CXCR4抑制剂AMD3100对2型登革热病毒诱导血管内皮细胞株Eahy926凋亡的影响*
2011-11-20龙喜贵郑毅涛齐一鸣黄俊琪
龙喜贵, 李 颖, 郑毅涛, 齐一鸣, 黄俊琪
(中山大学中山医学院免疫教研室,免疫学研究所,教育部热带病防治研究重点实验室, 广东 广州 510080)
CXCR4抑制剂AMD3100对2型登革热病毒诱导血管内皮细胞株Eahy926凋亡的影响*
龙喜贵, 李 颖, 郑毅涛, 齐一鸣, 黄俊琪△
(中山大学中山医学院免疫教研室,免疫学研究所,教育部热带病防治研究重点实验室, 广东 广州 510080)
目的探讨趋化因子受体CXCR4抑制剂AMD3100对2型登革热病毒(DV2)诱导人脐静脉血管内皮细胞株 Eahy926凋亡的影响。方法免疫组织化学法检测Eahy926细胞的Ⅷ因子。Eahy926细胞分成未感染组和DV2感染组,流式细胞术检测两组细胞不同时点(24 h、36 h、48 h和60 h)CXCR4的表达水平。流式细胞术分析未感染组、DV2感染组及DV2+AMD3100组不同时点的细胞凋亡率。免疫荧光法检测细胞膜表面磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)。结果Eahy926细胞有Ⅷ因子表达。在DV2感染Eahy926后的4个时点中,CXCR4的表达均有上调,其中以48 h感染组最明显(66.13%±10.30%,Plt;0.05)。DV2感染能诱导Eahy926细胞凋亡,其中36 h感染组凋亡率出现高峰(29.85%±15.78%,Plt;0.05)。应用AMD3100后在各时点均能上调DV2感染组的凋亡率,免疫荧光观察到DV2感染组及DV2+AMD3100组绿色荧光标记的细胞增多。结论DV2感染能诱导血管内皮细胞Eahy926凋亡并上调CXCR4的表达,CXCR4抑制剂AMD3100促进DV2诱导Eahy926细胞凋亡的发生。
登革热病毒; 凋亡; 受体,CXCR4; 血管内皮细胞
登革热病毒(dengue virus, DV),登革热( dengue fever, DF)的病原体,已经成为重要的人类虫媒病毒,威胁到热带和亚热带超过100个国家的25亿人口[1]。普遍认为2型登革热病毒(dengue virus type 2, DV2)流行最广,毒力较强,可引起重症DF,即登革出血热(dengue hemorrhagic fever, DHF)和登革休克综合征(dengue shock syndrome, DSS),其主要的特征是血浆渗漏。有报道表明DV引起的宿主细胞凋亡在其致病机制中发挥了重要作用[2]。我们前期研究表明,DV2可通过Fas/FasL途径诱导原代人脐静脉内皮细胞(human umbilical veins endothelium cells,HUVECs)产生凋亡[3]。在后续研究中我们又发现DV2感染HUVECs后趋化因子受体CXCR4(C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4)的基因水平表达增加。CXCR4是人免疫缺陷病毒 (human immunodeficiency virus,HIV)感染的辅助受体,与血管生成密切相关[4],但其在DV感染血管内皮细胞中的作用尚未明确。本研究采用流式细胞术检测人脐静脉内皮细胞株Eahy926感染DV2前后CXCR4 的表达,并研究CXCR4特异性抑制剂AMD3100对DV2诱导Eahy926细胞凋亡率的影响,探索CXCR4在DV2感染血管内皮细胞中的作用。
材 料 和 方 法
1材料
1.1细胞系 Eahy926 是由人肺腺癌细胞株A549与原代培养的人脐静脉血管内皮细胞融合构建而成的永生化细胞株,具有血管内皮细胞的特性[5],为中山医学院干细胞与组织工程研究中心惠赠。
1.2病毒 DV2病毒株(new guinea Cstrain)来自中山医学院微生物学教研室, 本实验室已进行病毒扩增和定量保存。
1.3主要试剂 DMEM/F12培养基、胎牛血清、青链霉素双抗等为Gibco产品。凋亡检测试剂盒为南京凯基(含FITC-AnnexinⅤ组份)产品,CXCR4流式抗体为BD产品,Ⅷ因子Ⅰ抗为Thermo产品,Ⅱ抗为上海基因科技产品。
2方法
2.1细胞培养 Eahy926 用100 mL/L胎牛血清及青链霉素双抗为1.0 ×105U/L DMEM/F12培养液, 37 ℃、5%CO2孵育箱中培养。
2.2Ⅷ因子染色 取对数期生长的Eahy926细胞,经4%多聚甲醛固定20 min后,0.2%Triton打孔10 min,3%H2O2处理10 min,5%BSA封闭20 min,加抗Ⅷ因子 Ⅰ 抗,37 ℃ 60 min,Ⅱ 抗37 ℃ 30 min,DAB显色。
2.3登革病毒感染及抑制剂应用 取已定量好的2 型登革病毒液( 109PFU/L) 加入Eahy926 细胞培养板中吸附2 h,弃去上清,加入培养液,应用抑制剂AMD3100(1 mg/L)于感染2 h后弃去多余病毒时,加入培养基,37℃、5%CO2培养,在各时点弃去培养液, 收集细胞。CXCR4的流式细胞术检测分4个时间点(24 h、36 h、48 h和60 h),每个时点设未感染组和DV2感染组。Eahy926的凋亡检测时点设置同CXCR4检测,每时点设未感染组、DV2感染组及DV2+AMD3100组,病毒及试剂浓度参照文献[6]。
2.4流式细胞术检测Eahy926细胞的CXCR4表达 取对数期生长的Eahy926 细胞,500×g离心5 min, 用PBS 洗涤2 遍。用buffer重悬并调整细胞数为1×109cells/L 吸取100 μL 转移至5 mL 的流式离心管中,加CXCR4的流式抗体12 μL,室温孵育30min, PBS 洗涤2遍后用buffer 200 μL重悬,流式细胞仪检测。
2.5流式细胞术检测Eahy926细胞的凋亡 取对数期生长的Eahy926 细胞离心,500×g离心5 min,用PBS 洗涤2 遍。用binding buffer 重悬并调整细胞数为1×109cells/L 吸取100 μL 转移至5 mL 的流式离心管中, 加入FITC-AnnexinⅤ 5 μL、PI 5 μL 混匀, 室温避光放置15 min,加入binding buffer 400 μL,流式细胞仪检测。
2.6荧光显微镜观察Eahy926细胞表面的磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS) 细胞经DV2刺激及AMD3100处理后,PBS漂洗2次,加含有FITC-AnnexinⅤ的buffer,室温反应5 min,荧光显微镜下观察。
3统计学处理
结 果
1Eahy926细胞Ⅷ因子染色呈阳性
Eahy926细胞经内皮细胞特性Ⅷ因子染色后出现棕黄色的阳性反应,见图1,证实其具有内皮细胞的特性。

Figure 1. Immunohistochemistry staining of factor Ⅷ in Eahy926 cells(DAB staining,×200).
2DV2感染上调了Eahy926的CXCR4表达
Eahy926细胞未感染组设4个时点(24 h、36 h、48 h和60 h),各时点表面表达CXCR4的Eahy926细胞百分比分别是:47.23% ±17.85%、 55.90%±11.48%、45.65%±20.93%和46.23%±21.47%。DV2感染Eahy926细胞各个相应时点细胞表面CXCR4表达的百分比分别为52.90%±16.28%,58.93%±11.3%, 66.13%±10.30%,46.23%±21.47%,与感染前比均上升,其中48 h组感染前后差异最明显(Plt;0.05,n=3) ,见图2、3。
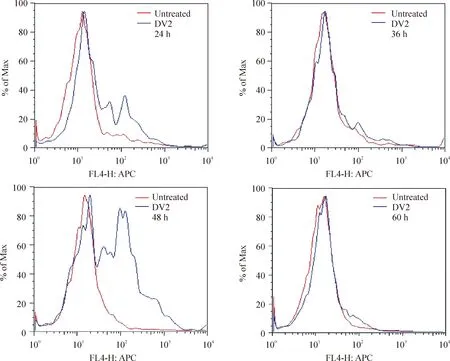
Figure 2. Expression of CXCR4 in Eahy926 cells before or after DV2 infection at 24 h, 36 h, 48 h and 60 h detected by flow cytometry.
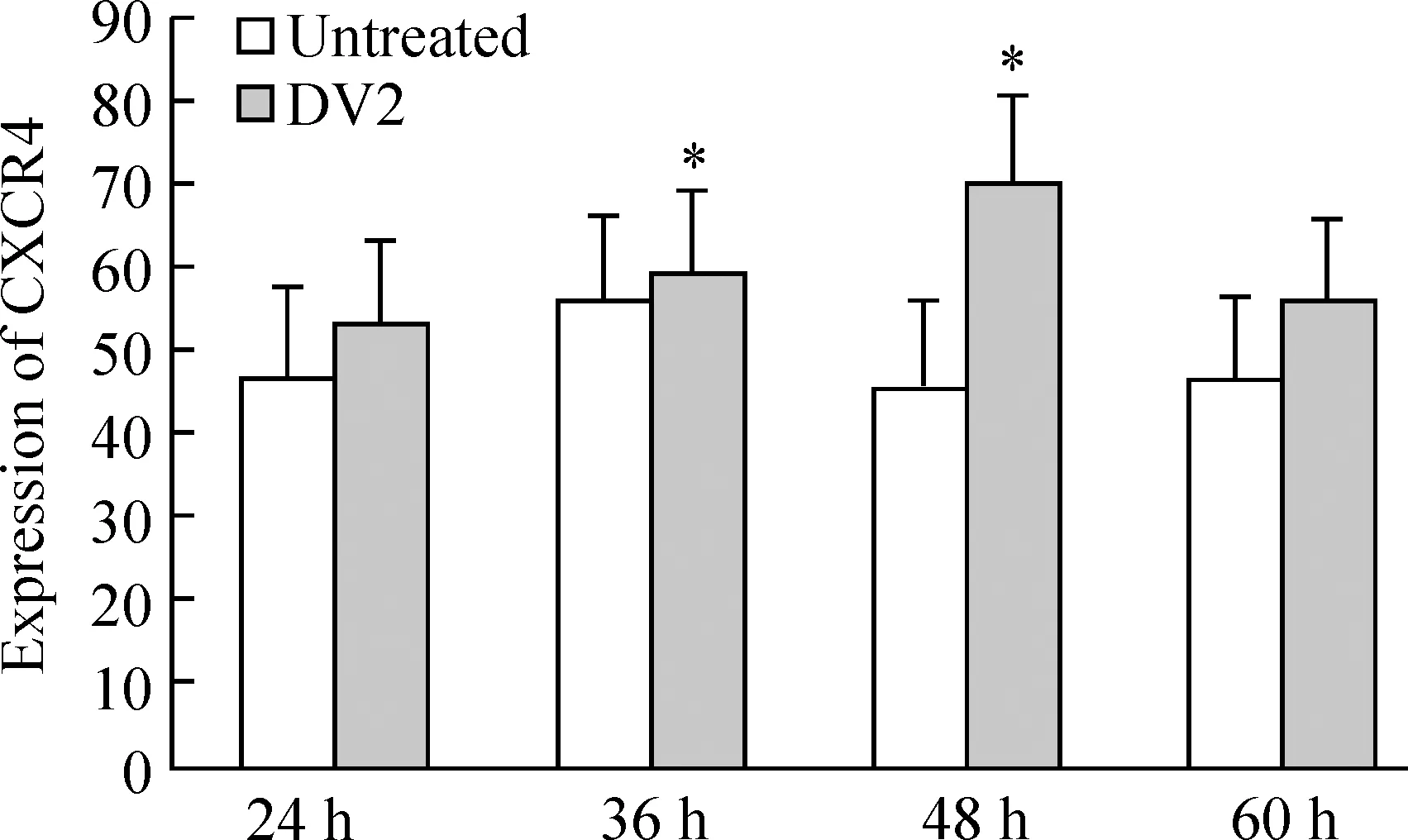
Figure 3. CXCR4 expression in Eahy926 cells before or after DV2 infection at 24 h, 36 h, 48 h and 60 h .±s.n=3 *Plt;0.05 vs untreated cells
3DV2感染与应用AMD3100后增加了Eahy926的凋亡率
图4结果显示DV2感染组4个时点(24 h、36 h、48 h和60 h)Eahy926细胞凋亡率分别为:25.18% ±8.82%、29.85% ±15.78%、19.95% ±4.96%和29.29% ±10.08%,均高于未感染组的Eahy926细胞凋亡率(18.95% ±9.00%、22.92% ±13.06%、18.91%±2.37%和25.73% ±9.35%)。而DV2+AMD3100组各时点Eahy926细胞凋亡率为39.39% ±15.94%、30.45% ±16.88%、27.46% ±8.26%和36.37% ±18.86%。48 h DV2+AMD3100组Eahy926细胞凋亡率高于DV2相应时点组(Plt;0.05,n=3),见图4、 5。
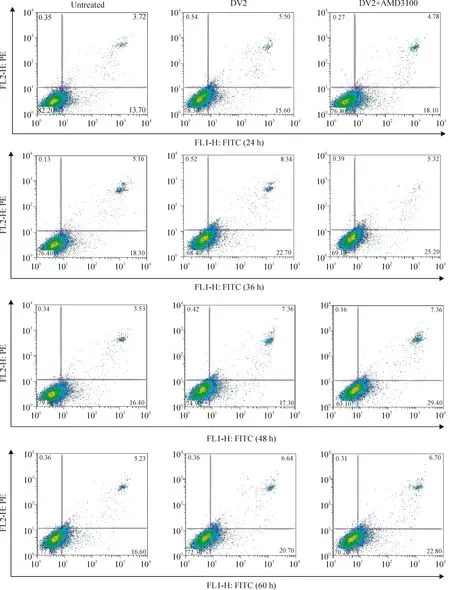
Figure 4. Apoptosis of Eahy926 cells treated with or without AMD3100 before or after DV2 infection at 24 h,36 h,48 h and 60 h detected by flow cytometry.
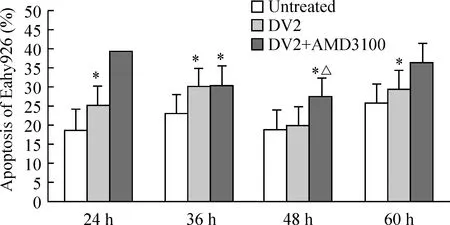
Figure 5. Apoptosis of Eahy926 cells treated with or without AMD3100 24 h, 36 h, 48 h and 60 h after DV2 infection±s.n=3. *Plt;0.05 vs untreated group; △Plt;0.05 vs DV2 group.
4免疫荧光法检测发现DV2感染组和DV2+AMD3100组Eahy926细胞表面磷脂酰丝氨酸表达增多
结果显示未感染组绿色荧光标记的磷脂酰丝氨酸极少,DV2感染组及DV2+AMD3100组绿色荧光标记的细胞增多,见图6。
讨 论
细胞凋亡(apoptosis) 或细胞程序性死亡( programmed cell death, PCD)在维持机体正常发育、清除病毒感染细胞、肿瘤细胞等有着极其重要的意义。Clarke等[7]认为呼肠病毒引起的细胞凋亡可能是由肿瘤坏死因子相关诱导凋亡配体 (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand,TRAIL) 介导的, Kim等[8]研究表明HIV病毒可上调获得性免疫缺陷综合征 (acquired immune deficiency syndrome,AIDS) 易感病人体内抗原提呈细胞的TRAIL从而介导凋亡,Larochelle等[9]曾报道EB病毒 (Epstein-Barr virus,EBV)引起细胞凋亡可能是FasL的作用,我们研究发现DV2感染原代HUVECs可通过Fas/FasL途径诱导凋亡的发生[3],HUVECs感染DV2后CXCR4的基因水平表达增加。
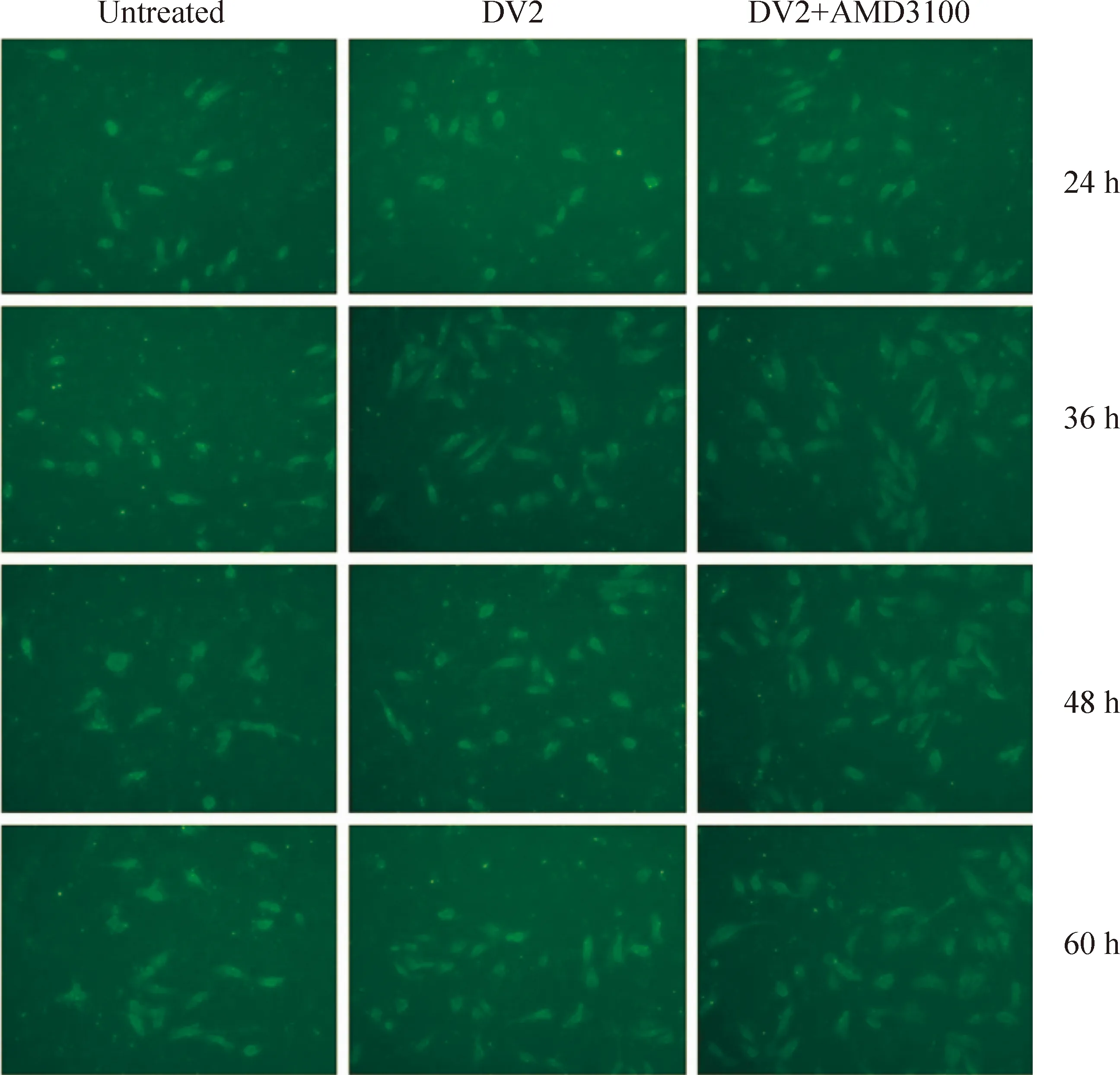
Figure 6. Direct immunofluorescence staining of phosphatidylserine in Eahy926 cells with FITC-Annexin V(×100)
为了进一步研究CXCR4在DV2感染血管内皮细胞中的作用,我们选择人静脉血管内皮细胞株Eahy926细胞作为细胞模型。Eahy926细胞来源于HUVECs[5],与原代HUVECs相比易于培养且无原代细胞分离培养过程中杂细胞的影响。但Eahy926细胞在长期不断传代培养后是否依然具有内皮细胞特性?我们对其进行了内皮细胞特性Ⅷ因子染色,证实了这一点。
CXCR4是基质细胞衍生因子-1 (stromal cell derived factor 1,SDF-1)的特异性受体[10],属于7次跨膜的G蛋白偶联受体家族。CXCR4与配体SDF-1结合传递的细胞间信号在造血干细胞归巢、淋巴细胞迁移、促肿瘤细胞侵袭[11]、促血管细胞增殖生长[ 12,13]等方面发挥着重要作用。有报道表明下调CXCR4的表达抑制了肿瘤细胞的代谢和侵袭性[14],增加CXCR4的表达抑制了过敏性紫癜血小板的自身凋亡[15]。有报道应用CXCR4的单克隆抗体或其特异性的抑制剂AMD3100可上调Fas等凋亡相关因子的表达[16]。AMD3100是SDF-1受体CXCR4的非肽类阻断剂,能特异性与CXCR4结合而不产生激动作用,阻断SDF-1/CXCR4轴参与的生理过程。本文初步研究了AMD3100对DV2诱导血管内皮细胞Eahy926凋亡的影响。
本实验结果显示DV2感染Eahy926细胞后能上调CXCR4的表达,48 h升高最为明显。根据SDF-1/CXCR4轴参与的生理过程,其CXCR4于感染后表达增加可能为DV2诱导Eahy926细胞凋亡后的保护性上调。DV2感染可以诱导Eahy926细胞凋亡,其中36 h凋亡率增高最为明显;AMD3100能上调DV2诱导的Eahy926细胞的凋亡率,48 h DV2感染组与DV2+AMD3100组凋亡率存在显著差异,其原因可能为48 h时点CXCR4的表达增加最为明显,从而AMD3100对SDF-1/CXCR4轴产生的抑制作用也会更加明显。综上可以看出AMD3100在DV2感染血管内皮细胞株Eahy926中可以促进病毒诱导的细胞凋亡的发生,但其作用机制还有待进一步研究。
[1] Guzmán MG, Kourí G. Dengue: an update [J].Lancet Infect Dis, 2002, 2(1): 33-42.
[2] Matsuda T, Almasan A, Tomita M, et al. Dengue virus-induced apoptosis in hepatic cells is partly mediated by Apo2 ligand/tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand [J] . Gen Virol, 2005, 86(4): 1055-1065.
[3] Liao H, Xu J, Huang J. FasL/Fas pathway is involved in dengue virus induced apoptosis of the vascular endothelial cells [J]. Med Virol, 2010,82(8):1392-1399.
[4] Yang SX, Chen JH, J iang XF, et al. Activation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in malignant glioma cells promotes the production of vascular endothelial growth factor [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2005, 335 (2): 523 - 528.
[5] Lidinqton EA , Moves DL , McCormack AM, et al . A comparison of primary endothelial cells and endothelial cell lines for studies of immune interactions [J] . Transpl Immunol , 1999 , 7 (4): 239-246.
[6] 廖红舞,黄俊琪. 2型登革病毒诱导ED25细胞凋亡及死亡受体的表达变化[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(12):2401-2404.
[7] Clarke P, Tyler KL. Down-regulation of cFLIP following reovirus infection sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis [J]. Apoptosis,2007, 12(1): 211-223.
[8] Kim N,Dabrowska A, Jenner RG, et al. Human and simian immunodeficiency virus-mediated upregulation of the apoptotic factor TRAIL occurs in antigen-presenting cells from AIDS-susceptible but not from AIDS-resistant species [J] . J Virol, 2007, 81(14): 7584-7597.
[9] Larochelle B, Flamand L, Gourde P, et al. Epstein-Barr virus infects and induces apoptosis in human neutrophils [J] . Blood, 1998, 92(1): 291-299.
[10]Altundag K, Morandi P, Altundag O, et al. Possible role of CXCR4 - mediated chemotaxis in breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2005 , 89(3): 317-321.
[11]Juarez J, Bendall L, Bradstock K. Chemokines and their receptors as therapeutic targets: the role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2004, 10(11): 1245-1259.
[12]Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F, et al. CXCR4 and CXCL12 are inversely expressed in colorectal cancer cells and modulate cancer cell migration, invasion and MMP29 activation[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2005,310 (1): 117 - 130.
[13]Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, et al. CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2004,64 (23): 8604 - 8612.
[14]Yadav VR, Sung B,Prasad S, et al. Celastrol suppresses invasion of colon and pancreatic cancer cells through the downregulation of expression of CXCR4 chemokine receptor [J]. J Mol Med, 2010,88(12):1243-1253.
[15]Wang JD, Ou TT,Wang CJ, et al. Platelet apoptosis resistance and increased CXCR4 expression in pediatric patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura[J].Thromb Res,2010, 126(4):311-318.
[16]魏 立,孔佩艳,陈幸华,等. 抗CXCR4 单克隆抗体对HL260细胞粘附性及Bcl-2、Fas 蛋白表达的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2004,12(4):436-440.
EffectofAMD3100ondenguevirustype2-inducedapoptosisinEahy926cells
LONG Xi-gui, LI Ying, ZHENG Yi-tao, QI Yi-ming, HUANG Jun-qi
(DepartmentofImmunology,InstituteofImmunology,ZhongshanSchoolofMedicine,SunYet-senUniversity,KeyLaboratoryofTropicalDiseaseControl,MinistryofEducation,Guangzhou510080,China.E-mail:junqi_huang@yahoo.com.cn)
AIM: To investigate the role of AMD3100 (an inhibitor of CXCR4) in dengue virus type 2 (DV2)-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cell line Eahy926.METHODSThe expression of factor Ⅷ in Eahy926 cells was examined by immunohistochemistry staining. The cells were divided into untreated group, DV2 infection group and DV2+AMD3100 group. Flow cytometric analysis was used to detect the expression of CXCR4 in Eahy926 cells 24 h, 36 h, 48 h and 60 h after DV2 infection. In addition, the percentage of apoptotic cells was also analyzed by flow cytometry. Immunofluorescence was performed to detect the phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of Eahy926 cells.RESULTSEahy926 cells were factor Ⅷ-positive. Compared with untreated group, the expression of CXCR4 increased in DV2 infection group, most markedly 48 h after infection (66.13%±10.30%,Plt;0.05). The percentage of apoptotic Eahy926 cells after DV2 infection was the highest at 36 h (29.85%±15.78%,Plt;0.05). The percentage of DV2-induced apoptotic cells in DV2+AMD3100 group was higher than that in DV2 infection group. The green fluorescence-labeled cells in DV2 infection group and DV2+AMD3100 group were more than those in untreated group.CONCLUSIONDV2 infection induces apoptosis and increases the expression of CXCR4 in Eahy926 cells. AMD3100, the inhibitor of CXCR4, may be a promoter of apoptosis in Eahy926 cells after DV2 infection.
Dengue virus; Apoptosis; Receptors,CXCR4; Vascular endothelial cells
1000-4718(2011)04-0632-06
R373.33
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2011.04.002
2010-09-05
2011-02-24
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. 30872350;No. 30400371;No. 30571736 );广东省自然科学基金资助项目(No.8151008901000017);广东省团队项目(No. 06201946);广东省科技计划项目(No.2007B031516008;No. 2010B050700008);广州市科技计划项目(No. 2006Z3-E4081; No.2008Z1-E221);高校基本科研业务费中山大学青年教师培育项目(No.10YKPY31)
△通讯作者Tel: 020-87330068-838;E-mail: junqi_huang@yahoo.com.cn
