配合物[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O的水热合成、晶体结构及荧光性质
2011-11-10屈景年陈满生
聂 雪 屈景年 陈满生
(衡阳师范学院化学与材料科学系,衡阳 421008)
配合物[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O的水热合成、晶体结构及荧光性质
聂 雪 屈景年*陈满生*
(衡阳师范学院化学与材料科学系,衡阳 421008)
由二苯甲酮-4,4′-二甲酸和邻菲咯啉为配体合成了1个新的镉化合物[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O(1)(H2bpndc=二苯甲酮-4,4′-二甲酸),并对其进行了元素分析、IR及X-射线衍射法表征。晶体结构表明:配合物1属于四方晶系,I41/a空间群。配合物1中心镉原子是六配位的变形八面体构型,该单核化合物通过氢键拓展成一维链状结构。配合物1的荧光测试研究表明它具有蓝色荧光。
镉(Ⅱ)配合物;晶体结构;氢键;荧光性质
Recently,a great deal of interest in transition metal complex assembly has been devoted to the development of rational synthetic routes to novel one-,two-and three-dimensional crystal frameworks,due to their potential applications in many areas such as ionexchange,nonlinear optics,molecular sieves,gas storage,magnetism,catalysis,and molecular sensing[1-8].Furthermore,the self-assembly of highly organized metal-organic frameworks comprised of metal ions as nodes and bridged ligands as spacers has achieved considerable progress in supramolecular chemistry and material chemistry.As we know,benzophenone-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid (H2bpndc)is a typical example of V-shaped flexible ligands.It can be used as a logic ligand to construct new functional complexes due to its multiple coordination sites and potential hydrogen-bond identification points[9-14].With the aim of synthesizing stable functional materials,herein,we introduced 1,10-phenanthroline (phen)asauxilliary ligand,and obtained a new Cd(Ⅱ)coordination complex,[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O(1).The details of their synthesis and structure are reported.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and instruments
The reagents were used as commercial sources without further purification.Elemental analyses were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 240C elemental analyzer.The IR spectra were recorded on Bruker Vector22 FTIR spectrophotometer using KBr discs.Thermogravimetric analyses were performed on a simultaneous SDT 2960 thermal analyzer under nitrogen with a heating rate of 10 ℃·min-1.The luminescent spectra for the solid powdered samples were recorded at room temperature on an Aminco Bowman Series 2 spectrophotometer with xenon arc lamp as the light source.In the measurements of the emission and excitation spectra,the pass width was 4.0 nm.All the measurements were carried out under the same conditions.
1.2 Synthesis of the complex 1
Complex 1 was synthesized by hydrothermal method in a 16 mL Teflon-lined autoclave by heating a mixture containingCd(NO3)2·4H2O (30.9 mg,0.1 mmol),H2bpndc(16.7 mg,0.1 mmol),phen(20.1 mg,0.1 mmol)and NaOH (8.0 mg,0.2 mmol)dissolved in 10 mL H2O and heated at 140 ℃ for 4 d.Block colorless single crystals of 1 were collected by filtration and washed by water and ethanol for several times with a yield of 38% (based on phen).Anal.calcd.for C39H30CdN4O8(%):C 58.86;H 3.77;N 7.04;found(%):C 58.92;H 3.69;N 7.11.IR (KBr pellet,cm-1):3433(s),1642(s),1524(s),1431(s),1418(w),1373(w),1297(s),1253(s),1113(s),971(w),938(m),857(m),756(m),661(m),608(m).
1.3 X-ray crystallography
The X-ray diffraction measurement for 1 was performed on the Bruker Smart ApexⅡCCD diffractometer with graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)at room temperature.A total of 31 274 reflections were collected in the range of 1.82°≤θ≤26.00°by using an ω-scan mode,of which 7 514 were unique and 5 352(I>2σ(I))were used in the succeeding structure calculations.Data intensity was corrected by Lorentz and polarization effect,which also were integrated by using the SAINT program[15].An empirical absorption correction was applied using the SADABS program[16].The structure was solved by direct methods using the program SHELXS-97 and all the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically on F2by the full-matrix least-squares technique using the SHELXL-97 crystallographic software package[17-18].Crystal data and structure refinement parameters are listed in Table 1.The selected bond lengths and bond angles are given in Table 2.
CCDC:827905.
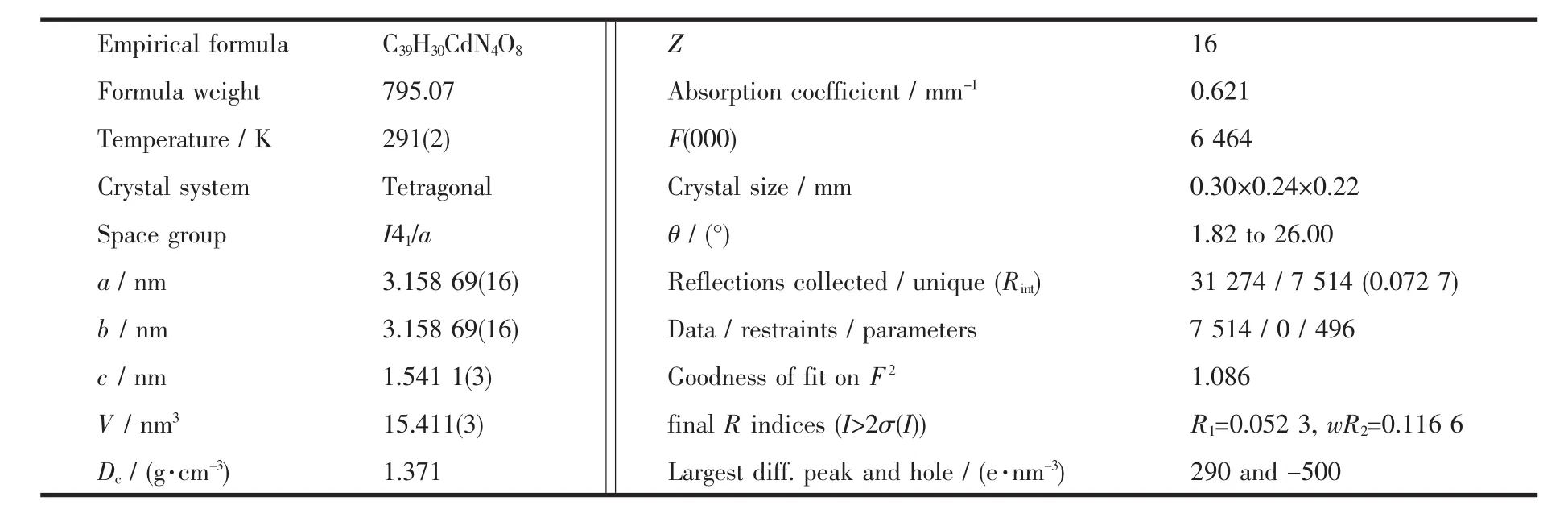
Table 1 Crystal data and structure parameters for complex 1
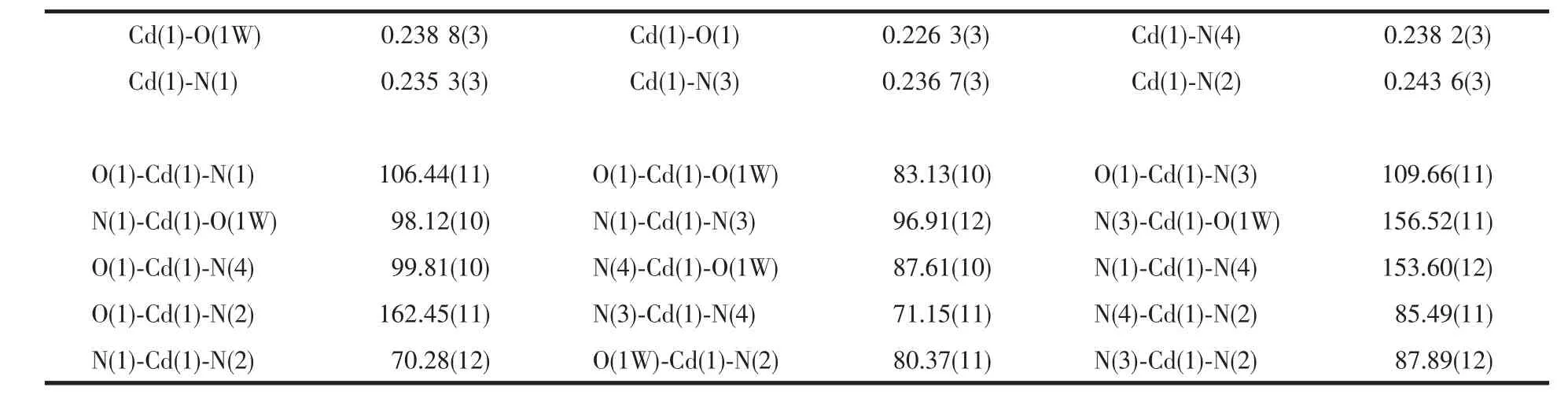
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angle(°)
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Structure description
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction study reveals that 1 crystallizes in space group I41/a.A perspective view of the coordination unit with the atom-labeling scheme is given in Fig.1,the asymmetric unit of 1 contains one Cd(Ⅱ),one bpndc2-ligand,one coordinated and two free water molecules.As shown in Fig.1,the Cd1 atom is six-coordinated butthe geometry isa distorted octahedron with N2 and O1 at the apical positions,principally due to the “bite” of the phen ligands.The Cd-N bonds range from 0.235 3(3)to 0.243 6(3)nm,while the Cd-O bonds from 0.2263(3)to 0.2388(3)nm.The sum of bond angles O1W-Cd1-N1(98.12(10)°),N1-Cd1-N3(96.91(12)°),N3-Cd1-N4(71.15(11)°)and N4-Cd1-O1W(87.61(10)°)is 353.79°,showing the O1W,N1,N3 and N4 atoms are coplanar.These data indicate that the Cd(1)atom of the complex is in a slightly distorted octahedral configuration.
It is noteworthy that these mononuclear complex are further connected by O-H…O bonds(Table 3)into a one-dimensional(1D)supramolecular chain architecture (Fig.2).The 1D chain finally packed together through C-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions to
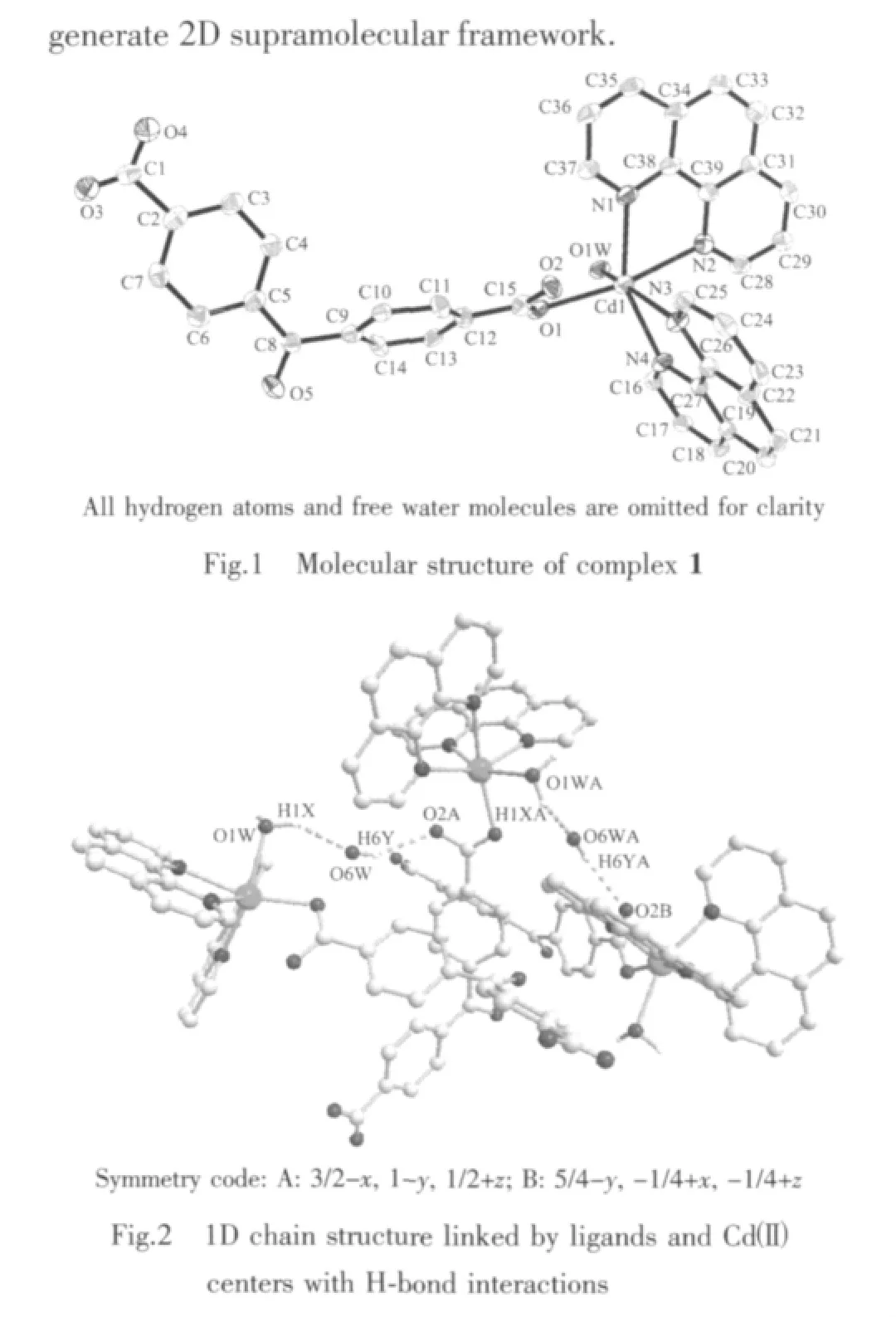
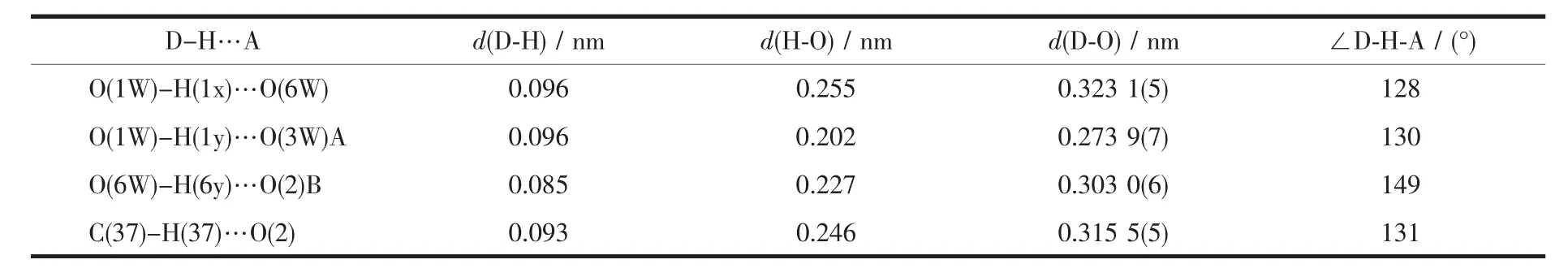
Table 3 Parameters of hydrogen bonds for the complex 1
2.2 IR,TG and photoluminescence property
The IR spectrum of the complex exhibits a medium broad band centered at ca.3 433 cm-1,due to the ν(O-H)absorptions of water molecules.One feature of the IR data is the separation between νas(COO-)and νs(COO-),which have often been used to diagnose the coordination modes in the carboxylate ligands.The separation for monodentate carboxylate groups is>200 cm-1,whereas it is <200 cm-1in bidentate groups[19].The separation(Δν)between νas(COO-)and νs(COO-)is 224 cm-1for 1,indicating monodentate coordinating modes for the coordinated carboxylate groups.As far as phen,its adsorption peaks 1431,857 and 756 cm-1respectively,these IR results are coincident with the crystallographic structural analyses.
The results of thermogravimetric analyses(TGA)indicate that complex 1 lost its coordinated and noncoordinated water molecules in the temperature range of 25~205 ℃.The weight loss of 6.83%is consistent with calculated one of 6.79%.After the loss of all the water molecules,the supramolecular framework is stable up to 340℃,followed by another weight loss at high temperature.
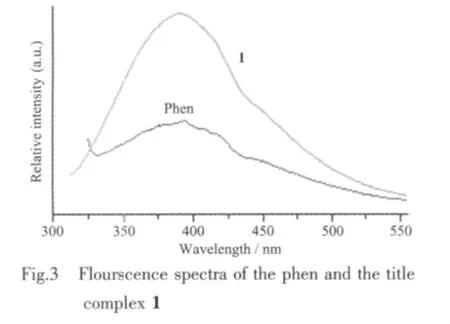
The photoluminescence property of 1 and free ligand phen was examined in solid state at room temperature.As shown in Fig.3,intense emission bands were observed at 383 nm (λex=290 nm)for 1,378 nm(λex=230 nm)for phen,respectively.These emissions can be attributed to neither metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT)nor ligand-to-metal charge transfer(LMCT)because the Cd(Ⅱ)ions are ind10configuration and difficult to oxidize or to reduce[20-21].Therefore the emission observed in 1 is attributed to the π-π*intraligand photoluminescence due to its resemblance to that of phen ligand.The result suggests that the complex 1 may be good candidate of potential bluefluorescent materials,since it is highly thermally stable and insoluble in common solvents.
[1]Cote A P,Benin A I,Ockwig N W,et al.Science,2005,310:1166-1170
[2]Yaghi O M,O′Keeffe M,Ockwig N W,et al.Nature,2003,423:705-714
[3]Wu C D,Hu A,Zhang L,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2005,127:8940-8941
[4]Fang Q R,Zhu G S,Xue M,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2008,8:319-329
[5]Hong C S,Yoon J H,Lim J H,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2005,23:4818-4821
[6]Dong Y B,Smith M D,Layland R C,et al.Chem.Mater.,2000,12:1156-1161
[7]Dong Y B,Smith M D,zur Loye H C.Inorg.Chem.,2000,39:4927-4935
[8]Dong Y B,Zhao X,Huang R Q.Inorg.Chem.,2004,43:5603-5612
[9]Park H J,Suh M P.Chem.Commun.,2010,46:610-612
[10]Park H J,Suh M P.Chem.Eur.J.,2008,14:8812-8821
[11]Sun C Y,Jin L P.J.Mol.Struct.,2006,782:171-176
[12]Sun C Y,Jin L P.J.Mol.Struct.,2005,733:63-68
[13]Furukawa H,Kim J,Ockwig N W,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2008,130:11650-11661
[14]Tanaka D,Nakagawa K,Higuchi M,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.,2008,47:3914-3918
[15]SAINT,Version6.02a,Bruker AXS Inc.,Madison,WI,2002.
[16]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,Program for Bruker Area Detector Absorption Correction,University of Göttingen,Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[17]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,Program for Crystal Structure Solution,University of Göttingen,Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[18]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for Crystal Structure Refinement,University of Göttingen,Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[19]Nakamoto K.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds.New York:John Wiley&Sons,1986.
[20]Bunz U H F.Chem.Rev.,2000,100:1605-1644
[21]Yang W Y,Schmider H,Wu Q G,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2000,39:2397-2404
Hydrothermal Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Luminescence of Complex[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O
NIE Xue QU Jing-Nian*CHEN Man-Sheng*
(Department of Chemistry and Materials Science,Hengyang Normal University,Hengyang,Hunan 421008,China)
A new cadmium complex[Cd(bpndc)(phen)2(H2O)]·2H2O(1)was obtained by hydrothermal assembly of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O with a benzophenone-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid(H2bpndc)in the presence of N-donor ligands,1,10-phenanthroline(phen).Complex 1 crystallizes in tetragonal,space group I41/a with a=3.158 69(16)nm,b=3.158 69(16)nm,c=1.544 59(17)nm,V=15.411(3)nm3,Z=16,C39H30N4CdO8,Mr=795.07,Dc=1.371 g·cm-3,μ=0.621 mm,F(000)=6464,Rint=0.0727,R1=0.0523,wR2=0.1166.Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that each metal center located in a distorted octahedron coordination environment,and it is further connected by hydrogen-bond interactions to give a one-dimensional(1D)supramolecular structure.In addition,the luminescent property of complex 1 has been investigated at room temperature.CCDC:827905.
Cd(Ⅱ)complex;crystal structure;hydrogen bond;luminescent property
O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2011)11-2267-04
2011-01-09。收修改稿日期:2011-05-10。
湖南省教育厅项目(No.10C0473),衡阳师范学院科学启动基金(No.10B67)和衡阳市科技局(No.2009KJ28)资助项目。
*通讯联系人。 E-mail:cmsniu@163.com,qujnan@126.com;会员登记号:S06N7223M1009。
综 述
