扩散制造组织中的耦合模型及其应用
2011-04-19廖文和
郭 宇 安 波 廖文和
(南京航空航天大学机械工程学院,南京,210016,中国)
INTRODUCTION
Networked manufacturing is one of development tendencies of advanced manufacturing,and according to special requirements,there are several derivations of the networked manufacturing model,such as virtual enterprise[1],networked manufacturing based on ASP[2],and collaborative manufacturing chain[3]. These models mostly adopt the loose coupling management and emphasize the autonomy of enterprises,but some problems still exist,such as,the confidentiality cannot be assured in the manufacturing process,the manufacturing progress cannot be kept abreast of the times, and quality problems cannotbe tracked,etc.Therefore they cannot satisfy the controllability,measurability and reliability requirements of manufacturing process for complex armament.Extended manufacturing[4]is a new networked manufacturing model and orients to the rapid production of complex armament.The construction method of extended manufacturing organization based on coupling is proposed in this paper.
At present,design task planning of the complex product based on the coupling arouses great attention of researchers.Ref.[5]presented a process model with structure of design structure matrix family based on the study of design structure matrix.Ref.[6]developed an effective model to transform the binary task relation into the quantifiable task coupling length and decompose the large interdependent task group into smaller and manageable sub-groups.Ref.[7]developed a method for measuring functional dependency and sequencing of coupled tasks in engineering design to improve the design process.But there are few researches for manufacturing domain.In order to clearly discuss the extended manufacturing coupling and construction process,some definitions are given as follows:
Definition 1 Networked manufacturing coupling.Networked manufacturing tasks are undertaken by manufacturing resources distributed in different areas.Due to differences in organiza-tional structure,production practices,information platform,and geographical location among different enterprises,the continuous manufacturing process performed in one enterprise is divided into several discrete manufacturing nodes in the whole network. Two ormore manufacturing nodes interact and influence the whole manufacturing system.This is called networked manufacturing coupling.
Definition 2 Extended nodes(ENs).It refers to those extended manufacturing resources (ERs)that are able to afford extended tasks (ETs)delivered by the dominant enterprise.ENs can be expressed as the following formula

The coupling in networked manufacturing is due to the manufacturing tasks distributed in different places discretely,and there is the stronger coupling between extended manufacturing nodes. Two reasons are listed as follows:
(1) The complex manufacturing process. Due to the particular requirements in security, quality and schedule,all suppliers are brought into the extended manufacturing system,thus a controllable organization in whole manufacturing is constructed.ETs are undertaken by different ERs,so raw material,semi-finished and finished products are transmitted between different ENs, and a complex and huge network for material transmission is formed.
(2)The complex tasks.The development of complex armament is a technology-intensive engineering.For example,a plane is composed of millions of parts,and during the manufacturing process,the quality of parts should be ensured and the coordination between ETs should be satisfied,such as the manufacturing coordination between different processes of one part,and assembly coordination between parts.Hence,lots of information should be transmitted between the dominant enterprise and ERs in order to coordinate production schedule and control product quality.
Complex transmission of material and information cause many difficulties for the dominant enterprise to control the manufacturing process and the coordinate between ERs.If there is random disturbance during the manufacturing process in one ENs,the production schedule and the product quality of the others are affected too.So the closely-related ETs are performed by closelyrelated ERs,thus enhancing the coupling between ERs.It makes easy for manufacturing,assembly,debugging,and maintenance,reduces the bad impacts of interruption during manufacturing process,and improves controllability, measurability and reliability of the extended manufacturing process.
The construction of extended organization is divided to two steps.One is reduce-coupling decomposition strategy,i.e.,closely-related ETs are grouped into clusters to reduce the effect of complex ETs correlation and improve the independence of ETs and the parallelism during manufacturing process.The other is improve-coupling allocation,i.e.,on the basis of the reduce-coupling decomposition, the dominant enterprise chooses closely-related ERs for ETs in the same clusters.
1 MATCHING FOR ETs AND ERs
Supposing that nTis the totality of ETs and nRis the totality of ERs.Several ERs having the manufacturing capability can be retrieved to match the manufacturing requirements of ETs,so the matching relation of one ET to several ERs is formed,as shown in Fig.1①.ERi-p(p=1,2,…, ni-R)represent that the extended resource p has the capability to fulfill taski,and ni-Ris the totality of resources capable of fulfill task i.
2 REDUCE-COUPLING STRATEGY
The reduce-coupling strategy includes two steps,which is the correlation analysis of ETs and the reduce-coupling decomposition based on correlation of ETs as shown in Fig.1②.

Fig.1 Construction process of extended manufacturing
2.1 Correlation analysis of ETs
The complex relations between ETs are the reasons for coupling in extended manufacturing. In order to explain the correlation of ETs,it is classified into two categories as follows:
(1)CorrelationⅠ The material transmission correlation.
Due to the limit of due date and the manufacturing capability,the finished ETs should be transmitted to other ERs in order to finish the next manufacturing or assembly tasks.Supposing that fij∈{0,1}is the value of material transmission correlation.fij=1 represents that there is a correlation between ETiand ETj,i.e.,the finished ETishould be transmitted to another ER to finish ETj.fij=0 represents that there is no correlation.
(2)CorrelationⅡ Correlation besides material transmission.
① The assembly coordination:Lots of parts are assembled into complex products,and several factors such as assembly accuracy,assembly sequence,assembly interference,and production schedule of parts in different enterprises,can affect the product quality and the due date,so parts with assembly relations have stronger correlation.
② Manufacturing process correlation:Many manufacturing processes of complex parts need to be finished in different ERs,so manufacturing processes of the same part have stronger correlation.
③ Function realization correlation:In order to realize a sub-function of a product,parts should coordinate with each other,and power, data and signal are transmitted between them.It is convenient for function debugging if the parts are sent to ERs with a closer relationship.So, the production and assembly tasks with function realization relationship have stronger correlation.
Supposing that rTmij(m= 1,2,3)are the indexes of coordination,manufacturing process, and function realization correlation respectively between ETiand ETj.According to the importance or closeness of relationship,is ranked into six levels[8],i.e.,{no correlation,the weakest, weaker, mediate, stronger, the strongest}={0,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1},so the degree of correlationⅡ can be calculated by using Eq.(1).

where rTⅡijis the degree of correlationⅡ between ETiand ETj,kTm(m=1,2,3)are the weight of correlationⅡ.
The correlation model can be established by correlationsⅠ andⅡ.Supposing that fi jis in the first quadrant,and rTijis in the second quadrant,as shown in Fig.2.

Fig.2 Correlation model of ETs
In Fig.3,an example is given to explain the model.Solid lines represent the transmission direction of material,and dotted lines indicate the second correlation existed between different ETs. The manufacturing process includes seven ETs. ET0is product assembly,which is completed in the dominantenterprise; ET1 iscomponent assembly,which assemblesthe partsmanufactured by ET2and ET3;ET4is a part of manufacturing task;ET5and ET6are the processes of ET4. It should be noted that all the above tasks are completed in ERs. The correlation matrix is shown in Fig.4.

Fig.3 Correlation directed graph of ETs

Fig.4 Matrix model of ETs correlation
2.2 Reduce-couplingdecomposition based on correlationⅡof ETs
ETs based on correlation II are decomposed by fuzzy clustering[9],i.e.,ETs with stronger correlation are grouped into the same cluster,and the weaker relationship between ETs is eliminated,so clusters consisting of ETs with strong correlation can be formed.The value type of correlationⅡ is also transformed from Numeric to Boolean,this is r∈{0,1}.If ETs in the same cluster have strong correlationⅡ ,r′TⅡij=1;otherwise,j= 0.
As shown in Fig.3(b),after the reduce-coupling decomposition for the seven ETs,the correlations between ET3and ET4,ET1and ET7are eliminated.ET7is an independent task,thus three clusters{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7}are formed, and the process of decomposition is shown in Fig.5.

Fig.5 Decomposition process of correlation matrix based on correlationⅡ
3 IMPROVE-COUPLING STRATEGY
The correlation between ERs determines the degree of coupling between ENs,so the correlation between ERs should be considered in order to realize the improve-coupling allocation,by which the extended organization based on"the whole process controlled"is constructed.The improvecoupling strategy includes two steps:the correlation analysis of ERs and the improve-coupling optimization allocation,as shown in Fig.1③.
3.1 Correlation analysis of ERs
Tighter coupling between ENs produces bettercommunication and coordination between ERs,so enhancing the coupling between ENs is an effective method to improve controllability, measurability and reliability of manufacturing process.The correlation of ERs is classified into two categories as follows:
(1)CorrelationⅠ Geographic distance correlation.
Geographic distance between ERpand ERq (dⅠpq)also affects the possibility for cooperation. The shorter dⅠpqcomes less transport time and cost,and vice versa.
(2)CorrelationⅡ The correlation besides geographic distance.
① The manufacturing capability:The manufacturing capability is one of the key factors that determine the cooperating willingness of ERs. The stronger manufacturing capability the ER have,the more cooperation opportunities it enjoys,and vice versa.Several indices that reflect the manufacturing capability can be considered, such as,manufacturing time(T),manufacturing cost(C),product quality(Q).rR1pqis defined as correlation manufacturing capability between ERqand ERp.The larger the rR1pqis,the stronger manufacturing capability the ERqhas,and the easier the ERqis chosen as the cooperator of the ERp. The enterprise strength of EEqhas the same effect on another enterprise,so rR1pqin the same column of RR 1is identical.The value rR1pqis from 0 to 1 by expert scoring method,and the better cooperation results in higher score.The correlation matrix of manufacturing capability is shown in Eq.(2).

② The industry correlation:There are many similarities in resource types like technicians, equipment and information platform,and in production habit between the extended enterprises in identical or related industry.After accepting the manufacturing tasks,the enterprises in identical or related industry can perform the tasks without changing much of the existing production condition.This can meet the requirement of rapid response to armament production.According to the Industrial Classification of National Economic Industries(GB/T4754—2002)enacted by General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine,an industry structure tree is constructed,as shown in Fig.6.
According the method introduced in Ref. [10],the industry correlation between enterprises can be obtained.Supposing that liand ljrepresent the distance between the position of the industry of ERp,ERqand their common parent node in Fig.7,andthen the industry correlated degree can be calculated by Eq.(3).2pqis normalized by usingand rR2pq∈ [0,1].

Fig.6 Industry structure tree

Fig.7 Affiliation structure tree

③ The affiliation correlation:The enterprises in the same group have the same higher authority,and it is easy for technicians to find out and solve problems in the manufacturing process, thusmaking extended manufacturing process much smoother.The affiliation structure tree is shown in Fig.7.In reference to the solution method of rR 3pq,the affiliation correlated degree rR3pqcan be obtained.So the degree of correlation II can be calculated using Eq.(4).The correlationⅡ matrix is show n in Eq.(5)
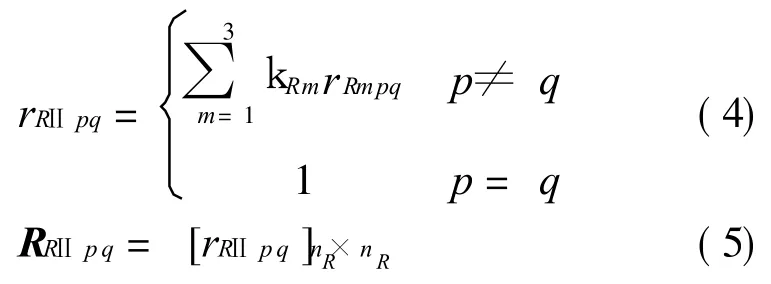
where rRⅡpqis the degree of correlationⅡ between ERpand ERq,andkRm(m=1,2,3)are the weight of correlationⅡ.
The distance based on correlationⅡ can be obtained by using Eqs.(6,7).
(1)Before the distance calculation,the effect on distance should be reduced through normalizing processing,so

where STD is maximum difference normalization formula.
(2)dⅡpqstands for the"distance"between extended enterprises ERpand ERq,which is the possibility for cooperation between ERpand ERq. The smaller dⅡpq,the more possibility for cooperation,and vice versa.The distance dⅡpqcan be calculated using Euclid distance Eq.(7).

The distance based on correlationⅡ matrix D can be constructed corresponding to the correlation matrix RRⅡpq.,as shown in Eq.(8).

The correlation model can be established by correlationsⅠ andⅡ.dpqis in the first quadrant, and dⅡpqis in the second quadrant,as shown in Fig.8.

Fig.8 Correlation model of ETs
3.2 Improve-coupling optimization allocation
Besides manufacturing capability existing in usual method of resource optimization allocation, resource correlation is also taken into consideration in improve-coupling resource allocation,thus making it a multi-objective allocation strategy, which is more complex than the traditional resource allocation. The optimization objectives based on resources correlation are analyzed as follows.
(1)When the dominant enterprise selects ERs as its cooperators,the correlationⅡ between ERs(Eq.9)need to be considered.

where rRⅡ(i-p)is the distance based on correlationⅡ between the dominant enterprise and ERs.
(2)Closely-related ERs should be allocated for ETs in the same cluster(Ⅱij= 1),so the coupling between ENs is enhanced.Coordination between ENs is made easily,and the production schedule and quality of product can be ensured. The distance based on correlation II between ERi-pand ERj-qis shown as follows

(3)The geographical distance from ERi-pto ERj-qcan be calculated by using Eq.(11)
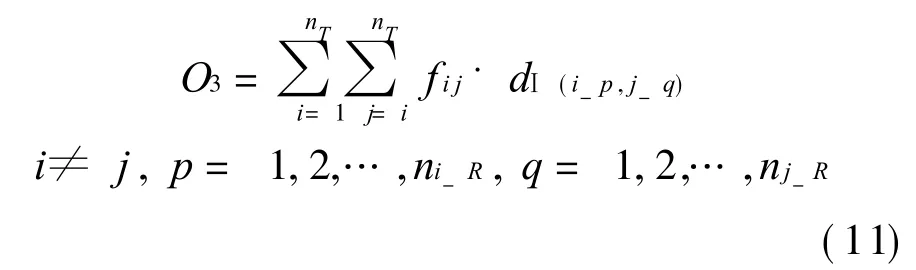
According to the above analysis,a mathematic model of improve-coupling optimization allocation is formulated as

wherekm(m=1,2,3)are the weight and for O1, O2,O3,λm(m= 1,2,3)are standardized coefficients to eliminate morbid effects of dimension.

Genetic algorithm(GA)is adopted for the realization of resource allocation based on correlation,and the construction of the extended organization details of GA is not discussed in this paper.
4 CASE STUDY
The structures of a wing of aircraft are shown in Fig.9.The manufacturing tasks need to be extended to external enterprises.

Fig.9 Structures of wing and aileron
Firstly,the correlation of ETs is analyzed, and the correlation matrix is shown in Fig.10. Weak correlation iseliminated by using the method of reduce-coupling decomposition,and five clusters are formed:{1,2,5,10},{3,4,6}, {8,11},{7},{9}.
Secondly,the improve-coupling process consists of two steps:(1)The information of ERs is input,including manufacturing capability,industry,affiliate,and geographic position,so the degree of correlation can be obtained.(2)Through the improve-coupling allocation,the extended organization based on tight coupling can be constructed.In the extended manufacturing process, the dominant enterprise and ERs supervise production schedule,record and analyze quality data by using management tools of coordinative plat-form,which ensures the normal operation of extended manufacturing.

Fig.10 Correlation matrix of ETs
5 CONCLUSION
The coupling of extended manufacturing is studied in the paper,and the features of the coupling model are analyzed,by which a method for building manufacturing organization on internet is put forward.And a system of extended manufacturing allocation based on coupling model is developed.Finally,a case is given to show the validation of the coupling theory.Results show that the theory can greatly improve rationalization and optimization of decision about how to organize the manufacturing resources.But the theory of coupling is not fully mature,especially in how to abstract the coupling relationship between different manufacturing organizations on internet.So many problems need to be studied to refine the theory.
[1] Martinez M T,Fouletier P,Park K H,et al.Virtual enterprise-organization,evolution and control[J]. International Journalof Production Economics, 2001,74(6):225-238.
[2] SuYan,Liao Wenhe,Guo Yu,et al.An ASP-based product customization service system for SM Es: a case study in construction machinery[J].International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems, 2008,4(1):1125-1130.
[3] Feng Ji,He Weiping,Wang Dongcheng,et al.Research on collaborative manufacturing chain for complex parts in networked manufacturing environment [J].Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2006,12(1):72-77.(in Chinese)
[4] Yu Feng,Liao Wenhe,Guo Yu.Research on process rapid proliferative system[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2006,18(19):2322-2325.(in Chinese)
[5] Guo Feng.Research on methodology for mechanical product design process modeling,evaluation and optimization[D].Hangzhou:University of Zhejiang, 2007.(in Chinese)
[6] Chen Shijie.Decomposition of inter-dependent task group for concurrent engineering[J].Computer& Industrial Engineering,2003,44(5):435-459.
[7] Sun J C Y,Chen Shijie,Lin Li.A structured approach to measuring functional dependency and sequencing of coupled tasks in engineering design[J]. Computer& Industrial Engineering,2003,45(6): 195-214.
[8] Zhu Jianying.Intelligent system non-classical mathematics method[M].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press,2004.(in Chinese)
[9] Wang Haijun,Wei Xiaopeng.Numerical programming approaches for the development of modular product family[J].Journal of Computer Aided Design&Computer Graphics,2005,17(3):473-478.(in Chinese)
[10]Zong Mingdi,Cai Ying,Liu Xudong,et al.A multi-perspective hierarchical division approach for a product in its modular design[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology,2003,23(5):552-556.
