膝关节半月板周缘性脱位的磁共振诊断价值分析
2012-01-04初占飞赵静徐刚
初占飞,赵静,徐刚
膝关节半月板周缘性脱位的磁共振诊断价值分析
初占飞,赵静,徐刚
目的探讨膝关节半月板周缘性脱位磁共振成像(MRI)特征,提高临床医生对本病的认识及诊断。方法回顾性分析2008年2月—2012年2月我院收治的22例经临床手术证实的膝关节半月板周缘性脱位患者的MRI征象。结果22例患者中,内侧半月板周缘性脱位16例,外侧半月板脱位6例。膝关节半月板周缘性脱出伴半月板撕裂12例。膝关节半月板脱位并骨关节炎12例。MRI征象:半月板脱离膝关节面,伴有撕裂,可见T2WI稍高信号,T1WI为等信号。结论MRI能够很好地诊断膝关节半月板周缘性脱位,并评价其损伤情况。
膝关节;半月板,胫骨;膝脱位;磁共振成像
半月板是人体膝关节的重要组成部分,其既能直接承受载荷,还能保护关节透明软骨,抵御关节退变,是不可替代的生理性膝关节腔填充组织。但是半月板充分发挥生理功能的前提是保持正常形态结构和解剖位置。目前,磁共振成像(MRI)是诊断膝关节半月板病变公认的首选影像学检查方法。本文通过回顾性分析22例半月板周缘性脱位病例的膝关节MRI资料,旨在探讨半月板周缘性脱位的MRI特征及临床意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料选取本院2008年2月—2012年2月经临床手术确诊的22例半月板周缘性脱位患者,其中男14例,女8例;年龄35~76岁,平均58岁。右膝半月板周缘性脱位14例,左膝半月板周缘性脱位8例。其中16例患者因外伤就诊,6例患者无外伤史及手术史。临床症状为膝关节疼痛、肿胀、关节绞锁或弹响等功能障碍。
2 结果
半月板周缘性脱位的MRI征象:22例患者中,18例半月板超出基线>3 mm,4例等于3 mm;其中16例为内侧半月板,6例为外侧半月板。12例患者出现关节面退变伴周围骨赘形成。16例外伤患者均出现关节腔积液,关节腔内见条形长T2信号,其中12例半月板周缘性脱出伴半月板撕裂,半月板内示线样高信号,达半月板边缘,在MRI上T2WI呈略高信号,T1WI为等或低信号。典型MRI图像见图2~4。
3 讨论
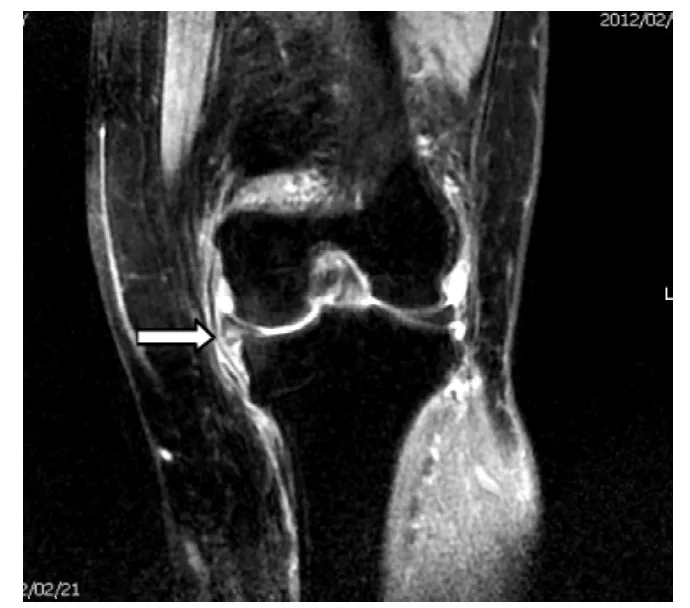
图2 MRI示左膝内侧半月板周缘性脱位Figure 2 MRI showing meniscus peripheral dislocation of the medial border of left knee
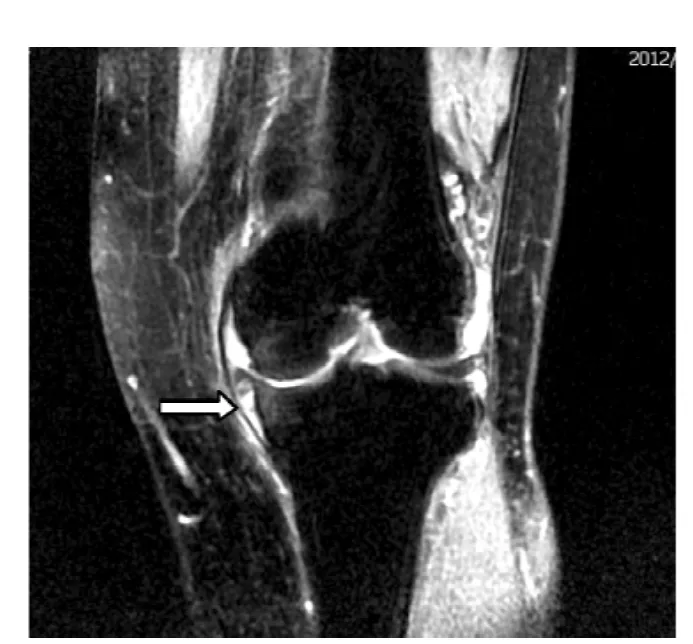
图3 MRI示合并右侧半月板损伤(内部长T2WI信号)及关节腔积液(与图2为同一病例)Figure 3 MRI showing the merging right side of the meniscus injury(the internal long T2WI signal)and joint effusion
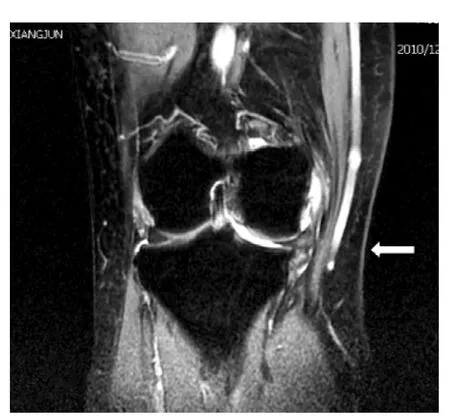
图4 MRI示右膝内侧半月板周缘性脱位Figure 4 MRI showing meniscus peripheral dislocation of the medial border of right knee
半月板是人体膝关节腔内重要的组成部分,在膝关节承重和生理功能中具有重要作用,能够保护关节软骨,抵御退行性病变的发生。半月板周缘性脱位是指半月板脱离正常的生理解剖位置,也就是说半月板完全脱离胫骨平台边缘或股骨内外侧髁边缘。Vedi等[2]通过在人体正常负重状态下动态MR研究,证明半月板存在生理性周缘脱位征象;而Sugita等[3]采用非负重状态下静态MR检查,结果证明同样存在周缘性半月板脱位征象,这与Vedi等研究相反。有关半月板脱位诊断研究国内报道很少,Breitenseher等[4]将半月板外周缘与胫骨平台边缘的距离≥3 mm定义为半月板周缘性脱位。
本组22例患者中有16例为内侧半月板脱位,笔者认为内侧半月板中后部由于纤维排列及分布不均,更容易变形,其结构特点和力学特征表明内侧半月板较外侧易于损伤和脱位。国内外文献报道内侧半月板脱位发生率较外侧明显增高[5-6],本研究结果与文献报道一致。本组16例外伤患者中有12例半月板周缘性脱位伴半月板撕裂,这可能是由于半月板损伤增加了半月板的不稳定性,如果撕裂达到半月板边缘时,破坏了半月板抵抗箍形应力的作用,加上自身体质量对半月板的压迫,导致半月板向外移位。12例半月板周缘脱位患者均合并周围骨质增生及退变,笔者分析可能是由于纤维分离和微囊变引起退变,半月板体积增大,对应力的负载能力降低,继而使纤维放射状向外伸展,导致半月板周缘性脱位,这与Cos等[7]研究结果一致。George等[7]也认为半月板脱位与膝关节骨关节炎及其症状产生有关,其退变的程度与脱位的发生密切相关。本文与国内黄加张等[9]研究结果相符合,半月板周缘性脱位,约70%伴有半月板损伤,约69%伴有骨关节病及骨赘增生。
总之,半月板损伤是引起半月板周缘性脱位的重要原因之一,而半月板周缘性脱位又与膝关节退行性关节炎密切相关。MRI是评价半月板首选的无创性检查方法,可准确评价半月板损伤情况[10],早期明确半月板周缘性脱位诊断,以争取早期治疗。
1 Madan-Sharma R,Kloppenburg M,Kornaat PR,et al.Do MRI features at baseline predict radiographic joint space narrowing in the medial compartment of the osteoarthritic knee 2 years later?[J].Skeletal Radiol,2008,37(9):805-811.
2 Vedi V,Williams A,Tennant SJ,et al.Meniscal movement.An in-vivo study using dynamic MRI[J].J Bone Joint Surg Br,1999,81(1):372.
3 Sugita T,Kawamata T,Ohnuma M,et al.Radial displacement of the medial meniscus in varus osteoarthritis of the knee[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001(387):171-177.
4 Breitenseher MJ,Trattnig S,Dobrocky I,et al.MR imaging of meniscal subluxation in the knee[J].Acta Radiol,1997,38(5):876-879.
5 Kenny C.Radial displacement of the medial meniscus and Fairbank's signs[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1997(339):163-173.
6 Sugita T,Kawamata T,Ohnuma M,et al.Radial displacement of the medial meniscus in varus osteoarthritis of the knee[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001(387):171-177.
7 Costa RC,Morrison WB,et al.Medial meniscus extrusion on knee MRI:is extent associated with severity of degeneration or type of tear[J].AJR,2004,183(1):7-23.
8 George M,Wall EJ.Locked knee caused by meniscal subluxation:magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic verification[J].Arthroscopy,2003,19(8):885-888.
9 黄加张,顾湘杰.膝关节半月板半脱位的相关因素分析[J].复旦大学学报(医学版),2006,32(4):433-435.
10 Fox MG.MR imaging of the meniscus:review,current trends and clinical implications[J].Radio Clin North Am,2007,45(6):1033-1053.
Value of MR Diagnosis on Meniscus Peripheral Dislocation of Knee Joint
CHU Zhan-fei,ZHAO Jing,XU Gang.Department of Radiology,Siping Hospital of China Medical University,Siping 136000,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the features of MR imaging of meniscus peripheral dislocation in knee joint to improve the understanding and diagnosis accuracy of this disease in clinic.MethodsMRI features of 22 patients with meniscus peripheral dislocation in knee joint confirmed by surgery admitted to our hospital from February 2008 to February 2012 were retrospectively analyzed.ResultsAmong the 22 patients,16 cases had meniscus peripheral dislocation on inner side,6 cases were on the outside.12 cases had meniscus peripheral dislocation combined with meniscus tear and 12 cases had meniscus peripheral dislocation combined with osteoarthritis.MRI showed that meniscus was separated from knee articular surface and was combined with tear.T2WI showed slightly high signal and T2WI showed equisignal.ConclusionMRI can accurately diagnose meniscus peripheral dislocation and evaluate its damage.
Knee joint;Menisci,tibial;Knee dislocation;Magnetic resonance imaging
R 684.76
B
1007-9572(2012)11-3917-02
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2012.11.117
136000吉林省四平市,中国医科大学四平医院影像科(初占飞,徐刚),超声科(赵静)
1.2 方法回顾性分析22例患者MRI特征。
1.2.1 MRI检查方法患者均采用美国GE高场超导HDe 1.5T MR扫描仪,膝关节专用线圈。患者采取仰卧位,膝关节呈生理性自然伸直状态,扫描过程中嘱患者保持静止不动。检查层面:矢状面、冠状面及横轴位。采用SE T1WI、T2WI、脂肪抑制序列,扫描层厚设定为4 mm,间距为1 mm。
1.2.2 图像分析及测量方法所有患者扫描图像传输至GE ADW 4.4工作站,由分析软件进行测量,每个图像测量2次,由2人分别测量,取其平均值为最终数据。测量方法:在膝关节MRI冠状位图像上,分别从股骨远端关节面内外侧缘和胫骨平台内外侧缘做连线,以此为基线,若关节面边缘存在骨赘,则取骨质原始的边缘作为连线参考点。如果半月板组织向外超出该基线≥3 mm时,即定义为半月板周缘性脱位[1](见图1)。
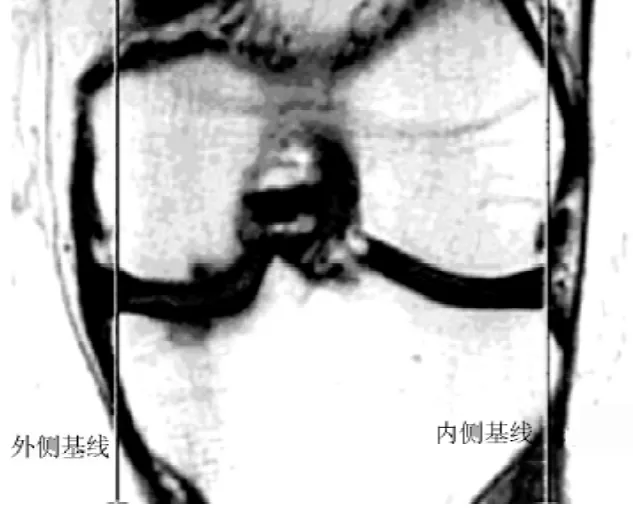
图1 测量图示:从股骨远端关节面内外侧缘和胫骨平台内外侧缘做连线,正常半月板在此基线内侧
Figure 1 Measurement diagram:lines were drawn between lateral border of articular surface of distal femur and lateral border of tibial plateau as well as between medial borders,normal meniscus should be inside the baseline
2012-03-16;
2012-10-11)
(本文编辑:刘莉)
