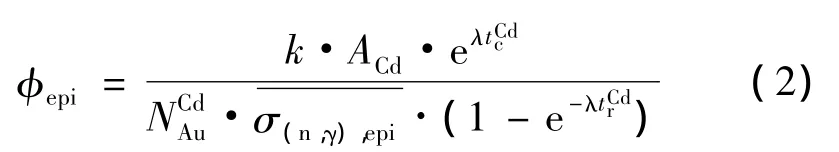
式(2)中,ACd为包镉金箔测量时刻的活度;为包镉 金 箔 内197Au 的 原 子 核 数 目;为197Au(n,γ)反应在超热能区的谱平均截面;trCd和tcCd分别为包镉金箔的辐照时间和冷却时间。

式(3)中,F为经阈下损失修正后的裂变碎片计数率;Rf为包硼盒后裂变电离室的注量响应。
计算了197Au箔在不同能区的谱平均截面(见表1)和电离室包硼壳后235U的有效群平均截面(见图7)。计算结果表明,通过以上设计,快中子对197Au箔以及热中子和超热中子对235U裂变电离室的测量影响得到有效控制。利用235U裂变电离室扫描测量孔道外中子通量密度空间分布,利用197Au箔测量孔道内中子通量密度空间分布。
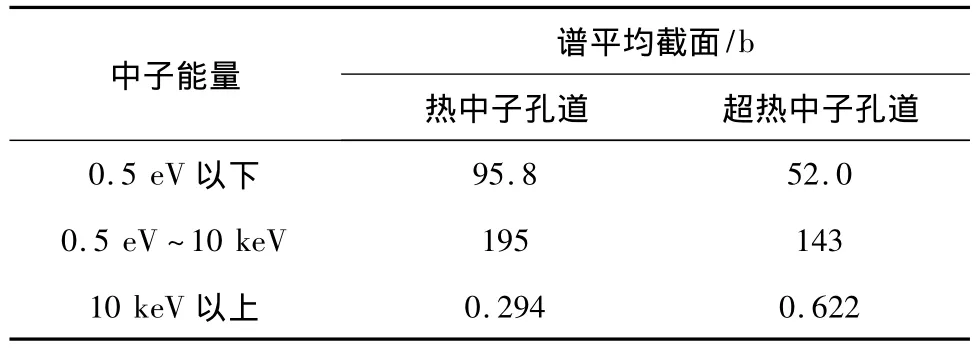
表1 197Au在不同能区的谱平均截面Table 1 Spectrum-averaged cross sections of197Au in different energy ranges

图7 235U裂变电离室包30 mm厚硼壳后235U的有效群平均截面Fig.7 Effective group-averaged cross sections of235U while the235U fission chamber covered by a 30 mm thick boron shell
3.3 中子和γ射线吸收剂量率及其空间分布测量
利用TLD-600和TLD-700(美国Harshaw公司)和TEPC(美国Far West公司的LET-1/2型)测量中子及γ射线的吸收剂量率及其空间分布。其中,利用TLD(裸和包镉)测量热中子、超热中子和γ射线剂量率,利用包40 mm厚硼壳(1 mm铝包裹天然B4C粉末)的TEPC测量快中子剂量率。并利用热中子参考辐射场、137Cs γ源和252Cf中子源对TLD和TEPC进行校准和线能刻度。
利用MCNP-4C程序优化设计TEPC探测系统结构。计算不同厚度硼壳对中子通量密度的衰减情况,如图8所示,结果表明,40 mm厚的硼壳对热中子孔道和超热中子孔道10 keV以下中子通量密度分别衰减了180倍和10倍,而对10 keV以上中子只衰减了20%。
4 初步测量结果
对各照射孔道中子通量密度及其空间分布和镉比进行了测量,结果见表2和图9~图12。

图8 模拟计算的不同厚度硼壳对中子通量密度的衰减情况Fig.8 Simulation of the attenuation of neutron flux densities resulted from boron shells with different thickness
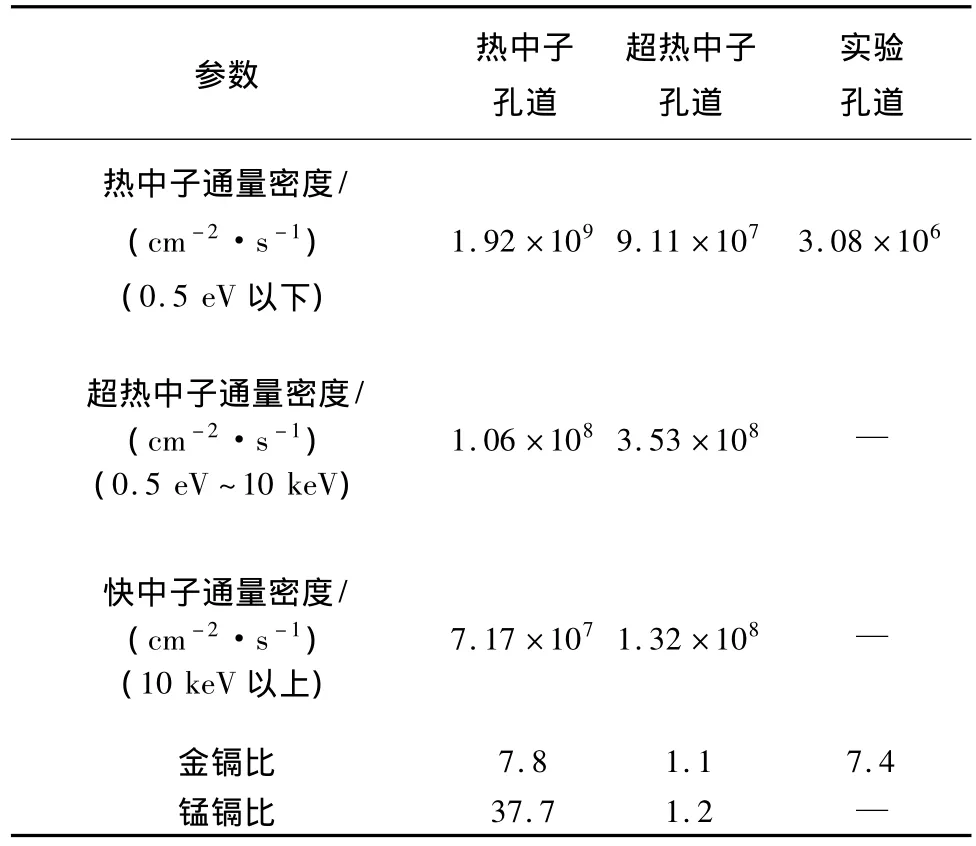
表2 中子通量密度及其空间分布和镉比的初步测量结果Table 2 Preliminary results of neutron flux densities and their spatial distributions and cadmium-ratio
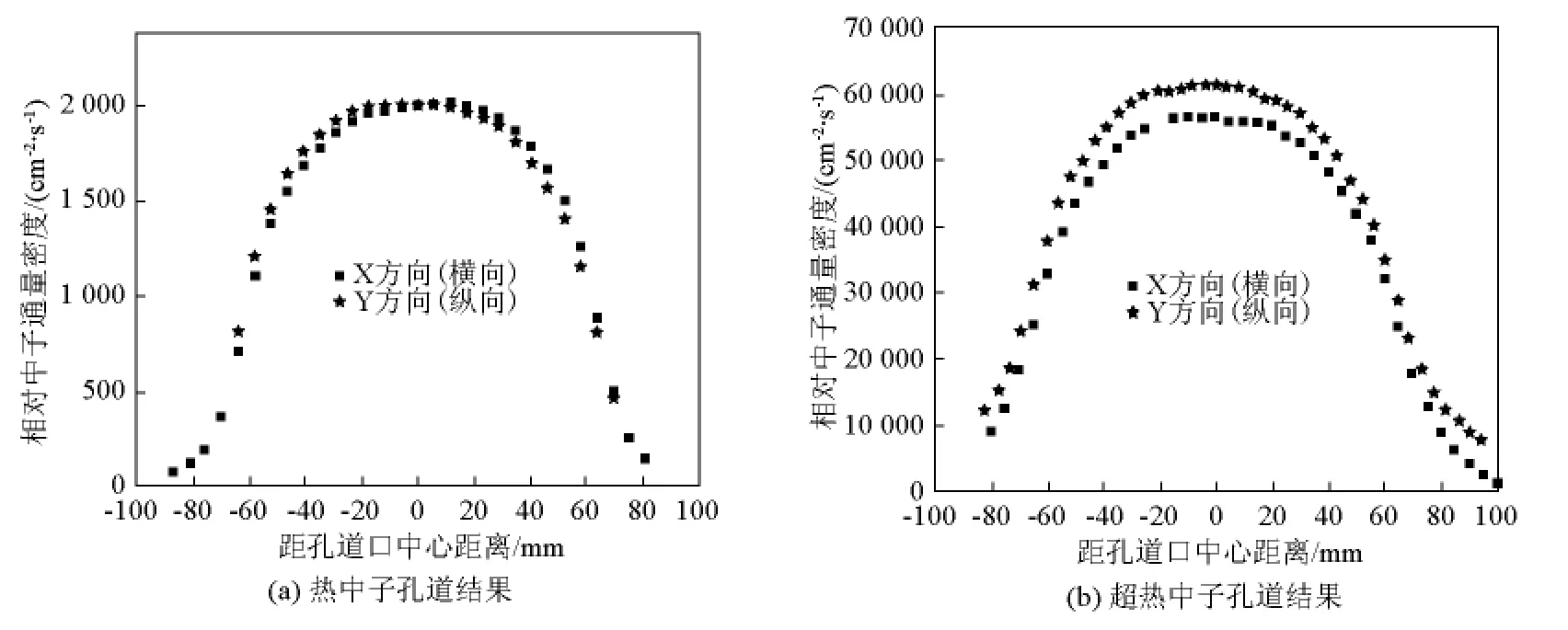
图9 孔道口处中子通量密度径向空间分布Fig.9 Radial spatial distributions of neutron flux densities at the exit of neutron beam
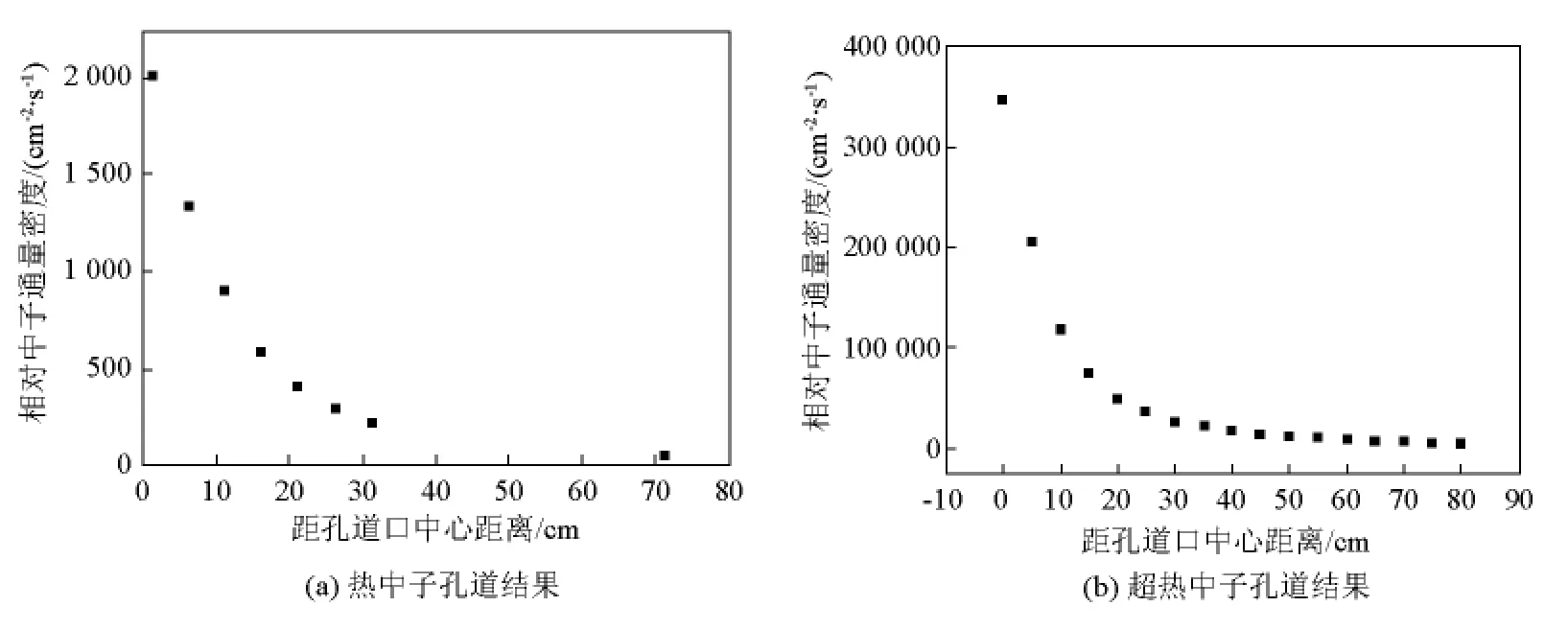
图10 孔道口外中子通量密度轴向空间分布Fig.10 Axial spatial distributions of neutron flux densities outside the exit of neutron beam
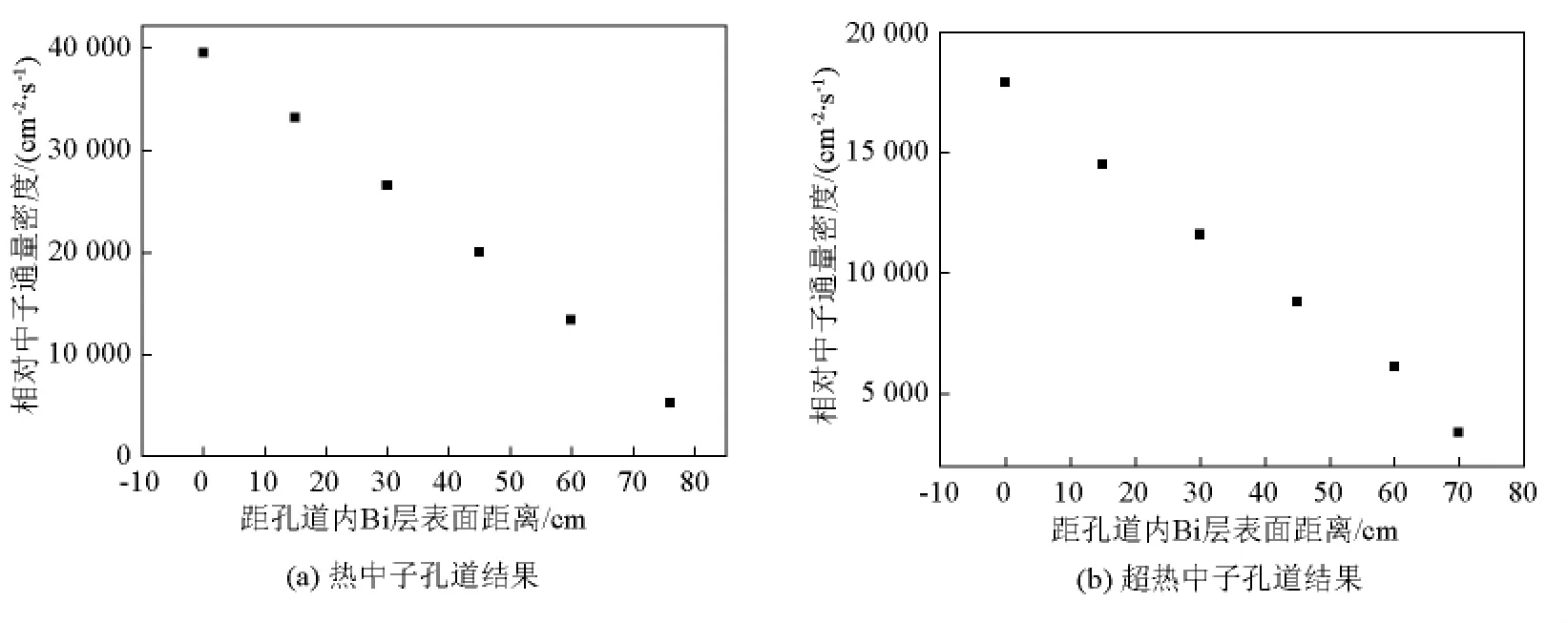
图11 孔道口内中子通量密度轴向空间分布Fig.11 Axial spatial distributions of neutron flux densities inside the exit of neutron beam
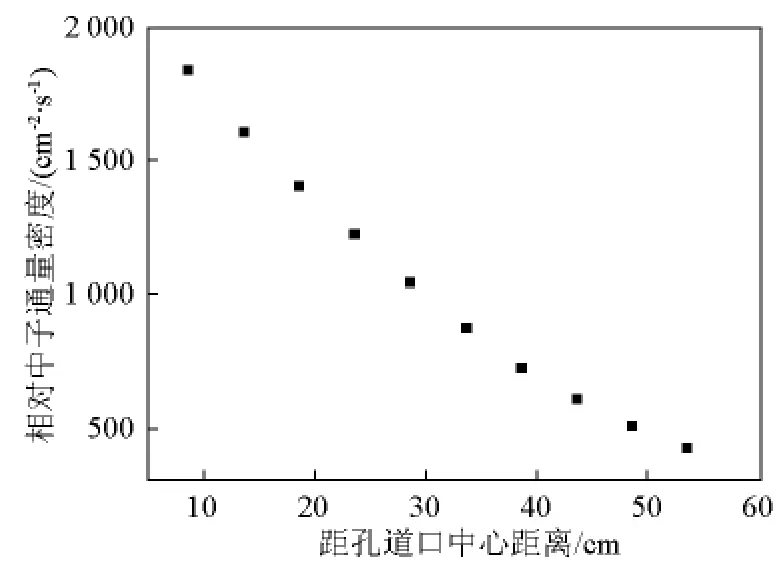
图12 实验孔道口外中子通量密度轴向空间分布Fig.12 Axial spatial distributions of neutron flux density outside the exit of neutron beam for the analysis of blood-boron concentration
5 结语
针对BNCT医院中子照射器开展了辐射场特性参数测量方法研究,建立了相关测量装置,初步获得了各照射孔道的中子通量密度及其空间分布。结果表明,该BNCT照射器的中子通量密度达到了预期设计指标,为进一步开展临床研究奠定了基础。
[1] Locher G L.Biological effects and therapeutic possibilities of neutrons[J] .American Journal of Roentgenology,1936,36:1 - 13.
[2] Auterinen I, Serén T, Anttila K,et al.Measurement of free neutron spectra at eight BNCT facilities worldwide[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2004,61:1021-1026.
[3] Elisabetta Nava,Stefano Agosteo,Maurizio Angelone,et al.Preliminary characterization of the epithermal beam at the TAPIRO reactor[C] //Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Neutron Capture Therapy.Florence,2008:537 -540.
[4] Ueda H,Tanaka H,Maruhashi A,et al.Spectral evaluation of cyclotron-based epithermal neutron irradiation field for BNCT using Bonner Sphere[C] //Proceedings of 14th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy.Buenos Aires,Argentina,2010:459 -462.
[5] Errico F d’,Ciolini R,Fulvio A Di,et al.Angle-and energydifferential neutron spectrometry for the SPES BNCT facility[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2009,67(7 -8 suppl.):141 -144.
[6] Yasuhiro Unno,Shunsuke Yonai,Mamoru Baba,et al.Benchmark experiments on neutron moderator assembly for cyclotronbased boron neutron capture therapy[C] //Proceedings of ICNCT -1212th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy.Takamatsu,Kagawa,Japan,2006:331 -334.
[7] Kononov V N,Bokhovko M V,Kononov O E,et al.The time-offlight epithermal neutron spectrum measurement from accelerator based BNCT facility[C] //Proceedings of ICNCT -1212th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy.TakamatsFu,Kagawa,Japan,2006:368 -370.
[8] Hamidi S,Scott M C.BNCT neutron beam characterization using a resonance absorption filter method[J] .Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A,2002,476:99-105.
[9] Antoaneta Roca,Yuan-Hao Liu,Cecile Wojnecki,et al.A preliminary inter-centre comparison study for photon,thermal neutron and epithermal neutron responses of two pairs of ionization chambers used for BNCT[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2009,67(7 -8 suppl.):134 -136.
[10] Fujii T,Tanaka H,Maruhashi A,et al.Study on optimization of multi ionization-chamber system for BNCT[C] //Proceedings of 14th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy.Buenos Aires,Argentina,2010:177 -180.
[11] Almaviva S,Macro Marinelli,Milani E,et al.Thermal neutron dosimeter by synthetic single crystal diamond devices[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2009,67(7 - 8 suppl.):183-185.
[12] Marek M,Viererbl L.Spatial characterization of BNCT beams[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2004,61:1051 -1055.
[13] Ming-Chen Hsiao,Wei-Lin Chen,Pi-En Tsai,et al.A preliminary study on using the radiochromic film for 2D beam profile QC/QA at the THOR BNCT facility[C] //Proceedings of 14th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy.Buenos Aires,Argentina,2010:203 -206.
[14] Gambarini G,Klamert V,Agosteo S,et al.Study of a method based on TLD detectors for in-phantom dosimetry in BNCT[J] .Radiation Protection Dosimetry,2004,110(1 -4):631 -636.
[15] Endo S,Onizuka Y,Ishikawa M,et al.Microdosimetry of neutron field for boron neutron capture therapy at Kyoto University reactor[J] .Radiation Protection Dosimetry,2004,110(1 -4):641-644.
[16] Fang-Yuh Hsu,Hsiu-Wen Hsiao,Chuan-Jong Tung,et al.Microdosimetry study of THOR BNCT beam using tissue equinalent proportional counter[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2009,67(7-8 suppl.):175 - 178.
[17] Bartolotta A,M C D’Oca,B Lo Giudice,et al.Combined TL and10B-Alanine ESR dosimetry for BNCT[J] .Radiation Protection Dosimetry,2004,110(1-4):627-630.
[18] Baetesaghi G,Burian J,Gambarini G,et al.Evaluation of all dose components in the LVR-15 reactor epithermal neutron beam using Fricke gel dosimeter layers[J] .Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2009,67(7 -8 suppl.):199 -201.
