磷酸化转录激活因子5在胰腺癌细胞的表达及生长激素的干预作用
2011-11-22石毅孙跃明白剑锋陆文熊傅赞奚春华赵翰林苗毅
石毅 孙跃明 白剑锋 陆文熊 傅赞 奚春华 赵翰林 苗毅
·论著·
磷酸化转录激活因子5在胰腺癌细胞的表达及生长激素的干预作用
石毅 孙跃明 白剑锋 陆文熊 傅赞 奚春华 赵翰林 苗毅
目的检测磷酸化转录激活因子5(pSTAT5)在7株胰腺癌细胞株中的表达,观察生长激素(GH)处理SW1990细胞及其移植瘤后pSTAT5表达的变化,探讨GH的分子作用机制。方法体外培养人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990、Cap-1、Colo、Mia、Aspc、P3、PANC1,Western blotting检测各株细胞的pSTAT5表达; 收集指数生长期的SW1990细胞接种于BALB/C裸鼠,成瘤后随机分为GH组(瘤内注入GH 4 mg·kg-1·d-1,连续2周)和对照组(NS组),最后一次注射GH后1、2、24 h分批处死裸鼠,Western blotting检测SW1990细胞和移植瘤pSTAT5蛋白表达的变化。结果所有胰腺癌细胞(SW1990、Cap-1、Colo、Mia、Aspc、P3、PANC1)均有pSTAT5表达。GH(50 ng/ml)刺激后5 min,SW1990细胞pSTAT5的表达量为0.57±0.05,较刺激前显著增高,10 min达到0.64±0.04,15 min很快下降至0.39±0.03,但直至1 h仍高于对照组(0.33±0.02对0.25±0.06),2 h后表达量为0.26±0.03,回落到基础水平。移植瘤pSTAT5表达无明显变化。结论GH可迅速上调SW1990细胞的pSTAT5表达,但维持时间较短,而对胰腺癌移植瘤pSTAT5的表达无显著影响。
胰腺肿瘤; STAT5转录因子; 生长激素; 信号转导
生长激素(GH)作为合成代谢剂对增进蛋白合成、改善氮平衡有确切效应,但是否刺激肿瘤的生长仍有争议。我们前期动物实验发现,GH在体外能刺激胰腺癌细胞的增殖,但对在体肿瘤的生长无明显影响。本实验观察GH刺激后胰腺癌细胞株的胞内信号转导蛋白——磷酸化转录激活因子5(pSTAT5)的动态变化,旨在从生长因子-细胞信号的角度探讨外源性GH的作用机制。
材料与方法
一、细胞培养及pSTAT5检测
7株人胰腺癌细胞SW1990、Cap-1、Colo、Mia、Aspc、P3、PANC1由北京协和医院基本外科实验室提供。除Mia用DMEM培养基外,其他6株细胞均用1640培养基培养、传代。Western blotting检测各细胞株pSTAT5的表达。
二、移植瘤模型及分组
雌性BALB/c裸小鼠28只,由复旦大学医学部动物所提供,在北京协和医院动物房按SPF级标准饲养。收集指数生长期的SW1990细胞,于裸鼠背部皮下注射5×106个细胞,成瘤后按完全随机法将28只裸鼠分为GH组(21只)和对照组(7只)。GH组瘤内注射GH(瑞士Serono公司)4 mg·kg-1·d-1,连续2周。对照组注射等容积生理盐水。
三、SW1990细胞和移植瘤pSTAT5蛋白的检测
SW1990细胞以完全培养基培养2 d后更换为无血清培养基继续培养24 h,加入GH,终浓度为50 ng/ml。在GH作用后5、10、15、30、45 min及1、2 h分别弃去培养液,胰蛋白酶消化,收集细胞。荷瘤裸鼠于最后一次注射GH后1、2、24 h分批处死裸鼠,切除肿瘤后置-80℃低温保存。细胞或组织4℃超声破碎,加入新鲜配制含特殊稳定剂的裂解液(Tris-HCl10 mmol/L,EDTA5 mmol/L,NaCl 50 mmol/L,焦磷酸钠30 mmol/L,氟化钠50 mmol/L,原矾酸钠1 mmol/L,1%Triton-100,PMSF1 mmol/L,抑肽酶5 μg/ml,亮肽素1 μg/ml,胃蛋白酶抑制剂A 2 μg/ml,pH 8),4℃ 14 000 r/min离心20 min,取上清,BCA蛋白检测试剂盒(美国Piece公司)测定蛋白浓度,常规行Western blotting。山羊抗人pSTAT5多抗(美国Santa Cruz公司)1∶100稀释, 兔抗山羊-HRP-IgG (中山生物技术公司)1∶5000稀释,以β-actin为内参,最后ECL(美国Santa Cruz公司)发光, 暗室内压片,数字成像系统(美国UVP公司)扫描。以目的蛋白与β-actin灰度值的比值表示蛋白的相对表达量。
四、统计学分析

结 果
一、胰腺癌细胞pSTAT5的表达
SW1990、Cap-1、Colo、Mia、Aspc、P3、PANC1均有pSTAT5表达,其中以Colo的表达最强(图1)。
二、GH对SW1990细胞pSTAT5表达的影响
外源性GH可增强体外培养细胞SW1990中pSTAT5的表达(图2)。GH刺激后5 min,pSTAT5的表达量为0.57±0.05,较刺激前增高,10 min时达到峰值,为0.64±0.04(P<0.01),15 min很快下降至0.39±0.03,但直至1 h仍高于对照组0.33±0.02对0.25±0.06,2 h时回落至0.26±0.03。
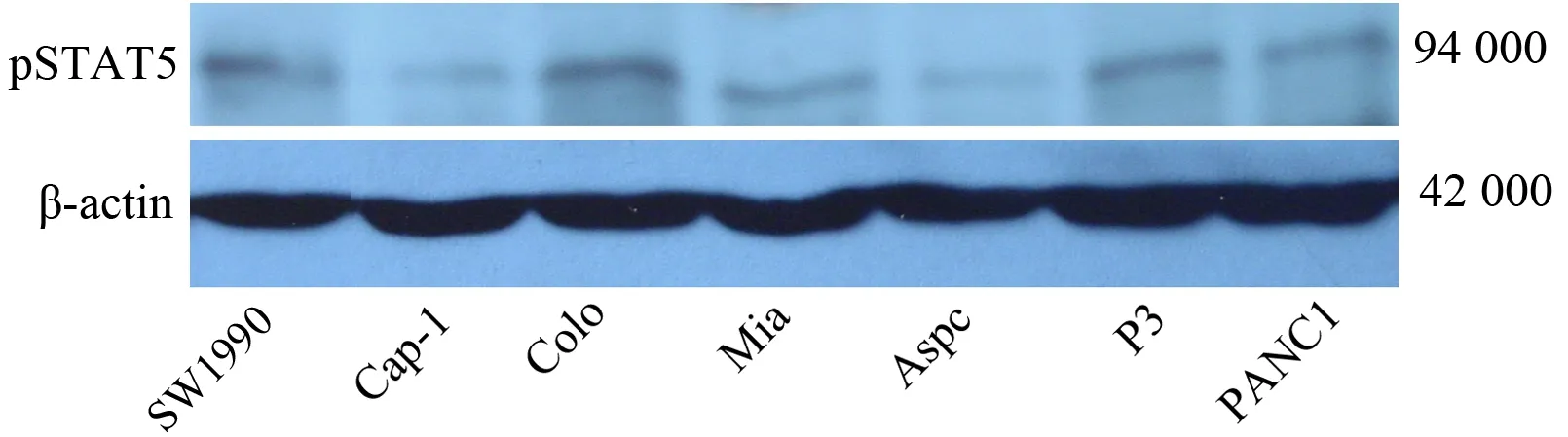
图1 pSTAT5在7株胰腺癌细胞中的表达

图2 GH刺激后SW1990中pSTAT3的表达
三、GH对移植瘤pSTAT5表达的影响
对照组pSTAT5的表达量为0.25±0.04,注射GH后1、2、24 h移植瘤组织中pSTAT5表达量分别为0.27±0.07、0.28±0.06、0.21±0.05,各组间无显著差异(图3)。
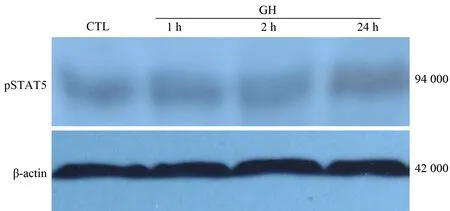
图3 移植瘤组织pSTAT5的表达(Western blotting)
重组GH广泛调节机体物质代谢、体液平衡及免疫功能[1]。理论上,恶病质患者的营养支持具有正面意义,而作为合成代谢剂的GH在促进氮平衡的同时是否也刺激肿瘤细胞的生长一直是临床关注的问题。我们前期研究[2]发现,GH对胰腺癌细胞增殖的影响存在着体内外差异,因此有必要进一步深入观察这一过程。
GH主要通过JAK-STAT通路向核内传递。随着JAK的激活,GH发生自体磷酸化,并诱导细胞内转录激活因子STAT5的激活[3],形成二聚体,并以这种形式穿过核膜结合到特定DNA序列,继而发挥生物学功能[4]。
有研究认为,多种肿瘤细胞,如前列腺癌、乳癌等可持续表达pSTAT5,且这种活化状态作为这些肿瘤细胞的标记,并与预后有关[5]。
本组选用低分化的人胰腺癌SW1990细胞,在加入GH后仅5 min, 细胞内pSTAT5的表达就显著增强,10 min时达峰值,提示GH能在短时间内迅速促进pSTAT5的表达。2 h后表达减弱至基础水平,说明STAT5表达升高时间短暂,但仍足以引发细胞分裂、增殖等下游事件的发生。
与体外实验相反,移植瘤内注射GH后1、2、24 h时pSTAT5表达无显著改变。这是因为细胞因子在体内环境中对效应细胞的作用受到神经、内分泌的多重调节,机体复杂的网络调控系统与体外单纯的培养环境有很大差距。由于仅限于动物实验,本组结果并不能成为临床上GH可安全应用于肿瘤的依据。
[1] Perrini S,Carreira MC,Conserva A,et al.Metabolic implications of growth hormone therapy.J Endocrinol Invest,2008,31:79-84.
[2] 石毅,廖泉,陈革,等.生长激素受体在胰腺癌细胞的表达及生长激素对胰腺癌细胞周期的影响.中华实验外科杂志,2004,21:441-443.
[3] Eleswarapu S,Gu Ze,Jiang H,et al.Growth hormone regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression may be mediated by multiple distal signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 binding sites.Endocrinology,2008,149:2230-2240.
[4] Beirer S,Höfer T.Control of signal transduction cycles:general results and application to the Jak-Stat pathway.Genome Inform,2006,17:152-162.
[5] Tan SH,Nevalainen MT.Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A/B in prostate and breast cancers.Endocr Relat Cancer,2008,15:367-390.
2009-10-09)
(本文编辑:屠振兴)
ExpressionofpSTAT5inpancreaticcarcinomacellsandeffectofgrowthhormoneonpSTAT5
SHIYi,SUNYue-ming,BAIJian-feng,LUWen-xiong,FUZan,XIChun-hua,ZHAOHan-lin,MIAOYi.
DepartmentofGeneralSurgery,FirstAffiliatedHospital,NanjingMedicalUniversity,Nanjing210029,China
SHIYi,Email:chxiay@yahoo.com.cn
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of pSTAT5 in 7 pancreatic carcinoma cell lines, and the change of expression of pSTAT5 in pancreatic carcinoma cells SW1990 after growth hormone (GH) treatment, and explore its molecular mechanism.MethodsHuman pancreatic carcinoma cell lines (SW1990, Cap-1, Colo, Mia, AsPc, P3, PANC1) were cultured in vitro, and Western blotting was used to detect the expression of pSTAT5 in these cell lines. SW1990 in exponential growth phase was collected and nude Balb/c mice were inoculated with SW1990 cells. When tumors became palpable after inoculation, mice were randomized to receive GH (intratumorally 4 mg·kg-1·d-1once daily for 2 weeks) and control group (normal saline group). 1 h, 2 h and 24 h after the last dose of GH treatment, the mice were sacrificed. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of pSTAT5 in SW1990 and inoculation tumor cells after GH injection.ResultsPositive expression of pSTAT5 was observed in all human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines (SW1990, Cap-1, Colo, Mia, Aspc, P3, PANC1). 5 minutes after GH (50 ng/ml) stimulation, the expression of pSTAT5 in SW1990 was 0.57±0.05, which was significantly increased; and it reached 0.64±0.04 at 10 minutes, then decreased to 0.39±0.03 at 15 minutes, however, it remained higher than that in the control group at 1 h (0.33±0.02 vs 0.25±0.06), and its expression at 2 h was 0.26±0.03 and returned to the normal level. The expression of pSTAT5 in xenograft was not significantly changed.ConclusionsGH could rapidly up-regulate the expression of pSTAT5 in SW1990 but the effect lasted for a relatively short period. GH had no significant effect on the expression of pSTAT5 in xenograft.
Pancreatic neoplasms; STAT5 transcription factor; Growth hormone; Signal transducing
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2011.01.012
210029 江苏南京,南京医科大学第一附属医院普外科
石毅,Email:chxiay@yahoo.com.cn
