Effects of Cyptopleurine on IκBα Degradation and NF-κB Activation in Breast Cancer Cells
2011-01-15IANGHeJINXuejun
L IANG He, JIN Xue-jun
(Key Laboratory for N atural Resources of the Changbai M ountain&Functional M olecules(Yanbian University),M inistry of Education,Yanji 133002,China)
Effects of Cyptopleurine on IκBα Degradation and NF-κB Activation in Breast Cancer Cells
L IANG He, JIN Xue-jun*
(Key Laboratory for N atural Resources of the Changbai M ountain&Functional M olecules(Yanbian University),M inistry of Education,Yanji 133002,China)
To investigate the effects of cryp top leurine on activation of NF-κB in breast cancer cells,we examined w hether cryp top leurine,a phenanthroquinolizidine alkaloid inhibited IκBαphosphorylation and degradation,and p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation.The results show that cryp topleurine significantly inhibited the induced exp ression of NF-κB repo rter gene by TNF in a dose-dependentmanner.A lso,cryp top leurine inhibited TNF-induced IκBαphospho rylation and degradation.Further analyses demonstrated that cryp top leurine inhibits TNF-induced p65 phospho rylation,and p65 nuclear translocation.Together,cryp top leurine could be valuable candidate fo r the intervention of NF-κB-dependent pathological condition such as inflammation.
cryp top leurine;NF-κB;inflammation
1 Introduction
The NF-κB(nuclear factor-κB)transcription factors controlmany physiological p rocesses including inflammation,imm unity,apop tosis,and tumor invasion[1-3].NF-κB rep resents a family of related DNA-binding p roteins,w hich in mammals includes five members:NF-κB1(or p50),NF-κB2(o r p52),RelA(o r p65),RelB and c-Rel.In an inactive state,NF-κB is sequestered in the cytop lasm as a heterotrimer consisting of p50,p65,and IκB subunits.On activation,IκBαundergoes phosphorylation and ubiquitination-dependent degradation leading to p65 nuclear translocation and binding to a specific consensus sequence in the DNA,w hich results
2 Materialsand Methods
2.1 Cell Culture and Reagents
Human breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Essential M edium(Invitrogen Co rpo ration,Carlsbad,CA,USA).Thismedia was supplemented w ith penicillin (100 units/mL)-strep tomycin (100 units/m L)(Invitrogen Corporation,Carlsbad,CA,USA)and 10%heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Hyclone,Logan,U T,USA).Cryp top leurine w as isolated from Boehmeria pannosa and confirmed its structure in comparison w ith the p revious report and its purity is mo re than 98%in HPLC analysis[8].
2.2 Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assay
A pNF-κB-Luc p lasmid for NF-κB luciferase in gene transcrip tion.
NF-κB inhibitors including a variety of natural p roducts,chem icals,metals,metabolites,synthetic compounds,pep tides,p rotein(cellular,viral,bacterial,fungal)and physical conditions can be divided into different groups depended on the target levels of NF-κB signaling:upstream of IKK,directly at the IKK comp lex or IκB phospho rylation,ubiquitination,p roteasomal degradation of IκB,nuclear translocation of NF-κB,NF-κB-DNA binding,and NF-κB transactivation[4-5].To date,a large number of natural compounds have been repo rted as NF-κB inhibitors and some of these have been further investigated fo r the app lication in diseases treatment[6-7].
A s part of our continuing search for NF-κB inhibitors from natural p roducts,a phenanthroquinolizidine alkaloid,cryp top leurine,w as identified as an inhibitor of NF-κB activation from the roo ts of Boehmeria pannosa(U rticaceae).We here describe the anti-inflammatory effect of cryp top leurine.This compound inhibited the induced activation of NF-κB in TNF-stimulated MDA-MB231 cells.Cryp top leurine inhibited not only the degradation of IκBαbut also the p65 phosphorylation,and p65 nuclear translocation.reporter assay was obtained from Strategene.Transfections were performed using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen)acco rding to the manufacturer’s instructions.NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity w as determined in M icrolumat p lus luminometer by injecting 100μL of assay buffer containing luciferin and measuring light emission for 10 seconds.The results were normalized to the activity of renilla exp ressed by cotransfected Rluc gene under the control of a constitutive p romoter.Data w ere analyzed using ANOVA(Analysis of variance).
2.3 Measuremen t of Cell Viability
Cell viability was measured by a M TT[3-(4,5-dimethy lthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay (Sigma-A ldrich).Briefly,untreated cells or treated cells w ith cryp top leurine in a 96-well p late were incubated fo r 24 h follow ed by the addition of M TT to the cells.Op tical densitieswere determined on amicrop late reader(Molecular Devices,Sunnyvale,CA,USA).
2.4 Western Blotting Analysis
Whole-cell extracts were obtained by lysing cells in ice-co ld lysis buffer(50 mM Tris-HCl,p H 7.5,1%Nonidet P-40,1mM EDTA,1mM phenylmethyl sulfonylfluoride) supp lemented w ith the p rotease inhibitor cocktail(BD Biosciences,San Diego,CA,USA).In certain experiments,the nuclear extractswere p repared using NE-PER reagent(Pierce,Rockfo rd,IL,USA),according to the instructions of manufacturer.An aliquot of p rotein extracts w as used to determine p rotein concentration by the Bradford method.Fiftyμg of w ho le-cell extracts o r thirty μg of nuclear extract p rotein per lane was separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gels and followed by transferring to a polyvinylidene difluoride mem brane(M illipo re,Bedfo rd,M A,USA).The membrane was blocked w ith 5%skim milk,and then incubated w ith the co rresponding antibody.Antibodies for IκBα,phosphor(Ser32)-specific IκBα,p65,and phospho r(Ser536)-specific p65 were purchased from Cell Signaling
Technology(Beverly,MA,USA).Antibody for a-tubulin was from Sigma(St.Louis,MO,USA).Antibody fo r Topo-I was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology(Santa Cruz,CA,USA).A fter binding of an app rop riate secondary antibody coup led to horseradish peroxidase,p roteins were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence according to the instructionsof themanufacturer(Amersham Pharmacia Bio tec,Buckinghamshire,U K).
3 Resultsand Discussion
3.1 Cryptopleur ine Inhibits TNF-induced NF-κB Activation
In an effort to identify NF-κB inhibito rs from natural p roducts,we have identified a phenanthroquinolizidine alkaloid, cryp top leurine,from the roots of Boehmeria pannosa.To investigate the effect of this compound on the induced NF-κB activation by TNF,we performed a NF-κB reporter gene assay.Cryp top leurine dose dependently inhibited the TNF-induced exp ression of N F-κB repo rter gene construct(Fig.1A).On the other hand,M TT assay indicated that cryp top leurine did not show a significant cytotoxicity on the MDA-MB231 cells up to 30 nM(Fig.1B).

Fig.1 Effect of cryptopleurine on NF-κB reporter gene expression under TNF stimulation
3.2 Cryptopleurine Inhibits TNF-induced IκBα Degradation and Phosphorylation
Since degradation of IκBαp roteins is an essential step fo r NF-κB activation by various stimuli,w e examined the effect of cryp top leurine on the induced degradation and phospho rylation of IκBαp rotein by TNF(Fig.2).MDAMB231 cells were p retreated w ith the indicated concentrations of cryp topleurine,and subsequently stim ulated w ith TNF fo r 30 m in.To tal cell extracts were analyzed the p resence of IκBα w ith w estern blotting.Cryp top leurine dose dependently inhibited the TNF-induced degradation of IκBαFurthermore,determination of phosphorylation of IκBαby western blotting using a phospho r-specific IκBαantibody revealed that cryp top leurine significantly affected the TNF-induced phosphorylation of IκBα.These results indicate that cryp top leurine p revents the TNF-induced IκBαdegradation through inhibiting IκBαphosphorylation,thereby interfering w ith one of the common steps in the signaling cascade leading to the NF-κB activation.
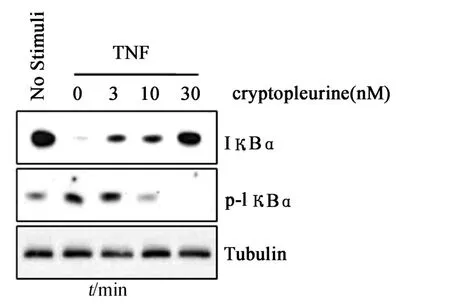
Fig.2 Effect of cryptopleurine on IκBα degradation and phosphorylation under TNF stimulation
3.3 Cryptopleurine Inhibits TNF-induced p65 Phosphorylation and p65 Nuclear Translocation
TNF also induces the phospho rylation of p65,w hich is required fo r its transcrip tional activity[9].We assessed w hether cryp top leurine affects TNF-induced phosphorylation of p65.In the nuclear fraction from the TNF-treated cells,cryp top leurine supp ressed the phosphorylated fo rm of p65(Fig.3,top panel).We further showed that cryp top leurine supp ressed TNF-induced nuclear translocation of p65,as measured by western blotting(Fig.3,middle panel).These results indicate that cryp top leurine p revents the TNF-induced p65 phosphorylation and p65 nuclear translocation,w hich is required fo r efficient transcrip tional activation of NF-κB.

Fig.3 Effect of cryptopleurine on p65 phosphorylation and p65 nuclear translocation
[1] Hayden M S,Ghosh S.Signaling to NF-kappaB[J].Genes Dev,2004,18:2195-2224.
[2] Karin M.Nuclear Fctor-kappaB in Cancer Development and Progression[J].Nature,2006,441:431-436.
[3] Sung B,Ahn K S,Aggarwal B B.Noscapine,a Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloid,Sensitizes Leukemic Cells to Chemotherapeutic Agentsand Cytokines by Modulating the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway[J].Cancer Res,70:3259-3268.
[4] Gilmore T D.Introduction to NF-kappaB:Players,Pathways,Perspectives[J].Oncogene,2006,25:6680-6684.
[5] Gilmore T D,Herscovitch M.Inhibito rs of NF-kappa B Signaling:785 and Counting[J].Oncogene,2006,25:6887-6899.
[6] Karin M,Yamamoto Y,Wang Q M.The IKK NF-kappa B system:a Treasure Trove for Drug Development[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2004,3:17-26.
[7] Newman D J,Cragg G M.Natural Products as Sources of New D rugs over the Last 25 Years[J].J Nat Prod,2007,70:461-477.
[8] Cai X F,Jin X,Lee D,Yang Y T,et al.Phenanthroquinolizidine A lkaloids from the Roo tsof Boehmeria Pannosa Potently Inhibit Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 in AGS Human Gastric Cancer Cells[J].J Nat Prod,2006,69:1095-1097.
[9] Ghosh S,May M J,Kopp E B.NF-kappa B and Rel Proteins:Evolutionarily Conserved Mediators of Immune Responses[J].Annu Rev Immunol,1998,16:225-260.
1004-4353(2011)02-0176-04
小穗苎麻素对乳腺癌细胞 IκBα降解和 NF-κB活化的影响
梁贺, 金学军*
(长白山生物资源与功能分子教育部重点实验室(延边大学),吉林延吉133002)
为探讨小穗苎麻素对乳腺癌MDA-MB231细胞中NF-κB活化的影响,从黄背苎麻中提取生物碱类单体小穗苎麻素,通过蛋白免疫印迹实验检测小穗苎麻素对IκBα磷酸化和降解的影响以及对p65的磷酸化和核转移的影响.结果显示:小穗苎麻素呈剂量依赖性抑制了 TNF诱导的NF-κB报告基因的表达,同时抑制了乳腺癌MDA-MB231细胞中IκBα的磷酸化和降解,以及p65的磷酸化和核转移.这表明,小穗苎麻素通过抑制乳腺癌MDA-MB231细胞中IκBα的磷酸化和降解以及p65的磷酸化和核转移,进而抑制了NF-κB的活化.
小穗苎麻素;核因子NF-κB;炎症
2011-03-27
R392.5
A
*通信作者:金学军(1970—),男,博士,副研究员,研究方向为细胞分子生物学.
